Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cut Off Active Saturation
Uploaded by
Jasgt SinghOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cut Off Active Saturation
Uploaded by
Jasgt SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
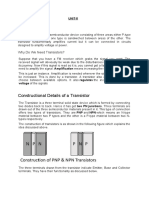
Cut off, Active and saturation regions of a transistor: Transistor Biasing:The application of suitable dc voltages across the transistor
terminals is called biasing. Each junction of a transistor may be forward biased or reverse biased independently.These are following three different ways of biasing a transistor ,which is also known as modes of transistor operation.
Forward active:Emitter-Base junction is forward biased Collector- base junction is reverse biased.
Saturation Region:Emitter-Base junction is forward biased Collector- base junction is forward biased In this mode transistor has a very large value of current. The transistor is operated in this mode, when it is used as a closed switch.
Cut- off Region:Emitter-Base junction is reverse biased Collector- base junction is reverse biased In this region both the junctions are Reverse Biased. In this mode transistor has zero current. The transistor is operated in this mode, when it is used as an open switch.
Output characteristics of Common Emitter Transistor
Modes of transistor action: S.no 1. 2. 3. Junction bias condition Mode Forward-Active Saturation Cut-off Emitter-base Forward Forward Reverse Collector-base Reverse Forward Reverse
You might also like
- Cut Off, Active and Saturation Regions of A Transistor: Transistor BiasingDocument2 pagesCut Off, Active and Saturation Regions of A Transistor: Transistor BiasingSomnath YadavNo ratings yet
- Transistor Regions: Active, Saturation, Cut-offDocument2 pagesTransistor Regions: Active, Saturation, Cut-offRishabh GoyalNo ratings yet
- Cut Off Active SaturationDocument2 pagesCut Off Active SaturationAnonymous rVSx7Y30CNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument33 pagesUntitledSahithi RNo ratings yet
- TRANSISTORDocument60 pagesTRANSISTORNaty SeyoumNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Juction TransistorDocument26 pagesBipolar Juction TransistorLalit KanojeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Week 03Document54 pagesLecture Week 03عبدالله قيس محمود الحيدريNo ratings yet
- Microwave Semiconductor Devices and Transistor Surface GeometriesDocument21 pagesMicrowave Semiconductor Devices and Transistor Surface GeometriesjohnmechanjiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document46 pagesUnit 2Manan JainNo ratings yet
- Tesla Coil NPN TransistorDocument16 pagesTesla Coil NPN TransistorRaj TokasNo ratings yet
- Transistor Definition & HistoryDocument30 pagesTransistor Definition & HistoryLaxman BabuNo ratings yet
- Ecad Exp8Document7 pagesEcad Exp8Saturn MoonNo ratings yet
- Mod 2Document99 pagesMod 2SREEHARI V ANo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument70 pagesUnit VVani SenthilNo ratings yet
- NNNNNNDocument3 pagesNNNNNNAly Sherif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument26 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorsmunashetakazNo ratings yet
- ELectronics 2Document10 pagesELectronics 2abdallaNo ratings yet
- Bec (BJT Transistor)Document23 pagesBec (BJT Transistor)aditi pawarNo ratings yet
- SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS OF DEVICES Unit 3Document15 pagesSWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS OF DEVICES Unit 3abdulkadir mohamedNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor: 1) Different Between Majority and Minority ChargeDocument2 pagesSemiconductor: 1) Different Between Majority and Minority ChargeCabdiquwi Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Transistor Basics ExplainedDocument3 pagesTransistor Basics Explained2K19/EC/005 AASTIKNo ratings yet
- Transistor NPNDocument18 pagesTransistor NPNdiktoNo ratings yet
- Thyristor (Autosaved)Document13 pagesThyristor (Autosaved)Muaavia QayyumNo ratings yet
- TRANSISTORSDocument13 pagesTRANSISTORSAbad Kurt ChristianNo ratings yet
- BJT Transistor GuideDocument10 pagesBJT Transistor GuideShreepad Shivkar100% (1)
- Monostable Multivibrator Using TransistorsDocument4 pagesMonostable Multivibrator Using TransistorsHemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Circuits - Blocking OscillatorsDocument6 pagesPulse Circuits - Blocking OscillatorsNakib AhsanNo ratings yet
- Blockk PDFDocument5 pagesBlockk PDFIsaias Bartolomeu SambgaNo ratings yet
- Class 1 Transistor As A SwitchDocument11 pagesClass 1 Transistor As A Switchermaheshkumar4No ratings yet
- Transistor Unit 2Document5 pagesTransistor Unit 2DINESH SINGH100% (1)
- Electronic Workshop Presentation by Zainab Sajjad (2k20-TE-19)Document9 pagesElectronic Workshop Presentation by Zainab Sajjad (2k20-TE-19)zainabsajjad1to7No ratings yet
- Transistor EnglishDocument5 pagesTransistor EnglishArif KusumaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Transistors and Their WorkingDocument22 pagesDifferent Types of Transistors and Their WorkingVenki EdeNo ratings yet
- 5 MultivibratorsDocument12 pages5 MultivibratorsTeshale AlemieNo ratings yet
- BJT Electronics Transistor PHY 234 Fall 2021Document22 pagesBJT Electronics Transistor PHY 234 Fall 2021Fatima KhanNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Transistor BasicsDocument18 pagesBipolar Transistor Basicssreenadh reddyNo ratings yet
- BJT Transistor CharacteristicsDocument21 pagesBJT Transistor CharacteristicsKrisna Adji SyahputraNo ratings yet
- BJT Transistor As A SwitchDocument1 pageBJT Transistor As A SwitchKingNo ratings yet
- Transistor As A SwitchDocument3 pagesTransistor As A SwitchbofshafiqueNo ratings yet
- Thyristor or SCRDocument7 pagesThyristor or SCRsaravananvietwNo ratings yet
- Transistor As A Switch 1 Eelectronic Devices and Circuit Active Learning AssignmentDocument5 pagesTransistor As A Switch 1 Eelectronic Devices and Circuit Active Learning AssignmentAmanNo ratings yet
- BJT Basics: Understanding Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument48 pagesBJT Basics: Understanding Bipolar Junction Transistorsbelacheweshetu222No ratings yet
- BJT Transistor As A SwitchDocument12 pagesBJT Transistor As A SwitchRoaa AlfakeehNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCRsDocument19 pagesIntroduction to Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCRsAlbin RobinNo ratings yet
- ThyristorDocument20 pagesThyristorMuaavia QayyumNo ratings yet
- Module 2-18EE53Document59 pagesModule 2-18EE53AshwiniNo ratings yet
- PNP TransistorDocument17 pagesPNP TransistorsuhaybNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits - BJT L6pptxDocument12 pagesElectronic Circuits - BJT L6pptxbosefe6716No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document32 pagesChapter 3AdsbymeNo ratings yet
- Transistor Operating Conditions:: AnswerDocument7 pagesTransistor Operating Conditions:: Answersara khanNo ratings yet
- What is a Thyristor? Understanding Semiconductor DevicesDocument44 pagesWhat is a Thyristor? Understanding Semiconductor DevicesKhalid Abdirashid AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Transistors Question and Answers Doc by PranghiDocument15 pagesTransistors Question and Answers Doc by PranghiPRANGHI80% (10)
- #12: Transistor As A Switch DiscussionDocument1 page#12: Transistor As A Switch DiscussionMischelle NohayNo ratings yet
- DISCUSSIONDocument3 pagesDISCUSSIONHarsha MadushanNo ratings yet
- Clipper Circuits: Reverse and Forward Bias ModesDocument4 pagesClipper Circuits: Reverse and Forward Bias ModesSK LAMIGAN100% (1)
- Electrical Devices & Circuits EEE-0103 - EEE - 205: Jubayer Al MahmudDocument21 pagesElectrical Devices & Circuits EEE-0103 - EEE - 205: Jubayer Al MahmudMd Kabir HassanNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Engg Unit 2Document25 pagesBasic Electronics Engg Unit 2Harshal VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1) Transistors: Marks 24: IntroductionDocument24 pagesTopic 1) Transistors: Marks 24: IntroductionSudershan Dolli100% (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Must Read Parallel PortDocument8 pagesMust Read Parallel PortJasgt SinghNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed Control Using C++Document77 pagesDC Motor Speed Control Using C++eraditya2001100% (11)
- Gaming Over Ad-Hoc Peer-To-Peer Networks WPDocument10 pagesGaming Over Ad-Hoc Peer-To-Peer Networks WPJasgt SinghNo ratings yet
- EWSDDocument40 pagesEWSDJasgt SinghNo ratings yet