Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sem 3
Uploaded by
mabhatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sem 3
Uploaded by
mabhatCopyright:
Available Formats
SCHEME OF TEACHING AND EXAMINATION M. TECH. DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION III SEMESTER No. of Hrs.
./Week Course Code Subject Code Name of Subject Lecture 4 4 4 Practical Tutorial 2 2 2 Duration of Exam in Hours 3 3 3 Marks for I.A. 50 50 50 50 Exam 100 100 100 Total Marks
10LEC31 10LEC32 10LEC33 10LCS34
10EC039 10ECxxx 10ECxxx 10EC931
Error Control Coding Elective-III (10LEC32x) Elective-IV (10LEC33x) Evaluation of Project Phase I
150 150 150 50
Project Phase-II must be carried out for 3 days a week during III semester. It will be evaluated during IV semester.* Total 12 0 06 09 200 300 500
ELECTIVE III 10LEC321 10LEC322 10LEC323 10EC012 10EC052 10EC071 ASIC Design Multimedia Communications RF & Microwave Circuit Design
ELECTIVE IV 10LEC331 10LEC332 10LEC333 10EC118 10EC119 10EC127 Advanced Embedded Systems Broadband Wireless Networks RF MEMS
SEMESTER III ERROR CONTROL AND CODING Subject Code No. of Lecture Hours /week Total no. of Lecture Hours : 10EC039 : 04 : 52 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 50 : 03 : 100
Introduction to Algebra: Groups, Fields, Binary Field Arithmetic, Construction of Galois Field GF (2 m) and its basic properties, Computation using Galois Field GF (2 m) Arithmetic, Vector spaces and Matrices. Linear Block Codes: Generator and Parity check Matrices, Encoding circuits, Syndrome and Error Detection, Minimum Distance Considerations, Error detecting and Error correcting capabilities, Standard array and Syndrome decoding, Decoding circuits, Hamming Codes, Reed Muller codes, The (24, 12) Golay code, Product codes and Interleaved codes. Cyclic Codes: Introduction, Generator and Parity check Polynomials, Encoding using Multiplication circuits, Systematic Cyclic codes Encoding using Feed back shift register circuits, Generator matrix for Cyclic codes, Syndrome computation and Error detection, Meggitt decoder, Error trapping decoding, Cyclic Hamming codes, The (23, 12) Golay code, Shortened cyclic codes. BCH Codes: Binary primitive BCH codes, Decoding procedures, Implementation of Galois field Arithmetic, Implementation of Error correction. Non binary BCH codes: q ary Linear Block Codes, Primitive BCH codes over GF (q), Reed Solomon Codes, Decoding of Non Binary BCH and RS codes: The Berlekamp Massey Algorithm. Majority Logic Decodable Codes: One Step Majority logic decoding, one step Majority logic decodable Codes, Two step Majority logic decoding, Multiple step Majority logic decoding. Convolutional Codes: Encoding of Convolutional codes, Structural properties, Distance properties, Viterbi Decoding Algorithm for decoding, Soft output Viterbi Algorithm, Stack and Fano sequential decoding Algorithms, Majority logic decoding
Concatenated Codes & Turbo Codes: Single level Concatenated codes, Multilevel Concatenated codes, Soft decision Multistage decoding, Concatenated coding schemes with Convolutional Inner codes, Introduction to Turbo coding and their distance properties, Design of Turbo codes. Burst Error Correcting Codes: Burst and Random error correcting codes, Concept of Inter leaving, cyclic codes for Burst Error correction Fire codes, Convolutional codes for Burst Error correction. Reference Books: 1. 2. Shu Lin & Daniel J. Costello, Jr. Error Control Coding Pearson / Prentice Hall, Second Edition, 2004. (Major Reference) Blahut, R.E. Theory and Practice of Error Control Codes Addison Wesley, 1984 ELECTIVE III ASIC DESIGN Subject Code No. of Lecture Hours /week Total no. of Lecture Hours : 10EC012 : 04 : 52 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 50 : 03 : 100
Note All Designs Will Be Based On VHDL Introduction: Full Custom with ASIC, Semi custom ASICS, Standard Cell based ASIC, Gate array based ASIC, Channeled gate array, Channel less gate array, structured get array, Programmable logic device, FPGA design flow, ASIC cell libraries Data Logic Cells: Data Path Elements, Adders, Multiplier, Arithmetic Operator, I/O cell, Cell Compilers ASIC Library Design: Logical effort: practicing delay, logical area and logical efficiency logical paths, multi stage cells, optimum delay, optimum no. of stages, library cell design. Low-Level Design Entry: Schematic Entry: Hierarchical design. The cell library, Names, Schematic, Icons & Symbols, Nets, schematic entry for ASICS, connections, vectored instances and buses, Edit in place attributes, Netlist, screener, Back annotation Programmable ASIC: programmable ASIC logic cell, ASIC I/O cell A Brief Introduction to Low Level Design Language: an introduction to EDIF, PLA Tools, an introduction to CFI designs representation. Half gate ASIC. Introduction to Synthesis and Simulation; ASIC Construction Floor Planning and Placement And Routing: Physical Design, CAD Tools, System Partitioning, Estimating ASIC size, partitioning methods. Floor planning tools, I/O and power planning, clock planning, placement algorithms, iterative placement improvement, Time driven placement methods. Physical Design flow global Routing, Local Routing, Detail Routing, Special Routing, Circuit Extraction and DRC. Reference Books: 1. 2. M.J.S .Smith, - Application - Specific Integrated Circuits Pearson Education, 2003. Jose E.France, Yannis Tsividis, Design of Analog-Digital VLSI Circuits for Telecommunication and signal processing, Prentice Hall, 1994. 3. 4. Malcolm R.Haskard; Lan. C. May, Analog VLSI Design - NMOS and CMOS, Prentice Hall, 1998. Mohammed Ismail and Terri Fiez, Analog VLSI Signal and Information Processing, McGraw Hill, 1994.
MULTIMEDIA COMMUNICATION Subject Code No. of Lecture Hours/Week Total No. of Lecture Hours : 10EC052 : 04 : 52 IA Marks Exam Marks Exam Hours : 50 : 03 : 100
Multimedia Communications: multimedia information representation, multimedia networks, multimedia applications, network QoS and application QoS. Information Representation: text, images, audio and video, Text and image compression, compression principles, text compression, image compression. Audio and video compression, audio compression, video compression, video compression principles, video compression standards: H.261, H.263, P1.323, MPEG 1, MPEG 2, Other coding formats for text, speech, image and video. Detailed Study of MPEG 4: coding of audiovisual objects, MPEG 4 systems, MPEG 4 audio and video, profiles and levels. MPEG 7 standardization process of multimedia content description, MPEG 21 multimedia framework, Significant features of JPEG 2000, MPEG 4 transport across the Internet. Synchronization: Notion of synchronization, presentation requirements, reference model for synchronization, Introduction to SMIL, Multimedia operating systems, Resource management, process management techniques. Multimedia Communication Across Networks: Layered video coding, error resilient video coding techniques, multimedia transport across IP networks and relevant protocols such as RSVP, RTP, RTCP, DVMRP, multimedia in mobile networks, multimedia in broadcast networks. Assignments / Practicals can be given on writing the programs to encode and decode the various kinds of data by using the algorithms. Students can collect several papers from journals/conferences/Internet on a specific area of multimedia communications and write a review paper and make a presentation. Reference Books: 1. 2. 3. 4. Fred Halsall, Multimedia Communications, Pearson education, 2001 K. R. Rao, Zoran S. Bojkovic, Dragorad A. Milovanovic, Multimedia Communication Systems, Pearson education, 2004 Raif steinmetz, Klara Nahrstedt, Multimedia: Computing, Communications and Applications, Pearson education, 2002 John Billamil, Louis Molina, Multimedia : An Introduction, PHI, 2002
RF AND MICROWAVE CIRCUIT DESIGN Subject Code No. of Lecture Hours /week Total no. of Lecture Hours : 10EC071 : 04 : 70 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 50 : 03 : 100
Wave Propagation in Networks: Introduction to RF/Microwave Concepts and applications; RF Electronics Concepts; Fundamental Concepts in Wave Propagation; Circuit Representations of two port RF/MW networks Passive Circuit Design: The Smith Chart, Application of the Smith Chart in Distributed and lumped element circuit applications, Design of Matching networks. Basic Considerations in Active Networks: Stability Consideration in Active networks, Gain Considerations in Amplifiers, Noise Considerations in Active Networks. Active Networks: Linear and Nonlinear Design: RF/MW Amplifiers Small Signal Design, Large Signal Design, RF/MW Oscillator Design, RF/MW Frequency Conversion Rectifier and Detector Design, Mixer Design, RF/MW Control Circuit Design, RF/MW Integrated circuit design.
Reference Books: 1. Matthew M. Radmanesh, Radio Frequency and Microwave Electronics Illustrated, Pearson Education (Asia) Pte. Ltd., 2004. 2. Reinhold Ludwig and Pavel Bretchko, RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications, Pearson Education (Asia) Pte. Ltd., 2004.
ELECTIVE IV Advanced Embedded Systems Subject Code No. of Lecture Hours /week Total no. of Lecture Hours : 10EC118 : 04 : 70 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 50 : 03 : 100
Typical Embedded System : Core of the Embedded System, Memory, Sensors and Actuators, Communication Interface, Embedded Firmware, Other System Components Characteristics and Quality Attributes of Embedded Systems : Hardware Software Co-Design and Program Modelling : Fundamental Issues in Hardware Software CoDesign, Computational Models in Embedded Design, Introduction to Unified Modelling Language, Hardware Software Trade-offs Embedded Firmware Design and Development : Embedded Firmware Design Approaches, Embedded Firmware Development Languages. Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) based Embedded System Design : Operating System Basics, Types of OS, Tasks, Process and Threads, Multiprocessing and Multitasking, Task Scheduling, Threads, Processes and Scheduling: Putting them altogether, Task Communication, Task Synchronization, Device Drivers, How to Choose an RTOS The Embedded System Development Environment: The Integrated Development Environment (IDE), Types of Files Generated on Cross-compilation, Disassembler/Decompiler, Simulators, Emulators and Debugging, Target Hardware Debugging, Boundary Scan Trends in the Embedded Industry : Processor Trends in Embedded System, Embedded OS Trends, Development Language Trends, Open Standards, Frameworks and Alliances, Bottlenecks Reference Books:: 1. Shibu K V, Introduction to Embedded Systems, Tata McGraw Hill Education Private Limited, 2009 2. James K Peckol, Embedded Systems A contemporary Design Tool, John Wiely, 2008 Broadband wireless networks Subject Code No. of Lecture Hours /week Total no. of Lecture Hours : 10EC119 : 04 : 70 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 50 : 03 : 100
Wimax genesis and framework: 802.16 std., wimax forum, other 802.16 stds. Protocol layer topologies: layers of wimax, CS, MAC CPS, security layer, phy layer, reference model, topology. Frquency utilization and system profiles: cellualar concept, licensed and unlicensed frequencies, fixed wimax system profiles, mobile wimax profiles. Wimax physical layer: OFDM transmission, SOFDMA, subcarrier permutation, 802.16 transmission chains, channel coding, turbo coding, burst profile. Wimax MAC and QOS: CS layer, MAC function and frames, multiple access and burst profile, uplink bandwidth allocation and request mechanisms, network entry and QoS magmt.
Radio engg considerations, radio resource management, advance antenna technology in wimax, MBS. Wimax architecture, mobility handover and power save modes. Security. Reference Books: 1. Loutfi Nuyami, WIMAX: technology for broadband access, John Wiley, 2007 2. Yan Zhang, Hsia Hwa Chen, Mobile WIMAX, Aurobech publications, 2008. RF MEMS Subject Code No. of Lecture Hours /week Total no. of Lecture Hours : 10EC127 : 04 : 52 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 50 : 03 : 100
Review Introduction to MEMS. Fabrication for MEMS, MEMS transducers and Actuators . Microsensing for MEMS, Materials for MEMS. MEMS materials and fabrication techniques Metals, Semiconductors, thin films, Materials for Polymer MEMS, Bulk Machining for silicon based MEMS, Surface machining for Silicon based MEMS, Micro Stereo Lithography for Polymer MEMS. RF MEMS Switches and micro relays. Switch Parameters, Basics of Switching, Switches for RF and microwave Applications , Actuation mechanisms, micro relays and micro actuators, Dynamics of Switch operation, MEMS Switch Design and design considerations. MEMS Inductors and capacitors. Micromachined RF Filters and Phase shifters. RF Filters, Modeling of Mechanical Filters, Micromachanical Filters, SAW filters Basics, Design considerations. Bulk Acoustic Wave Filters, Micromachined Filters for Millimeter Wave frequencies. Micromacbined Phase Shifters, Types and Limitations, MEMS and Ferroelectric Phase shifters, Applications. Micromachined transmission lines and components. Micromachined Transmission Lines Losses in Transmission lines, coplanar lines, Meicroshield and membrane supported lines, Microshield components, Micromachined waveguides, directional couplers and mixers, Resonators and Filters.. Micomachined antennas. Design, Fabrication and Measurements. Integration and Packaging for RF MEMS. Roles and types of Packages, Flip Chip Techniques, Multichip module packaging and Wafer bonding, Reliability issues and Thermal issues. Reference Books : 1 2. 3. RF MEMS V K Varadan, A Laktakia and K J Vinoy, John Wiley, 2003 Reprint RF MEMS Circuit Design J De Los Santos, Artech House, 2002 Transaction Level Modeling with SystemC: TLM Concepts and Applications for Embedded Systems, by Frank Ghenassia, Springer, 2005 Networks on Chips: Technology and Tools, by Luca Benini and Giovanni De Micheli , Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2006.
You might also like
- +DSP Based Proportional Integral Sliding Mode Controller ForDocument8 pages+DSP Based Proportional Integral Sliding Mode Controller FormabhatNo ratings yet
- B.E Electronics & Communication Engineering / Telecommunication Engineering (Common To Electronics & Communication and Telecommunication Engineering)Document3 pagesB.E Electronics & Communication Engineering / Telecommunication Engineering (Common To Electronics & Communication and Telecommunication Engineering)mabhatNo ratings yet
- +design and Implementation of A Low CostDocument9 pages+design and Implementation of A Low CostmabhatNo ratings yet
- June July 2017 PDFDocument2 pagesJune July 2017 PDFmabhatNo ratings yet
- Linear LCS: ApplicationsDocument2 pagesLinear LCS: ApplicationsmabhatNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Teaching and Examination B.E.: Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument4 pagesScheme of Teaching and Examination B.E.: Electronics & Communication EngineeringmabhatNo ratings yet
- B.E.: Electronics & Communication Engineering: (Not For E&C Students)Document5 pagesB.E.: Electronics & Communication Engineering: (Not For E&C Students)mabhatNo ratings yet
- Dec 2013 Jan 2014Document1 pageDec 2013 Jan 2014mabhatNo ratings yet
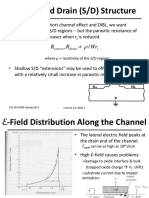
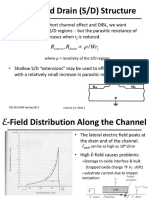
- Source and Drain (S/D) Structure: WR R RDocument7 pagesSource and Drain (S/D) Structure: WR R RmabhatNo ratings yet
- New NotesDocument7 pagesNew NotesmabhatNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Teaching and Examination B.E.: Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument8 pagesScheme of Teaching and Examination B.E.: Electronics & Communication EngineeringmabhatNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Teaching and Examination B.E.: Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument8 pagesScheme of Teaching and Examination B.E.: Electronics & Communication EngineeringmabhatNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- BluetoothDocument39 pagesBluetoothਗੁਰਪਰੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਸੂਰਾਪੁਰੀNo ratings yet
- Atr4518r3 PDFDocument2 pagesAtr4518r3 PDFanon_556921642No ratings yet
- Exam #2 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #1Document4 pagesExam #2 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #1svahidsNo ratings yet
- Gps Tracker VT 310 BB ManualDocument21 pagesGps Tracker VT 310 BB ManualMarcos AragaoNo ratings yet
- Arctic GPRS and EDGE RouterDocument2 pagesArctic GPRS and EDGE RouterrazvansasuNo ratings yet
- Practical Wireless - February 2018Document76 pagesPractical Wireless - February 2018JokoliNo ratings yet
- Common Conversion Tables and EquationsDocument1 pageCommon Conversion Tables and Equationsshilpa_rehalNo ratings yet
- Data Security & Encryption: Navneet Kapoor HCL Infosystems LTDDocument30 pagesData Security & Encryption: Navneet Kapoor HCL Infosystems LTDKarthikeyan RamajayamNo ratings yet
- Unit of Competency Learning Outcome Methodology Assessment ApproachDocument1 pageUnit of Competency Learning Outcome Methodology Assessment ApproachEmer ArcitaNo ratings yet
- 1 MBX4 - User - Guide - 8750188000 - RevA1 PDFDocument94 pages1 MBX4 - User - Guide - 8750188000 - RevA1 PDFAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- MQTT Vs Opc Ua,: When To Use ThemDocument8 pagesMQTT Vs Opc Ua,: When To Use ThemTomas GVNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering and ApplicationsDocument2 pagesMicrowave Engineering and Applicationsarkin dwiansyah100% (1)
- Frequency Shift CodeDocument7 pagesFrequency Shift CodeKranthi VenkatNo ratings yet
- Obstacles To Internet Growth in NigeriaDocument6 pagesObstacles To Internet Growth in Nigeriaumar daddaNo ratings yet
- FTM-400XDR de Om Eng Eh034m210 PDFDocument219 pagesFTM-400XDR de Om Eng Eh034m210 PDFcraigerrington8911No ratings yet
- David - sm15 - Case - Im - 14 NetgearDocument17 pagesDavid - sm15 - Case - Im - 14 NetgearBayarmaa TsolmonNo ratings yet
- BUS317D - StarHub SAVED PresentationDocument21 pagesBUS317D - StarHub SAVED PresentationChattyduckyNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1EveNo ratings yet
- ROUTE 642-902 Training Policy Based Routing Sim PDFDocument24 pagesROUTE 642-902 Training Policy Based Routing Sim PDFmailbanwariNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument22 pagesDocumentJohn Loayza100% (1)
- AMEEncoding Error LogDocument2 pagesAMEEncoding Error LogGómez Dávila Diego AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Https - Maxtrain - Com - Product - F5-Networks-Setting-Up-Big-Ip-Advanced-Waf-V14-Web-Application-Firewall-Formerly-Asm - Export - PDF TrueDocument4 pagesHttps - Maxtrain - Com - Product - F5-Networks-Setting-Up-Big-Ip-Advanced-Waf-V14-Web-Application-Firewall-Formerly-Asm - Export - PDF TrueDDDDNo ratings yet
- Coiler Repeater Portfolio - Band SelectiveDocument2 pagesCoiler Repeater Portfolio - Band SelectiveShaunVermaakNo ratings yet
- Muhammad 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1577 012029Document10 pagesMuhammad 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1577 012029sabhan 119400066No ratings yet
- Harmonic Cable Spectrum MibDocument4 pagesHarmonic Cable Spectrum MibJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- TES-T-111.08-R0 ACC & FDM Circuit PerfromanceDocument14 pagesTES-T-111.08-R0 ACC & FDM Circuit PerfromanceNauman Habib KhanNo ratings yet
- GH CP343-1-EX30 76 en-USDocument76 pagesGH CP343-1-EX30 76 en-USMancamiaicuruNo ratings yet
- Brochure SRT 4672 - enDocument2 pagesBrochure SRT 4672 - enbejanNo ratings yet
- QUALcomm 5G IntroDocument10 pagesQUALcomm 5G Intromehran_4xNo ratings yet
- Understanding Technology Options For Deploying Wi-Fi White PaperDocument43 pagesUnderstanding Technology Options For Deploying Wi-Fi White Paperophyx007No ratings yet