Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Requirement Determination: Source of Supply Determination
Uploaded by
piwalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Requirement Determination: Source of Supply Determination
Uploaded by
piwalCopyright:
Available Formats
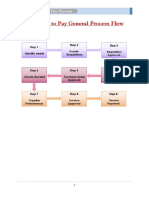
Requirement Determination Before we can start with an external procurement process, we would need to have a requirement for it.
A requirement can come from a few sources. Example, when there is a need for a new Printer in the Finance Department, therefore a user over there would raise a Purchase Requisition manually. Another example, when we have a MRP Procedure for a particular material (MRP Planning/Reorder Point/etc), SAP is able to generate Purchase Requisitions automatically or create a Planned Order first, which would be converted to Purchase Requisitions later on individually. Source of Supply Determination In SAP, we can also classify Vendors where we are allowed to procure from. There are also various methods in SAP to help you identify the possible sources to procure the goods. By doing so, you will be able to send Request for Quotations to the respective sources. This step is however optional, you can actually proceed to create a Purchase Order immediately. Vendor Selection If you chose to send Request for Quotations to a few sources, SAP automatically performs price comparisons based on the Quotations that they have provided. SAP is also able to send rejection letters to the vendors that did not qualify for the purchase. Order Processing This is where you create the official Purchasing Document called Purchase Order. You can create them manually in SAP or Automatically by the system. In SAP, you do not have to re-enter the Data in Purchase Order, but instead, you can copy the data from Purchase Requisition, RFQ, or Outline Agreements. Purchase Order Monitoring After creating a Purchase Order, it is necessary to check from time to time, the statuses of the Purchase Orders. In the Purchase Order report, it is possible to check for each PO, how much has been delivered, invoiced, etc. It is also possible at this stage to remind vendors of outstanding deliveries. Goods Receipt When you enter incoming deliveries (by looking at the delivery order provided by vendor), you will be referring to the Purchase Order, therefore, entry work is minimized. SAP is also able to check how much quantity is still open for receiving, and it is also possible to set tolerance levels. For example, If your Purchase Order quantity is 100, you can set a over delivery and/or under delivery tolerance. Therefore, system will check against the tolerance % that you have set, and if you enter a quantity that exceeds this, SAP will throw you an error message. Invoice Verification When performing Invoice Verification in SAP, you will be referring to either the Purchase Order or Goods Receipt document. SAP will perform the necessary checks to ensure that you do not over or under pay the Vendor. Once this is completed, the MM Cycle is over. The next step "Payment Processing" is under the FI Module. Payment Processing This is the final step where the payment program authorizes payment to the creditor liabilities. This covers the Standard External Procurement Cycle. Apart from the above, there are other special procurement processes such as Vendor Consignment, Subcontracting, Stock Transfer, etc. They will be explained later. For now, we should all be clear of the Standard cycle because the whole of MM evolves around it.
You might also like
- P2P Cycle Shirazul SAP ConsultantDocument2 pagesP2P Cycle Shirazul SAP ConsultantMithun Kumar ENo ratings yet
- P2P Cycle MM.: 1. Determination of RequirementsDocument3 pagesP2P Cycle MM.: 1. Determination of RequirementsSher ZamanNo ratings yet
- 1.3 SAP Procure To Pay ProcessDocument11 pages1.3 SAP Procure To Pay ProcessChathura Gunarathne100% (3)
- Determination of Requirements: Procurement CycleDocument4 pagesDetermination of Requirements: Procurement CyclerobvicNo ratings yet
- Sales Order ProcessingDocument5 pagesSales Order ProcessingSadaab HassanNo ratings yet
- Sap MM Integration With SD PM Ps Fi WM QMDocument6 pagesSap MM Integration With SD PM Ps Fi WM QMemily66850% (2)
- Solution Manual For Accounting Information Systems 11th Edition by BodnarDocument30 pagesSolution Manual For Accounting Information Systems 11th Edition by BodnarAmyBowmanngdq100% (37)
- Procurement DetailDocument3 pagesProcurement DetailNauman ZiaNo ratings yet
- Resume Unit 4Document5 pagesResume Unit 4Muhammad Rizki NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Sales & Distribution ProcessDocument39 pagesSales & Distribution ProcessLokamNo ratings yet
- AP Materials ManagementDocument14 pagesAP Materials Managementanon_60611043No ratings yet
- Sap Flow MMDocument1 pageSap Flow MMDoreen Quatre BornesNo ratings yet
- Sap S4hana SDDocument38 pagesSap S4hana SDSuraj jha100% (1)
- SD ProcessDocument28 pagesSD ProcessVeena PindiNo ratings yet
- Procure To PayDocument2 pagesProcure To PayNaveen BhaiNo ratings yet
- Invoice Verification End User ManualDocument19 pagesInvoice Verification End User ManualHendrik BudyhartonoNo ratings yet
- Procurement ProcessDocument1 pageProcurement Processram9199No ratings yet
- Procure To Pay Process Flow in Oracle FusionDocument4 pagesProcure To Pay Process Flow in Oracle FusionDellibabu DNo ratings yet
- Sap s4 Hana Procure To Pay Process (p2p)Document100 pagesSap s4 Hana Procure To Pay Process (p2p)Muhammad Kashif Shabbir100% (1)
- Procure To PayDocument18 pagesProcure To PayCeekay InweregbuNo ratings yet
- Sap MM Quick GuideDocument47 pagesSap MM Quick GuideEstefa QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Oracle Apps Order Management Interview QuestionsDocument9 pagesOracle Apps Order Management Interview Questionsnet6351100% (2)
- Expenses Purchasing ProcessDocument6 pagesExpenses Purchasing ProcessManuela MagnoNo ratings yet
- Sap-Srm Ref ManualDocument593 pagesSap-Srm Ref Manualdebdutta.sarangi6279100% (4)
- Procure To PayDocument14 pagesProcure To PaymeegunNo ratings yet
- SAP SD - Sales Order - ATP PDFDocument28 pagesSAP SD - Sales Order - ATP PDFSandip SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sap ProcurementDocument1 pageSap ProcurementKalyan ChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- AIS Packing Slip/ Bill of LadingDocument4 pagesAIS Packing Slip/ Bill of LadingLyka Liwanag NonogNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Topic On Sales Order To CashDocument17 pagesWelcome To The Topic On Sales Order To CashYogesh Mane0% (1)
- The Following Are The Features and Benefits of SAP SDDocument4 pagesThe Following Are The Features and Benefits of SAP SDGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- SAP ModulesDocument9 pagesSAP ModulesMuhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Sap MM - Quick Guide Sap MM - OverviewDocument140 pagesSap MM - Quick Guide Sap MM - Overviewcvalent100% (1)
- Order Sales and Entry ProjectDocument15 pagesOrder Sales and Entry ProjectAnonymous PfFi2XANo ratings yet
- Sap MMDocument8 pagesSap MMcnewaskarNo ratings yet
- Point of Sale System Review of Related LiteratureDocument5 pagesPoint of Sale System Review of Related Literatureafdttatoh100% (1)
- Sap Questions1Document13 pagesSap Questions1happy1558No ratings yet
- Business Blueprint RequirementsDocument6 pagesBusiness Blueprint Requirementsmehedi_orchidNo ratings yet
- Question Chap 3Document4 pagesQuestion Chap 3tuan100% (2)
- Oracle Apps Tutorial Payment Batches Creation in r12Document1 pageOracle Apps Tutorial Payment Batches Creation in r12Ravindra Reddy Thota100% (1)
- SAP MM TutorialDocument236 pagesSAP MM TutorialAnil S50% (2)
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Process in SAP Business OneDocument33 pagesMaterial Requirements Planning (MRP) Process in SAP Business OneaunhavcNo ratings yet
- Automation Beyond Accounts Payable in Sap ArticleDocument1 pageAutomation Beyond Accounts Payable in Sap ArticleSivaramakrishna MandapatiNo ratings yet
- Overview of Logistics Execution: ContentsDocument34 pagesOverview of Logistics Execution: ContentsSaikiran81100% (1)
- Purchase Requisition ProcessDocument7 pagesPurchase Requisition ProcessCabral Wa NgazimbiNo ratings yet
- Sap MM - Quick GuideDocument236 pagesSap MM - Quick GuideGaphur shaik100% (4)
- B1 90 TB1000 02 01 PDFDocument16 pagesB1 90 TB1000 02 01 PDFdabrandNo ratings yet
- SAP Order To Cash Process - SDDocument14 pagesSAP Order To Cash Process - SDd91867829No ratings yet
- E Commerce BasicsDocument300 pagesE Commerce BasicsPrarthanaRavikumarNo ratings yet
- Point of Sale System Thesis PDFDocument7 pagesPoint of Sale System Thesis PDFjennifermooreknoxville100% (2)
- Us DFDTN 15 8c Controlling RevenueDocument5 pagesUs DFDTN 15 8c Controlling RevenueKhairul Ikhwan DalimuntheNo ratings yet
- 6 Essential Steps in The Procurement Process FlowDocument9 pages6 Essential Steps in The Procurement Process FlowMohammed SayeeduddinNo ratings yet
- Section: Purchasing and Condition Technique: © Sap Ag TAMM10 4.0B 10-1Document19 pagesSection: Purchasing and Condition Technique: © Sap Ag TAMM10 4.0B 10-1lymacsauokNo ratings yet
- SAP MM OverviewDocument282 pagesSAP MM OverviewAnil Kumar100% (1)
- Tata - INVOICEDocument75 pagesTata - INVOICEVivek Bhoir0% (2)
- MM Process FlowDocument2 pagesMM Process FlowAbhijit PrinceNo ratings yet
- Om-Back To Back OrderDocument18 pagesOm-Back To Back OrderGanesh ZopeNo ratings yet
- What Is A Point of Sale SystemDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Point of Sale SystemTaha QamarNo ratings yet
- 06 - Merchandise Distribution LogisticsDocument15 pages06 - Merchandise Distribution LogisticsMariusz SamselNo ratings yet
- GSTDocument4 pagesGSTpiwalNo ratings yet
- SBI Pre. 4Document24 pagesSBI Pre. 4abdNo ratings yet
- GCC V - A - T F - Aq - SDocument16 pagesGCC V - A - T F - Aq - SPradeep JagirdarNo ratings yet
- GCC V - A - T F - Aq - SDocument16 pagesGCC V - A - T F - Aq - SPradeep JagirdarNo ratings yet
- SBI Pre-2Document27 pagesSBI Pre-2atingoyal1No ratings yet
- SBI Pre. 3Document24 pagesSBI Pre. 3arumugamrajendranNo ratings yet
- Fab-M Analysis On Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana of Bank of MaharashtraDocument2 pagesFab-M Analysis On Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana of Bank of MaharashtrapiwalNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs - July 2016 - EbookDocument332 pagesCurrent Affairs - July 2016 - EbookpiwalNo ratings yet
- Expected Questions From 1 To 15 December, 2015: ST THDocument16 pagesExpected Questions From 1 To 15 December, 2015: ST THpiwalNo ratings yet
- Bank Po Question Pattern ExpectDocument3 pagesBank Po Question Pattern ExpectpiwalNo ratings yet
- English BookDocument184 pagesEnglish Bookarijit17No ratings yet
- English Grammar NotesDocument85 pagesEnglish Grammar Notesminushastri3367% (3)
- GK Power Capsule March 2014Document11 pagesGK Power Capsule March 2014g_vasumails71579No ratings yet
- Capsule For Sbi Po Mainsrrbrbi Assistant 2015 UpdatedDocument55 pagesCapsule For Sbi Po Mainsrrbrbi Assistant 2015 UpdatedSoumya RanjanNo ratings yet
- 50 Most Popular Bank Interview Questions: Must ReadDocument6 pages50 Most Popular Bank Interview Questions: Must ReadpiwalNo ratings yet
- GK Power Capsule April 2014 2Document9 pagesGK Power Capsule April 2014 2Srikanth Reddy ChityalaNo ratings yet
- Financial Awareness Capsule 2014Document39 pagesFinancial Awareness Capsule 2014Prakash PudipeddiNo ratings yet
- Feb 2014Document11 pagesFeb 2014Udita BadolaNo ratings yet
- Ibps RRB Po Mains Clerk Nabard GK Power Capsule 2016 17 FinalDocument70 pagesIbps RRB Po Mains Clerk Nabard GK Power Capsule 2016 17 FinalebythomasNo ratings yet
- Financial Awareness Capsule 2014Document39 pagesFinancial Awareness Capsule 2014Prakash PudipeddiNo ratings yet
- Transport Packing (RTP)Document3 pagesTransport Packing (RTP)piwalNo ratings yet
- GK Power Capsule March 2014Document11 pagesGK Power Capsule March 2014g_vasumails71579No ratings yet
- Forbes List: Fortune /forbes / World /Asia-pacific/Britain - 2015Document6 pagesForbes List: Fortune /forbes / World /Asia-pacific/Britain - 2015piwalNo ratings yet
- Transport Packing (RTP)Document3 pagesTransport Packing (RTP)piwalNo ratings yet
- Imp .Data Migration Methodology For SAP V01aDocument44 pagesImp .Data Migration Methodology For SAP V01apiwalNo ratings yet
- ExceelDocument7 pagesExceelpiwalNo ratings yet
- Imp .Data - MigratDocument42 pagesImp .Data - MigratpiwalNo ratings yet
- Transport Packing (RTP)Document3 pagesTransport Packing (RTP)piwalNo ratings yet
- PO Release StrategyDocument21 pagesPO Release StrategyShalanki ShashankNo ratings yet
- PO Release StrategyDocument21 pagesPO Release StrategyShalanki ShashankNo ratings yet
- SAFe 4 Scrum Master Exam Study Guide (4.6)Document21 pagesSAFe 4 Scrum Master Exam Study Guide (4.6)Carlos Alberto Porras Porta100% (1)
- 7 Steps For KK Activities On Railway Problem-17.09.2020Document35 pages7 Steps For KK Activities On Railway Problem-17.09.2020sohag shahNo ratings yet
- How To Make Resume For Digital Marketing Fresher JobsDocument1 pageHow To Make Resume For Digital Marketing Fresher Jobscandice flynnNo ratings yet
- JJM StrategyDocument3 pagesJJM Strategyvkisho5845No ratings yet
- Stock Market Math - Essential FormulasDocument319 pagesStock Market Math - Essential Formulasనా పేరు శశి100% (1)
- How Has Technology Impacted The Global Business Environment?Document2 pagesHow Has Technology Impacted The Global Business Environment?Husnain Mustafa100% (1)
- Hedge Fund Primer Vanguard)Document24 pagesHedge Fund Primer Vanguard)Lee BellNo ratings yet
- MCI City Investment Promotion Handbook FINALDocument146 pagesMCI City Investment Promotion Handbook FINALEnsenada EdcNo ratings yet
- CLEOFAS ComparativeAnalysisDocument12 pagesCLEOFAS ComparativeAnalysiskeithNo ratings yet
- HPB Scurta Prezentare (Compatibility Mode)Document17 pagesHPB Scurta Prezentare (Compatibility Mode)aleximperiumNo ratings yet
- What Is Engineering InsuranceDocument4 pagesWhat Is Engineering InsuranceParth Shastri100% (1)
- 020 2003 MercantDocument22 pages020 2003 MercantRamVasiNo ratings yet
- Dissolution of PartnershipDocument2 pagesDissolution of PartnershipGail FernandezNo ratings yet
- Term Paper - Case Study: Ashok AmbashankerDocument7 pagesTerm Paper - Case Study: Ashok Ambashankercollinpaul0% (1)
- DMCI ConstructionDocument3 pagesDMCI ConstructionMara Ysabelle VillenaNo ratings yet
- Homework Chapter 2: BE 3-4 Larned Corporation Recorded The Following Transactions For The Past MonthDocument3 pagesHomework Chapter 2: BE 3-4 Larned Corporation Recorded The Following Transactions For The Past MonthLee Xing100% (1)
- An Introduction To Supply Base Management PDFDocument16 pagesAn Introduction To Supply Base Management PDFAmrin Diba100% (1)
- Performance Management of AfrotechDocument3 pagesPerformance Management of Afrotechrabica123No ratings yet
- Help Desk Tips TricksDocument46 pagesHelp Desk Tips TricksGenaro Quispe BallascoNo ratings yet
- Embroidery Cost AnalysisDocument13 pagesEmbroidery Cost Analysisequanimity1913No ratings yet
- Entrep Pretest 2022-2023Document3 pagesEntrep Pretest 2022-2023kate escarilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Supplement: Operational Decision-Making Tools: Facility Location ModelsDocument27 pagesChapter 7 Supplement: Operational Decision-Making Tools: Facility Location Modelsvinurules20No ratings yet
- 03laborsupply PracticeDocument31 pages03laborsupply PracticeCesarNo ratings yet
- Assignment (Esbm)Document13 pagesAssignment (Esbm)Jai KumarNo ratings yet
- Rushika EcommerceDocument18 pagesRushika EcommerceketkiNo ratings yet
- E-Logistics and E-Supply Chain Management: Applications For Evolving BusinessDocument21 pagesE-Logistics and E-Supply Chain Management: Applications For Evolving BusinessRUCHI RATANNo ratings yet
- Majesco To Present at The Aegis Capital Corp. 2016 Growth Conference On September 22, 2016 (Company Update)Document2 pagesMajesco To Present at The Aegis Capital Corp. 2016 Growth Conference On September 22, 2016 (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- 260CT Revision NotesDocument30 pages260CT Revision NotesSalman Fazal100% (4)
- PCIB V CADocument1 pagePCIB V CAVener Angelo MargalloNo ratings yet
- What Is Social Capital PDFDocument26 pagesWhat Is Social Capital PDFSelma KoundaNo ratings yet