Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ground Fault Protection Technical Guide
Uploaded by
msuri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views12 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views12 pagesGround Fault Protection Technical Guide
Uploaded by
msuriCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
GROUND FAULT
PROTECTION
TECHNICAL GUIDE
CONVERTING UNGROUNDED SYSTEMS TO
HIGH RESISTANCE GROUNDING
® Post Glover
4750 Olympic Blvd.
Erlanger, KY 41018 USA
Phone: 859-283-0778
Toll-Free: 800-537-6144
FAX: 859-283-2978
Web: www.postglover.com
® Post Glover
Table of Contents
1.1. What is Grounding? 1
1.2 What is a Grounded System? 1
1.3. What are the Different Types of System Grounding?. 1
1.4. What is the Purpose of System Grounding? 1
1.5 What is a Ground Fault? 2
1.6 Why are Ground Faults a Concern?. 2
2.1. What is an Ungrounded System?. 2
2.2 What Does IEEE Say About Ungrounded Systems?. 3
3.1. Why Consider Grounding Your System?. 3
3.2. What is a Resistance Grounded System? 4
3,3. What is a Low Resistance Grounded System?....
3.4 What is a High Resistance Grounded System’
4.1. Why Consider High Resistance Grounding?..
4.2. Why Limit the Current Through Resistance Grounding?...
4.3. What are the Requirements for Sizing the Resistor?.
4.4 Measuring the System Capacitive Charging Current...
4.5. Rule of Thumb for System Charging Current...
4.6 Is There Any Performance Downside to Applying a SA Resistor to a System that
May Only Have 1A of Charging Current?. 8
4.7 Whats the Probability that a 480V Industrial System
4000 KVA Would Require More Than a 5A Resistor? 8
4.8 Whatare the Necessary Steps to Upgrade My System? 8
® Post Glover
1.1 What is Grounding?
The term grounding is commonly used in the electrical industry to mean both
“equipment grounding” and “system grounding” “Equipment grounding” means the
connection of a non-current carrying conductive materials such as conduit, cable trays,
junction boxes, enclosures and motor frames to earth ground. “System grounding”
means the connection of the neutral points of current carrying conductors such as the
neutral point of a circuit, a transformer, rotating machinery, or a system, either solidly or
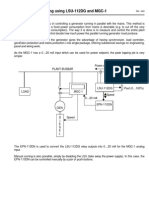
with a current limiting device to earth ground. Figure 1 illustrates the two types of
grounding.
FIGURE 1
--- SSS |_ EQUIPMENT
Transformer GROUNDING “GROUNDING
1.2 What is a Grounded System?
Grounded System — a system with at least one conductor or point (usually the middle
wire or neutral point of transformer or generator windings) is intentionally grounded,
either solidly or through an impedance, IEEE Standard 142-1991 1.2
1.3 What are the Different Types of System Grounding?
‘The types of system grounding normally used in industrial and commercial power
systems are:
1) Solid grounding
2) Low resistance grounding
3) High resistance grounding
4) Ungrounded IEEE Std 242-2001 8.2.1
1.4 What is the Purpose of System Grounding?
‘System grounding, or the intentional connection of a phase or neutral conductor to earth,
is for the purpose of controlling the voltage to earth, or ground, within predictable limits.
It also provides for a flow of current that will allow detection of an unwanted connection
between system conductors and ground [a ground fault}
You might also like
- 2458 2474Document17 pages2458 2474Shahzad BhattiNo ratings yet
- Reignition and Restrikes in Power SystemsDocument5 pagesReignition and Restrikes in Power SystemsmsuriNo ratings yet
- Double Circuit ProtectionDocument17 pagesDouble Circuit Protection1453hNo ratings yet
- A Novel Phase Selection Method Based On Instantaneous Reactive PowerDocument5 pagesA Novel Phase Selection Method Based On Instantaneous Reactive PowermsuriNo ratings yet
- Phasor Measurement UnitDocument45 pagesPhasor Measurement UnitKrishna VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- Best Protection Practices Report 1Document28 pagesBest Protection Practices Report 1shehnozmohdNo ratings yet
- Ground Distance Relays-Residual Compensation JVDocument33 pagesGround Distance Relays-Residual Compensation JVmatthijsvisser174100% (1)
- Sub Synchronous ResonanceDocument15 pagesSub Synchronous ResonanceryreddyNo ratings yet
- Neutral Point Treatment and Earth Fault Suppression PDFDocument6 pagesNeutral Point Treatment and Earth Fault Suppression PDFmsuriNo ratings yet
- ABB - False Applications of Reliable Relaying Principles RevisitedDocument8 pagesABB - False Applications of Reliable Relaying Principles RevisitedmsuriNo ratings yet
- ABB The Performance of Faulted Phase Selectors Used in Transmission Line Distance Applications PDFDocument7 pagesABB The Performance of Faulted Phase Selectors Used in Transmission Line Distance Applications PDFmsuriNo ratings yet
- ABB - False Applications of Reliable Relaying Principles RevisitedDocument8 pagesABB - False Applications of Reliable Relaying Principles RevisitedmsuriNo ratings yet
- 6662 ProtectiveRelaying FC 20140911 WebDocument12 pages6662 ProtectiveRelaying FC 20140911 WebmsuriNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Transformer Substation enDocument32 pagesIntelligent Transformer Substation enmsuriNo ratings yet
- Directional Overcurrent Relaying ConceptsDocument14 pagesDirectional Overcurrent Relaying ConceptsAji Istanto Rambono100% (1)
- Load Shedding and Underfrequency Relay Protection GuideDocument34 pagesLoad Shedding and Underfrequency Relay Protection GuideRagab TolbaNo ratings yet
- Negative Sequence Directional RelayDocument22 pagesNegative Sequence Directional RelaymsuriNo ratings yet
- Peak LoppingDocument1 pagePeak LoppingmsuriNo ratings yet
- IesengghDocument7 pagesIesengghNaveen Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- InTech-Grid Integration of Renewable Energy SystemsDocument24 pagesInTech-Grid Integration of Renewable Energy SystemsmsuriNo ratings yet
- HV Circuit BreakerDocument10 pagesHV Circuit BreakerlallyprabhNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)