Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cues
Uploaded by
Katrina PonceOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cues
Uploaded by
Katrina PonceCopyright:
Available Formats
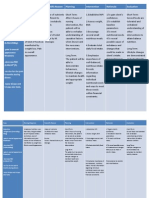
Cues: Subective: Nahihirapan po akong huminga as verbalized by the patient
Problem/Diagnosis: Ineffective Airway Clearance
Obective: T: PR: RR: (+)Persistent
cough (+)Wheezing (+)Dyspnea (+)Restlessnes s (+)Cyanosis
Scientific Reason: Chronic Bronchitis is an inflammatory response to the offending microorganism. The defense mechanisms of the lungs lose effectiveness and allow organisms to penetrate the sterile respiratory tract, as a result inflammation develops. The inflammation and increased secretions make it difficult to maintain a patent airway.
Intervention: Establish rapport to the pt. and SO Assess the patient condition Monitor and record V/S Position head midline with flexion on appropriate for age/condition Elevate HOB Observe S/Sx of infections Auscultate breath sounds & assess air movt Instruct the patient to increase fluid intake Demo Demonstrate effective coughing and deep-breathing techniques. Keep back dry Turn the patient q 2 hours Demonstrate chest physiotherapy, such as bronchial tapping when in cough, proper postural drainage. Administer bronchodilators if prescribed.
Rationale: To gain trust and active participation To know the condition of the pt To have a baseline data. To gain or maintain open airway To decrease pressure on the diaphragm and enhancing drainage To identify infectious process To ascertain status & note progress To help to liquefy secretions. To maximize effort To prevent further complications To prevent possible aspirations These techniques will prevent possible aspirations and prevent any untoward complications More aggressive measures to maintain airway patency.
Evaluation: Short term: The patient shall have demonstrated effective clearing of secretions.
Long term: The patient shall have maintained effective airway clearance
Cues: S: Reports of dyspnea O: The patient may manifest the manifest the ffg.: with wheezes /crackles upon auscultation on BLF increase RR above normal range presence of productive cough use of accessory muscle when breathing presence of nasal flaring and retractions
Problem/Diagnosis: Ineffective Breathing Pattern RT Retained Secretions
Scientific Reason: The presence of microorganisms in the lungs causes body to increase the secretory activity of goblet cells to get rid of the invading organism but the mechanism is not enough which allows the stasis of mucus secretion leading to ineffective breathing pattern.
Intervention: Establish rapport to the pt. and SO Assess the patient condition Monitor and record V/S especially RR Provide rest periods Place pt in semi-fowlers position Increase fluid intake Keep patient back dry Change position every 2 hours Perform CPT Place a pillow when the client is sleeping Instruct how to splint the chest wall with a pillow for comfort during coughing and elevation of head over body as appropriate Maintain a patent airway, suctioning of secretions may be done as ordered Provide respiratory support. Oxygen inhalation is provided per doctors order Administer prescribed cough suppressants and analgesics and be cautious, however,
Rationale: To gain trust and active participation To know the condition of the pt To have a baseline data. To reduce fatigue and obtain rest To have a maximum lung expansion To liquefy secretions To avoid stasis of secretions and avoid further complication To facilitate secretion movt and drainage To loosen secretion To provide adequate lung expansion while sleeping. To promote physiological ease of maximal inspiration To remove secretions that obstructs the airway To aid in relieving patient from dyspnea To promote deeper respirations and cough
Evaluation: Short term:The patient shall have improved breathing pattern.Long term: The patient shall have maintained a respiratory rate within normal limits.
because opioids may depress respirations more than desired.
Cues:
Problem/Diagnosis: Impaired Gas Exchange RT Altered Oxygen Balance
Scientific Reason:
Intervention:
Rationale:
Evaluation:
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Distance Relay Setting CalculationDocument8 pagesDistance Relay Setting Calculation1453h100% (7)
- Unit 5-People Should Manage Nature-Ts-Planning Guide-Grade 5Document1 pageUnit 5-People Should Manage Nature-Ts-Planning Guide-Grade 5api-457240136No ratings yet
- Safe SuctioningDocument31 pagesSafe SuctioningKatrina Ponce100% (2)
- 5.casts and MoldsDocument30 pages5.casts and MoldsKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Chemical Recycling of Textile PolymersDocument8 pagesChemical Recycling of Textile PolymersVaishali RaneNo ratings yet
- Operating Room TeamDocument18 pagesOperating Room TeamKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Principles of Patient Skin PreparationDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Patient Skin PreparationKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- GIT DisordersDocument171 pagesGIT DisordersKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Hex 33 X 80Document1 pageHex 33 X 80PurchaseNo ratings yet
- 2.balance Skeletal TractionDocument18 pages2.balance Skeletal TractionKatrina Ponce75% (4)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- Air Defence Systems: Export CatalogueDocument105 pagesAir Defence Systems: Export CatalogueserrorysNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of The Perioperative PatientDocument19 pagesNursing Management of The Perioperative PatientKatrina Ponce100% (4)
- Caldwell LucDocument1 pageCaldwell LucKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Patient S AssignmentDocument1 pagePatient S AssignmentKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Oxygen MasksDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of Oxygen MasksKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Hernandez, Dionne Cedric P. BSN4B Group 8Document24 pagesPrepared By: Hernandez, Dionne Cedric P. BSN4B Group 8Katrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Operating Room Equipments and Machineries: By: RICACHO, Ma. Norilyn BSN4B - Group8Document38 pagesOperating Room Equipments and Machineries: By: RICACHO, Ma. Norilyn BSN4B - Group8Katrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Defense MechanismDocument2 pagesDefense MechanismKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- DwarfismDocument2 pagesDwarfismKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Oxygen MasksDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of Oxygen MasksKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- NE2.1 Ward RoutinesDocument3 pagesNE2.1 Ward RoutinesKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Community AcquiredDocument21 pages"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Community AcquiredKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- NCP Epidural HemDocument32 pagesNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Closed Displacement Segmental FemurDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Closed Displacement Segmental FemurKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Steel Sections PDFDocument36 pagesSteel Sections PDFTonderai RusereNo ratings yet
- 2008 IASS SLTE 2008 Chi Pauletti PDFDocument10 pages2008 IASS SLTE 2008 Chi Pauletti PDFammarNo ratings yet
- Nickel 200 201 PDFDocument20 pagesNickel 200 201 PDFwdavid81No ratings yet
- Tcs IntroDocument12 pagesTcs IntroRomi.Roy1820 MBANo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument24 pagesCapital BudgetingHassaan NasirNo ratings yet
- The Design and Development of Organic Chemistry Module For College StudentsDocument6 pagesThe Design and Development of Organic Chemistry Module For College StudentsEight AlykNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases and Salts Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 ScienceDocument5 pagesAcid Bases and Salts Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 Scienceclashhunting123123No ratings yet
- Proplanner Assembly Planner PFEPDocument5 pagesProplanner Assembly Planner PFEPAya MdimeghNo ratings yet
- Likert Scale Video Presentation RubricsDocument1 pageLikert Scale Video Presentation RubricsALDWIN B. BAYLONNo ratings yet
- Iecex Bas 13.0069XDocument4 pagesIecex Bas 13.0069XFrancesco_CNo ratings yet
- 5EMA BB Dem&Sup VW Bu&Se - 2.35&48&PDDocument13 pages5EMA BB Dem&Sup VW Bu&Se - 2.35&48&PDkashinath09No ratings yet
- 1349122940100212diggerDocument24 pages1349122940100212diggerCoolerAdsNo ratings yet
- Installation ManualDocument16 pagesInstallation ManualJosé Manuel García MartínNo ratings yet
- AWP 4A Syllabus Fall 2021 (Misinformation)Document11 pagesAWP 4A Syllabus Fall 2021 (Misinformation)camNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Saba Khan 15 Shahbad Diwan Khana, Bareilly, City, Bareilly, Bareilly, Utt AR PRADESH, 243003,9219172265Document28 pagesMrs. Saba Khan 15 Shahbad Diwan Khana, Bareilly, City, Bareilly, Bareilly, Utt AR PRADESH, 243003,9219172265amitNo ratings yet
- Social and Professional Issues Pf2Document4 pagesSocial and Professional Issues Pf2DominicOrtegaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Teaching PracticeDocument14 pagesThe Impact of Teaching PracticemubarakNo ratings yet
- R820T Datasheet-Non R-20111130 UnlockedDocument26 pagesR820T Datasheet-Non R-20111130 UnlockedKonstantinos GoniadisNo ratings yet
- Chen Probable Cause Affidavit 050714Document7 pagesChen Probable Cause Affidavit 050714USA TODAYNo ratings yet
- Quantum Data-Fitting: PACS Numbers: 03.67.-A, 03.67.ac, 42.50.DvDocument6 pagesQuantum Data-Fitting: PACS Numbers: 03.67.-A, 03.67.ac, 42.50.Dvohenri100No ratings yet
- Ricoh Aficio SP C420DN PARTS CATALOGDocument82 pagesRicoh Aficio SP C420DN PARTS CATALOGYury Kobzar100% (2)
- Essentials of Repertorization Tiwari Link PageDocument11 pagesEssentials of Repertorization Tiwari Link PageBibin TSNo ratings yet
- Fulltext PDFDocument454 pagesFulltext PDFVirmantas JuoceviciusNo ratings yet
- How To Install Mesa (OpenGL) On Linux Mint - 6 StepsDocument2 pagesHow To Install Mesa (OpenGL) On Linux Mint - 6 Stepsankitfrnd45No ratings yet
- Analog Digital Thermopile Application Note PDFDocument18 pagesAnalog Digital Thermopile Application Note PDFGopal HegdeNo ratings yet