Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Schematic Diagram of Pneumonia
Uploaded by
Kent MasadoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Schematic Diagram of Pneumonia
Uploaded by
Kent MasadoCopyright:
Available Formats
Schematic Diagram of Pneumonia
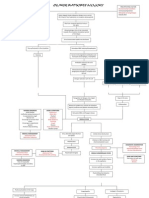
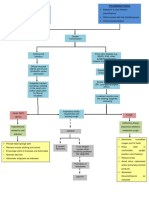
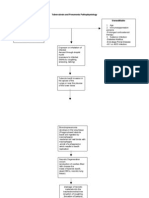
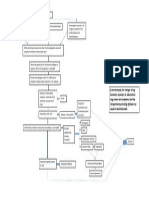
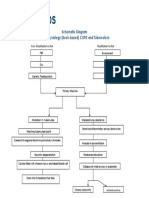
Alteration in net bacterial lung resistance caused by either: Decreased bactericidal ability of the alveolar macrophages Extreme virulence of the bacteria Increased susceptibility of host to infection
Acute inflammation occurs that causes excess water and plasma proteins go to the dependent areas of the lower lobes
RBCs, fibrin, and polymorphonuclear leukocytes infiltrate the alveoli
Containment of the bacteria within the segments of pulmonary lobes by cellular recruitment
Consolidation of leukocytes and fibrin within the affected area
Stage of congestion: Engorgement of alveolar spaces with fluid and hemorrhagic exudates
Proliferation and rapid spread of organism through the lobe
Stage of red hepatization: Coagulation of exudates occurs resulting to the red appearance of the affected lung
Stage of gray hepatization: The decrease in number of RBC in the exudates is replaced by neutrophils; which infiltrate the alveoli making the lung tissue to be solid and grayish in color.
PNEUMONIA
You might also like
- Bronchitis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBronchitis PathophysiologyFerry Reyes0% (1)
- Pneumonia PathoDocument2 pagesPneumonia PathoDerick Nyl PascualNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Histolytica, ADocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Histolytica, AkristennemarieNo ratings yet
- Patho DengueDocument3 pagesPatho DengueLindy Shane BoncalesNo ratings yet
- Concept Map AsthmaDocument4 pagesConcept Map AsthmaAstrid Moreno De LeonNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument6 pagesAnatomyKadulum100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of VSDDocument1 pagePathophysiology of VSDMarlon CruzNo ratings yet
- Intravenous ImmunoglobulinDocument5 pagesIntravenous ImmunoglobulinTeslim RajiNo ratings yet
- CROUP Concept MapDocument3 pagesCROUP Concept Mapingrid50% (2)
- Acc Phu Case NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageAcc Phu Case NCP Hyperthermiamacy_bautistaNo ratings yet
- TB PathoPhysiologyDocument6 pagesTB PathoPhysiologyChloé Jane HilarioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverKenneth Lagman100% (1)
- PathophysiologyDocument6 pagesPathophysiologyElbert Hermogino ﭢNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Phsyiology of MeningococcemiaDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Phsyiology of MeningococcemiaKevin Comahig100% (1)
- Diabetes InsipidusDocument60 pagesDiabetes Insipidusperie_md100% (1)
- Case Study PcapDocument3 pagesCase Study PcapClaire PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Rabi PurDocument3 pagesRabi PurDiana Laura LeiNo ratings yet
- 02 Bronchial Asthma Circ 2018-2019Document15 pages02 Bronchial Asthma Circ 2018-2019Mooha Alanzy100% (1)
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument1 pagePneumoniaAyen FornollesNo ratings yet
- BFCDocument8 pagesBFCIrene GunongNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology TBDocument2 pagesPathophysiology TBJhen DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- Acute Post-Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument15 pagesAcute Post-Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisJeanne Marie ValesNo ratings yet
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Document6 pagesDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogNo ratings yet
- NCA2 PosttestsDocument20 pagesNCA2 PosttestsCzarena Ysabelle PayotNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AmoebiasisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AmoebiasisCathy AcquiatanNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements R/T Diarrhea Due To Excessive OutputDocument2 pagesImbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements R/T Diarrhea Due To Excessive OutputMark BarengNo ratings yet
- NCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioDocument5 pagesNCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioRio BonifacioNo ratings yet
- 2 Nursing-Process-in-the-care-of-the-Community - FGBDocument41 pages2 Nursing-Process-in-the-care-of-the-Community - FGBKim Bok JooNo ratings yet
- Cap MRDocument4 pagesCap MRKit BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 2023 F-ACAD-29 - Syllabus Template (Rev 6)Document63 pagesNCM 109 2023 F-ACAD-29 - Syllabus Template (Rev 6)Joyce EricaNo ratings yet
- Meropenem: Antibiotic ClassDocument2 pagesMeropenem: Antibiotic ClassAynshbNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Case Study of PneumoniaDocument13 pagesActivity 2 Case Study of PneumoniaEdelweiss Marie Cayetano100% (1)
- Pneumonia Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPneumonia Drug Studyatienza02No ratings yet
- MedSurg Notes - Cancer of The LiverDocument2 pagesMedSurg Notes - Cancer of The LiverMae CeaesarNo ratings yet
- Measles PathophysiologyDocument1 pageMeasles PathophysiologyAl TheóNo ratings yet
- B. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyDocument3 pagesB. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyKenneth Torres100% (1)
- Myocardial Infarction (Diseases For Oral Revalida)Document12 pagesMyocardial Infarction (Diseases For Oral Revalida)Suzette PipoNo ratings yet
- AmoebiasisDocument1 pageAmoebiasisYakumaNo ratings yet
- NCP AgnDocument2 pagesNCP Agnj3nann3No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PharyngitisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of PharyngitisKRISTINE BULACAN100% (1)
- Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and TuberculosisDocument1 pageSchematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and Tuberculosispragna novaNo ratings yet
- ErcefloraDocument2 pagesErcefloraNílo Stárn100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888No ratings yet
- Course in The WardDocument1 pageCourse in The WardKyrie Jarvis videosNo ratings yet
- A: Hydrolyzed To Active Drug: Cebu Normal University - College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument1 pageA: Hydrolyzed To Active Drug: Cebu Normal University - College of Nursing Drug StudyMaki Dc100% (1)
- Drug Study Pyrantel & CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDrug Study Pyrantel & CefuroximeMikhael Briones ApasNo ratings yet
- Febrile SeizuresDocument24 pagesFebrile SeizuresShrikant Hemant JoshiNo ratings yet
- SLE PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesSLE PathophysiologyyasiraNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Pleural Effusion: Union Christian CollegeDocument8 pagesCase Study: Pleural Effusion: Union Christian CollegeJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 (Pneumonia)Document13 pagesCase Study 1 (Pneumonia)Kate EscotonNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument3 pagesConcept MapKevin T. KatadaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion - NCPDocument7 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion - NCPVianah Eve EscobidoNo ratings yet
- POTTs Disease PathoDocument3 pagesPOTTs Disease PathoEdgel QuidolesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaIrene Demegillo SalongaNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi PneumoniaDocument3 pagesPatofisiologi PneumoniainggridNo ratings yet
- Image Session of Respiratory System IDocument31 pagesImage Session of Respiratory System IZain Ul AbidinNo ratings yet
- 3 BronchiectasisDocument29 pages3 BronchiectasisЕвгений ХанькоNo ratings yet
- Non Tuberculous Infections (Updated)Document54 pagesNon Tuberculous Infections (Updated)ZijieNo ratings yet
- Etiology: 1. Compare Lobar Pneumonia With Lobular Pneumonia On The ListDocument3 pagesEtiology: 1. Compare Lobar Pneumonia With Lobular Pneumonia On The Listselam kalayuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 303. Nursing Peer ReviewDocument7 pagesChapter 303. Nursing Peer ReviewKent MasadoNo ratings yet
- Meds Medical Treatment and EvaluationDocument1 pageMeds Medical Treatment and EvaluationKent MasadoNo ratings yet
- Case Study PIHDocument11 pagesCase Study PIHManuel Lavarias100% (1)
- Pa Tho Physiology of LymphomasDocument17 pagesPa Tho Physiology of LymphomasKent MasadoNo ratings yet