Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Current Strategies
Uploaded by
Ivon ChongOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Current Strategies
Uploaded by
Ivon ChongCopyright:
Available Formats
Apples Current Expansion Strategy Apple is highly innovated company, providing high quality products and services including
the personal computer industry (MacBook Air, MacBook Pro), the consumer electronic industry (iPod, iPhone, iPad) and the software (iTune). The market for Apple is also very strong. For several years Apple's product strategy involved creating innovative products and services and also focused on global market development. With increase in technology, Apple has expanded into global markets, recording unprecedented levels of revenue and profit. In today's business environment, Apple has to stay ahead to be knowledgeable about changes in technology as well as continuing to find new ways to be competitive and meet customer demands. There are many different ways to access the global market through a number of different strategies. Apples utilization of multiple strategies simultaneously has allowed it to flourish despite the recovering global economy. Global Strategy Apple uses global strategies as their major strategies to expand into global market. 'Global Strategy' is a shortened term that covers three areas: global, multinational and international strategies. These three areas refer to those strategies designed to enable an organization to achieve its objective of international expansion. Apple focuses on global strategy, whereby their international activities are developed in an extent that they essentially treat the world as one market with very limited variations for each country or world region. For example, the iPhone 4S, iPod, MacBook that Apple exported are essentially the same products in every country. Besides, the Apple product was essentially following the same strategy everywhere in the world: in this case, the advertising billboard was in North America but it could have been anywhere. Apple utilizes several different strategies to expand its presence in global markets including foreign outsourcing and exporting. First strategy that Apple adopted is exporting (major mode of entry). The biggest breakthrough of Apple in exporting to the global market is the unveiling of the iPhone4. It was released in 88 countries (Kane and Rohwedder 2010). The shift shows how important overseas sales have become for Apple,
which struggled before the iPhone to become a global player. Chief Operating Officer Tim Cook said in the quarterly earnings call that iPhone sales were seeing strong tripledigit growth in Europe and Asia. Apple called it "the fastest international roll out" for iPhone (Kane and Rohwedder 2010). Tim Bajarin, an analyst at researcher Creative Strategies, estimates that about 55% of iPhone sales are now made outside of the U.S., from about 25% two years ago. The major foreign operations of Apple are conducted in the Americas, Europe, Japan, and Asia Pacific.
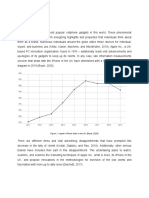
Figure 1: iPhone revenue growth in December 2009 compare with March 2010
Figure 2: The major foreign operations of Apple are conducted in the Americas, Europe, Japan, and Asia Pacific. Another global strategies that implemented by Apple is foreign outsourcing. This means contracting with foreign suppliers to produce products, usually at a fraction of the cost of domestic production. Apple Inc. depends on firms in China and Taiwan to produce the iPod, iPhone, iMac, MacBook Pros and most of the products that they offer.
The key reasons why Apple using exporting and foreign outsourcing as global strategies: 1. Emergence of new markets By expanding operations to an international scale, Apple can increase their total sales from essentially the same products. Besides, Apple gained global brand
recognition (the benefit that derives from having a brand that is recognized throughout the world) and global customer satisfaction (multinational customers who demand the same product, service and quality at various locations around the world).
2. Diversification Diversification enable Apple to avoids volatile swings in market prices and sales in any one market, allowing other markets to support these occurrences. For examples, on March 11, 2011, Japan experienced a severe earthquake followed by a tsunami. These geological events have caused significant damage in the region. The production and the sales of Apple have been affected; however, Apple global strategies allow them to diversify the losses in Japan because of the backup from the sales in other countries.
3. Gaining Economies of Scale The most significant benefit that Apple gained is the economics of scales. Apple endures cost savings by increasing the scale or size of its operations and size of the market. The may directly contribute to the price per unit of output falls, allowing for a reduction in price or an increase in profits. Besides, through international expansion, Apple obtains a better economy of scale by selling worldwide or establishing production opportunities in low cost labor localities. For examples, foreign outsourcing and importing provide production at cheaper costs which makes products such as the iPad sell for $499 instead of $14,970 (Gewirtz 2010).
You might also like
- Marketing CIA 1Document6 pagesMarketing CIA 1abhishek kushwahaNo ratings yet
- What Would Apple Do?: How You Can Learn from Apple and Make MoneyFrom EverandWhat Would Apple Do?: How You Can Learn from Apple and Make MoneyNo ratings yet
- Apple DistributionDocument7 pagesApple DistributionDanniel Ding60% (5)
- Apple Inc 2012Document5 pagesApple Inc 2012Gulfam Ansari100% (2)
- Apple Innovative StrategyDocument7 pagesApple Innovative StrategyTonya Merrigan100% (1)
- AssignmentDocument9 pagesAssignmentridwanurrahman72No ratings yet
- Report On AppleDocument12 pagesReport On Applemiss HalaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Management Cases and Assigments (1) v.2Document22 pagesContemporary Management Cases and Assigments (1) v.2osama sallamNo ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis of Apple Inc.Document37 pagesStrategic Analysis of Apple Inc.juststitch87% (30)
- JURNALDocument6 pagesJURNALrahmat razeeqNo ratings yet
- Functional Strategy of Apple CompanyDocument5 pagesFunctional Strategy of Apple CompanyAngeline Sahagun67% (3)
- Birmingham City Business School Postgraduate Degrees: April 2014Document23 pagesBirmingham City Business School Postgraduate Degrees: April 2014Faizan ShowkatNo ratings yet
- Birmingham City Business School Postgraduate Degrees: April 2014Document23 pagesBirmingham City Business School Postgraduate Degrees: April 2014Faizan ShowkatNo ratings yet
- I. Iphone Production Network: SourcingDocument9 pagesI. Iphone Production Network: SourcingPhanHiềnLươngNo ratings yet
- Case IphoneDocument9 pagesCase IphonePhanHiềnLươngNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy and Plan For New Product LaunchesDocument15 pagesMarketing Strategy and Plan For New Product LaunchesachwalotienoNo ratings yet
- Employee WelfareDocument13 pagesEmployee WelfareIshita GuptaNo ratings yet
- Apple in ThailandDocument58 pagesApple in ThailandYi Ren100% (2)
- Contemporary Management Cases and Assigments (1) v.2Document22 pagesContemporary Management Cases and Assigments (1) v.2osama sallamNo ratings yet
- Discussion Module 2 IBTDocument5 pagesDiscussion Module 2 IBTJessie FranzNo ratings yet
- Apple Computer, INC: Marketing Management (BUSS 0001)Document10 pagesApple Computer, INC: Marketing Management (BUSS 0001)ZumuruDa Al HashliNo ratings yet
- Apple's Marketing AnalysisDocument14 pagesApple's Marketing AnalysisHuy Nguyen Tran NhatNo ratings yet
- AppleDocument5 pagesAppleAarit shahNo ratings yet
- Business Economics: Topic - Monopolistic Competition Apple IncDocument16 pagesBusiness Economics: Topic - Monopolistic Competition Apple Incsanika patilNo ratings yet
- Functional Strategy of Apple CompanyDocument6 pagesFunctional Strategy of Apple CompanyNahom G KassayeNo ratings yet
- Basic Information of AppleDocument7 pagesBasic Information of AppleTang LinhNo ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis of Apple IncDocument19 pagesStrategic Analysis of Apple IncAhmet Babayev100% (1)
- Chapter 3-Analysis of Organizational EnvironmentDocument7 pagesChapter 3-Analysis of Organizational EnvironmentTạ Xuân TrườngNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument9 pagesProjectnatalia starostaNo ratings yet
- Company Analysis-APPLE Inc. SampleDocument7 pagesCompany Analysis-APPLE Inc. SampleFely BinanNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy of Apple Inc - Apple Marketing StrategyDocument17 pagesMarketing Strategy of Apple Inc - Apple Marketing StrategyvdevevNo ratings yet
- Cellphone PresentationDocument12 pagesCellphone PresentationBakir AlikalficNo ratings yet
- Ch3-Apple Biz Environment - NewDocument6 pagesCh3-Apple Biz Environment - Newánh TrầnNo ratings yet
- How To Write A ProposalDocument8 pagesHow To Write A Proposalraydookie0% (1)
- Product Report G.L.S AnuradhaDocument9 pagesProduct Report G.L.S AnuradhaShehan AnuradaNo ratings yet
- Apple Iphone Marketing PlanDocument22 pagesApple Iphone Marketing PlanSameer KodeNo ratings yet
- Apple Case Write-Up FinalDocument13 pagesApple Case Write-Up FinalNgọc Anh VõNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - SM AssignmentDocument33 pagesGroup 4 - SM AssignmentFAOZIA QURAISHI MBA 2021-23 (Delhi)No ratings yet
- Apple CompanyDocument4 pagesApple CompanyPrezidentasiyaNo ratings yet
- Apple: Whats Next?Document18 pagesApple: Whats Next?Yacki LuengoNo ratings yet
- The Market Strategies of Apple in China: Bingyan LuDocument4 pagesThe Market Strategies of Apple in China: Bingyan LuDanh VôNo ratings yet
- UFA 1005 Case StudyDocument5 pagesUFA 1005 Case StudyCamie Li MinNo ratings yet
- Individual AssigmentDocument29 pagesIndividual AssigmentNguyen Ngoc Minh Chau (K15 HL)No ratings yet
- Apple Marketing Mix: Check CommentsDocument10 pagesApple Marketing Mix: Check CommentschrisNo ratings yet
- APPLE Inc Case Study 2011Document18 pagesAPPLE Inc Case Study 2011Emmanuel RoyoNo ratings yet
- Apple Case Study OKDocument16 pagesApple Case Study OKHadvianti Fuyoh100% (1)
- 2020:3 Summer, BUAD6800 (MERGED) Info Technology and E-Business Assignment ReportDocument5 pages2020:3 Summer, BUAD6800 (MERGED) Info Technology and E-Business Assignment ReportAnitra ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Plan and PresentationDocument19 pagesStrategic Plan and PresentationTierney KennedyNo ratings yet
- Apple Marketing ProjectDocument26 pagesApple Marketing ProjectVidhya Malwade67% (6)
- Advice To Tim CookDocument5 pagesAdvice To Tim CookJaydeep SarnaikNo ratings yet
- Group Project Report Pbs3233Document10 pagesGroup Project Report Pbs3233SITI NURAISYAH BINTI SHAHABUDDIN (BG)No ratings yet
- Apple's Innovation StrategyDocument6 pagesApple's Innovation Strategydbear100% (1)
- SWot Analysis of AppleDocument13 pagesSWot Analysis of AppleJunaid ShahNo ratings yet
- Apple Marketing ProjectDocument25 pagesApple Marketing ProjectSomendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On Apple IncDocument4 pagesTerm Paper On Apple Incaflsimgfs100% (1)
- Innovation and Technology ManagementDocument13 pagesInnovation and Technology ManagementAravinth PalpandianNo ratings yet
- Apple Inc. in 2015: Marketing Management-IDocument4 pagesApple Inc. in 2015: Marketing Management-ISaketNo ratings yet
- Business Plan AppleDocument10 pagesBusiness Plan Applelaviza khan niaziNo ratings yet
- Godiva South Korea PDFDocument65 pagesGodiva South Korea PDFBuğra BakanNo ratings yet
- SYNOPSIS Make in IndiaDocument7 pagesSYNOPSIS Make in IndiaMathew George KNo ratings yet
- Quiz Ibm 530 (Ans 13-18) ZammilDocument5 pagesQuiz Ibm 530 (Ans 13-18) Zammilahmad zammilNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 - IM Environment (Political and Economic Environment)Document13 pagesChap 2 - IM Environment (Political and Economic Environment)Lê Đỗ Tuấn MinhNo ratings yet
- Case 8Document5 pagesCase 8Zayn LachowskiNo ratings yet
- Solutions ME Chapter 1Document7 pagesSolutions ME Chapter 1Puji Hikmah100% (3)
- International Procurement & Contracting: Ernest G. Gabbard, J.D., C.P.M., CPCM Allegheny Technologies, IncDocument16 pagesInternational Procurement & Contracting: Ernest G. Gabbard, J.D., C.P.M., CPCM Allegheny Technologies, IncukalNo ratings yet
- Licensing FAQsDocument14 pagesLicensing FAQsArthur RimbaudNo ratings yet
- Netherlands Trust Fund III Kenya - IT&ITeS Project PlanDocument60 pagesNetherlands Trust Fund III Kenya - IT&ITeS Project PlanICT AUTHORITY100% (1)
- Introduction of International BusinessDocument42 pagesIntroduction of International Businesstrustme77100% (1)
- Case 2 I.TDocument3 pagesCase 2 I.TsiddhantNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument59 pagesNatural ResourcesSohel BangiNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Globalization IBDocument18 pagesCh. 1 Globalization IBnikowawaNo ratings yet
- Import and ExportDocument20 pagesImport and ExportAnuska ThapaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lecture NotesDocument64 pagesWeek 1 Lecture NotesPilgrim OmbulNo ratings yet
- Structural Change and Economic Dynamics: Fabricio Missio, Ricardo Azevedo Araujo, Frederico G. Jayme JRDocument9 pagesStructural Change and Economic Dynamics: Fabricio Missio, Ricardo Azevedo Araujo, Frederico G. Jayme JRikhsan syahabNo ratings yet
- TC4066BF TC4066BP en Datasheet 071001Document11 pagesTC4066BF TC4066BP en Datasheet 071001Juan_Manuel_Ut_2909No ratings yet
- 2023 Facts Figures Global AfricaDocument120 pages2023 Facts Figures Global Africabedada legesseNo ratings yet
- Profile of Indian Foundry IndustryDocument7 pagesProfile of Indian Foundry IndustryaminunishaNo ratings yet
- Pan Y, Tse D, 2000, The Hierarchical Model of Market Entry ModesDocument21 pagesPan Y, Tse D, 2000, The Hierarchical Model of Market Entry ModesGian Carlos Tarifeño SanchezNo ratings yet
- CPSD Rwanda PDFDocument127 pagesCPSD Rwanda PDFNgendahayo EricNo ratings yet
- Buffalo Meat Report PDFDocument18 pagesBuffalo Meat Report PDFKarthic C MNo ratings yet
- Ib Econ Unit 3 PyszczekDocument113 pagesIb Econ Unit 3 Pyszczekapi-196719233No ratings yet
- Commercial Bank of Ethiopia: Business Development DivisionDocument43 pagesCommercial Bank of Ethiopia: Business Development DivisionZenebe ZelelewNo ratings yet
- IM 2 - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument33 pagesIM 2 - Multiple Choice QuestionsHeirvy Nicolas100% (1)
- Creation, Adoption, and Transfer of New TechnologyDocument42 pagesCreation, Adoption, and Transfer of New TechnologySUBHASHRATHORENo ratings yet
- Assignment Plastic ProductsDocument10 pagesAssignment Plastic Productsneel_nknNo ratings yet
- Opplanet Ear Export Form v1.7Document1 pageOpplanet Ear Export Form v1.7Raul SosaNo ratings yet
- ECON 461 Final ExamDocument18 pagesECON 461 Final Examttran198450% (2)
- Prebisch Singer Thesis TradeDocument5 pagesPrebisch Singer Thesis Tradespqeyiikd100% (2)
- The Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerFrom EverandThe Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (121)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeFrom EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (69)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0From EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Sales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinFrom EverandSales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsFrom EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (48)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffFrom EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (61)
- The Ruler's Guide: China's Greatest Emperor and His Timeless Secrets of SuccessFrom EverandThe Ruler's Guide: China's Greatest Emperor and His Timeless Secrets of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffFrom EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Strategic Analytics: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandStrategic Analytics: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- Systems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessFrom EverandSystems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (80)
- Elevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingFrom EverandElevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Strategy Skills: Techniques to Sharpen the Mind of the StrategistFrom EverandStrategy Skills: Techniques to Sharpen the Mind of the StrategistRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Play Bigger: How Pirates, Dreamers, and Innovators Create and Dominate MarketsFrom EverandPlay Bigger: How Pirates, Dreamers, and Innovators Create and Dominate MarketsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (73)
- Blue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantFrom EverandBlue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (387)
- Impact Networks: Create Connection, Spark Collaboration, and Catalyze Systemic ChangeFrom EverandImpact Networks: Create Connection, Spark Collaboration, and Catalyze Systemic ChangeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (104)
- HBR Guide to Building Your Business Case (HBR Guide Series)From EverandHBR Guide to Building Your Business Case (HBR Guide Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdFrom EverandLean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- 2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesFrom Everand2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Learn and Understand Business AnalysisFrom EverandLearn and Understand Business AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (31)
- Harvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsFrom EverandHarvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Summary of Richard Rumelt's Good Strategy Bad StrategyFrom EverandSummary of Richard Rumelt's Good Strategy Bad StrategyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Managing Yourself, Vol. 2From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Managing Yourself, Vol. 2Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Why Digital Transformations Fail: The Surprising Disciplines of How to Take Off and Stay AheadFrom EverandWhy Digital Transformations Fail: The Surprising Disciplines of How to Take Off and Stay AheadRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Create the Future: Tactics for Disruptive ThinkingFrom EverandCreate the Future: Tactics for Disruptive ThinkingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)