Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BEF22903 Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
Patricia KCOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BEF22903 Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
Patricia KCCopyright:
Available Formats
BEF 22903 ENGINEERING ELECTROMAGNETICS TUTORIAL 1
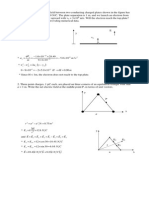
1. The charges on the charged plastic rod can be transferred to a metal sphere by conduction or induction technique. Explain both techniques. 2. Briefly explain on the conservation of electric charged. 3. State and explain Coulombs Law. 4. Point charges Q1 = 5 C and Q2 = -4 C are placed at (3, 2, 1 ) and (-4, 0, 6), respectively. Determine the force on Q1. (Ans: -1.8291 x - 0.5226 y +1.3065 z mN) 5. Point charges Q1 and Q2 are, respectively, located at (4, 0, -3) and (2, 0, 1). If Q2 = 4 nC, find Q1 such that r (a) The E at (5, 0, 6) has no z-component. (b) The force on a test charge at (5, 0, 6) has no x-component. (Ans: (a) -8.3232 nC, (b) -44.945 nC) 6. Three surface charge distributions are located in free space as follows: 10 C/m2 at r y = 2, -20 C/m2 at y = -3, and 30 C/m2 at y = -5. Determine E at (a) P(5, -1, 4) (b) R(0, -4, 1) (c) Q(3, 4, -5) (Ans: (a) 0 V/m, (b) 2.258 x 106 y V/m, (c) 1.13 x 10 6 y V/m) 7. A uniform line charge density of 10 nC/m is positioned at x = 0, y = 2, while another r uniform line charge density of -10 nC/m is positioned at x = 0, y = -2. Find E at the origin. (Ans: -180 y V/m ) 8. Infinite uniform line charges of 5 nC/m lie along the (positive and negative) x and y
axes in free space. Find E at: (a) PA(0, 0, 4); (b) PB(0, 3, 4). (Ans: (a) 45 z V/m, (b) 10.8 y + 36.9 z V/m) 9. An infinite uniform line charge L = 2 nC/m lies along the x-axis in free space, while point charge of 8 nC each are located at (0, 0, 1) and (0, 0, -1). r (a) Find E at (2, 3, -4).
(b) To what value should L be changed to cause E to be a zero at (0, 0, 3)? (Ans:(a) 2.008 x + 7.325 y V/m, (b) -3.75 nC/m)
10. A uniform line charge of 2C/m is located on the z - axis. Find in rectangular coordinates at P(1, 2, 3) if the charge exists from: (a) - < z < (b) -4 z 4 (Ans: (a) 7.2 x + 14.4 y kV/m, (b) 4.9 x + 9.8 y + 4.9 z kV/m)
ERB.EE.BEF22903
11. A ring placed along the y2 + z2 = 4, x = 0 carries a uniform charge 5 C/m.
(a) Find D at P(3, 0, 0). (b) If two identical point charges Q are placed at (0, -3, 0) and (0, 3, 0) in addition to
the ring, find the value of Q such that D = 0 at P. (Ans: (a) 0.32 x C/m2, (b)-51.182 C ) 12. A spherical charge distribution is given by
v = r 2
10 3 mC/m , 1< r < 4 0 , otherwise
(a) Find the net flux crossing surface r = 2 m and r = 6 m. r (b) Determine D at r = 5 m. (Ans: (a) 125.7 mC, 377 mC (b) 1.2 r mC/m2) 13. A spherical charge distribution is given by
r
Find E everywhere.
r 3 o mC/m , r < a v = a 0 , r >a
(Ans: E =
r r 2 0 r a3 r mV/m , E = 2 0 r mV/m ) 4 a 0 4r 0
14. Two point charges Q1 = 2 nC and Q2 = -4 nC are located at (1, 0, 3) and (-2, 1, 5), respectively. Determine the potential at P(1, -2, 3). (Ans: 1.32V) 15. Three point charges Q1 = 1mC, Q2 = -2 mC, and Q3 = 3 mC are, respectively, located at (0, 0, 4), (-2, 5, 1), and (3, -4, 6). (a) Find the potential Vp at P(-1, 1, 2). (b) Calculate the potential difference VPQ if Q is (1, 2, 3). (Ans: (a) 3 x 106 V, (b) 0.69 x 106 V)
ERB.EE.BEF22903
You might also like
- Physics Question BankDocument209 pagesPhysics Question BankRoberto De La Paz93% (15)
- Tutorial 4 Solution EmagnetDocument6 pagesTutorial 4 Solution Emagnethafiz azman100% (3)
- Electrostatics ExerciseDocument20 pagesElectrostatics ExerciseUtkarsh Mittal86% (7)
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksFrom EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Electrostatics Solved QBPDFDocument75 pagesElectrostatics Solved QBPDFMohammed Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- Problems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionFrom EverandProblems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Bansal Classes Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEDocument445 pagesBansal Classes Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEESankar Kumarasamy100% (5)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Aee1 SkriptDocument186 pagesAee1 SkriptCristian PanaNo ratings yet
- NEET Electrostatics NotesDocument40 pagesNEET Electrostatics Notesavinash_friends21100% (1)
- Iit Jee Physics Full Packed PDFDocument180 pagesIit Jee Physics Full Packed PDFAyush Kumar100% (1)
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Minutes Meeting of Integrated Design Project 1 (BEE22002) : Item Particulars Action byDocument2 pagesMinutes Meeting of Integrated Design Project 1 (BEE22002) : Item Particulars Action byPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Physics 21 SolutionsDocument92 pagesPhysics 21 SolutionsOğuzhan Odbay100% (1)
- EME Tutorial - 2 To 5Document5 pagesEME Tutorial - 2 To 5Aditya Gadgil100% (1)
- Assignment2 PDFDocument9 pagesAssignment2 PDFSuresh ThallapelliNo ratings yet
- 2 Electrostaic Work SheetDocument1 page2 Electrostaic Work Sheetnebauzumaki111No ratings yet
- Field (A) Electromagnetic Sheet 10th of RamadanDocument6 pagesField (A) Electromagnetic Sheet 10th of RamadanaboashoorNo ratings yet
- Sheet2 Waves2Document4 pagesSheet2 Waves2Ahmed NaserNo ratings yet
- ElectromagneticsDocument2 pagesElectromagneticsSyarfa ZahirahNo ratings yet
- Assignment New IDocument2 pagesAssignment New IRanjith Bhoopal100% (1)
- Physics 1653 Exam 3 - Review Questions: Sphere A Sphere BDocument39 pagesPhysics 1653 Exam 3 - Review Questions: Sphere A Sphere BPi PoliNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 1jawaidaligNo ratings yet
- 07 08 II ms1Document5 pages07 08 II ms1Mahmoud FariedNo ratings yet
- Fields Assignment 1Document2 pagesFields Assignment 1checkitoutwitharjunNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Assignment: Gravity ClassesDocument6 pagesElectrostatics Assignment: Gravity Classesjagan9912342495No ratings yet
- 1st Year E & M Problem Sheet 1Document3 pages1st Year E & M Problem Sheet 1vsinisa1No ratings yet
- 3.electromagnetic Theory NET-JRF VKSDocument31 pages3.electromagnetic Theory NET-JRF VKSSijil SalimNo ratings yet
- Physics Electrostatics MCQDocument8 pagesPhysics Electrostatics MCQRupinder SidhuNo ratings yet
- Ch21 SSMDocument18 pagesCh21 SSMFranko UrciaNo ratings yet
- Assignment3 PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment3 PDFSuresh ThallapelliNo ratings yet
- Mahavir Swami College of Engineering and Technology: Question BankDocument2 pagesMahavir Swami College of Engineering and Technology: Question BankNana's LysosomeNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit 1 SJP PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment Unit 1 SJP PDFUtkarshsingh GroverNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGDocument20 pagesElectrostatics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGSubhashChandraMishraNo ratings yet
- Scan May 10, 2021Document11 pagesScan May 10, 2021yashwant bhaduNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit-I: A A H H EDocument2 pagesAssignment Unit-I: A A H H Evamshi gundepanguNo ratings yet
- DPP - 07 - ElectrostaticsDocument4 pagesDPP - 07 - ElectrostaticsYash GhorpadeNo ratings yet
- Field and Wave Sample Paper97-2003Document6 pagesField and Wave Sample Paper97-2003Abhimanyu NainNo ratings yet
- 2019 PHY 2 CLC BTapDocument15 pages2019 PHY 2 CLC BTapzuuuNo ratings yet
- Two Small Spheres in MotionDocument12 pagesTwo Small Spheres in MotionharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Combined DPP ElectrostaticDocument27 pagesCombined DPP ElectrostaticUpendra YadavNo ratings yet
- S. No Questions Solutions Sol:1 (D) : L L T S L LDocument8 pagesS. No Questions Solutions Sol:1 (D) : L L T S L LVaibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Respuestas de TallerDocument5 pagesRespuestas de TallerSergio Andres Molina MendietaNo ratings yet
- 23 - 26 - solutions 물리Document9 pages23 - 26 - solutions 물리전삼기No ratings yet
- Electrostatics For JEEDocument7 pagesElectrostatics For JEEGokul NathNo ratings yet
- PEF Assignment 1Document3 pagesPEF Assignment 1Dhanush GNo ratings yet
- DPP-3 (Electric Field, Field Intensity and Superposition of Electric Field)Document6 pagesDPP-3 (Electric Field, Field Intensity and Superposition of Electric Field)Youtuber RSNo ratings yet
- Final 2018Document3 pagesFinal 2018Ashraf WaleedNo ratings yet
- Jam 2009Document8 pagesJam 2009sairajdreamNo ratings yet
- p240w12 Mid1-2Document14 pagesp240w12 Mid1-2shlaeaNo ratings yet
- Dpp-2 ElectrostaticDocument8 pagesDpp-2 ElectrostaticYash GhorpadeNo ratings yet
- IFS Physics 2009Document15 pagesIFS Physics 2009Anonymous 8KlaOOWojNo ratings yet
- JEE ADV and ManisDocument14 pagesJEE ADV and Manisbrm1shubhaNo ratings yet
- 115 A9 2nd AttemptDocument2 pages115 A9 2nd AttemptPearl ArcamoNo ratings yet
- Elec Assign 2Document5 pagesElec Assign 2paulaNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam 1.0.0Document24 pagesSample Exam 1.0.0Cameron LeungNo ratings yet
- Tutorial2 2Document2 pagesTutorial2 2Muhammad Harith B. BadzliNo ratings yet
- PG Brainstormer - 1 H (Electromagneticsm)Document6 pagesPG Brainstormer - 1 H (Electromagneticsm)Harsh VardhanNo ratings yet
- Tables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiFrom EverandTables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiNo ratings yet
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryFrom EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Standard Practice Hair Dresser - 1Document29 pagesStandard Practice Hair Dresser - 1Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Kalendar MUET 2014 (Ed. 19.09.2013) - BIDocument1 pageKalendar MUET 2014 (Ed. 19.09.2013) - BIPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Jadual Pmbahgian WIM AMALIDocument2 pagesJadual Pmbahgian WIM AMALIPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Carry Out Safety Assessment at Work AreaDocument2 pagesCarry Out Safety Assessment at Work AreaPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Final Report Content MULTIMEDIADocument1 pageFinal Report Content MULTIMEDIAPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- MOSFET - The Metal Oxide FETDocument1 pageMOSFET - The Metal Oxide FETPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Borang Akaun Affin BankDocument2 pagesBorang Akaun Affin BankPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Report Osha CompleteDocument16 pagesReport Osha CompletePatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Lamp Iran NNNNDocument7 pagesLamp Iran NNNNPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Siap - Analysis and Result - Lab5Document24 pagesSiap - Analysis and Result - Lab5Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation Signal of Data UsingDocument17 pagesDigital Modulation Signal of Data UsingPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Graph - Internet (n0 6 N No 7)Document4 pagesGraph - Internet (n0 6 N No 7)Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Conclusion LabDocument3 pagesConclusion LabPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Lamp Iran NNNNDocument7 pagesLamp Iran NNNNPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Isi EyeDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Isi EyePatricia KCNo ratings yet
- BEC30403 Assignment1 v3Document3 pagesBEC30403 Assignment1 v3Eika MuhamadNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro Workshop Arduino 1dayDocument14 pages1 Intro Workshop Arduino 1dayPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- RPP04 Bee32102Document4 pagesRPP04 Bee32102Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Dcomm 0 IntroDocument5 pagesDcomm 0 IntroPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Coa07 PDFDocument17 pagesCoa07 PDFPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Worker Injuried by Forklift AccidentDocument1 pageWorker Injuried by Forklift AccidentPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Answer Assigment 2Document1 pageAnswer Assigment 2Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 CPU InstructionsDocument16 pagesLab 4 CPU InstructionsPatricia KC0% (1)
- Bee 3223Document8 pagesBee 3223Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Tda8551 T 2Document21 pagesTda8551 T 2Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Paper Consists of Eight PagesDocument9 pagesUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: This Paper Consists of Eight PagesPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- cs757 ns2 Tutorial1Document16 pagescs757 ns2 Tutorial1Sameer SalamNo ratings yet
- Bee 3223Document8 pagesBee 3223Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Flowchart MtorDocument1 pageFlowchart MtorPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Photorefractive EffectDocument22 pagesPhotorefractive EffectMohammed ZiaNo ratings yet
- Halliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics 8 Edition: Classroom Response System QuestionsDocument41 pagesHalliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics 8 Edition: Classroom Response System QuestionsGPFanNo ratings yet
- Magnetostatics BahanDocument11 pagesMagnetostatics BahanBaho Kristanti HutagalungNo ratings yet
- MIT8 02SC Challenge Sol05Document23 pagesMIT8 02SC Challenge Sol05Sagar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Maxwell Equations PDFDocument406 pagesApplications of Maxwell Equations PDFMousumi JenaNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Practice ProblemsDocument13 pagesElectric Field Practice ProblemsJaymar F. NabungNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Sheet by VishalDocument2 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet by Vishalabhinav yadavNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 CHEMISTRyDocument101 pagesUNIT 1 CHEMISTRyRishabh KothariNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics II: George SiopsisDocument127 pagesQuantum Mechanics II: George SiopsisSoumajit DasNo ratings yet
- Course Outlines For BS Physics (Sylabous) PDFDocument37 pagesCourse Outlines For BS Physics (Sylabous) PDFNasir AliNo ratings yet
- Nikola Tesla - Electromagnetic EngineeringDocument13 pagesNikola Tesla - Electromagnetic EngineeringFurby HankNo ratings yet
- Physics 152 SI Midterm I ReviewDocument7 pagesPhysics 152 SI Midterm I ReviewMina GergesNo ratings yet
- Paper - 1 (Question Paper) - 6Document17 pagesPaper - 1 (Question Paper) - 6Saumya MundraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 06Document40 pagesLecture 06Reddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2kalshkinguNo ratings yet
- LKya Xko 27 A EQG4 Ei Kyej P2 DCR LM MWKFT9 OHdem YEDocument10 pagesLKya Xko 27 A EQG4 Ei Kyej P2 DCR LM MWKFT9 OHdem YESEBASTIAN CRISTOBAL DOMINGUEZ GALARZANo ratings yet
- PH Ysicsguide: Introduction To EMTDocument14 pagesPH Ysicsguide: Introduction To EMTRithish BarathNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument1 pageElectrostaticsSamNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Worksheet - ElectrostatisticsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Worksheet - ElectrostatisticsSanjukthNo ratings yet
- CH 20 (Coulomb)Document31 pagesCH 20 (Coulomb)Baktynur AzhybaevNo ratings yet
- Chapter-28 The Electric FieldDocument22 pagesChapter-28 The Electric FieldBurak BayarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21: Electric Charge and Electric FieldDocument30 pagesChapter 21: Electric Charge and Electric FieldNguyễn Ngoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Introducción A La Electrodinamica 3ra Edición David J. Griffiths Solution PDFDocument1,142 pagesIntroducción A La Electrodinamica 3ra Edición David J. Griffiths Solution PDFhenry levin parada contrerasNo ratings yet
- Lecture-11 Flux Density and Gauss LawDocument12 pagesLecture-11 Flux Density and Gauss LawDanish FalakNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 A SolutionsDocument2 pagesQuiz 2 A SolutionsTamanna 1303No ratings yet
- Gauss's LawDocument3 pagesGauss's LawSanjay PandeyNo ratings yet