Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oil Rig Components Explained
Uploaded by
Jennifer MàrtinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oil Rig Components Explained
Uploaded by
Jennifer MàrtinCopyright:
Available Formats
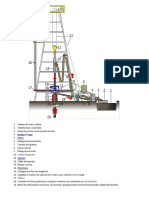
List of components of oil drilling rigs:
1. Mud tank (#1) 2. Shale shaker (#2) 3. Suction line (#3) 4. Mud pump (#4) 5. Kelly (#5) 6. Vibrating hose (#6) 7. Draw-works (#7) 8. Standpipe (#8) 9. Kelly hose (#9) 10. Goose-neck (#10) 11. Traveling block (#11) 12. Drill line (#12) 13. Crown block (#13) 14. Derrick (#14) 15. Monkey board (#15) 16. Stand (#16) 17. Pipe rack (#17) 18. Swivel (#18) 19. Drill Pipe (#19) 20. Rotary table (#20) 21. Drill floor (#21) 22. Bell nipple: (#22) 23. Blowout preventers (BOPs) (#23 & #24) 24. Pipe rams and Blind rams (#24) 25. Drill string (#25) 26. Drill Bit (#26) 27. Casing head (#27) 28. Flow line (#28) 29. Centrifuge (Not pictured) 30. Degasser (Not pictured) 31. Desander / desilter (Not pictured) 32. Elevators (Not pictured) 33. Mud motor (Not pictured)
1. Mud tank: (#1) often called mud pits, provides a reserve store of drilling fluid until it is required down the wellbore. 2. Shale shaker: (#2) separates drill cuttings from the drilling fluid before it is pumped back down the wellbore.
3. Suction line: (#3) intake line for the mud pump to draw drilling fluid from the mud tanks. 4. Mud pump: (#4) reciprocal type of pump used to circulate drilling fluid through the system.
5. Kelly: (#5) a square, hexagonal or octagonal shaped tubing that is inserted through and is an integral part of the rotary table that moves freely vertically while the rotary table turns it.
6. Vibrating hose: (#6) is a flexible, high pressure hose (similar to the kelly hose) that connects the mud pump to the stand pipe. It is called the vibrating hose because it tends to vibrate and shake (sometimes violently) due to its close proximity to the mud pumps.
7. Draw-works: (#7) is the mechanical section that contains the spool, whose main function is to reel in/out the drill line to raise/lower the traveling block.
8. Standpipe: (#8) a thick metal tubing, situated vertically along the derrick, that facilitates the flow of drilling fluid and has attached to it and supports one end of the kelly hose. 9. Kelly hose: (#9) is a flexible, high pressure hose that connects the standpipe to the kelly (or more specifically to the gooseneck on the swivel above the kelly) and allows free vertical movement of the kelly, while facilitating the flow of the drilling fluid through the system and down the drill string. 10. Goose-neck: (#10) thick metal elbows connected to the swivel and standpipe that supports the weight of and provides a downward angle for the kelly hose to hang from. 11. Traveling block: (#11) The moving end of the block and tackle, together they give a significant mechanical advantage for lifting.
12. Drill line: (#12) Thick, stranded metal cable threaded through the two blocks (traveling & crown) to raise and lower the drill string.
13. Crown block: (#13) The stationary end of the block and tackle.
14. Derrick: (#14) the support structure for the equipment used to lower and raise the drill string into and out of the wellbore. 15. Monkey board: (#15) the structure used to support the top-end of the stands of drill pipe vertically situated in the derrick. 16. Stand: (#16) sections of 2 or 3 joints of drill pipe connected together and stood upright in the derrick. When pulling out of the hole, instead of laying down each joint of drill pipe, 2 or 3 joints are left connected together and stood in the derrick to save time. 17. Pipe rack: (#17) a part of the drill floor (#21) where the stands of drill pipe are stood upright. Typically made of a metal frame structure with large wooden beams situated within it. The wood helps to protect the end of the drill pipe from damage.
18. Swivel: (#18) the top-end of the kelly that allows the rotation of the drill string without twisting the block.
19. Drill Pipe: (#19) joints of hollow tubing used to connect the surface equipment to the bottom hole assembly (BHA) and acts as a conduit for the drilling fluid. In the diagram, these are stands of drill pipe which are 2 or 3 joints of drill pipe connected together and stood in the derrick vertically, usually to save time while Tripping pipe.
20. Rotary table: (#20) rotates, along with its constituent parts the kelly and kelly bushing, the drill string and the attached tools and bit.
21. Drill floor: (#21) the area on the rig where the tools are located to make the connections of the drill pipe, bottom hole assembly, tools and bit. It is considered the main area where work is performed. 22. Bell nipple: (#22) a section of large diameter pipe fitted to the top of the blowout preventers that the flow line attaches to via a side outlet, to allow the drilling fluid to flow back to the mud tanks. 23. Blowout preventers: (BOPs) (#23 & #24), are devices installed at the wellhead to prevent fluids and gases from unintentionally escaping from the wellbore. #23 is the Annular (often referred to as the Hydril, which is one manufacturer) and #24 is the Pipe rams and Blind rams.
24. and #24 is the Pipe rams and Blind rams. 25. Drill string: (#25) an assembled collection of drill pipe, heavy weight drill pipe, drill collars and any of a whole assortment of tools, connected together and run into the wellbore to facilitate the drilling of a well. The collection of which is referred to singularly as the drill string. 26. Drill Bit: (#26) device attached to the end of the drill string that breaks apart the rock being drilled. It contains jets through which the drilling fluid exits.
27. Casing head: (#27) a large metal flange welded or screwed onto the top of the conductor pipe (also known as drive-pipe) or the casing and is used to bolt the surface equipment to. Equipment such as the blowout preventers (for well drilling) or the Christmas tree (oil well) (for well production). 28. Flow line: (#28) is large diameter pipe that is attached to the bell nipple and extends to the shale shakers to facilitate the flow of drilling fluid back to the mud tanks. 29. Centrifuge: (Not pictured) an industrial version of the device that separates fine silt and sand from the drilling fluid. Typically mounted on top or just off of the mud tanks. 30. Degasser: (Not pictured) a device that separates air and/or gas from the drilling fluid. Typically mounted on top of the mud tanks. 31. Desander / desilter: (Not pictured) contains a set of Hydrocyclones that separate sand and silt from the drilling fluid. Typically mounted on top of the mud tanks.
32. Elevators: (Not pictured) a hinged device that is used to latch to the drill pipe or casing to facilitate the lowering or lifting (of pipe or casing) into or out of the wellbore. 33. Mud motor: (Not pictured) a hydraulically powered device positioned just above the drill bit used to spin the bit independently from the rest of the drill string.
You might also like
- Oil Rig Components ListDocument9 pagesOil Rig Components ListsamirgoranNo ratings yet
- Rig Components PDFDocument19 pagesRig Components PDFBalant AxNo ratings yet
- Rig component definitions guide under 40 charactersDocument70 pagesRig component definitions guide under 40 charactersHarpreetk87No ratings yet
- Drawworks and Rig Sizing PDFDocument8 pagesDrawworks and Rig Sizing PDFAmine Mimo100% (1)
- Ohsar PDFDocument40 pagesOhsar PDFMohammed Ali YoussefNo ratings yet
- SB Drill CollarDocument51 pagesSB Drill CollarJeff ZhangNo ratings yet
- Cyber BaseDocument39 pagesCyber BaseayhamNo ratings yet
- Shenkai Detail of Sensors CmsDocument9 pagesShenkai Detail of Sensors CmsAhmed Imtiaz RaoNo ratings yet
- Koomey Accumulator Bottle Isolation DOP-PR-R76-080Document5 pagesKoomey Accumulator Bottle Isolation DOP-PR-R76-080cmrig74No ratings yet
- HSE Alert 07-16 Damage To Drilling Mast IncidentDocument1 pageHSE Alert 07-16 Damage To Drilling Mast IncidentSajid HussainNo ratings yet
- API SPEC 16C Choke and KillDocument26 pagesAPI SPEC 16C Choke and Killu04ajf3No ratings yet
- Drilling Rig ComponentsDocument18 pagesDrilling Rig ComponentsIsmail A. IsmailNo ratings yet
- Series 150 Overshots: Instruction Manual 1150Document25 pagesSeries 150 Overshots: Instruction Manual 1150Rares PetreNo ratings yet
- Drilling EDrilling - Equip2013 - PUE - Web - 2quip2013 PUE Web 2Document40 pagesDrilling EDrilling - Equip2013 - PUE - Web - 2quip2013 PUE Web 2MEREUEULEUNo ratings yet
- Choke & Kill Line InstructionsDocument6 pagesChoke & Kill Line InstructionskrishnsgkNo ratings yet
- Daily Tool Pusher ChecklistDocument2 pagesDaily Tool Pusher ChecklistKaleem UllahNo ratings yet
- Drillpipe and Bottom Hole Assembly StandardsDocument2 pagesDrillpipe and Bottom Hole Assembly StandardsSasan Abbasi100% (1)
- Tesco 250 EMI 400 Top DriveDocument12 pagesTesco 250 EMI 400 Top DriveBrandon Nowlin100% (1)
- 02 Drillmec HH SeriesDocument12 pages02 Drillmec HH SeriesPopa Adrian100% (1)
- Casing Integrity TestingDocument1 pageCasing Integrity TestingKim MissonNo ratings yet
- Replacing Gas - Lift ValveDocument21 pagesReplacing Gas - Lift ValveDanish KhanNo ratings yet
- ABS Fire and Safety Features For MODU - Part5Document40 pagesABS Fire and Safety Features For MODU - Part5Eyoma Etim100% (1)
- Control Unit - Day3 - Test IntroDocument46 pagesControl Unit - Day3 - Test IntroMrityunjay Dhanraj100% (1)
- Wellhead Equipment Acc. To Api Spec. 6a PDFDocument36 pagesWellhead Equipment Acc. To Api Spec. 6a PDFermusatNo ratings yet
- Rotary Slips "RDL" "RD" "RDS": Side Door Elevator 150 TON 250 TON 350 TONDocument11 pagesRotary Slips "RDL" "RD" "RDS": Side Door Elevator 150 TON 250 TON 350 TONShaikh Sabir HussainNo ratings yet
- 14a - Joe Hurt-John Auth Rig Pass PresentationDocument36 pages14a - Joe Hurt-John Auth Rig Pass PresentationEduardo Guajardo100% (1)
- Rig Inspection Check ListDocument4 pagesRig Inspection Check ListEd Calhe100% (1)
- Nov Mission Drilling SolutionsDocument24 pagesNov Mission Drilling SolutionsahnafNo ratings yet
- Approved Around The World: Bentec RigsDocument20 pagesApproved Around The World: Bentec RigsCesar Gamboa100% (1)
- Rig ComponentsDocument114 pagesRig ComponentskumoziNo ratings yet
- Strata RCDDocument2 pagesStrata RCDDavid VilchesNo ratings yet
- Concept of Operations For Directional Drilling On AmphionDocument11 pagesConcept of Operations For Directional Drilling On AmphionTaymoor MalekNo ratings yet
- Field Welding of Casing To WellheadsDocument2 pagesField Welding of Casing To Wellheadsabrar100% (2)
- WWC Technical Data BookDocument73 pagesWWC Technical Data BookSylvan BorgNo ratings yet
- Download IADC Well Control Manual PDFDocument4 pagesDownload IADC Well Control Manual PDFHendra JurbonNo ratings yet
- Check List For SOBM Take On BoardDocument5 pagesCheck List For SOBM Take On BoardVimal SinghNo ratings yet
- Components of Christmas Tree On WellDocument2 pagesComponents of Christmas Tree On WellJosé TimanáNo ratings yet
- Trip TankDocument23 pagesTrip TankNaser KhanNo ratings yet
- Top Drive Systems Dropped Objects Prevention White PaperDocument4 pagesTop Drive Systems Dropped Objects Prevention White PaperneusadNo ratings yet
- Hoisting SystemDocument42 pagesHoisting SystemBadut Sarkas100% (3)
- 37 Drill Stem Tools 1 PDFDocument2 pages37 Drill Stem Tools 1 PDFRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- AOT Tubular HandlingDocument112 pagesAOT Tubular HandlingrolandNo ratings yet
- Drilling Rig Operations & A To Z Rotary Drilling Rig ComponentsDocument130 pagesDrilling Rig Operations & A To Z Rotary Drilling Rig ComponentsAhmad93% (28)
- IADC Rig Crew SkillsDocument73 pagesIADC Rig Crew SkillsGoutam Manna100% (4)
- 18-3/4Document60 pages18-3/4proabbey100% (1)
- Control Choke GuideDocument16 pagesControl Choke Guidegacm9875% (4)
- Valves HCR CameronDocument5 pagesValves HCR CameronmanuelperdomotNo ratings yet
- Final Inspection Report With Codes ExampleDocument23 pagesFinal Inspection Report With Codes Exampleeraswasta100% (1)
- Bomba Lodo MotorDocument3 pagesBomba Lodo MotorRubén López LemaNo ratings yet
- Lists Ofdrilling EquipmentsDocument9 pagesLists Ofdrilling EquipmentsNicat NezirovNo ratings yet
- List of Components of Oil Drilling RigsDocument5 pagesList of Components of Oil Drilling RigsAlzaki AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Oil Rig ComponentsDocument3 pagesOil Rig ComponentsIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- List of Components of Oil Drilling Rigs PDFDocument7 pagesList of Components of Oil Drilling Rigs PDFAdelina96No ratings yet
- List of Components of Oil Drilling RigsDocument3 pagesList of Components of Oil Drilling RigsExpertise MlcsNo ratings yet
- List of Components of Oil Drilling-1Document2 pagesList of Components of Oil Drilling-1binoyraj2010No ratings yet
- Unit 1 4th Topic Oil Rig SystemDocument14 pagesUnit 1 4th Topic Oil Rig SystemUmaNo ratings yet
- Oil Rig ComponentsDocument5 pagesOil Rig ComponentsMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Oil Drilling RigsDocument21 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Oil Drilling RigsOmosigho Osaro100% (1)
- 04 - Basic Schematic Diagram of A Rotary Drilling RigDocument3 pages04 - Basic Schematic Diagram of A Rotary Drilling RigNaufal Syafiq Mohd IsaNo ratings yet
- Welding Duplex Stainless Steel Piping SpecDocument44 pagesWelding Duplex Stainless Steel Piping SpecAlaa100% (1)
- 2011 Devcon Permatex CatalogDocument52 pages2011 Devcon Permatex CatalogEBPENICHE6400No ratings yet
- Alloytech VACCDocument8 pagesAlloytech VACCDaniel Hernandez100% (2)
- Theme Based Safety Discussion (TBT) For Manual Grinding OperationDocument3 pagesTheme Based Safety Discussion (TBT) For Manual Grinding OperationMr. XNo ratings yet
- INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINEDocument30 pagesINTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE周庆卓No ratings yet
- Cimac Paper 21Document11 pagesCimac Paper 21ozakyusNo ratings yet
- Hunting Catalog - PCE PDFDocument30 pagesHunting Catalog - PCE PDFtebengzNo ratings yet
- BS 5306 0 2011, Fire ProtectionDocument72 pagesBS 5306 0 2011, Fire ProtectionVedran KosanovicNo ratings yet
- SM Si50-402A CompressorDocument61 pagesSM Si50-402A Compressorttt44967% (3)
- Technology Growth Vehicle Fuel EfficiencyDocument22 pagesTechnology Growth Vehicle Fuel Efficiencymelumzin1577No ratings yet
- D6X6 Navigator D6X6 Navigator: Horizontal Directional Drill Horizontal Directional DrillDocument2 pagesD6X6 Navigator D6X6 Navigator: Horizontal Directional Drill Horizontal Directional DrillImam BuchairiNo ratings yet
- EU10 IDocument61 pagesEU10 IMarina IksNo ratings yet
- Xp13000Eh Generator: User ManualDocument66 pagesXp13000Eh Generator: User ManualANGEL MALAVERNo ratings yet
- 3.safe Handling and Storage of ChemicalsDocument3 pages3.safe Handling and Storage of Chemicalsjacobpm2010100% (1)
- How Cooling Systems Work and the Cost of an OverheatDocument32 pagesHow Cooling Systems Work and the Cost of an OverheatAiman NasirNo ratings yet
- Parts Catalogue For Coolcar A PDFDocument144 pagesParts Catalogue For Coolcar A PDFJavier Amorin100% (1)
- Isolation of Process Equipment Procedure Rev 0Document39 pagesIsolation of Process Equipment Procedure Rev 0eulalio_méndezNo ratings yet
- 2013 Hilti Hit-Hy 200 With His - (R) NDocument4 pages2013 Hilti Hit-Hy 200 With His - (R) NDifa LiuNo ratings yet
- Engineering Training I: AlternatorDocument49 pagesEngineering Training I: AlternatorChambo JackNo ratings yet
- Volvo FL PDFDocument19 pagesVolvo FL PDFBenNo ratings yet
- Gas WeldingDocument20 pagesGas WeldingVikas LavaniaNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual For LPG Recovery Unit No. 05/55: Persian Gulf Star Oil Company REF - No.: 3034-PR-MAN-AA020 (A0)Document105 pagesOperating Manual For LPG Recovery Unit No. 05/55: Persian Gulf Star Oil Company REF - No.: 3034-PR-MAN-AA020 (A0)Behnam Ramouzeh100% (1)
- Skin Effect Heat Management System ExplainedDocument19 pagesSkin Effect Heat Management System ExplainedPIpelinesTebodinNo ratings yet
- Anfo Vs EmulsionDocument38 pagesAnfo Vs EmulsionRitesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- John Paul de Villa: Work Experience SkillsDocument1 pageJohn Paul de Villa: Work Experience SkillsJohn De VillaNo ratings yet
- 00 Chemistry 2 UDocument48 pages00 Chemistry 2 UHarkaraj KangNo ratings yet
- ALP Progressing Cavity Pumps Nov2010Document6 pagesALP Progressing Cavity Pumps Nov2010Steve MarfissiNo ratings yet
- Yamaha F150FET Owners ManualDocument92 pagesYamaha F150FET Owners ManualNur Fadly Ryzqy0% (1)
- Hybrid Vehicle Operation and DiagnosisDocument78 pagesHybrid Vehicle Operation and DiagnosisMinh Nhat PhanNo ratings yet
- Brake Accumulator Test and ChargeDocument8 pagesBrake Accumulator Test and ChargeBarzola Soto Omar100% (1)