Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aldol Condensation
Uploaded by
rjbagh08Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aldol Condensation
Uploaded by
rjbagh08Copyright:
Available Formats
CHEM 3220
Aldol Condensation
Harris/ Dandekar
Aldol Condensation
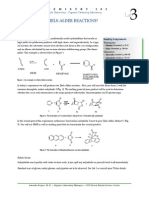
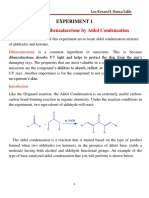
Chapter 37 37.1: Synthesis of dibenzalacetone
O O O
+ acetone
NaOH 95% EtOH (solvent) dibenzalacetone (E,E isomer)
benzaldehyde
Theory:
Reactivity: o Acidity of alpha hydrogen atoms: pKa of hydrogen atoms to >C=O groups: ~20 SO:
o
In presence of base, proton abstraction affords enolate ions: Resonance stabilized Excellent Nucleophiles Nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl group gives the addition product: aldol adduct Spontaneous dehydration of the adduct: aldol condensation product Why is dehydration so facile? o Conjugated enal or enone E isomers tend to predominate
Different types of aldol condensations: o Normal Same aldehyde (or ketone) as substrate and nucleophile o Crossed Two different aldehydes (or ketones) Up to 4 products obtained under these conditions Synthetically useful when one reactant lacks - hydrogens
o
Claisen-Schmidt (mixed aldol) Condensation reaction between an aldehyde and a ketone The aldehyde carbonyl is moe reactive than that of the ketone, and therefore, reacts rapidly with the anion of the ketone to give a beta-hydroxyketone, which easily undergoes base-catalyzed dehydration Good to use NaOH so that the ketones dont significantly self-condense
CHEM 3220
Aldol Condensation
Harris/ Dandekar
Forms conjugation between carbonyl group, alkene, and benzene ring
Reaction Mechanism:
:O :
H O
:O :
:
:O :
OH
: H 2O
:O :
:
enolate ion
OH
aldol adduct [- H 2O]
O
OH dibenzalacetone (E,E isomer)
repeat all steps at the other - position
aldol condensation product (E isomer)
Note Stoichiometry: o Need 2 moles of benzaldehyde : 1 mole acetone By-product: o Self-condensation product(s): It is possible for the enolate ion (from acetone) to add to the carbonyl group of a second acetone molecule, ultimately leading to the corresponding condensation product(s).
:O: : + :O: :O:
OH
[- H2O] : O :
:O:
CHEM 3220
Aldol Condensation
Harris/ Dandekar
It is often possible to minimize the formation of this type of by-product by careful experimental design By adding acetone (diluted with solvent) dropwise to a mixture of benzaldehyde and base, the statistical possibility of selfcondensation is minimized.
Experiment:
Aldol Condensation: Exp 37.1: Synthesis of Dibenzalacetone Follow the procedure given on pp. 485-486. Stoichiometry is critical: o Insufficient quantity of benzaldehyde (i.e., less than 2 mol equivalents) will decrease yield Note the role of the solvent(s): o Protic solvent: water (from aq NaOH) and/or ethanol is involved in the mechanism o Quantity of ethanol is critical: Enough to allow the reactants as well as the principal intermediate ( benzalacetone ) to be soluble, but not enough to dissolve the product SO: The product precipitates out o Drives the reaction to completion During work-up: o The base residue is removed by thorough washing with water Why not simply neutralize with acid ? Can the product react with aqueous acid?
You dont need to: o weigh your product and o determine the percent yield. Do record the melting point of the product.
Pre-Lab Assignment
LabBook: Q 3- 4 pp. 488
Reading Assignment
LabBook: Chapter Ch 37 Also Read: Aldol condensation and related reactions from an organic textbook (e.g., Jones/Fleming or Solomons/Fryhle)
Post-Lab Assignment
Draw the structures of the (E,Z) and (Z,Z) isomers of dibenzal.
3
CHEM 3220
Aldol Condensation
Harris/ Dandekar
Do you expect dibenzal to have a characteristic UV absorption? Explain.
You might also like
- Aldol Notes PDFDocument8 pagesAldol Notes PDFAna100% (1)
- Aldehyde & Ketone ReactionsDocument21 pagesAldehyde & Ketone ReactionsAinsssNo ratings yet
- CHEM35.1 E5 Aldol Condensation: Synthesis of DibenzalacetoneDocument3 pagesCHEM35.1 E5 Aldol Condensation: Synthesis of DibenzalacetoneGlenn Vincent Tumimbang50% (2)
- Aldol CondensationDocument2 pagesAldol CondensationGian Wyatt Gamboa100% (1)
- Synthesis of Dibenzalacetone via Mixed Aldol CondensationDocument12 pagesSynthesis of Dibenzalacetone via Mixed Aldol Condensationvicky_law_2No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Practical 301Document22 pagesOrganic Chemistry Practical 301geetesh waghela100% (1)
- Diels Alder LabDocument8 pagesDiels Alder Labfatevilcow0% (1)
- Synthesis of An Alkyl HalideDocument4 pagesSynthesis of An Alkyl HalideJoseph CatiisNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 The Preparation of AcetanlideDocument12 pagesExperiment 8 The Preparation of AcetanlideRadhwanNo ratings yet
- Aldol Condensation Product IdentificationDocument5 pagesAldol Condensation Product IdentificationKatherine McLarneyNo ratings yet
- Di Benz Al AcetoneDocument3 pagesDi Benz Al AcetoneKristine Mae De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Obtaining Pure Acetanilide From Crude Acetanilide by Recrystallization ProcessDocument5 pagesObtaining Pure Acetanilide From Crude Acetanilide by Recrystallization ProcessCharlot NavarroNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Dibenzalacetone via Aldol CondensationDocument4 pagesPreparation of Dibenzalacetone via Aldol CondensationMichael E G Byers100% (1)
- Sythesization and Purification of Acetanilide by Acetylation and Re CrystallizationDocument4 pagesSythesization and Purification of Acetanilide by Acetylation and Re CrystallizationToni Sy EncinaresNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 5Document5 pagesLab Activity 5Jasmin CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Aldol CondensationDocument4 pagesAldol CondensationLevy Medina Traya100% (1)
- Aldol Condensation Reaction Lab ReportDocument4 pagesAldol Condensation Reaction Lab ReportAvril Watson100% (3)
- Aldol Condensation LabDocument6 pagesAldol Condensation LabChristian AmpeNo ratings yet
- Recrystallization PDFDocument5 pagesRecrystallization PDFMikee GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Purification of An Alkyl Halide FRDocument6 pagesPreparation and Purification of An Alkyl Halide FRCamille GrefaldiaNo ratings yet
- 11 Synthesis DibenzalacetoneDocument7 pages11 Synthesis DibenzalacetoneHyuReaper100% (1)
- Recrystallize Aspirin & Purify Salicylic AcidDocument32 pagesRecrystallize Aspirin & Purify Salicylic AcidYosita RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Emperiment 4 The Entire DocumentDocument8 pagesEmperiment 4 The Entire Documentapi-242183251No ratings yet
- Experiment 32Document14 pagesExperiment 32Morgan Elizabeth Lepley100% (6)
- Nitrating Methyl BenzoateDocument6 pagesNitrating Methyl BenzoateOstap 奧斯塔普67% (3)
- Aldol CondensationDocument10 pagesAldol CondensationVanessa Nguyen0% (1)
- Lab 10 - Diels AlderDocument4 pagesLab 10 - Diels AlderAlison NguyenNo ratings yet
- Determination of Fluoride Concentration Using Ion Selective ElectrodeDocument7 pagesDetermination of Fluoride Concentration Using Ion Selective ElectrodeAmanda WangNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument1 pageAldehydes and KetonesThea Mae Dino0% (1)
- Formal Diazo Dye ReportDocument9 pagesFormal Diazo Dye Reportbig504075% (4)
- Exp 6 Williamson Ether SynthesisDocument5 pagesExp 6 Williamson Ether SynthesisSherry0% (1)
- KKDocument3 pagesKKKatrinne Clea PincaNo ratings yet
- Benzoin Exp7Document4 pagesBenzoin Exp7Liz Hackett0% (1)
- ManualDocument8 pagesManualSweta Suman100% (1)
- Oxidation of Cyclohexanol To CyclohexanoneDocument5 pagesOxidation of Cyclohexanol To CyclohexanoneChandrani Chakraborti100% (1)
- Santa Monica College Chem 22 Lab ManualDocument59 pagesSanta Monica College Chem 22 Lab ManualMide Ogundipe100% (1)
- Lab Report 3Document9 pagesLab Report 3ainnorNo ratings yet
- Name Reactions in Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesName Reactions in Organic Chemistrysatyamd1979No ratings yet
- Synthesis of Tert-Butyl ChlorideDocument6 pagesSynthesis of Tert-Butyl ChlorideJoone Xyron CreenciaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Report - Diels-Alder ReactionDocument3 pagesLab 1 Report - Diels-Alder Reactionlucyli115100% (2)
- DibenzalacetoneDocument3 pagesDibenzalacetoneDrGajanan VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Lab+Manual+2014 Cbe 2207Document63 pagesLab+Manual+2014 Cbe 2207Krishnan MohanNo ratings yet
- Exer2 PrelabDocument3 pagesExer2 Prelabkarinadegoma100% (1)
- Chem 31 AtqE1Document3 pagesChem 31 AtqE1Anonymous GO6JVW9WudNo ratings yet
- Preparation of DibenzalacetoneDocument7 pagesPreparation of DibenzalacetoneHaiqal AzizNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Determination of Mixed AlkaliDocument2 pagesExperiment 3 - Determination of Mixed AlkaliPeter BrayNo ratings yet
- Mononitration of TolueneDocument4 pagesMononitration of TolueneNur Syafiqah Izzuddin100% (1)
- NaBH4 Reduction of Cyclohexanone to Cyclohexanol (87Document8 pagesNaBH4 Reduction of Cyclohexanone to Cyclohexanol (87hahadindongNo ratings yet
- 2 BenzophenoneDocument3 pages2 BenzophenoneElizabeth LawsonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 125 Laboratory 11Document5 pagesChemistry 125 Laboratory 11SmaeUBNo ratings yet
- Lab C-Methyl OrangeDocument4 pagesLab C-Methyl Orangetopikamew100% (1)
- Co3O4 Nanocrystals Catalyze Cyclohexane OxidationDocument6 pagesCo3O4 Nanocrystals Catalyze Cyclohexane OxidationSuhaila MohammadNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Isoamyl AcetateDocument3 pagesSynthesis of Isoamyl AcetateClaire TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 123456 1 PDFDocument18 pagesExperiment 123456 1 PDFHardi Ahmed100% (1)
- Recrystallization of AcetanilideDocument2 pagesRecrystallization of Acetaniliderm_gabriel07No ratings yet
- Organic - Lab 8 - ReductionDocument6 pagesOrganic - Lab 8 - ReductionQuynhTrang DaoNo ratings yet
- Aldol Condensation Synthesis of Dibenzalacetone Using The Claisen-Schmidt ReactionDocument6 pagesAldol Condensation Synthesis of Dibenzalacetone Using The Claisen-Schmidt ReactionRhonda Lewis-Morenzoni86% (7)
- EXP4 The Diels Alder ReactionsDocument3 pagesEXP4 The Diels Alder ReactionsLaura GuidoNo ratings yet
- Lab 6-283gDocument11 pagesLab 6-283gAnonymous 4KuItFhNo ratings yet
- 19 Enolates Enamines-2Document59 pages19 Enolates Enamines-2ronNo ratings yet
- 67 Power Steering Squeaking Repair ProcedureDocument4 pages67 Power Steering Squeaking Repair Procedurerjbagh08No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 PDFDocument29 pagesChapter 9 PDFYhunie Nhita Itha50% (2)
- Chapter 5Document28 pagesChapter 5Shoaib ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Frog Muscle ProtocolDocument13 pagesFrog Muscle Protocolrjbagh08No ratings yet
- CH 3 ProblemsDocument2 pagesCH 3 Problemsrjbagh08No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 3Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry 3api-659209201No ratings yet
- ACS Review 18 Enols and EnolatesDocument11 pagesACS Review 18 Enols and EnolatesJana BazziNo ratings yet
- Chapter1312 PDFDocument21 pagesChapter1312 PDFSamreena KanwalNo ratings yet
- Reaction MechanismDocument19 pagesReaction Mechanismtapas kunduNo ratings yet
- SN1 Vs SN2 PDFDocument1 pageSN1 Vs SN2 PDFAnup PatelNo ratings yet
- SN1 and SN2 reactions of haloalkanes and haloarenesDocument4 pagesSN1 and SN2 reactions of haloalkanes and haloarenesSachin B SNo ratings yet
- Substitution Reactions - PMDocument64 pagesSubstitution Reactions - PMprasoon jhaNo ratings yet
- OzonolysisDocument2 pagesOzonolysisAnubhav RajNo ratings yet
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution DPPDocument35 pagesElectrophilic Aromatic Substitution DPPAsif Hoda0% (1)
- CY 1001 - Structure, Bonding, and Reactivity: Organic ChemistryDocument22 pagesCY 1001 - Structure, Bonding, and Reactivity: Organic ChemistryIron BusterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 NotesDocument21 pagesChapter 6 NotesJesús Adrián Gómez OrtizNo ratings yet
- Organic Reaction MechanismDocument15 pagesOrganic Reaction Mechanismrohit13339No ratings yet
- FGT-part 2Document38 pagesFGT-part 2Nhung NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Ketene Chemistry and The Application in Synthesis - Xuan ZhouDocument38 pagesKetene Chemistry and The Application in Synthesis - Xuan ZhouMominaNo ratings yet
- Index of M. S. Chauchan Book PDFDocument7 pagesIndex of M. S. Chauchan Book PDFsoumengoswami10No ratings yet
- CSS Past Paper Css Chemistry Paper 2021Document2 pagesCSS Past Paper Css Chemistry Paper 2021Ali TaraNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Joule PDFDocument46 pagesSolucionario Joule PDFcarlosNo ratings yet
- Carbanions IDocument40 pagesCarbanions INurhan KishaliNo ratings yet
- 14 Addition of Enolates To Enones The Michael ReactionDocument8 pages14 Addition of Enolates To Enones The Michael ReactionNikola NinkovNo ratings yet
- Cm3031 - Organic Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis: Mihaiela C. StuparuDocument8 pagesCm3031 - Organic Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis: Mihaiela C. StuparuCatherine TiongNo ratings yet
- Name ReactionsDocument32 pagesName ReactionsM.NandabalanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Organic Reactions: Reaction FormatDocument2 pagesSummary of Organic Reactions: Reaction FormatBem LimNo ratings yet
- Olefination ReactionsDocument38 pagesOlefination Reactionskatechem3No ratings yet
- Chem 223 SI - Chapter 19 Part 2Document5 pagesChem 223 SI - Chapter 19 Part 2Yvonne ChuehNo ratings yet
- SN1 ReactionDocument2 pagesSN1 ReactionAmlan KalitaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Hydroxy Derivatives ReactionsDocument46 pagesOrganic Chemistry Hydroxy Derivatives ReactionsJagan EashwarNo ratings yet
- Pericyclic Reaction Theory: Orbital Symmetries and Transition State AromaticityDocument29 pagesPericyclic Reaction Theory: Orbital Symmetries and Transition State AromaticityprejudicedNo ratings yet
- Assignment-CA SIC2002Document6 pagesAssignment-CA SIC2002Baginda RamleeNo ratings yet
- L LabsDocument7 pagesL LabsHoodRomelNo ratings yet
- Pericyclic Reactions, 1Document7 pagesPericyclic Reactions, 1Aparna SahaNo ratings yet