Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.2 Gas Ideal
Uploaded by
vapeani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesThis document discusses the ideal gas law and how to use it to solve gas problems. It introduces Avogadro's principle that equal volumes of gases contain equal numbers of moles. It then presents the ideal gas law equation as PV=nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is moles of gas, R is the universal gas constant, and T is temperature in Kelvin. The document provides examples of using the ideal gas law to calculate pressure and volume of gases in different conditions.
Original Description:
Original Title
1.2 Gas ideal
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the ideal gas law and how to use it to solve gas problems. It introduces Avogadro's principle that equal volumes of gases contain equal numbers of moles. It then presents the ideal gas law equation as PV=nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is moles of gas, R is the universal gas constant, and T is temperature in Kelvin. The document provides examples of using the ideal gas law to calculate pressure and volume of gases in different conditions.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pages1.2 Gas Ideal
Uploaded by
vapeaniThis document discusses the ideal gas law and how to use it to solve gas problems. It introduces Avogadro's principle that equal volumes of gases contain equal numbers of moles. It then presents the ideal gas law equation as PV=nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is moles of gas, R is the universal gas constant, and T is temperature in Kelvin. The document provides examples of using the ideal gas law to calculate pressure and volume of gases in different conditions.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Ch.
10 & 11 - Gases
III. Ideal Gas Law
(p. 334-335, 340-346)
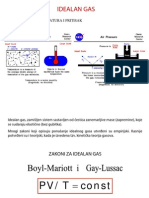
A. Avogadros Principle Avogadros
Equal volumes of gases contain equal numbers of moles at constant temp & pressure true for any gas
V =k n
n
A. Ideal Gas Law
Merge the Combined Gas Law with Avogadros Principle:
PV V k =R nT T n
UNIVERSAL GAS CONSTANT R=0.0821 Latm/molK 3kPa/molK R=8.315 dm You dont need to memorize these values!
A. Ideal Gas Law
PV=nRT
UNIVERSAL GAS CONSTANT R=0.0821 Latm/molK 3kPa/molK R=8.315 dm You dont need to memorize these values!
C. Ideal Gas Law Problems
Calculate the pressure in atmospheres of 0.412 mol of He at 16C & occupying 3.25 L.
GIVEN: WORK:
P = ? atm PV = nRT n = 0.412 mol P(3.25)=(0.412)(0.0821)(289) L mol Latm/molK K T = 16C = 289 K V = 3.25 L P = 3.01 atm R = 0.0821Latm/molK
C. Ideal Gas Law Problems
Find the volume of 85 g of O2 at 25C and 104.5 kPa.
GIVEN: WORK:
V=? 85 g 1 mol = 2.7 mol n = 85 g = 2.7 mol 32.00 g T = 25C = 298 K PV = nRT P = 104.5 kPa (104.5)V=(2.7) (8.315) (298) kPa mol dm3kPa/molK K R = 8.315 dm3kPa/molK V = 64 dm3
You might also like
- Ideal Gas Law (Part 4)Document5 pagesIdeal Gas Law (Part 4)asapamore100% (1)
- 5 - Behaviour of GasesDocument37 pages5 - Behaviour of Gasessiaskel100% (1)
- GAS LAWS Powerpoint Good OneDocument45 pagesGAS LAWS Powerpoint Good OneLerie Lou R. Penarroyo60% (5)
- Chapter 5 Gas Laws and Kinetic Theory - 2Document43 pagesChapter 5 Gas Laws and Kinetic Theory - 2Rahim RahimunNo ratings yet
- Gas Behaviour EOSDocument59 pagesGas Behaviour EOSMurugavel ChandranNo ratings yet
- 6 Gases PDFDocument70 pages6 Gases PDFRogerine RoyNo ratings yet
- THE IDEAL GAS (Topic6)Document18 pagesTHE IDEAL GAS (Topic6)Ted Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument31 pagesGas Lawsapi-546066323No ratings yet
- State of Matter-Gas)Document48 pagesState of Matter-Gas)bigsnailz100% (1)
- GasesDocument34 pagesGasesPaul Jeremiah Serrano NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Phase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas LawDocument10 pagesIdeal Gas Lawchaotictrust28No ratings yet
- G10 Science Q4 - Week 1-2-Constant Temp of GasDocument34 pagesG10 Science Q4 - Week 1-2-Constant Temp of GasMelissa Ganituen-BautistaNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasDocument12 pagesIdeal GassteveislaryNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Ideal Gas LawDocument9 pagesLesson 5 - Ideal Gas LawTeacher JoanNo ratings yet
- Section 3-7Document32 pagesSection 3-7api-245255231No ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law NotesDocument4 pagesIdeal Gas Law NotesPrincess Jean GalabinNo ratings yet
- Gay Lussac Combined Avogadro Ideal Gas Law ApplicationDocument28 pagesGay Lussac Combined Avogadro Ideal Gas Law ApplicationAlexandra Venice Ann M. PerezNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Ideal Gas Law 5584a8a9dcd51Document25 pagesDokumen - Tips - Ideal Gas Law 5584a8a9dcd51Earl CruzNo ratings yet
- 9.3 Ideal GasDocument53 pages9.3 Ideal GasshahoodaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Gases Gas LawsDocument22 pagesLecture 2 - Gases Gas LawsWillie MojataleNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasDocument12 pagesIdeal GasJasminSutkovicNo ratings yet
- 1 23 Gas Calculations PDFDocument6 pages1 23 Gas Calculations PDFschool adressNo ratings yet
- 1-Ideal Gas LectureDocument60 pages1-Ideal Gas LecturemahmoudNo ratings yet
- 1.23 Gas Calculations: Molar Gas Volume (OCR +EDEXCEL)Document7 pages1.23 Gas Calculations: Molar Gas Volume (OCR +EDEXCEL)SunnyNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument66 pagesGas LawsLorilieNo ratings yet
- Chem 105-8, Sections 8.1, 8.2, 8.5 NotesDocument36 pagesChem 105-8, Sections 8.1, 8.2, 8.5 NotesKhang TrầnNo ratings yet
- GaslawsDocument32 pagesGaslawsDiane Telo ParaguisonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Sept13Document57 pagesChapter 10 Sept13chandro57No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Ideal Gas LawDocument8 pagesLesson 5 - Ideal Gas LawJoanNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Gas LawsDocument53 pagesWeek 7 Gas LawsMica Shane billedo PapaNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law Derivation For The Equations of The Ideal Gas LawDocument4 pagesIdeal Gas Law Derivation For The Equations of The Ideal Gas LawIan Kirk VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Question On GasesDocument9 pagesQuestion On GasesAhmad AlnajjarNo ratings yet
- 05 Gases Without AnswersDocument17 pages05 Gases Without Answersapi-287405319No ratings yet
- The Ideal Gas LawDocument3 pagesThe Ideal Gas LawGovind RaoNo ratings yet
- Chem 181 Chemistry of GasesDocument15 pagesChem 181 Chemistry of GasesJoey PooleNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Gases StudentDocument48 pagesCH 10 Gases StudentTrọng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 5.0 States of MatterDocument106 pages5.0 States of MatterTasya KassimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 CHEM110Document59 pagesChapter 5 CHEM110gracetetu102No ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry 1Document49 pagesEngineering Chemistry 1Rasha HajaratNo ratings yet
- Gas LawDocument37 pagesGas LawSupasinee RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document42 pagesChapter 14Aubrey LanotNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GasesDocument100 pagesChapter 5 GasesFABIO DE LIMANo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 2)Document45 pagesTopic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 2)Joshua LaBordeNo ratings yet
- Gases and Their Properties: Exercises, Examples, and BOLD Numbered ProblemsDocument106 pagesGases and Their Properties: Exercises, Examples, and BOLD Numbered ProblemsMia YukimuraNo ratings yet
- Ideal & Combined Gas LawsDocument13 pagesIdeal & Combined Gas LawsJihan LuNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Gases - PDFDocument7 pagesBehaviour of Gases - PDFNasih AhmadNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Ideal Gas LawDocument15 pages3.4 Ideal Gas LawfaridaisepicNo ratings yet
- Notes Solutions Chapter 05Document22 pagesNotes Solutions Chapter 05steveislaryNo ratings yet
- Prac-6 - Ideal GasesDocument18 pagesPrac-6 - Ideal GasesCristiano PassarelliNo ratings yet
- The Gas Laws: Equations of StateDocument32 pagesThe Gas Laws: Equations of Stateyiye rubyNo ratings yet
- Idealan GasDocument17 pagesIdealan Gasmferi92No ratings yet
- Gases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783Document34 pagesGases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783ade dosmariaNo ratings yet
- Gases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783Document34 pagesGases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783ade dosmariaNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 Lecture Note-Gas LawsDocument11 pagesCHM 101 Lecture Note-Gas LawsMichael DanielsNo ratings yet
- Gas TheoryDocument65 pagesGas TheoryNicole OssaNo ratings yet
- CHEM103 LW4 AnnotatedDocument25 pagesCHEM103 LW4 AnnotatedOmar MatarNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws (Schools - Nbisd.org-Page-Open-16436-0-Ideal PDFDocument14 pagesGas Laws (Schools - Nbisd.org-Page-Open-16436-0-Ideal PDFbinzNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws HandoutDocument10 pagesGas Laws HandoutVenu ReddyNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)