Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary Retention
Uploaded by
Reginald JuliaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary Retention
Uploaded by
Reginald JuliaCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan Second Year
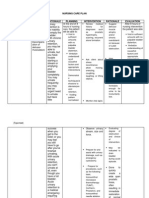
Pt. initials: BS Student: Dave Porter Medical Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Ref.s> Nursing Care Plans (Mosby)[NCP]/Med Surge RN Car (Mosby)[MSNC] Date: 3/12/07 Systems Key: WC: Wholly Compensatory PC: Partially Compensatory N/S Nursing system Key: Long-Term Goal (with deadline) SE: Supportive-Educative Patient will be free or urinary retention by means of indwelling catheter for next 7 days and will follow up with MD at that time.
Nursing Diagnosis with defining characteristics (ASB) N/S Expected outcome (Short-term objectives) with criteria and deadline Nursing Interventions Rationale for Action Evaluation (Criteria met?)
At risk for urinary retention related to blood clots in bladder over the next 7 days.
PC
1. Patient will empty bladder completely via Foley catheter by discharge.
The nurse will; 1. Visually inspect and palpate lower abdomen for distention and use bladder scanner to check for urinary retention.
1. The bladder lies below the umbilicus and distension can be seen or palpated for firmness. The bladder scanner detects residual urine in the bladder via ultrasound. Geriatric male patients often have an enlarged prostate gland which decreases force or urinary flow and/or leading to tendency for bladder retention.. [NCP pg 181] 2. Retention of urine in the bladder predisposes the geriatric patient to UTI's and may indicate the need for an intermittent catheterization program. [NCP pg 181] 3. Geriatric patients may have impaired renal function. However, this will differentiate between urinary retention and urinary failure. [NCP pg 181]
1. Yes. Patient voided approx 1800 ml during my shift without displaying signs or symptoms of retention.
2. Use an indwelling Foley or straight catheter and measure residual urine if incomplete emptying is suspected. 3. Monitor BUN and CR lab values.
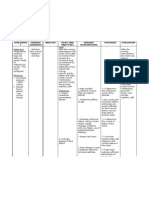
PC
2. Patient will keep the irrigation Foley catheter in place, secured, attached to the leg bag, and kept patient by discharge.
1. Insert the indwelling irrigation catheter as ordered; secure catheter tube access using a catheter tape and Velcro retaining device and attach a leg bag to the catheter system. 2. Encourage intake of fluids
1. This prevents the catheter from dislodging or inadvertent displacement, which may contribute to urinary retention. The bag acts as a reservoir to hold urinary drainage. Kinks in the tubing may restrict proper drainage. [NCP pg 182] 2. Geriatric patients are typically dehydrated. Unless medically contraindicated, fluid intake should be at least 1500ml/24 hours. This stimulates urine production and keeps a min of 30ml/hr output rate. The continued flow rate helps to prevent blockage at the tip. [NCP pg 182]
2. Yes. Foley maintained a consistent flow and catheter was secured and draining properly.
You might also like
- Urinary Retention, RevisedDocument2 pagesUrinary Retention, RevisedKim Beverly100% (5)
- NCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFNoel Cabamongan88% (8)
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumerobbychuaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationHaon Anasu67% (3)
- NCP For Urinary RetentionDocument5 pagesNCP For Urinary RetentionColeen Comelle Huerto60% (5)
- NCP-impaired Urinary Elimination-TAHBSODocument3 pagesNCP-impaired Urinary Elimination-TAHBSOtinatin9890% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Impaired Urinary Eliminationderic86% (14)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanSHeenah Qo100% (1)
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesImpaired Urinary Eliminationcamziii89% (18)
- SIMO-NCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument11 pagesSIMO-NCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationGrey FujoshiNo ratings yet
- Altered Bowel EliminationDocument1 pageAltered Bowel EliminationneoclintNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument19 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationEmeEmeka100% (1)
- Activity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDocument3 pagesActivity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDarkCeades100% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Planmjoie_baby6568470100% (6)
- To Promote Good Hygiene and Physical Comfort.: Coli (E. Coli), NormallyDocument2 pagesTo Promote Good Hygiene and Physical Comfort.: Coli (E. Coli), NormallyFran LanNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFAnonymous FgT04krgymNo ratings yet
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument4 pagesNCP Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Tract InfectionsRaveen mayi89% (9)
- Constipation NCPDocument2 pagesConstipation NCPDemilyn Olofernes-Fat100% (1)
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPRachel PerandoNo ratings yet
- NCP DysuriaDocument1 pageNCP DysuriaJerico Geronimo DacutNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Renal FailureMark Jason Rabadan100% (1)
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPJo Chiko FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Urinary RetentionDocument6 pagesUrinary Retentionjakenathanielvelasco50% (2)
- NCP For UtiDocument3 pagesNCP For UtiAaron Sanchez100% (1)
- Risk For Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument4 pagesRisk For Impaired Skin IntegrityArelys Rodriguez100% (2)
- Diarrhea NCPDocument2 pagesDiarrhea NCPNoriel FabrosNo ratings yet
- Hiv NCPDocument2 pagesHiv NCPHeindrich Cardenas0% (1)
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument5 pagesImpaired Urinary Eliminationbby_hael17100% (1)
- NCP Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 pagesNCP Urinary Tract InfectiondollythesheepNo ratings yet
- NCP-Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument1 pageNCP-Deficient Fluid Volumejanmichael8No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Problem: Acute Intermittent Moderate PainDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Problem: Acute Intermittent Moderate PainDiana Laura Lei100% (3)
- Fever NCPDocument3 pagesFever NCPBruno MercuryNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- NCP Risk For ConstipationDocument1 pageNCP Risk For Constipationjorgeacct50% (4)
- NCP UtiDocument1 pageNCP Utitsunami_cutieNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPMichelleNo ratings yet
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationMatty-b AskalaniNo ratings yet
- NCP ConstipationDocument3 pagesNCP Constipationjlucando50% (2)
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNo ratings yet
- NCP ConstipationDocument3 pagesNCP ConstipationNika LoNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Imbalance NCPDocument8 pagesElectrolyte Imbalance NCPManuel Jacob YradNo ratings yet
- Anticipatory GrievingDocument2 pagesAnticipatory GrievingKM100% (5)
- NCP For BronchitisDocument2 pagesNCP For BronchitisJefherrson Nericua Jemilo50% (2)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassRheegell Ellar-Fuertes100% (3)
- Risk For Unstable Blood GlucoseDocument24 pagesRisk For Unstable Blood GlucoseFerreze Ann100% (1)
- Activity Intolerance (NCP)Document3 pagesActivity Intolerance (NCP)Sonia Letran Singson100% (3)
- RenalDocument25 pagesRenalCamaligan RockyNo ratings yet
- Colonoscopy ProcedureDocument3 pagesColonoscopy Procedurejmarcos84No ratings yet
- Colonoscopy ProcedureDocument2 pagesColonoscopy ProcedureNick Arngel CorporalNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Biliary SystemDocument49 pagesModule 4 Biliary SystemJoverl DavidNo ratings yet
- CYSTOCLYSIS3Document9 pagesCYSTOCLYSIS3Alvin OccianoNo ratings yet
- Continuous Bladder IrrigationDocument4 pagesContinuous Bladder IrrigationToto Ryan100% (2)
- Abdominal ParacentesisDocument5 pagesAbdominal Paracentesisw wNo ratings yet
- ERCP Procedure GuideDocument7 pagesERCP Procedure GuideFachrur RodjiNo ratings yet
- Surgery Case Write UpDocument8 pagesSurgery Case Write UpKaarthigan RamaiahNo ratings yet
- MS QuizDocument18 pagesMS QuizCharlyn JenselNo ratings yet
- Bladder Irrigation 4Document23 pagesBladder Irrigation 4Jay Shree100% (2)
- Notice: Grant and Cooperative Agreement Awards: Public Housing Neighborhood Networks ProgramDocument3 pagesNotice: Grant and Cooperative Agreement Awards: Public Housing Neighborhood Networks ProgramJustia.comNo ratings yet
- Seangio Vs ReyesDocument2 pagesSeangio Vs Reyespja_14No ratings yet
- Iii. The Impact of Information Technology: Successful Communication - Key Points To RememberDocument7 pagesIii. The Impact of Information Technology: Successful Communication - Key Points To Remembermariami bubuNo ratings yet
- ANI Network - Quick Bill Pay PDFDocument2 pagesANI Network - Quick Bill Pay PDFSandeep DwivediNo ratings yet
- 978-1119504306 Financial Accounting - 4thDocument4 pages978-1119504306 Financial Accounting - 4thtaupaypayNo ratings yet
- Pea RubricDocument4 pagesPea Rubricapi-297637167No ratings yet
- Haloperidol PDFDocument4 pagesHaloperidol PDFfatimahNo ratings yet
- Responsive Docs - CREW Versus Department of Justice (DOJ) : Regarding Investigation Records of Magliocchetti: 11/12/13 - Part 3Document172 pagesResponsive Docs - CREW Versus Department of Justice (DOJ) : Regarding Investigation Records of Magliocchetti: 11/12/13 - Part 3CREWNo ratings yet
- Iluminadores y DipolosDocument9 pagesIluminadores y DipolosRamonNo ratings yet
- Abnormal PsychologyDocument4 pagesAbnormal PsychologyTania LodiNo ratings yet
- Filehost - CIA - Mind Control Techniques - (Ebook 197602 .TXT) (TEC@NZ)Document52 pagesFilehost - CIA - Mind Control Techniques - (Ebook 197602 .TXT) (TEC@NZ)razvan_9100% (1)
- English 10-Dll-Week 3Document5 pagesEnglish 10-Dll-Week 3Alyssa Grace Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Fix List For IBM WebSphere Application Server V8Document8 pagesFix List For IBM WebSphere Application Server V8animesh sutradharNo ratings yet
- Picc Lite ManualDocument366 pagesPicc Lite Manualtanny_03No ratings yet
- Topic 6Document6 pagesTopic 6Conchito Galan Jr IINo ratings yet
- ch-1 NewDocument11 pagesch-1 NewSAKIB MD SHAFIUDDINNo ratings yet
- Astm D1895 17Document4 pagesAstm D1895 17Sonia Goncalves100% (1)
- ANSI-ISA-S5.4-1991 - Instrument Loop DiagramsDocument22 pagesANSI-ISA-S5.4-1991 - Instrument Loop DiagramsCarlos Poveda100% (2)
- What Is An Ethical Dilemma?: Decision-Making ProcessDocument7 pagesWhat Is An Ethical Dilemma?: Decision-Making ProcessGauravsNo ratings yet
- End of Semester Student SurveyDocument2 pagesEnd of Semester Student SurveyJoaquinNo ratings yet
- 5f Time of Legends Joan of Arc RulebookDocument36 pages5f Time of Legends Joan of Arc Rulebookpierre borget100% (1)
- August 2023 Asylum ProcessingDocument14 pagesAugust 2023 Asylum ProcessingHenyiali RinconNo ratings yet
- 1INDEA2022001Document90 pages1INDEA2022001Renata SilvaNo ratings yet
- Damodaram Sanjivayya National Law University VisakhapatnamDocument6 pagesDamodaram Sanjivayya National Law University VisakhapatnamSuvedhya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ev Wireless Charging 5 PDFDocument27 pagesEv Wireless Charging 5 PDFJP GUPTANo ratings yet
- Living Greyhawk - Greyhawk Grumbler #1 Coldeven 598 n1Document2 pagesLiving Greyhawk - Greyhawk Grumbler #1 Coldeven 598 n1Magus da RodaNo ratings yet
- LR 7833Document11 pagesLR 7833Trung ĐinhNo ratings yet
- A Practical Guide To Transfer Pricing Policy Design and ImplementationDocument11 pagesA Practical Guide To Transfer Pricing Policy Design and ImplementationQiujun LiNo ratings yet
- Placement TestDocument6 pagesPlacement TestNovia YunitazamiNo ratings yet
- OptiX OSN 8800 6800 3800 Configuration Guide (V100R007)Document924 pagesOptiX OSN 8800 6800 3800 Configuration Guide (V100R007)vladNo ratings yet