Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electric Force & Electric Fields
Uploaded by
Desejo SozinandoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electric Force & Electric Fields
Uploaded by
Desejo SozinandoCopyright:
Available Formats
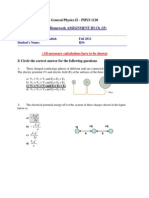
PHYSICS 1
Solution by DF Sozinando Mechanical Eng.
student at the Vaal University of Technology
Tutorial questions:
1- A rod made f rom insulat ing material carries a net charge, whil e a small copper sphere is neutral. The rod and the
sphere do not touch. Is it possible for the rod and sphere to attract or repel each other? Explain your answer in detail.
No, it is impossible for attract or repel each other because the rod carries a net charge, means that the rod has the proton
and the electron, the sphere is neutral does not have electric charge that's way they they will not attract or repel each
other.
2- In a vacuum two particles have charges of q
1
and q
2,
where q
1
=-4mC. A distance of 0.26m separates them, and q
1
experiences an attractive force of 6N. What is the magnitude and polarity of q
2
?
DATA:
q
1
4 - C := r 0.26m := F 6N := k 8.99 10
9
N m
2
C
2
:=
SOLUTION:
F k
q
1
q
2
r
2
=
solve q
2
,
explicit
F r
2
k q
1
q
2
F r
2
k q
1
:= q
2
11.279 10
6 -
C =
3- Two charges, -16 and +4mC are fixed in place and separated by 3m. Where along the line joining and going through
the two charges will the net electric field be zero? Locate this point relative to the positive charge.
(Hint: this point does not necessarily lie between the charges!). Explain your reasoning.
It is the same point that separate two charges because the distance between this two charges does no electric field,
mean they will not be attracted or repel each other reason way the point relative to the positive charge is 3m.
PHYSICS 1
Solution by DF Sozinando Mechanical Eng.
student at the Vaal University of Technology
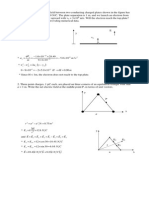
4- Three charges 2 positive and 1 negative has a magnitude of 5mC. They are placed at corners of a equilateral triangle
with sides 40cm. Calculate the resultant force on the negative charge.
DATA:
q
1
5C := q
2
5C := q
3
5 - C := r 40cm := k 8.99 10
9
N m
2
C
2
:= 60deg :=
SOLUTION:
Horizontal components:
F
x
F
13
cos ( ) F
23
cos ( ) - =
F
x
k
q
1
q
3
r
2
cos ( ) k
q
2
q
3
r
2
cos ( ) - := F
x
0 N =
Vertical components:
F
y
F
13
sin ( ) F
23
sin ( ) + =
F
y
k
q
1
q
3
r
2
sin ( ) k
q
2
q
3
r
2
sin ( ) + := F
y
2.433 N =
F
res
F
x
( )
2
F
y
( )
2
+ := F
res
2.433 N =
PHYSICS 1
Solution by DF Sozinando Mechanical Eng.
student at the Vaal University of Technology
Conceptual questions in unit 13 (Electric force and electric fields)
1- Iron atoms have been detected in the sun's outer atmosphere, some with many of their electrons stripped away. What
is the net electric charge (in coulombs) of an iron atom with 26 protons and 7 electrons? Be sure to include the algebraic
sign (+ or - ) in your answer
DATA:
N
protons
26 := N
electrons
7 - := e 1.60 10
19 -
C :=
SOLUTION:
q
p
e N
protons
:=
q
e
e N
electrons
:=
q
total
q
p
q
e
+ := q
total
3.0399999999999996 10
18 -
C =
PHYSICS 1
Solution by DF Sozinando Mechanical Eng.
student at the Vaal University of Technology
10- When point charge q
1
=+7.1mC and q
2
=+5.6mC are brought near each other, each experiences a repul sive force
of magnitude 0.62N. Determine the distance between the charges.
DATA:
q
1
7.1C := q
2
5.6C := F 0.62N := k 8.99 10
9
N m
2
C
2
:=
SOLUTION:
Remember when you have straight brackets
means absolute value, the magnitude of the
charge must always be positive
F k
q
1
q
2
r
2
=
F k
q
1
q
2
r
2
=
solve r ,
explicit
k q
1
q
2
F
k q
1
q
2
F
-
|
\
|
|
|
|
|
|
.
r
k q
1
q
2
F
:= r 0.759 m =
PHYSICS 1
Solution by DF Sozinando Mechanical Eng.
student at the Vaal University of Technology
14- Two tiny spheres have the same mass and carry charges of the same magnitude. The mass of each sphere is
2.00 x 10
-6
kg. The gravitational force that each sphere exerts on the other is balanced by the electric force.
a) What algebraic signs can the charges have?
b) Determine the charge magnitude.
DATA:
m
sp
2.00 10
6 -
kg := m
p
1.672 10
27 -
kg :=
SOLUTION:
Since the sphere have the same mass and carry charges of the same magnitude they are repel each other, means
that the algebraic signs of the charges can be both positive or negative. In another word the algebraic signs are the
same.
N
p_and_n
m
sp
m
p
:= N
p_and_n
1.196 10
21
= e 1.60 10
19 -
C :=
About one-half, so
N
p_and_n
2
5.981 10
20
= means that N
p
5.981 10
20
:= and N
e
5.981 10
20
:=
N
p
N
p
=
( )
the charge on proton and electrons and given by: q e N =
q
pr
e N
p
:= q
el
e N
e
:=
PHYSICS 1
Solution by DF Sozinando Mechanical Eng.
student at the Vaal University of Technology
18- Two smal l obj ects, A and B fixed in placed and separated by 3.00 cm in a vacuum. Object A has a charge of
+2.00mC, and object B has a charge of -2.00mC. How many electrons must be removed from A and put onto B to make
the electrostatic force that acts on each object an attractive force whose magnitude is 68.0 N ?
DATA:
r 3.00cm := q
A
2.00C := q
B
2.00 - C := F
A_B_68
68.0N := k 8.99 10
9
N m
2
C
2
=
SOLUTION:
consider the first state: consider the second state:
F
A_B
k
q
A
q
B
r
2
:= .................eq 1 F
A_B_68
k
q
A68
q
B68
r
2
= .................eq 2
q
A_B
q
A
q
B
:= q
A_B_68
q
A68
q
B68
=
cross multiplication between eq 1 and eq 2 to find q
A_B_68
q
A_B_68
F
A_B_68
q
A_B
F
A_B
:=
therefore q e N =
q
A_B_68
e N ( )
2
=
solve N ,
explicit
q
A_B_68
e
2 -
q
A_B_68
e
2 -
-
|
\
|
|
|
|
.
N
e
q
A_B_68
e
2 -
2
:= N
e
8.154 10
12
=
just to proof
F
new
k
q
A_B_68
r
2
:= F
new
68N =
PHYSICS 1
Solution by DF Sozinando Mechanical Eng.
student at the Vaal University of Technology
23- An electrically neutral model airplane is flying in a horizontal circle on a 3.0m guideline, which is nearly parallel to
the ground. The line breaks when kinetic energy of plane is 45.0J. Reconsider the same situation, except that now
there is a point charge of +q on the plane and a point charge of -q at the other end of the guideline. In this case, the line
breaks when the kinetic energy of the plane is 47.2J . Find the magnitude of the charge.
DATA:
r 3.0m := KE
uncharged
45.0J := KE
charged
47.2J := k 8.99 10
9
N m
2
C
2
=
SOLUTION:
F
c
m v
2
r
= -----------------------------eq 1
EK
1
2
m v
2
= -----------------------------eq 2
F k
q
2
r
2
= -----------------------------eq 3
Substituting eq 2 into eq 1, we get:
F
c
m v
2
r
=
2 KE
r
= -----------------------------eq 4
Applying this result to the situations with and without the charges, we get:
T
max
F + F
c
= -----------------------------eq 5
T
max
F
c
= -----------------------------eq 6
Substituting eq 6, 3 and 4 into eq 5, we get:
2 KE
uncharged
r
k
q
2
r
2
+
2 KE
charged
r
=
solve q ,
explicit
2 r KE
charged
KE
uncharged
-
k
2 r KE
charged
KE
uncharged
-
k
-
|
\
|
|
|
|
|
|
.
k 0 = if
0 k 0 = KE
charged
KE
uncharged
- 0 = . if
q
2 r KE
charged
KE
uncharged
-
k
:= q 3.832 10
5 -
C =
PHYSICS 1
Solution by DF Sozinando Mechanical Eng.
student at the Vaal University of Technology
29- Suppose you to determine the electric field in a certain region of space. You have a small object of known charge
and an instrument that measures the magnitude and direction of the force exerted on the object by the electric field.
a) The object has a charge of +30.0mC and the instrument indicates that the electrical force exerted on it is 50mN, due
east. What are the magnitude and direction of the electric field ?
b) What are the magnitude and direction of the electric field if the object has a charge of -10.0mC and the instrument
indicates that the force is 20.0mN, due west ?
DATA: 10
6 -
:=
q
o1
30C := F
1
50 N := q
o2
10 - C := F
2
20 N :=
SOLUTION:
E
F
q
o
=
E
1
F
1
q
o1
:= E
1
1.667
N
C
= East direction
E
2
F
2
q
o2
:= E
2
2 -
N
C
= West direction or E
2
2
N
C
= East direction
PHYSICS 1
Solution by DF Sozinando Mechanical Eng.
student at the Vaal University of Technology
33- The drawing shows two situation in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. They are all located at the same
distance of 6.1cm from the origin O. For each of the situation in drawing, determine the magnitude of the electric field at
the origin.
DATA:
r 6.1cm := a ( ) q
a1x
2.0C := q
a2x
3.0 - C := q
ay1
5.0 - C :=
k 8.99 10
9
N m
2
C
2
= b ( ) q
b1x
4.0C := q
b2x
1.0 - C := q
by1
1.0C := q
by2
6.0C :=
SOLUTION:
E k
q
r
2
=
Considering figure (a)
Horizontal components:
E
x
k
q
a1x
r
2
k
q
a2x
r
2
+ := E
x
1.208 10
7
N
C
=
Vertical components:
E
y
k
q
ay1
r
2
:= E
y
1.208 10
7
N
C
=
Resultant:
E
xy_a
E
x
( )
2
E
y
( )
2
+ := E
xy_a
1.708 10
7
N
C
=
PHYSICS 1
Solution by DF Sozinando Mechanical Eng.
student at the Vaal University of Technology
Considering figure (b)
Horizontal components:
E
bx
k
q
b1x
r
2
k
q
b2x
r
2
+ := E
bx
1.208 10
7
N
C
=
Vertical components:
E
by
k
q
by1
r
2
k
q
by2
r
2
+ := E
by
1.691 10
7
N
C
=
Resultant:
E
xy_b
E
x
( )
2
E
y
( )
2
+ := E
xy_a
1.708 10
7
N
C
=
PHYSICS 1
Solution by DF Sozinando Mechanical Eng.
student at the Vaal University of Technology
55- A charge Q is located i nsi de a rectangular box. The electric flux through each of the six surface of the box is:
F
1
=+1500Nm
2
/C, F
2
=+2200Nm
2
/C, F
3
=+4600Nm
2
/C, F
4
= -1800Nm
2
/C, F
5
= -3500Nm
2
/C, F
6
= -5400Nm
2
/C.
What is Q ?
DATA:
1
1500
N m
2
C
:=
2
2200
N m
2
C
:=
3
4600
N m
2
C
:=
4
1800 -
N m
2
C
:=
o
8.85 10
12 -
C
2
N m
2
:=
5
3500 -
N m
2
C
:=
6
5400 -
N m
2
C
:=
SOLUTION:
E
Q
o
=
solve Q ,
explicit
E
o
Q
E
o
=
Q
1
2
+
3
+
4
+
5
+
6
+
( )
o
:= Q 2.124 - 10
8 -
C =
PHYSICS 1
Solution by DF Sozinando Mechanical Eng.
student at the Vaal University of Technology
56- A spherical surface complete surrounds a collection of charges. Fi nd the electric flux through the surf ace if t he
collection consists of (a) a single +3.5x10
-6
C charge, (b) a single -2.3x10
-6
C charge, and (c) both of charges is (a)
and (b).
DATA:
a ( ) Q
a
3.5 10
6 -
C :=
b ( ) Q
b
2.3 - 10
6 -
C :=
o
8.85 10
12 -
C
2
N m
2
:=
SOLUTION:
a)
E
Q
o
=
a
Q
a
o
:=
a
3.955 10
5
N m
2
C
=
b)
b
Q
b
o
:=
b
2.599 - 10
5
N m
2
C
=
c) Q
c
Q
a
Q
b
+ :=
c
Q
c
o
:=
c
1.356 10
5
N m
2
C
=
Alternative:
c
a
b
+ :=
c
1.356 10
5
N m
2
C
=
PHYSICS 1
Solution by DF Sozinando Mechanical Eng.
student at the Vaal University of Technology
67- In a vacuum two particles have charges of q
1
and q
2,
where q
1
=+5.0mC. They are separated by a distance of
0.26m, and particle 1 experiences an attractive force of 5.6N. What is q
2
(magnitude and sign) ?
DATA:
q
1
5.0C := r 0.26m := F 5.6N := k 8.99 10
9
N m
2
C
2
=
SOLUTION:
F k
q
1
q
2
r
2
=
solve q
2
,
explicit
F r
2
k q
1
q
2
F r
2
k q
1
:= q
2
8.422 10
6 -
C =
You might also like
- 3 Soln Practice Assignment Ch25Document7 pages3 Soln Practice Assignment Ch25Eng MohammedNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Force and Field DiagramDocument76 pagesElectrostatics Force and Field DiagramNatalieCmFNo ratings yet
- Solutions HWT ElectrostaticsDocument11 pagesSolutions HWT ElectrostaticsShubhamKhannaNo ratings yet
- Electric Forces and Fields Sample ProblemsDocument4 pagesElectric Forces and Fields Sample ProblemsChristine Cayosa CahayagNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Forces Discrete ChargesDocument21 pagesElectric Field Forces Discrete ChargesaklothNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential and EnergyDocument6 pagesElectric Potential and Energykw2533No ratings yet
- PRACDocument11 pagesPRACVikram VikramNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and Potential ProblemsDocument5 pagesElectric Field and Potential ProblemsMahmoud FariedNo ratings yet
- ELECTRIC_FORCESDocument21 pagesELECTRIC_FORCESlololololol22100% (1)
- Electric Field Examples ExplainedDocument52 pagesElectric Field Examples ExplainedManisha YadavNo ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic Fields Answers To Week 2 Assignment Q1 (A)Document4 pagesElectric and Magnetic Fields Answers To Week 2 Assignment Q1 (A)ShootingStarPhotonsNo ratings yet
- 07 08 I FinalDocument9 pages07 08 I FinalMahmoud FariedNo ratings yet
- HW2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesHW2 Solutionsellie<3100% (1)
- E2 121 09-PreviewDocument14 pagesE2 121 09-PreviewTremendous JohnsonNo ratings yet
- NBF & KPK U-13Document8 pagesNBF & KPK U-13zoyarehan21No ratings yet
- Practice FinalDocument26 pagesPractice Finalchaseutd123No ratings yet
- Module 5 - Modern PhysicsDocument23 pagesModule 5 - Modern PhysicsANGELO NINO ALVARADONo ratings yet
- Electricity Homework SolutionsDocument34 pagesElectricity Homework SolutionsDascaliuc Daniel0% (1)
- Physics 9C Midterm SolutionsDocument7 pagesPhysics 9C Midterm SolutionsTiffany LeeNo ratings yet
- General Physics CH 23Document31 pagesGeneral Physics CH 23Wei HuangNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields NCERT SolutionsDocument23 pagesElectric Charges and Fields NCERT SolutionsRaja KarmaNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument9 pagesElectrostaticsapi-283216587No ratings yet
- Electrostatic For MurniDocument55 pagesElectrostatic For MurniAnonymous RMXuPuNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE Paper 1 SolutionsDocument9 pagesIIT-JEE Paper 1 SolutionsSrinivasulu KonetiNo ratings yet
- Midterm 01 Review-SolutionsDocument12 pagesMidterm 01 Review-Solutionsfajita2No ratings yet
- Ch22 SSM-1Document31 pagesCh22 SSM-1alyxs_1No ratings yet
- Physics Assignment 2Document15 pagesPhysics Assignment 2Vines 747No ratings yet
- Unit 3 - ElectrostaticsDocument33 pagesUnit 3 - Electrostaticsshinichi_kesian6117No ratings yet
- Part Test 10Document79 pagesPart Test 10Srinivasarao SrinuNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics (Part 1-Student Copy)Document40 pagesElectrostatics (Part 1-Student Copy)CasioEnervon100% (1)
- CBSE 12 Engineering Medical Physics Electric Charges and FieldsDocument21 pagesCBSE 12 Engineering Medical Physics Electric Charges and FieldsReena JainNo ratings yet
- Example Problem: SolutionDocument26 pagesExample Problem: SolutionRay TakazaNo ratings yet
- hw8 SolnsDocument9 pageshw8 SolnsJennyNo ratings yet
- MTPDF4 Electric FieldDocument33 pagesMTPDF4 Electric Field202312329No ratings yet
- Welcome To Electromagnetism: Ed CopelandDocument20 pagesWelcome To Electromagnetism: Ed CopelandDimitris ToubisNo ratings yet
- Physics Homework1Document7 pagesPhysics Homework1markolyinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Electric Field, Electric Flux, and Gauss LawDocument34 pagesLesson 2 Electric Field, Electric Flux, and Gauss LawErica QuirobNo ratings yet
- Samacheer Kalvi 12th Physics Problems (New Syllabus)Document52 pagesSamacheer Kalvi 12th Physics Problems (New Syllabus)Rahul Karthik80% (10)
- Tutorial Chapter 3 UpdatedDocument6 pagesTutorial Chapter 3 UpdatedJeffrey TehNo ratings yet
- 23 - 26 - solutions 물리Document9 pages23 - 26 - solutions 물리전삼기No ratings yet
- Ch21 SSMDocument18 pagesCh21 SSMFranko UrciaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 TS Exercise 14 Page 174Document20 pagesGrade 11 TS Exercise 14 Page 174Priyanka KanaNo ratings yet
- Answers For Pre Test 1Document4 pagesAnswers For Pre Test 1madbooks444No ratings yet
- Exam 2003 AnswersDocument10 pagesExam 2003 AnswersShootingStarPhotonsNo ratings yet
- Formula Rio 2014Document2 pagesFormula Rio 2014Alberto García WatsonNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Electrostatics Study MaterialDocument15 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Electrostatics Study MaterialAakaash C.K.100% (1)
- Lecture 2Document19 pagesLecture 2swarhiliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document10 pagesChapter 1cse.220840131017No ratings yet
- Suggested+Solutions+V1+VG MVG+Level+Test+FyANVC08+Ch+16 19+electricityDocument9 pagesSuggested+Solutions+V1+VG MVG+Level+Test+FyANVC08+Ch+16 19+electricityEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Coulomb's LawDocument14 pagesCoulomb's LawSpoodsNo ratings yet
- Physics 21 SolutionsDocument92 pagesPhysics 21 SolutionsOğuzhan Odbay100% (1)
- Electromagnetism. Module 1 - Electrical Current An PDFDocument32 pagesElectromagnetism. Module 1 - Electrical Current An PDFnesh07No ratings yet
- P-N JUNCTIONDocument18 pagesP-N JUNCTIONkhan47pkNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Test DemoDocument20 pagesPHYSICS Test Demomohits822No ratings yet
- Review Physics 3Document24 pagesReview Physics 3Thanh TrúcNo ratings yet
- p240w12 Mid1-2Document14 pagesp240w12 Mid1-2shlaeaNo ratings yet
- Physics II Mid Term ExamDocument11 pagesPhysics II Mid Term Examisellsani100% (1)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Beam ProgrammingDocument1 pageMathcad - Beam ProgrammingDesejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra39Document1 pageMathcad - Extra39Desejo Sozinando100% (1)
- Gyrops 22 08 2016Document7 pagesGyrops 22 08 2016Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machines IIIDocument73 pagesHydraulic Machines IIIDesejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra38Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra38Desejo Sozinando0% (1)
- Mathcad - Extra44Document1 pageMathcad - Extra44Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Test 1Document3 pagesMathcad - Test 1Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Test 2Document2 pagesMathcad - Test 2Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra30Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra30Desejo Sozinando50% (2)
- Mathcad - Extra43Document1 pageMathcad - Extra43Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Proramming Spot2Document2 pagesMathcad - Proramming Spot2Desejo Sozinando100% (1)
- Mathcad - Extra37Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra37Desejo Sozinando0% (1)
- Mathcad - Spot Questions1Document5 pagesMathcad - Spot Questions1Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - ProgrammDocument1 pageMathcad - ProgrammDesejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra42Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra42Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra41Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra41Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra33Document1 pageMathcad - Extra33Desejo Sozinando50% (2)
- Mathcad - Extra40Document1 pageMathcad - Extra40Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra31Document1 pageMathcad - Extra31Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra32Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra32Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra35Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra35Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra36Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra36Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra34Document1 pageMathcad - Extra34Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra29Document1 pageMathcad - Extra29Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra27Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra27Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra28Document3 pagesMathcad - Extra28Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra26Document1 pageMathcad - Extra26Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra24Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra24Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Extra25Document1 pageMathcad - Extra25Desejo Sozinando0% (1)
- Mathcad - Extra23Document2 pagesMathcad - Extra23Desejo SozinandoNo ratings yet
- 15Document74 pages15physicsdocs60% (25)
- Tutorial 1 ThermodyanamicsDocument1 pageTutorial 1 ThermodyanamicsKaustubh Mallik100% (1)
- CapacitorDocument98 pagesCapacitorklprasdNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Important MCQ PDF-Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics Part 2Document19 pagesCivil Engineering Important MCQ PDF-Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics Part 2Shweta NagpalNo ratings yet
- Intermot Hydraulic Motors IAM+ Series Technical CatalogueDocument81 pagesIntermot Hydraulic Motors IAM+ Series Technical CatalogueeduardoraulNo ratings yet
- D MukherjiDocument621 pagesD MukherjiAman gupta100% (3)
- Balkumari Higher Sec. School: 2. Answer, in Brief, Any Two QuestionsDocument3 pagesBalkumari Higher Sec. School: 2. Answer, in Brief, Any Two QuestionsRabindra Raj BistaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 2021-2022: 1. Static Equilibria, Stress, and StrainDocument9 pagesSyllabus 2021-2022: 1. Static Equilibria, Stress, and StrainKrrish Pradhani9C11No ratings yet
- Torque Vs Angle of Twist: Cast IronDocument4 pagesTorque Vs Angle of Twist: Cast IronPrateek K srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Optimal Daily Functionality of Industrial and Constructed Atmega328P Microcontrollers in Solar Energy Measurement SystemDocument8 pagesComparative Optimal Daily Functionality of Industrial and Constructed Atmega328P Microcontrollers in Solar Energy Measurement SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Ch-1-1 Introduction and DimensionsDocument34 pagesFluid Ch-1-1 Introduction and Dimensionsأزهار برديNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Week 6Document3 pagesWorksheet Week 6Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Quantities 6 QPDocument13 pagesElectrical Quantities 6 QPdhany aarunNo ratings yet
- SEO-Optimized title for physics exam questions documentDocument14 pagesSEO-Optimized title for physics exam questions documentprabs20069178No ratings yet
- Testing CTDocument65 pagesTesting CTAbel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan - Momentum and ImpulseDocument10 pagesDaily Lesson Plan - Momentum and ImpulseStephanNo ratings yet
- FullDocument909 pagesFullVIMALKAUMAR0% (1)
- Labvolt Todas Las Practicas Cwa8001Document70 pagesLabvolt Todas Las Practicas Cwa8001Yorgos J. Ramirez PNo ratings yet
- 3ph 4 To 12kwDocument2 pages3ph 4 To 12kwnataraNo ratings yet
- Q4-Another FormDocument63 pagesQ4-Another Form谢钊洋No ratings yet
- ER300P User ManualDocument17 pagesER300P User Manualm,.100% (1)
- Slides 04Document10 pagesSlides 04Anudwaipaon AntuNo ratings yet
- SCIM DesignDocument9 pagesSCIM DesignRafael BulaonNo ratings yet
- AGA2019 Laughton PPT CVDocument17 pagesAGA2019 Laughton PPT CVВіталій Роман100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Quick Revision NotesDocument2 pagesChapter 2 Quick Revision Noteshindu Jagran ekta samitiNo ratings yet
- Section A (10 Marks) Instructions: Answer All The Questions in This SectionDocument7 pagesSection A (10 Marks) Instructions: Answer All The Questions in This SectionAHMAD FAISALNo ratings yet
- Psychrometrics in daily life and food industryDocument29 pagesPsychrometrics in daily life and food industryKhoyrul HudaNo ratings yet
- Dec-19 Question - CorrectedDocument19 pagesDec-19 Question - CorrectedManish Singh BishtNo ratings yet
- Impact of Inductor Current Ringing in DCM On Output Voltage of DC-DC Buck Power ConvertersDocument11 pagesImpact of Inductor Current Ringing in DCM On Output Voltage of DC-DC Buck Power ConvertersMel Vin PinNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous and Synchronous Machines (EL-208) (IV SEM EL Session 2017-18) Tutorial Sheet 1 (Dated 08.01.2018) (3 Phase Induction MotorsDocument13 pagesAsynchronous and Synchronous Machines (EL-208) (IV SEM EL Session 2017-18) Tutorial Sheet 1 (Dated 08.01.2018) (3 Phase Induction Motorstrek juneNo ratings yet