Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Miet 2136 2008 Exam
Uploaded by
Chris NewmanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Miet 2136 2008 Exam
Uploaded by
Chris NewmanCopyright:
Available Formats
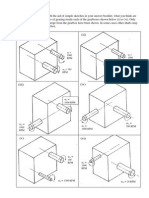
Question 1 [9 marks] a) Briefly describe with the aid of simple sketches in your answer booklet, what you think
are the most likely types of gearing inside each of the gearboxes shown below (i) to (vi). Only those shafts that emerge from the gearbox have been shown. In some cases other shafts may exist inside the gearbox.
(i)
(ii)
i = 1000 RPM
i = 1000 RPM
o = 340 RPM
o = 340 RPM
(iii)
(iv)
i =
1000 RPM
o =
1000 RPM
i =
1000 RPM
o =
500 RPM
(v)
(vi)
o =
100 RPM
i =
1000 RPM
i = 1500 RPM
o = 20 RPM
b)
(i) The Lewis equation and modern refinements of it are based on the determination of a particular stress in gear teeth. Explain with a sketch the location and nature of this stress. (ii) What damaging stress condition is not covered by the Lewis equation and those equations derived from it? (i) In your answer booklet complete the following statement of the kinematic law of gearing, which is missing approximately 12 words: "If the line drawn normal to the contacting surfaces of two rotating bodies ..., the angular velocity ratio of the two bodies will remain constant." (ii) Name two possible shapes of gear teeth that satisfy the law of gearing. What are two important operational advantages of helical gearing compared to spur gearing? What are herringbone gears, and what special attribute do they offer the designer? Use a sketch to explain.
c)
d)
e)
Question 2 [ 5 marks ] a) b) Make an isometric (3D) sketch of a Hooke's joint. Label the principal elements. What problems occur if a single Hooke's joint is used but which can be eliminated if a pair of them is used appropriately? For the shaft system shown schematically below, which runs between two parallel shafts with a given offset, sketch in your answer booklet an appropriate arrangement incorporating two Hooke's joints and an intermediate shaft.
c)
___________Y d) Explain in what circumstance it would be necessary to fit a sliding spline joint in the situation described in part c).
Question 3 [5 marks ] The horizontal shaft of a winch drum, which has a brake drum attached to it, is supported by two spherical roller bearings mounted in plummer blocks (also known as pillow blocks). These plummer blocks are bolted to a welded steel frame. The left hand bearing is fully located; the other is axially floating on its outer race. (a) Sketch a cross-section of one of the bearings and its plummer block. Label the: inner race outer race spherical rollers plummer block housing
(b) Sketch a simplified schematic of the mounting system showing both bearings, and with heavy dots indicating the restraints, for the locations where they are used, for each of the inner and outer races. (d) Give two reasons why this mounting system is appropriate for this application.
Question 4 [ 8 marks ] The short shoe brake shown in the figure below is applied by the spring and released by a hydraulic cylinder (not shown). (a) Determine, with the aid of appropriate free body diagrams, the spring force required to produce a braking torque of 175 Nm given that the co-efficient of friction is 0.35. (b) A shoe brake may be self actuating to some extent. Is this the case for either of the caliper arms shown? Explain your answer by reference to your free body diagrams. (c) For the most heavily loaded shoe, determine the minimum possible width of shoe (i.e. measured normal to the page) if the average pressure on the projected area of the shoe is not to exceed 500 kPa.
Question 5 [8 marks] DO THIS QUESTION OR QUESTION 6 (a) The figure below shows the hub of an idler gear into which plain bearing bushes have been pressed. When the hub is assembled and mounted on the shaft the permitted minimum and maximum values of axial clearance C are 0.15 and 1.05mm respectively. Determine the upper and lower limits of size the hub length H may have given that the distance between shoulders S is 150.00 0.15mm, and bush face-thickness B is 9.00 0.08mm.
(b)
In the operation of oil lubricated plain bearings we distinguish between two main regimes of lubrication. State what they are and describe the function of the lubricant in each. Use sketches to facilitate your explanation. Two important properties of the materials used in plain bearings are compressive strength and embeddability. Discuss what is meant by these terms; why they are important; and what conflict, if any, exists between them. On earth scooping machinery the pin joints on the linkage working the scoop obviously need bearings of some sort. Given that shock loadings occur would you use plain bearings or deep groove ball bearings in this application? Explain why.
(c)
(d)
Question 6 [8 marks] DO THIS QUESTION OR QUESTION 5 (a) Referring to the figure below, the load is applied to the flat bracket via a pin in the hole. Discuss with the aid of sketches the various modes of failure that a designer should consider when determining the necessary proportions of the pin and the plate near the hole.
(b)
The flat bracket is to be attached to a vertical surface using a pattern weld run as shown in Figure 3. The weld metal will be laid as an equal legged fillet weld. (i) Determine the location and magnitude of the maximum load on the weld (in N/mm of weld run). (ii) Suggest a size of the weld leg based on your findings assuming that the allowable resultant stress on the throat of the weld is 0.33 x the ultimate strength of the weld material, and that the weld material has an ultimate strength of 375 MPa.
91,000 N
320 mm
160mm
300 mm
The following formulas are provided, as are geometry factors for weld analysis on page 5: Loading type Direct Shear Force per mm run of weld
V Shear Force = L Aw V Normal Force = L Aw V T. r = L Jw V = L M Zw
Normal Force
Torque
Bending Moment
Weld dimensions
Bending
Torsion
Weld geometry factors. Source: Robert L Mott Machine Elements in Mechanical Design
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Komatsu 27R8-7Document264 pagesKomatsu 27R8-7ВикторNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- SKF Frecuently Questions With AnswersDocument16 pagesSKF Frecuently Questions With AnswersCarlos AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Lub Oil SystemDocument20 pagesLub Oil SystemSam83% (6)
- Operation and Maintenance DamperDocument4 pagesOperation and Maintenance DamperBharatsinh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- ZH Screw Compressor Presentation - CAW - EnglishDocument66 pagesZH Screw Compressor Presentation - CAW - Englishjmdc50% (2)
- 'TP-800B' Overhauling of Steam TurbineDocument35 pages'TP-800B' Overhauling of Steam TurbinewasayNo ratings yet
- Exxon IP 10-4-1 Reciprocating Process CompressorsDocument9 pagesExxon IP 10-4-1 Reciprocating Process CompressorsGilvan SilvaNo ratings yet
- 3.5 - MBR 15k Spare Part List 1-2-5 YearsDocument8 pages3.5 - MBR 15k Spare Part List 1-2-5 YearsWayneNo ratings yet
- WH28H3N mk2 (Jun-02)Document148 pagesWH28H3N mk2 (Jun-02)Erick CallejasNo ratings yet
- Understanding ISO Codes Appearance of Water in Oil: Viscosity Grading SystemsDocument1 pageUnderstanding ISO Codes Appearance of Water in Oil: Viscosity Grading SystemsPorfirioDuarteZarateNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics RevisionDocument2 pagesSolid Mechanics RevisionChris NewmanNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 (Wind Resources)Document18 pagesTopic 2 (Wind Resources)Chris NewmanNo ratings yet
- Miet 2136 2008 ExamDocument6 pagesMiet 2136 2008 ExamChris NewmanNo ratings yet
- Week2 TutorialDocument3 pagesWeek2 TutorialChris NewmanNo ratings yet
- Marelli 63 To 400 Frame Technical Catalogue PDFDocument48 pagesMarelli 63 To 400 Frame Technical Catalogue PDFRevi AdikharismaNo ratings yet
- EE 01728 1 - 44 R006 Device Summary of STGDocument45 pagesEE 01728 1 - 44 R006 Device Summary of STGVinoth Kumar100% (1)
- Martin Catalogue PDFDocument176 pagesMartin Catalogue PDFDavidNo ratings yet
- Aceco PV3 & PV4 BrochureDocument16 pagesAceco PV3 & PV4 BrochureLynn AlgerNo ratings yet
- Installation, Operation, and Maintenance Manual: Pah Series PumpDocument39 pagesInstallation, Operation, and Maintenance Manual: Pah Series PumpEric NguyenNo ratings yet
- IQ Range: Installation and Maintenance InstructionsDocument88 pagesIQ Range: Installation and Maintenance InstructionsmaituanNo ratings yet
- Manuel D'utilisation REDUREX Gear Unit - FLENDERDocument128 pagesManuel D'utilisation REDUREX Gear Unit - FLENDERAhmedNo ratings yet
- Tsurumi CatalogDocument35 pagesTsurumi CatalogfirfourNo ratings yet
- PP Troubleshooting Guide - 5580 - EN - 04 PDFDocument20 pagesPP Troubleshooting Guide - 5580 - EN - 04 PDFJorge BellidoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Bulletin - EB 99013-A: Multiple Position Lock System UpgradeDocument3 pagesEngineering Bulletin - EB 99013-A: Multiple Position Lock System UpgradeJean Dubois0% (1)
- Right Angle Drives 1 To 1 Ratio InchDocument11 pagesRight Angle Drives 1 To 1 Ratio InchFRANCISCO JAVIER NIEVES GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- Unidad Rotacion Serie l30Document22 pagesUnidad Rotacion Serie l30Raphael Ruiz RamosNo ratings yet
- Ycm VMCDocument18 pagesYcm VMCbhadriptNo ratings yet
- Section 3: Conveyor Chain Installation & MaintenanceDocument17 pagesSection 3: Conveyor Chain Installation & MaintenanceEduardo ParedesNo ratings yet
- ETR Series: A Full Spectrum of Products To Solve Your Application NeedsDocument106 pagesETR Series: A Full Spectrum of Products To Solve Your Application Needs周小安No ratings yet
- VATER Eltrak INFO List JULY19Document6 pagesVATER Eltrak INFO List JULY19GarryNo ratings yet
- ZeutechDocument9 pagesZeutechthaniNo ratings yet
- 8.bearing DesignDocument38 pages8.bearing DesignAbel MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Hiseal, High Performance, Double Offset Butterfly Valves Are Fully Rated To Ansi 150 and Ansi 300Document5 pagesHiseal, High Performance, Double Offset Butterfly Valves Are Fully Rated To Ansi 150 and Ansi 300aravindNo ratings yet
- Argo 8x8 Wheels Axle ChainsDocument73 pagesArgo 8x8 Wheels Axle ChainsGeorge finkleNo ratings yet