Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Steve Jobs Started Apple
Uploaded by
Cholo Bristy NamaiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Steve Jobs Started Apple
Uploaded by
Cholo Bristy NamaiCopyright:
Available Formats
Apple Computer:
Jobs and Steve Wozniak met in 1971, when their mutual friend, Bill Fernandez, introduced 21year-old Wozniak to 16-year-old Jobs. In 1976, Woz invented the Apple I computer. Jobs, Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne founded Apple computer in the garage of Jobs's parents in order to sell it. They received funding from a then-semi-retired Intel product-marketing manager and engineer A.C. "Mike" Markkula, Jr. As Apple continued to expand with Wozniak's next version, the Apple II, the company began looking for an experienced executive to help manage its expansion. In 1978, Apple recruited Mike Scott from National Semiconductor to serve as CEO for what turned out to be several turbulent years. In 1983, Jobs lured John Sculley away from Pepsi-Cola to serve as Apple's CEO, asking, "Do you want to sell sugar water for the rest of your life, or do you want to come with me and change the world?" Apple president Mike Markkula also wanted to retire and believed that Jobs lacked the discipline and temperament needed to run Apple on a daily basis and that Sculley's conventional business background and recent successes would give a more favorable image.
Apple logo in 1977, created by Rob Janoff with the rainbow color theme used until 1998.
In the early 1980s, Jobs was among the first to see the commercial potential of Xerox PARC's mouse-driven graphical user interface, which led to the creation of the Apple Lisa. One year later, Apple employee Jef Raskin invented the Macintosh. The following year, Apple aired a Super Bowl television commercial titled "1984". At Apple's annual shareholders meeting on January 24, 1984, an emotional Jobs introduced the Macintosh to a wildly enthusiastic audience; Andy Hertzfeld described the scene as "pandemonium". The Macintosh became the first commercially successful small computer with a graphical user interface. While Jobs was a persuasive and charismatic director for Apple, some of his employees from that time described him as an erratic and temperamental manager. An industry-wide sales slump towards the end of 1984 caused a deterioration in Jobs's working relationship with Sculley, as
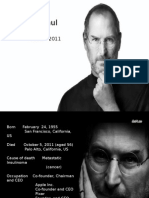
well as layoffs and disappointing sales performance. An internal power struggle developed between Jobs and Sculley. Jobs kept meetings running past midnight, sent out lengthy faxes, then called new meetings at 7:00 am. The Apple board of directors instructed Sculley to "contain" Jobs and limit his ability to launch expensive forays into untested products. Sculley learned that Jobsbelieving Sculley to be "bad for Apple" and the wrong person to lead the companyhad been attempting to organize a boardroom coup, and on May 24, 1985, he called a board meeting to resolve the matter. Apple's board of directors sided with Sculley and removed Jobs from his managerial duties as head of the Macintosh division. Jobs resigned from Apple five months later and founded NeXT Inc. the same year. In a speech Jobs gave at Stanford University in 2005, he said being fired from Apple was the best thing that could have happened to him; "The heaviness of being successful was replaced by the lightness of being a beginner again, less sure about everything. It freed me to enter one of the most creative periods of my life." And he added, "I'm pretty sure none of this would have happened if I hadn't been fired from Apple. It was awful-tasting medicine, but I guess the patient needed it.
You might also like
- Project On I PhoneDocument40 pagesProject On I PhoneSunil Soni100% (1)
- Steve JobsDocument38 pagesSteve JobsTabs NetNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs: Entrepreneur StaffDocument3 pagesSteve Jobs: Entrepreneur StaffBlst6No ratings yet
- Mac V PC RevisedDocument33 pagesMac V PC Revisedalicia_dietzmannNo ratings yet
- Chronicle About Steve JobsDocument1 pageChronicle About Steve JobsljulianaposadasNo ratings yet
- Tugas B.InggrisDocument2 pagesTugas B.InggrisMariahNo ratings yet
- Final Speech STEVE JOBSDocument16 pagesFinal Speech STEVE JOBScesar793No ratings yet
- Apple Case PDFDocument23 pagesApple Case PDFattiqueNo ratings yet
- Steve JobsDocument3 pagesSteve Jobsmgajen100% (1)
- Case Study-Steve JobsDocument7 pagesCase Study-Steve JobsAmrit KaurNo ratings yet
- Biography of Steven Paul JobsDocument4 pagesBiography of Steven Paul JobsAce LuatonNo ratings yet
- Steven Paul Jobs - Money MakerDocument5 pagesSteven Paul Jobs - Money MakerAdrian ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs Apple Barrel of Life Research ReportDocument6 pagesSteve Jobs Apple Barrel of Life Research Reportapi-305347935No ratings yet
- Oral PresentationDocument12 pagesOral PresentationRamadeviUmapathiNo ratings yet
- Steven Paul JobsDocument12 pagesSteven Paul JobsArslanNo ratings yet
- A Business Leader I Admire and Why - EditedDocument3 pagesA Business Leader I Admire and Why - EditedAshley WoodNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Apple Inc.Document11 pagesCase Study - Apple Inc.Uraza100% (1)
- My Favourite Person-1Document1 pageMy Favourite Person-1SabujNo ratings yet
- Apple IndustryDocument7 pagesApple Industryyomaira_matosNo ratings yet
- See Article History San Francisco California Palo Alto Apple Inc. Personal ComputerDocument8 pagesSee Article History San Francisco California Palo Alto Apple Inc. Personal ComputerEssential English CentreNo ratings yet
- An Inspirational StoryDocument2 pagesAn Inspirational StoryTanay GabhawalaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Apple IncDocument10 pagesCase Study Apple IncShahzer ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Apple by Steve Jobs:: What Is An Entrepreneur?Document5 pagesApple by Steve Jobs:: What Is An Entrepreneur?Abdullah ghauriNo ratings yet
- Apple by Steve Jobs:: What Is An Entrepreneur?Document5 pagesApple by Steve Jobs:: What Is An Entrepreneur?Abdullah ghauriNo ratings yet
- Title: Research Project On Apple Inc Student Name: Yogesh Karande Registration No. 12-2012 Course: MBADocument74 pagesTitle: Research Project On Apple Inc Student Name: Yogesh Karande Registration No. 12-2012 Course: MBAAmit GautamNo ratings yet
- Apple Inc Case StudyDocument10 pagesApple Inc Case StudySeema KhanNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs QuotesDocument19 pagesSteve Jobs QuotesDaniel Bălașa100% (1)
- Reading Comprehension Worksheet Steve JobsDocument1 pageReading Comprehension Worksheet Steve JobsLucky BiswasNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs Reading Comprehension Exercises - 11840Document2 pagesSteve Jobs Reading Comprehension Exercises - 11840Joshua100% (1)
- Jobs Timeline - San Jose Mercury NewsDocument1 pageJobs Timeline - San Jose Mercury NewsmbrackenburyNo ratings yet
- The Story of Steve Jobs: Naveed FarooqDocument25 pagesThe Story of Steve Jobs: Naveed FarooqNarendra PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Portfolio FOR English Theme Teve OBS Iography: Created By: Checked byDocument5 pagesPortfolio FOR English Theme Teve OBS Iography: Created By: Checked byPetru SlivinschiNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Summary ElsDocument6 pagesUnit-4 Summary Elsshaik mahemoodNo ratings yet
- Steve JobsDocument10 pagesSteve JobsNeacşu TeodorNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs BiographyDocument5 pagesSteve Jobs BiographyAriane VicenteNo ratings yet
- Steve JobsDocument8 pagesSteve JobsMOURTADA RMNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs: CreatedDocument2 pagesSteve Jobs: Createdmuhammad muzzammilNo ratings yet
- ESL Students / Jobs BiographyDocument9 pagesESL Students / Jobs BiographyCarlos TavinhoNo ratings yet
- Where Did Steve Jobs Grow Up?: CaliforniaDocument2 pagesWhere Did Steve Jobs Grow Up?: CaliforniaMAIKOL STEVENNo ratings yet
- Steve JobsDocument2 pagesSteve Jobsemirxan818No ratings yet
- Marketing - Apple INC. ProjectDocument23 pagesMarketing - Apple INC. ProjectWamiq TariqNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs BiographyDocument4 pagesSteve Jobs BiographyAlena JosephNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs TimelineDocument4 pagesSteve Jobs TimelineAnonymous zwCV8ZNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs BioDocument4 pagesSteve Jobs BioRashad StaffordNo ratings yet
- Steve JobsDocument2 pagesSteve JobsMariz Manongsong-Alzola100% (1)
- Name: Hassan Ahmad Class & Section: BBA (B) Roll No: SP18-BBA-044 Submitted To: Mam Aniqa Rehman Submission Date: 27-09-2019Document4 pagesName: Hassan Ahmad Class & Section: BBA (B) Roll No: SP18-BBA-044 Submitted To: Mam Aniqa Rehman Submission Date: 27-09-2019HASSAN AHMADNo ratings yet
- After Losing A Power Struggle With The Apple Board of Directors in 1985, Steve Jobswent On ToDocument6 pagesAfter Losing A Power Struggle With The Apple Board of Directors in 1985, Steve Jobswent On Tojoong kiNo ratings yet
- The Case Study of Steve JobsDocument5 pagesThe Case Study of Steve Jobspriyam_sanghviNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs PDFDocument2 pagesSteve Jobs PDFredcloud111No ratings yet
- Case Study2Document2 pagesCase Study2Ankit Sharma 028No ratings yet
- Computer: Assignment - 1Document33 pagesComputer: Assignment - 1Jay ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- 1 Who Was Steve Jobs?Document6 pages1 Who Was Steve Jobs?Krishna limNo ratings yet
- Cronica Ingles Miguel RuedaDocument2 pagesCronica Ingles Miguel RuedaMiguel Angel RuedaNo ratings yet
- Steve JobsDocument4 pagesSteve JobsMr ngunduhNo ratings yet
- JobsDocument21 pagesJobsanon_225009681No ratings yet
- Index HTMLDocument1 pageIndex HTMLPawan Thakur Roll no.95No ratings yet
- Becoming Steve Jobs by Brent Schlender and Rick Tetzeli | Summary & Analysis: The Evolution of a Reckless Upstart into a Visionary LeaderFrom EverandBecoming Steve Jobs by Brent Schlender and Rick Tetzeli | Summary & Analysis: The Evolution of a Reckless Upstart into a Visionary LeaderNo ratings yet
- Public Private Partnership - PhilippinesDocument24 pagesPublic Private Partnership - Philippinesann100% (1)
- Britney Spears Literally Rapes Michael Jackson On Stage! (The Way You Make Me Feel)Document2 pagesBritney Spears Literally Rapes Michael Jackson On Stage! (The Way You Make Me Feel)The Best Videos100% (8)
- 4 TuberiasDocument8 pages4 TuberiasVladimir VeraNo ratings yet
- Resume (Power BI Developer)Document7 pagesResume (Power BI Developer)Sasi Kumar MNo ratings yet
- Basic Simulation Lab ManualDocument97 pagesBasic Simulation Lab Manualshiva4105100% (1)
- 2 5 The TLBDocument6 pages2 5 The TLBPelebNo ratings yet
- Elitups TPH King Modular IngleseDocument4 pagesElitups TPH King Modular Inglesecouemba18th batchNo ratings yet
- DR - Jyothirmayi Degree College, Adoni.: Paper-III - Object Oriented Programming Using C++: Unit-1 FundamentalsDocument65 pagesDR - Jyothirmayi Degree College, Adoni.: Paper-III - Object Oriented Programming Using C++: Unit-1 FundamentalshafsaadnNo ratings yet
- General TreesDocument24 pagesGeneral TreesJeyakumar VenugopalNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Model 175944Document16 pagesUser Manual: Model 175944ZaidCorralesElFilNo ratings yet
- Authorization ObjectsDocument5 pagesAuthorization ObjectsbaithibabuNo ratings yet
- Alselectro Wordpress Com 2018-04-16 Esp8266 Wemos d1 With I2Document15 pagesAlselectro Wordpress Com 2018-04-16 Esp8266 Wemos d1 With I2Arieffin NatawidjajaNo ratings yet
- ProPlan CMF 3.0.1 - Release - NotesDocument8 pagesProPlan CMF 3.0.1 - Release - NotesbesiasnikosNo ratings yet
- Digital Technologies in Education TimelineDocument3 pagesDigital Technologies in Education Timelineapi-316829653No ratings yet
- Ids/IpsDocument7 pagesIds/Ipszaiby41No ratings yet
- IRacing VR Optimization Guide With UpdatesDocument28 pagesIRacing VR Optimization Guide With UpdatesAlyssonPachecoNo ratings yet
- ChangesDocument134 pagesChangesmariammariNo ratings yet
- Jane Smith CVDocument1 pageJane Smith CVCarles David Cristian AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Iris Unix PDFDocument79 pagesIris Unix PDFaliaskurganNo ratings yet
- DirectoryDocument12 pagesDirectorykavenindiaNo ratings yet
- Geeta Singh SAPDocument4 pagesGeeta Singh SAPBharath Reddy BandiNo ratings yet
- LicenseDocument91 pagesLicenseRavi AgrwlNo ratings yet
- Relyon SW Error in ClientDocument2 pagesRelyon SW Error in ClientslkamathNo ratings yet
- Write A Program To Display 10 Student Basic Information in A Table Form Using Table LayoutDocument8 pagesWrite A Program To Display 10 Student Basic Information in A Table Form Using Table LayoutSs1122No ratings yet
- Disk Compression - WikipediaDocument8 pagesDisk Compression - Wikipediarommel baldagoNo ratings yet
- 271 - AI Lect Notes PDFDocument128 pages271 - AI Lect Notes PDFkiransangeetaNo ratings yet
- Keyboard ShortcutDocument86 pagesKeyboard ShortcuttisonwuNo ratings yet
- Ansys CommandsDocument1,928 pagesAnsys Commandsmsb78No ratings yet
- Lenovo YOGA3 AIZY0 LA-B921P PDFDocument36 pagesLenovo YOGA3 AIZY0 LA-B921P PDFFernando Amaro HernandezNo ratings yet
- Alistair Free Presentation TemplateDocument25 pagesAlistair Free Presentation TemplateNindah IkaNo ratings yet