Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Soalan Add Math
Uploaded by
SukHarunOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Soalan Add Math
Uploaded by
SukHarunCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers
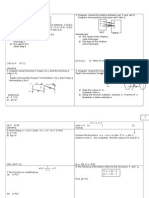
1. (a)
a + 4d = 9 1
12
(2a + 11d) = 126
2
2a + 11d = 21 2
1 2, 2a + 8d = 18 3
2 3,
3d = 3
d = 1
\ a = 9 4(1)
=5
(d)
a + 2d = 4 1
a + 11d = 23 2
2 1, 9d = 27
d = 3
\ a = 4 2(3)
= 10
10 [2(10) + 9(3)]
S10 =
2
= 35
10 [2(5) + 9(1)]
S10 =
2
= 95
n [2(4) + (n 1)(3)] . 125
2. (a)
2
n (8 + 3n 3) . 125
2
3n2 + 5n 250 . 0
5 (2a + 4d) = 5
(b)
2
a + 2d = 1 1
15
(2a + 14d) = 180
2
a + 7d = 12 2
2 1, 5d = 11
11
d =
5
If 3n2 + 5n 250 = 0
5 52 4(3)(250)
n =
2(3)
= 8.3 or 10
Since n is the number of terms,
therefore n = 9.
11
\ a = 1 2
5
17
=
5
10 [2(
17 ) + 9(
11 )]
S10 =
2
5
5
= 65
1 2
(c)
a + 8d =
2a + 2d =
a + d =
9
(2a + 8d) =
2 a + 4d =
1 + 2, 5d =
d =
\ a = d
=2
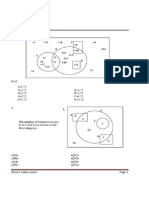
(b) For numbers divisible by 12,
108, 120, , 492
Tn = 108 + (n 1)(12) = 492
n 1 = 32
n = 33
33 [2(108) + 32(12)]
S33 =
2
= 9900
3(a + 2d)
0
0 1
90
10 2
10
2
Sum of all numbers from 100 to 500
inclusive is
401 [2(100) + 400(1)]
S401 =
2
= 120 300
\ Sum of all the integers from 100
to 500 inclusive which cannot be
divided by 12
= 120 300 9900
= 110 400
10 [2(2) + 9(2)]
S10 =
2
= 110
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
01 Amath F5 CD.indd 2
7/1/08 8:40:31 AM
3. (a) y + 2x, 2y + 2x, 3y + 2x,
d1 = 2y + 2x (y + 2x)
=y
d2 = 3y + 2x (2y + 2x)
=y
Since d1 = d2, therefore it is an
arithmetic progression and d = y.
(b) L = 120 cm, x = 2 cm, y = 3 cm
8 [2(y + 2x) + 7y]
S8 =
2
= 4[2(3 + 4) + 7(3)]
= 4(14 + 21)
= 140 cm
No, it is short by 20 cm.
10 [2(7) + 9(3)]
(c) S10 =
2
= 5(14 + 27)
= 205 cm
01 Amath F5 CD.indd 3
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
7/1/08 8:40:31 AM
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Us 20120080888Document34 pagesUs 20120080888Marian IONo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Book of ProcessDocument92 pagesBook of ProcessKapwa Para Hayahay83% (6)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Edexcel GCSE Physics P2 Topic 6 Test 16 - 17 With Mark SchemeDocument18 pagesEdexcel GCSE Physics P2 Topic 6 Test 16 - 17 With Mark SchemePaul BurgessNo ratings yet
- ATPL Summary PDFDocument60 pagesATPL Summary PDFAditya MehtaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Abduction Research (JAR) Issue 2Document35 pagesJournal of Abduction Research (JAR) Issue 2ella..100% (1)
- SchemhamphoraschDocument4 pagesSchemhamphoraschCostin AlexNo ratings yet
- Separation and Nadi AstrologyDocument3 pagesSeparation and Nadi AstrologyManish SankrityayanNo ratings yet
- Elias AshmoleDocument12 pagesElias AshmoleOops100% (1)
- 0 - BK2 - Item - Draf Latihan PDFDocument37 pages0 - BK2 - Item - Draf Latihan PDFShasha WiniNo ratings yet
- The 2007 ESO Instrument Calibration Workshop - Proceedings of The ESO Workshop Held in Garching, Germany, 23-26 January 2007 (PDFDrive)Document594 pagesThe 2007 ESO Instrument Calibration Workshop - Proceedings of The ESO Workshop Held in Garching, Germany, 23-26 January 2007 (PDFDrive)Adetunji Babatunde TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Man With The Hoe DLLDocument4 pagesMan With The Hoe DLLSelle QuintanoNo ratings yet
- Formula f4 KSSMDocument2 pagesFormula f4 KSSMSukHarunNo ratings yet
- #Shellcare Teacher's Day V1Document10 pages#Shellcare Teacher's Day V1SukHarunNo ratings yet
- BIL Nama Tingkatanjantina Kad Pengenalan: KehadiranDocument1 pageBIL Nama Tingkatanjantina Kad Pengenalan: KehadiranSukHarunNo ratings yet
- BIL Nama Tingkatanjantina Kad Pengenalan: KehadiranDocument1 pageBIL Nama Tingkatanjantina Kad Pengenalan: KehadiranSukHarunNo ratings yet
- The Middle Year Programme (MYP) Personal Project Allows Students To PracticeDocument4 pagesThe Middle Year Programme (MYP) Personal Project Allows Students To PracticeSukHarunNo ratings yet
- Kiri Kanan Cerah 0 S4 S1 Gelap 1 1 0 0 Forward 2 0 1 Turn Right 3 1 0 Turn Left 4 1 1 Stop/Count JucntionDocument1 pageKiri Kanan Cerah 0 S4 S1 Gelap 1 1 0 0 Forward 2 0 1 Turn Right 3 1 0 Turn Left 4 1 1 Stop/Count JucntionSukHarunNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test 4.4 Understanding The Gas Laws - Boyle's LawDocument2 pagesPre-Test 4.4 Understanding The Gas Laws - Boyle's LawSukHarunNo ratings yet
- Surat Data Prestasi 2020Document5 pagesSurat Data Prestasi 2020SukHarunNo ratings yet
- 4.4b Understanding Gas LawDocument3 pages4.4b Understanding Gas LawSukHarunNo ratings yet
- 4.4c Understanding Gas LawDocument3 pages4.4c Understanding Gas LawSukHarunNo ratings yet
- Quick Strategies For Self assessment:-WEBS (Spider Diagrams) ReflectionDocument1 pageQuick Strategies For Self assessment:-WEBS (Spider Diagrams) ReflectionSukHarunNo ratings yet
- 4.4b Understanding Gas LawDocument3 pages4.4b Understanding Gas LawSukHarunNo ratings yet
- Bahan Sumber Pengajaran Dan PembelajaranDocument5 pagesBahan Sumber Pengajaran Dan PembelajaranrezzmanNo ratings yet
- Program Jadual AnjalDocument3 pagesProgram Jadual AnjalSukHarunNo ratings yet
- 4.4c Understanding Gas LawDocument3 pages4.4c Understanding Gas LawSukHarunNo ratings yet
- Post Test Understanding of PhysicsDocument3 pagesPost Test Understanding of PhysicsSukHarunNo ratings yet
- 2.1analysing Linear MotionDocument19 pages2.1analysing Linear MotionSukHarunNo ratings yet
- Comment by Online FacilitatorDocument4 pagesComment by Online FacilitatorSukHarunNo ratings yet
- (450862914) Ranadd - Math - Form - 5yearplan2009 - 15Document27 pages(450862914) Ranadd - Math - Form - 5yearplan2009 - 15SukHarunNo ratings yet
- Buku Pengurusan Peribadi 2015 Terbaik Oleh Cikgu Suriati Ku IshakDocument24 pagesBuku Pengurusan Peribadi 2015 Terbaik Oleh Cikgu Suriati Ku Ishaks0feaNo ratings yet
- Modul Amuk P1 SoalanDocument34 pagesModul Amuk P1 SoalanSukHarunNo ratings yet
- Reflective Entry: Activity 6.3 FeedbackDocument1 pageReflective Entry: Activity 6.3 FeedbackSukHarunNo ratings yet
- Quick Strategies For Self Assessment:-Traffic Light Cards ReflectionDocument1 pageQuick Strategies For Self Assessment:-Traffic Light Cards ReflectionSukHarunNo ratings yet
- IB Learner ProfileDocument7 pagesIB Learner ProfileSukHarun0% (1)
- Venn DiagramDocument6 pagesVenn DiagramSukHarunNo ratings yet
- Modul Cemerlang Ting 4Document6 pagesModul Cemerlang Ting 4SukHarunNo ratings yet
- Kepler Law From NettDocument7 pagesKepler Law From NettIndah Septia NingsihNo ratings yet
- 2020 MCQ1Document8 pages2020 MCQ1Harshit BhattNo ratings yet
- Retrogression and Strength From Uttarakalamrta: Uttarakalamrta 1.2.6. A Vakri Graha's Strength Is Equivalent ToDocument32 pagesRetrogression and Strength From Uttarakalamrta: Uttarakalamrta 1.2.6. A Vakri Graha's Strength Is Equivalent ToGopi100% (1)
- Pat 2012 Paper PDF 10581Document28 pagesPat 2012 Paper PDF 10581Ahmad HaikalNo ratings yet
- NASA Facts Control Module Functional Cargo Block (FGB)Document2 pagesNASA Facts Control Module Functional Cargo Block (FGB)Bob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- Star of Bethlehem PresentationDocument50 pagesStar of Bethlehem PresentationJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Pnakotic Manuscripts: Amnesia Across Aeons by SunchalesDocument3 pagesPnakotic Manuscripts: Amnesia Across Aeons by SunchalesALLEN MACKEY100% (1)
- Satellites SeminarDocument22 pagesSatellites SeminarKartik KandanuruNo ratings yet
- Aryabhata and Axial Rotation of Earth: Amartya Kumar DutraDocument15 pagesAryabhata and Axial Rotation of Earth: Amartya Kumar DutraNandhaNo ratings yet
- Dynamicevidenceof Dark MatterDocument22 pagesDynamicevidenceof Dark MatterRandheer GautamNo ratings yet
- Integrated Operating Mode of The Apollo Mission SimulatorDocument3 pagesIntegrated Operating Mode of The Apollo Mission SimulatorKanishka Lankatillake100% (1)
- La Carta TrimsamsaDocument3 pagesLa Carta TrimsamsaRicardo RoyleNo ratings yet
- Up in The AirDocument13 pagesUp in The AirRobert MatheusNo ratings yet
- Madness and The Moon: The Lunar Cycle and Psychopathology: German Journal of Psychiatry July 2006Document6 pagesMadness and The Moon: The Lunar Cycle and Psychopathology: German Journal of Psychiatry July 2006brainhub50No ratings yet
- Taller 4 Week 3Document5 pagesTaller 4 Week 3LEIDY YURIDIANo ratings yet
- Did You Know: Fun Things ToDocument1 pageDid You Know: Fun Things ToHartford CourantNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Inner and Outer Planets: - Categorized UnderDocument4 pagesDifference Between Inner and Outer Planets: - Categorized UnderLovely CuananNo ratings yet
- Secret Base Kimi Ga Kureta Mono: Lyrics (Romaji)Document3 pagesSecret Base Kimi Ga Kureta Mono: Lyrics (Romaji)ichiyuRunaNo ratings yet
- Day 2 ConstellationDocument6 pagesDay 2 ConstellationMaureen Torres CastelNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Prediction by AstrologyDocument4 pagesEarthquake Prediction by AstrologychewmilNo ratings yet