Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Edet709 Comparison Matrix
Uploaded by
api-75736613Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Edet709 Comparison Matrix
Uploaded by
api-75736613Copyright:
Available Formats
EDET 709 Major Theoretical Perspectives
Comparison of Major Theoretical Perspectives
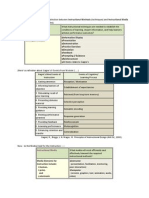
Directions: The partially-completed matrix depicts major theories of learning and your task is to move the contents of the far right yellow-filled column to the theoretically-appropriate column. (Basically, you cut and paste all items in the last column into the other columns. Each of the 3 columns of the matrix should be complete and reflect the theory at the top of the column. Click on view/complete to submit in Bb. Behaviorism Cognitivism Constructivism Complete the matrix by cutting and pasting contents from this column to the appropriate theory
Edward Thorndike Albert Bandura Dewey John B. Watson B. F. Skinner Lev Vygotsky Robert Gagn Jean Piaget Benjamin Bloom B. Learning is the creation of meaning from experience. C. Learning is an observable change in behavior. A change in the likelihood and frequency of a response, which is determined by reinforcement. A. 1. Multiple representation 2. Discovery learning 3. Inquiry-based instruction 4. Communal learning 5. Self-regulation 6. Authentic learning 7. Case-based learning B. 1. Three-stage information processing mode; sensory register, short- and long- term memory 2. Serial position effect 3. Scaffolding 4. Gagns theory of instruction 5. Schema theory
Ivan Pavlov
Jerome Bruner Rogoff Lave
1. M ajor Theorists
2.
ow does the theory define learning?
C. 1. Shaping 2. Chaining 3. Discrimination 4. Fading 5. Mind as a black box 6. Reinforcement
A. Learning results from the encoding of information into memory in an organized manner for later retrieval.
3. W hat are some of the key concepts?
4. W hat is the learning pedagogy? 5. W hat technology is associated?
A. 1. Schema techniques 2. Gagns instructional design B. 1. Piaget: Developmental constructivism 2. Vygotsky: Social constructivism C. 1. Reward and punishment 2. Behavioral instructional design 3. Taxonomies of learning A. 1. Learning-by-doing 2. Active and authentic learning B. 1. Computer assisted instruction (CAI) 2. Teaching machines C. 1. Intelligent tutoring systems
EDET 709 Major Theoretical Perspectives
A. 1. Provide corrective feedback. 2. Provide illustrations and examples. 3. Help students to organize information in a meaningful way. 4. Teach student appropriate and effective strategies 2. Artificial intelligence B. 1. Select the discriminative stimuli and reinforcement to elicit the desired response. 2. Provide practice paired with target stimuli. 3. Provide appropriate reinforcement for desired responses. 4. Provide multiple opportunities for practice. 5. Modify student behavior C. 1. Teach students how to construct meaning. 2. Facilitate learning. 3. Engage learner in using tools in authentic situations 4. Scaffold A. The learner acquires new behaviors by responding to the stimuli in the environment. C. The learner constructs knowledge and creates meaning based on interactions and experiences.
6. What is the role of the instructor?
5. What is the role of the learner?
B. The learner is an active participant seeking meaning.
EDET 709 Major Theoretical Perspectives
Behaviorism
Cognitivism
Constructivism
C. Constructivists considers memory as the accumulation of experiences, which is fluid, changing with new experiences and situations. A. Acquisition of behaviors are acquired through reinforcing consequences, and repetition enables the learner to quickly respond. B. Memory has a major role. Information is selected for further processing and encoded and stored in a meaningful way in it. B. Learning is transferred through prior learning; that is, knowledge and procedures in long term memory can be generalized or applied to a similar task. C. Learning is transferred when the learner is able to generalize knowledge in new situations A. The biggest appeal to apply this theory into practice is classroom management. B. The biggest appeal to apply this theory into practice is that it allows students to apply information learned in the classroom to real world situations. C. The biggest appeal to apply this theory into practice is that it is focuses on students mental structures and learning. It also views the students as active participants.
6. What is the role of memory?
7. How learning is transferred?
A. Learning is transferred through the involvement and completion of authentic tasks within a situation with some significance to the learner.
8. What is the biggest appeal to apply this theory into practice?
9. What makes it difficult to apply this theory into practice?
B. As cognitivism focuses on schemas and prior learning, it may be difficult for teachers to assess all students prior learning.
A. As students construct their own meaning, divergent meaning may cause some problems. It may be difficult to develop authentic activities that can be facilitated within a classroom setting. C. In a large classroom of 20+ students it is difficult to monitor behavior, thus applying immediate reinforcement contingent on behavior may be difficult. Mental cues might not be available to the learner when needed.
You might also like
- Module 2Document4 pagesModule 2Vencent Jasareno CanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture CH 12 Planning and Teaching LessonsDocument12 pagesLecture CH 12 Planning and Teaching LessonsRoberto Pereira da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Facilitating 223Document25 pagesFacilitating 223AnggayNo ratings yet
- Principles and Methods of Teaching 1Document4 pagesPrinciples and Methods of Teaching 1Thundèr FrèresNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learning: To GuideDocument7 pagesFacilitating Learning: To GuideMelissa MarvicNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Seminar 3Document14 pagesModule 2 Seminar 3Jayvee Payong PalmerNo ratings yet
- Facilitating LearningDocument4 pagesFacilitating LearningMay-Ann S. CahiligNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories Implications in Teache PDFDocument13 pagesLearning Theories Implications in Teache PDFVasia PapapetrouNo ratings yet
- Teaching Approaches and Methods Under K-12Document4 pagesTeaching Approaches and Methods Under K-12Monaida Umpar IbrahimNo ratings yet
- M-2 Mcqs Education Unit 4Document2 pagesM-2 Mcqs Education Unit 4shazia yasmeenNo ratings yet
- Nature of MathematicsDocument2 pagesNature of MathematicsJoshua Fred HilomaNo ratings yet
- MATH 18 CLP 2 Unit 6 To SendDocument7 pagesMATH 18 CLP 2 Unit 6 To SendIana Stephanie MayoNo ratings yet
- LP 542 Lesson 3Document3 pagesLP 542 Lesson 3api-233188563100% (1)
- Edm 325 2020-2021 Wk. 3 - Lesson 2Document2 pagesEdm 325 2020-2021 Wk. 3 - Lesson 2yukiyukina8No ratings yet
- Assignment No: 1: NAME: Hafiz Naveed Shahzad ROLLNO: cb661612 PROGRAM: Bed (1.5year)Document10 pagesAssignment No: 1: NAME: Hafiz Naveed Shahzad ROLLNO: cb661612 PROGRAM: Bed (1.5year)Naveed MughalNo ratings yet
- Teaching ModelsDocument38 pagesTeaching ModelsRomelynn SubioNo ratings yet
- Prod Ed Review QuestionaireDocument13 pagesProd Ed Review QuestionaireChristopher BaliguatNo ratings yet
- LAS 10 The Instructional CycleDocument5 pagesLAS 10 The Instructional CycleHiezel G LandichoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Effective Mathematics ClassroomDocument57 pagesLesson 2 The Effective Mathematics ClassroomRamilNo ratings yet
- Math 102Document13 pagesMath 102pascuafebbieanndNo ratings yet
- III-Day 1Document6 pagesIII-Day 1Rainman InsanityNo ratings yet
- Test Paper For Educ. 37Document4 pagesTest Paper For Educ. 37Saxrim TagubaNo ratings yet
- Instruction StrategyDocument3 pagesInstruction Strategyapi-300665697No ratings yet
- FS2 - 1Document12 pagesFS2 - 1Wyzty Delle83% (6)
- Principles of Teaching Sem Ed 2017-2018Document6 pagesPrinciples of Teaching Sem Ed 2017-2018Romelo MuldezNo ratings yet
- LEARNER-CENTERED THEORIES OF LEARNING by Trisha and RosaDocument29 pagesLEARNER-CENTERED THEORIES OF LEARNING by Trisha and RosaCARLO CORNEJO100% (1)
- Module 6 3 Ci MathDocument129 pagesModule 6 3 Ci Mathapi-199390118No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 3Document5 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 3Mary Cassey Golosino Devibar IINo ratings yet
- III-Day 37Document3 pagesIII-Day 37Ivan Rey Porras VerdeflorNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 7 Filsafat Ilmu (Pmat-C23)Document6 pagesKelompok 7 Filsafat Ilmu (Pmat-C23)Sabriah AbduhNo ratings yet
- III-Day 29Document4 pagesIII-Day 29EBENIZER DAJESNo ratings yet
- Title: Lesson 2 - Approaches To School CurriculumDocument3 pagesTitle: Lesson 2 - Approaches To School CurriculumJayson VargasNo ratings yet
- Module 3 CurrdevDocument9 pagesModule 3 CurrdevIlex AvenaNo ratings yet
- 9 PR 1Document2 pages9 PR 1Lee C. SorianoNo ratings yet
- BLESSINGSDocument38 pagesBLESSINGSleo simporiosNo ratings yet
- Complete Research Template UpdatedDocument34 pagesComplete Research Template UpdatedvenicehailieNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Effective Mathematics Classroom - LecDocument55 pagesLesson 2 The Effective Mathematics Classroom - LecRamilNo ratings yet
- G8DLL Q4W6Document5 pagesG8DLL Q4W6Mark Kiven MartinezNo ratings yet
- EDUC 13 - Midterm ExaminationDocument6 pagesEDUC 13 - Midterm ExaminationSaxrim TagubaNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed Sample QuestionsDocument33 pagesProf Ed Sample QuestionsECE CAPILINo ratings yet
- III-Day 11Document5 pagesIII-Day 11Melisa ManuelNo ratings yet
- Field Study 2 Episode 3Document9 pagesField Study 2 Episode 3Gina May Punzalan PanalanginNo ratings yet
- Effective TeachersDocument2 pagesEffective TeachersAzlina AnilzaNo ratings yet
- Malicse-Compilation of Teaching Methods and ApproachesDocument3 pagesMalicse-Compilation of Teaching Methods and ApproachesKHIM JOSEPH MALICSENo ratings yet
- Principles of TeachingDocument7 pagesPrinciples of TeachingCrystal RedublaNo ratings yet
- Lecture CH 6 Lecture, Discussion, DemonstrationDocument12 pagesLecture CH 6 Lecture, Discussion, DemonstrationRoberto Pereira da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Principles in The Selection and Organization of ContentDocument5 pagesPrinciples in The Selection and Organization of ContentTeodora Piamonte BatobalaniNo ratings yet
- DemonstrationDocument9 pagesDemonstrationMonika JosephNo ratings yet
- LET-questionnaire-principles of TeachingDocument6 pagesLET-questionnaire-principles of TeachingAishah SangcopanNo ratings yet
- At The End of This Lesson, Students Should Be Able To:: Unit 5 Course Intended Learning OutcomesDocument7 pagesAt The End of This Lesson, Students Should Be Able To:: Unit 5 Course Intended Learning Outcomesarmando licanda BSE Math 2ANo ratings yet
- Math Topic 2Document3 pagesMath Topic 2KAETH LAURENCE ORILLA NOTARIONo ratings yet
- Test-Drill-II-Prof.-Ed Edited For PDFDocument23 pagesTest-Drill-II-Prof.-Ed Edited For PDFrowenarodrigo22No ratings yet
- Explicit Teaching by AnneDocument18 pagesExplicit Teaching by AnneMarianne SaileNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Prof Ed Part 7Document2 pagesPractice Test Prof Ed Part 7Nanami Mae-chan100% (1)
- FS Lesson 1Document5 pagesFS Lesson 1Kimverly zhaira Domagan100% (1)
- Facilitating of Learning - JunDocument12 pagesFacilitating of Learning - Junjj100% (5)
- Principles of TeachingDocument6 pagesPrinciples of TeachingSean HooeksNo ratings yet
- Calculus: An Intuitive and Physical Approach (Second Edition)From EverandCalculus: An Intuitive and Physical Approach (Second Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Chap-3 Edu Theories..Document6 pagesChap-3 Edu Theories..Sanaa AslamNo ratings yet
- Roles of Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument18 pagesRoles of Technology For Teaching and LearningEricson PandesNo ratings yet
- Module 3 21st Century 2014Document1 pageModule 3 21st Century 2014api-75736613No ratings yet
- Module 2 Other Theories of Learning Readings and Tasks 2014Document2 pagesModule 2 Other Theories of Learning Readings and Tasks 2014api-75736613No ratings yet
- Mini Redesign Description and Rubric 2014Document2 pagesMini Redesign Description and Rubric 2014api-757366130% (1)
- Module 1 Traditional Theories of Learning Readings and TasksDocument2 pagesModule 1 Traditional Theories of Learning Readings and Tasksapi-75736613No ratings yet
- Big Redesign Description 2014Document3 pagesBig Redesign Description 2014api-75736613No ratings yet
- Midterm Map 2014Document2 pagesMidterm Map 2014api-75736613No ratings yet
- Midterm Synthesis Map 2013Document2 pagesMidterm Synthesis Map 2013api-75736613No ratings yet
- Material DevelopmentDocument9 pagesMaterial Developmentapi-75736613No ratings yet
- Vincent App RubricDocument1 pageVincent App Rubricapi-75736613No ratings yet
- Hilbert Et Al Worked Out ExamplesDocument9 pagesHilbert Et Al Worked Out Examplesapi-75736613No ratings yet
- Cognitive DesignDocument13 pagesCognitive Designapi-75736613No ratings yet
- Games and LearningDocument32 pagesGames and Learningapi-75736613No ratings yet
- Gestalt Principles of PerceptionDocument6 pagesGestalt Principles of Perceptionapi-75736613100% (1)
- 25principles of LearningDocument13 pages25principles of LearningLordOmniconsciousNo ratings yet
- First Principles of Instruction: M. David MerrillDocument17 pagesFirst Principles of Instruction: M. David Merrillapi-75736613No ratings yet
- Cognitive Load Theory SwellerDocument18 pagesCognitive Load Theory Swellerapi-75736613100% (1)
- Edpy 705 Syllabus Summer II 2011Document8 pagesEdpy 705 Syllabus Summer II 2011api-75736613No ratings yet
- Part-17 3Document5 pagesPart-17 3CzarilleNo ratings yet
- Ela 11 Unit 3 Elements of PersuasionDocument39 pagesEla 11 Unit 3 Elements of Persuasionapi-327147831No ratings yet
- RESEARCH ACTIVITY 1 Topics and Trends in ResearchDocument1 pageRESEARCH ACTIVITY 1 Topics and Trends in ResearchLDRRMO RAMON ISABELANo ratings yet
- Reflecting Senses Perception and Appearance in Lit... - (The Anthropological Persistence of The Aesthetic Real Shadows and Text... )Document14 pagesReflecting Senses Perception and Appearance in Lit... - (The Anthropological Persistence of The Aesthetic Real Shadows and Text... )Estela Ibanez-GarciaNo ratings yet
- Kim Wilkinson 2019 What Is Dialogic TeachingDocument17 pagesKim Wilkinson 2019 What Is Dialogic Teachinghirafazaljat1No ratings yet
- Performance Leadership PresentatiomDocument31 pagesPerformance Leadership PresentatiomMuhd HasansyukriNo ratings yet
- Truth Is Never Under Attack - Alfred AikenDocument6 pagesTruth Is Never Under Attack - Alfred AikenRonnye Simas100% (1)
- McLuhan and Phenomenology PDFDocument22 pagesMcLuhan and Phenomenology PDFJakub Albert FerencNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Notes (Word) - PhilosophyDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Notes (Word) - PhilosophyMarcie NelsonNo ratings yet
- Job EnrichmentDocument19 pagesJob Enrichmentadjibayu100% (2)
- Problem DefinitionDocument2 pagesProblem Definitionjohn regalaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 11 09 19 PDFDocument310 pagesPractical Research 1 11 09 19 PDFArjey B. Mangakoy100% (2)
- Philosophy LogicDocument3 pagesPhilosophy LogicJhynes RenomeronNo ratings yet
- Tesol Video QuestionsDocument3 pagesTesol Video QuestionsŁéī ŸáhNo ratings yet
- Cross Curriucular ElementsDocument2 pagesCross Curriucular ElementsGeneviene BongNo ratings yet
- Theoretical FrameworksDocument12 pagesTheoretical FrameworksANo ratings yet
- 8th HabitDocument8 pages8th HabitSudipta BoseNo ratings yet
- 10 Motivational TheoriesDocument26 pages10 Motivational TheoriessrcherNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Learning Strategies Colour KeyDocument9 pagesLesson Plan: Learning Strategies Colour Keyapi-534906604No ratings yet
- Brain Based Teaching StrategiesDocument19 pagesBrain Based Teaching StrategiesAnaly BacalucosNo ratings yet
- Soren KierkigaardDocument1 pageSoren KierkigaardKR ReborosoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2 - Uses of Natural ResourcesDocument4 pagesLesson Plan 2 - Uses of Natural Resourcesapi-349867855100% (3)
- ASHENDEN (Ed.) Foucault Contra Habermas PDFDocument229 pagesASHENDEN (Ed.) Foucault Contra Habermas PDFLucasTrindade880% (1)
- A Comparison of 5 Popular Models For Managing Business ChangeDocument8 pagesA Comparison of 5 Popular Models For Managing Business ChangeijayathungaNo ratings yet
- Optional: More On The Rhetorical Canons: Definitions of RhetoricDocument5 pagesOptional: More On The Rhetorical Canons: Definitions of RhetorickiranNo ratings yet
- Lesson: Curriculum Development: Processes and Models Curriculum Development ProcessDocument2 pagesLesson: Curriculum Development: Processes and Models Curriculum Development ProcessAlon Paulino Reyes BantogNo ratings yet
- Employee Perceptions and Their Influence On Training EffectivenessDocument19 pagesEmployee Perceptions and Their Influence On Training Effectivenessshweta_vanjariNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesAldrin Ray M. MendezNo ratings yet
- English Students Fear of Speaking in PublicDocument78 pagesEnglish Students Fear of Speaking in Publicapi-250854057100% (3)
- Book Review On Fides Et RatioDocument3 pagesBook Review On Fides Et RatioLuca InfantinoNo ratings yet