Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Optical Comm-EC734-OC - Vinay Jha Pillai
Uploaded by
Anith M ThomasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Optical Comm-EC734-OC - Vinay Jha Pillai
Uploaded by
Anith M ThomasCopyright:
Available Formats
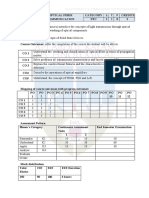
CHRIST UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING I SEMESTER-MTECH 2012-2013 COURSE HANDOUT Date: 25/06/2012 In addition to prescribed syllabus for all
courses appended to the timetable this portion gives further specific details regarding the course. Course No : EC 734 Course Title : OPTICAL COMMUNICATION Faculty : Vinay Jha Pillai Email : vinay.pillai@christuniversity.in 1. Course Description:
This course introduces the various optical fiber modes, configurations and various signal degradation factors associated with optical fiber. It also deals with the study about various optical sources and optical detectors and their use in the optical communication system. Finally it discusses about digital transmission and its associated parameters on system performance.
2. Scope and Objective:
To learn the basic elements of optical fiber transmission link, fiber modes configurations and structures. To understand the different kind of losses, signal distortion in optical wave guides and other signal degradation factors. Design optimization of SM fibers, RI profile and cutoff wave length.
To learn the various optical source materials, LED structures, quantum efficiency, Laser diodes and different fiber amplifiers. To learn the fiber optical receivers such as PIN APD diodes, noise performance in photo detector, receiver operation and configuration. To learn fiber slicing and connectors, noise effects on system performance, operational principles WDM and solutions.
3. Text Book:
T1. Gerd Keiser, Optical Fiber Communication McGraw Hill International, Singapore, 3rd ed., 2000
4. Reference Books:
R1. J.Senior, Optical Communication, Principles and Practice, Prentice Hall of India, 1994. R2. J.Gower, Optical Communication System, Prentice Hall of India, 2001.
5. Course Plan: Lecture No. Learning Objectives 1 Overview of the course 2 3 4 5,6&7 Fiber Evolutions Topics to be covered UNIT 1 Introduction to Optical Communication Evolution of Fiber optic system & Elements of an optical Transmission link Ray Optics Reference ------T1: 1.2 &1.3 T1 : 2.2 T1: 2.3 T1: 2.4 (2.4.1, 2.4.2 & 2.4.8) T1: 2.5 T1: 2.6
8 9
10,11 12,13 14,15 16 17,18
Fundamentals of Light and its propagation Fundamentals of Light Optical Fiber Modes & Configuration and its propagation Fundamentals of Light Mode theory of Circular Wave guides and its propagation (Overview of Modes-Key Modal concepts, Linearly Polarized Modes) Propagation in SM Single Mode Fibers Propagation in GI- fiber Graded Index fiber structure. UNIT 2 Signal Degradation in Optical Fiber Signal losses in Fiber Attenuations in fibers Signal losses in Fiber Signal losses in Fiber Signal losses in Fiber Signal Distortion in Optical Wave guides Pulse Broadening in GI fibers Mode Coupling Design Optimization of SM fibers-RI profile and cut-off wavelength UNIT 3 Fiber Optical Sources & Coupling
T1: 3.1 (3.1.1,3.1.2, 3.1.3, 3.1.4, & 3.1.5) T1: 3.2 (3.2.1 to 3.2.7) T1: 3.3 T1: 3.4 T1 : 3.5 (3.5.1 & 3.5.2)
19,20
Fundamentals of Light Direct & Indirect band Gap materials, sources Light-Emitting Diode- source
T1:4.1.4, 4.2 (4.2.1 to 4.2.4)
21,22,23
24 25 26 27
28,29 30 31 32 33 34,35 36
37,38,39 40,41 42 43 44,45
materials, Quantum efficiency & LED power, Modulation of a LED Fundamentals of Light LASER Diodes- modes & threshold sources condition, rate equation, external quantum efficiency, resonant frequencies, temperature effects,intro to quantum laser, Fiber amplifiers. Fundamentals of coupling Power launching and coupling Fundamentals of coupling Lensing Schemes Fundamentals of coupling Fiber to- Fiber joints Fundamentals of coupling Fiber splicing UNIT 4 Fiber Optical Receivers Fundamentals of Light PIN diode & APD Detectors SNR Photo-detector Noise- source &SNR Response time Detector Response Time Study of Avalanche Noise Avalanche Multiplication Noise Comparison between PIN Comparison of Photo detectors &APD Parameters of Receiver Fundamental Receiver Operationpreamplifiers, error sources, receiver configuration Parameters of Receiver Probability of Error & The Quantum Limit UNIT 5 Digital Transmission System Power Budgeting Point to Point Links- System considerations, Link Power Budget, Rise Time Budget System Performance to Noise effects on system performance various noises WDM Principle Operations Principles of WDM Light Amplifier Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier Fundamentals Networking Standards for Basics on concept of SONET/SDM Optical Communication Network
T1: 4.3.1 to 4.3.4 & 4.3.8
T1 : 5.1 T1: 5.2 T1: 5.3 T1: 5.5
T1: 6.1 T1: 6.2 T1: 6.3 T1: 6.4 T1: 6.7 T1: 7.1 (7.1.1 to 7.1.3) T1: 7.2
T1: 8.1 (8.1.1, 8.1.2 & 8.1.3 ) T1: 8.4 T1: 10.1 T1: 11.3 T1: 12.2
NB: Among the five hours of lectures in a week, one hour will be considered exclusively as a tutorial hour. The above-mentioned lecture hours are without taking into consideration the tutorial hours. Along with the above 45 lectures you would also be having 15 hours of tutorial sections, which would make it to a total of 60 hours. 6. Home assignments will be announced in the class.
7. Evaluation Scheme:
EC No. 1 2
Evaluation Module Component CIA I MSE CIA II Test I (Descriptive)
3 4
CIA III Semester Exam
Duration Date, Time & (minutes) Venue 120 Aug 2012 90 minutes Tentatively on 18-July 2012 and 19-SeptTest II (Objective- 60 minutes 2012 Quiz) respectively Assignments & Mini--Randomly projects allotted to the students ESE 180 Oct 2012
Nature of Component Closed Book Closed Book
Open Book/Source Closed Book
8. Chamber Consultation Hours: To be announced in the class. 9. Make-up Policy: Make Up for any component will be given only in genuine cases. In all cases prior intimation must be given to faculty concerned. In case of any kind of illness a Doctors certificate is mandatory. 10. Notices: Notices regarding the course will be displayed on the general notice board of Block II & the course web page.
Instructor - In charge Vinay Jha Pillai EC734
You might also like
- University of Mumbai: M. E. (Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering)Document51 pagesUniversity of Mumbai: M. E. (Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering)Rahul EkhandeNo ratings yet
- Bece308l Optical-Fiber-Communications TH 1.0 0 Bece308lDocument3 pagesBece308l Optical-Fiber-Communications TH 1.0 0 Bece308lyv5pgh7z84No ratings yet
- EC405 Optical Communication (CareerYuga)Document2 pagesEC405 Optical Communication (CareerYuga)Asha JohnNo ratings yet
- EC405 Optical CommunicationDocument2 pagesEC405 Optical CommunicationabhishekviNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics and NetworksDocument2 pagesFiber Optics and NetworksdakotarajaNo ratings yet
- 5 PDFDocument5 pages5 PDFjustsome teenagerNo ratings yet
- ECE1007 Syllabus Opto - March 2019Document3 pagesECE1007 Syllabus Opto - March 2019ASHUTOSH MOHAPATRA 18BLC1035No ratings yet
- EC SyllDocument4 pagesEC SyllDDIYNo ratings yet
- Lec2 ES475 2023 UploadDocument24 pagesLec2 ES475 2023 UploadEmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Ofc SyllabusDocument7 pagesOfc SyllabusARDHRA BNo ratings yet
- Optical CommunicationsDocument2 pagesOptical Communicationsalam065No ratings yet
- Dilla University College of Engineering and Technology School of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument2 pagesDilla University College of Engineering and Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineeringwendye13No ratings yet
- Updated-Optical Fibre m1 - AutosavedDocument176 pagesUpdated-Optical Fibre m1 - AutosavedMangala NageshwariNo ratings yet
- Optical FiberDocument105 pagesOptical FiberRaghu ReddyNo ratings yet
- Electronics Communication SCH and Syla Pages DeletedDocument6 pagesElectronics Communication SCH and Syla Pages DeletedAnanya AcharNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communications SyllabusDocument2 pagesOptical Fiber Communications SyllabusKrishna Prasad PheluNo ratings yet
- Nanoelectronics 18EC661 SyllabusDocument3 pagesNanoelectronics 18EC661 SyllabussmkeshkamatNo ratings yet
- 22BEE13Document4 pages22BEE13New GenieNo ratings yet
- Optical CommunicationDocument6 pagesOptical Communicationjigar16789No ratings yet
- BBEE103Document4 pagesBBEE103Kishor GowdaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Syllabus 1st SemesterDocument3 pagesElectronics Syllabus 1st SemesterLodhaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BME 313Document4 pagesSyllabus BME 313Mousum KabirNo ratings yet
- Ece 5870Document6 pagesEce 5870Kavuri Sai PradeepNo ratings yet
- RPT Instruction PlanDocument6 pagesRPT Instruction PlanIshantSood25No ratings yet
- B.E E&C Seventh Semester Syllabus Microwaves and AntennasDocument15 pagesB.E E&C Seventh Semester Syllabus Microwaves and AntennasKausthubha BkNo ratings yet
- EC 7th Sem SyllabusDocument16 pagesEC 7th Sem SyllabusNaga Vishnu KNo ratings yet
- VTU CBCS2015SCHEME Ecsyll8aemDocument14 pagesVTU CBCS2015SCHEME Ecsyll8aemsivarrrrrrrrrr0% (1)
- 2,4Document2 pages2,4anmolNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Communications With References New9docxDocument3 pagesFiber Optic Communications With References New9docxDurga Prasad TumulaNo ratings yet
- FibreDocument3 pagesFibreSHAKRAJIT SAHUNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusvamshiNo ratings yet
- Course PlanDocument3 pagesCourse Plansd_shahzaibNo ratings yet
- Ece1007 Opto-Electronics TH 1.1 47 Ece1007Document2 pagesEce1007 Opto-Electronics TH 1.1 47 Ece1007ritvikNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber CommunicationsDocument3 pagesOptical Fiber CommunicationsEmran KhanNo ratings yet
- UEI833 OPTICAL InstrumentationDocument2 pagesUEI833 OPTICAL InstrumentationLuv VermaniNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document4 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Premal PatelNo ratings yet
- 21 Phy 12Document4 pages21 Phy 12Sameer SNo ratings yet
- Updated OFC M3 PART3Document26 pagesUpdated OFC M3 PART3Mangala NageshwariNo ratings yet
- VII Sem Syllabus 2021-2022231121032932Document18 pagesVII Sem Syllabus 2021-2022231121032932Anand TiwariNo ratings yet
- BismillahDocument3 pagesBismillahobaiNo ratings yet
- Physics Digital NotesDocument83 pagesPhysics Digital NotesArun MozhiNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani Work Integrated Learning Programmes Digital LearningDocument5 pagesBirla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani Work Integrated Learning Programmes Digital Learningsudha mallikNo ratings yet
- University of Tripoli Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering DepartmentDocument2 pagesUniversity of Tripoli Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering DepartmentSara AliNo ratings yet
- NEW - UPDATED Course OutlineDocument9 pagesNEW - UPDATED Course Outlineabukimiftah18No ratings yet
- E1 Physics Sem2 SyllabusDocument12 pagesE1 Physics Sem2 SyllabusAkula DineshNo ratings yet
- Microwave Theory & AntennasDocument3 pagesMicrowave Theory & Antennasamitkumarkhg620No ratings yet
- Program Core: 22MM102453 Physics For ComputingDocument4 pagesProgram Core: 22MM102453 Physics For ComputingGirish KumarNo ratings yet
- Ocn Lesson Plan-FinalDocument4 pagesOcn Lesson Plan-FinalramkumarrajaNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic Engineering Program School of Engineering & Information Technology Universiti Malaysia SabahDocument4 pagesElectrical & Electronic Engineering Program School of Engineering & Information Technology Universiti Malaysia Sabahram010No ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Communication PDFDocument2 pagesFiber Optic Communication PDFluisperikoNo ratings yet
- Bme 311Document5 pagesBme 311salem aljohiNo ratings yet
- 1.meec-601 (Optoelectronics and Optical Fibre Communication)Document1 page1.meec-601 (Optoelectronics and Optical Fibre Communication)drogonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical EngineeringDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Engineeringmanyabhat2812No ratings yet
- BECE101L Basic-Electronics (Theory) NewDocument2 pagesBECE101L Basic-Electronics (Theory) NewNicky nirmalNo ratings yet
- Cio Ep501 Dis 2015Document3 pagesCio Ep501 Dis 2015api-118472949No ratings yet
- Course Outlines - MCT3234 - Analog ElectronicsDocument6 pagesCourse Outlines - MCT3234 - Analog ElectronicsMhdElHaqqNo ratings yet
- Seca 1701Document2 pagesSeca 1701Venkata naga Sai VarunNo ratings yet
- Reliability, Robustness and Failure Mechanisms of LED Devices: Methodology and EvaluationFrom EverandReliability, Robustness and Failure Mechanisms of LED Devices: Methodology and EvaluationNo ratings yet
- Reliability Investigation of LED Devices for Public Light ApplicationsFrom EverandReliability Investigation of LED Devices for Public Light ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- EpitaxyDocument19 pagesEpitaxyAnith M ThomasNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Lab ManualDocument50 pagesVlsi Lab ManualAnith M ThomasNo ratings yet
- Ec 731 Course Hand OutDocument3 pagesEc 731 Course Hand OutAnith M ThomasNo ratings yet
- Ec 731 Course Hand OutDocument3 pagesEc 731 Course Hand OutAnith M ThomasNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Introduction To Embedded Systems: Assignment1Document12 pagesUnit I - Introduction To Embedded Systems: Assignment1Anith M ThomasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Arrayed Waveguide Gratings, Application and DesignDocument18 pagesChapter 2 Arrayed Waveguide Gratings, Application and Designnobita3No ratings yet
- Allwave ZWP Fiber: (Zero Water Peak)Document2 pagesAllwave ZWP Fiber: (Zero Water Peak)Cyprian MetoboNo ratings yet
- DWDM Smartoptics MSeriesDocument8 pagesDWDM Smartoptics MSeriesdiego228111No ratings yet
- Introduction To Optical Communication SystemDocument180 pagesIntroduction To Optical Communication SystemRaja SekharNo ratings yet
- Driving Optical Network EvolutionDocument32 pagesDriving Optical Network Evolutionapi-19663123No ratings yet
- Advances in Optical AmplifiersDocument452 pagesAdvances in Optical AmplifiersMindaugas ArnašiusNo ratings yet
- Apn Apss AwgDocument24 pagesApn Apss AwgGiannis LazarouNo ratings yet
- Types of FiberDocument24 pagesTypes of FiberAmit SwarNo ratings yet
- Training Course WDM Principle V1.0-20080902Document92 pagesTraining Course WDM Principle V1.0-20080902ZannatoonNo ratings yet
- XDM SPEC A01 8 2 3 8 2 4 en PDFDocument242 pagesXDM SPEC A01 8 2 3 8 2 4 en PDFRaja SolaimalaiNo ratings yet
- Light Wave CommunicationDocument105 pagesLight Wave CommunicationVargheseMartinNo ratings yet
- Must Huawei OLP Be Used Together With The SFIU Board?Document25 pagesMust Huawei OLP Be Used Together With The SFIU Board?Thunder-Link.com0% (1)
- Hit 7300Document2 pagesHit 7300huiwcNo ratings yet
- Cisco ONS 15454 Product OverviewDocument54 pagesCisco ONS 15454 Product OverviewonderergunonderergunNo ratings yet
- Mbn100 1 GHZ Optical Node Data SheetDocument3 pagesMbn100 1 GHZ Optical Node Data SheetJimmy Diaz TorresNo ratings yet
- Optical Transport NetworkDocument26 pagesOptical Transport NetworknhlongdnNo ratings yet
- Mcs 8x16 Multicast Switch Module Data Sheet 540201Document3 pagesMcs 8x16 Multicast Switch Module Data Sheet 540201GLsun MallNo ratings yet
- ProfileDocument3 pagesProfileOmar AwaleNo ratings yet
- OTC119204 OptiX OSN 9800 Common Data Configuration ISSUE18.00Document37 pagesOTC119204 OptiX OSN 9800 Common Data Configuration ISSUE18.00Ernesto GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Scholar Cu Edu Eg PDFDocument24 pagesScholar Cu Edu Eg PDFFrancisco LeónNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibre Bragg Gratings For Acoustic Sensors: January 2010Document8 pagesOptical Fibre Bragg Gratings For Acoustic Sensors: January 2010HadiaFatimaNo ratings yet
- Optsim Application Notes and Examples: Synopsys, IncDocument458 pagesOptsim Application Notes and Examples: Synopsys, IncAdry Carrillo100% (1)
- Icon Library: Current As of March 7, 2002Document19 pagesIcon Library: Current As of March 7, 2002Henry MaestreNo ratings yet
- E1 and t1 SDH and PDH DWDM Cdma ClockingDocument44 pagesE1 and t1 SDH and PDH DWDM Cdma ClockingsajjadashrafNo ratings yet
- Presentation On PlasmonicsDocument20 pagesPresentation On Plasmonicspradeep0% (1)
- Digital Transmission FundamentalsDocument159 pagesDigital Transmission FundamentalsGil HaleNo ratings yet
- SDH Pocket Guide PDFDocument76 pagesSDH Pocket Guide PDFHorribilisUrsusNo ratings yet
- Documentation Guide: Optix Bws 1600G Backbone DWDM Optical Transmission System V100R007Document37 pagesDocumentation Guide: Optix Bws 1600G Backbone DWDM Optical Transmission System V100R007Martin FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Excel - LOOKUP, INDEX, MATCH, SUMIFSDocument56 pagesExcel - LOOKUP, INDEX, MATCH, SUMIFSNirmal KumarNo ratings yet