Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation Transcript
Uploaded by
bhakti_kumariOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Presentation Transcript
Uploaded by
bhakti_kumariCopyright:
Available Formats
Presentation Transcript Economic & Diseconomies scale of m.s.r.t.c : Economic & dis economies scale of m.s.r.t.
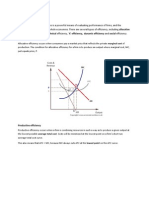
c By ANIKET- 01 SACHIN - 05 GUIDED BY - PROF MADAN SIR Economies of scale : Economies of scale Economies of scale :- Refers to the cost of advantages that a business obtains due to expansion. "Economies of scale" is a long run concept and refers to reductions in unit cost as the size of a facility and the usage levels of other inputs increase Slide 3: There are factors that cause a producers average cost per unit to fall as the scale of output is increased. As quantity of production increases from Q to Q2, the average cost of each unit decreases from C to C1. LRAC-Long Run Avg. Cost Slide 4: Economies of scale is a practical concept that is important for explaining real world phenomena such as patterns of international trade, the number of firms in a market, and how firms get "too big to fail". The exploitation of economies of scale helps explain why companies grow large in some industries and Sectors. Slide 5: Types of economies of scale: Internal Economies. External Economies. 1. Internal Economies: The term refers to those advantages which are enjoyed by an individual firm as an industry. For example- RCF company, The manager employ and all inside plant & company is getting advantage of it Slide 6: Internal economies enjoyed by an individual firm can be discussed under different categories as follows: 1. Technical Economies. 2. Managerial economies. 3. Marketing economies. 4. Financial economies. 5. Risk bearing economies. Internal economies enjoyed by an individual firm can be discussed under different categories as follows: 1. Technical Economies. 2. Managerial economies. 3. Marketing economies. 4. Financial economies. Slide 7: 2. External Economies:- As a result of growth of a particular industry may benefits are shared by all the firms. There are certain advantages which are enjoyed by all firms in an industry, this term is called external economies. Economies of Concentration Economies of Information Economies of Disintegration Economies of Large-scale production For example- The Passengers, Baggers, ST Canteen, people who sales food at stop, etc. MSRTC : MSRTC M.S.R.T.C The Economies scale Of MSRTC As per following Slide 9:
Internal Economies of M.S.R.T.C As the total number of customer increases the Company enjoy many benefits, such as increase in Profit, which in return benefits: Driver , Conductor, Employees, other subsidiary companies MSRTC : MSRTC 1. Technical Economies:- The economies are result of using better techniques of production facilitated by growth of the firm. it consist of online reservation, air Conditional system(SHIVNERI BUS). 2. Managerial Economies:- They appoint Several trained experts as managers of different department like depot manager, manager, Maintenance department . Slide 11: 3. Financial Economies:- MSRTC Firm is the largest firm so they form large capital by the fairs of passenger. They have a large passenger support also they enjoy the funds from government, and this enables them to manage the finance in more efficient and more balanced way. 4.Marketing Economies:- MSRTC offers various types of passes for 4 days,10 days ,senior citizen & physical handicap reservation. Because of that people give the preference to the ST buses . Secondly they make provision or observe the passengers because of that finally they establish the network e.g. during mahashivratri , extra buses from PUNE to BHIMASHANKAR. Slide 12: External Economies:- As firm earn profit, a number of benefits are also earn by the outsider, such as: 1. Revenue to government through Tax 2.Employment to food seller 3.Income to canteen owner 4.Income to Subsidiary firms such as body maker etc Slide 13: when the firm expands and becomes difficult to manage than diseconomies of scale arises. In large scale organizations increased production may cause certain diseconomies and disadvantages. In the firms course of expansion, a stage may reach when the firm becomes too large to manage. It may face several problems just because its size has become very large. DIS-ECONOMIES OF SCALE:Internal diseconomies of scale : Internal diseconomies of scale A firm find it difficult to manage during peak season as the summer vacation, govt. holiday, Diwali and visitors increases. And also there is shortage of buses and employees. Some times the staff also suffers, physically as well as mentally. External dis-economies of scale:- : MSRTC has captured mostly market of travel companies, hence many travel companies come in difficult to even survive. MSRTC stars the full AC buses in low charge, hence the profit ratio of competing travel companies keep on decreasing. External dis-economies of scale:Slide 16: References :- Lonavla Bus stop Text book of Managerial Economics ns??? Thanks
You might also like
- The Alchemy of Growth PDFDocument24 pagesThe Alchemy of Growth PDFanayoris100% (1)
- Unit - 1: Preliminaries in EconomicsDocument5 pagesUnit - 1: Preliminaries in EconomicsPrinceCharmIngMuthilyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Theory and Practice of Yield ManagementDocument12 pagesIntroduction To The Theory and Practice of Yield ManagementPeteMendezNo ratings yet
- Global Exame Questions 4Document4 pagesGlobal Exame Questions 4Sukh RajputNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Introduction To Corporate Finance 2nd Edition by MegginsonDocument27 pagesSolution Manual For Introduction To Corporate Finance 2nd Edition by Megginsona340726614No ratings yet
- By Aniket-01 Sachin - 05: Guided by - Prof Madan SirDocument17 pagesBy Aniket-01 Sachin - 05: Guided by - Prof Madan SirDhaval BotadaraNo ratings yet
- Small and Medium Enterprises As A Base For Restructuring Serbian EconomyDocument8 pagesSmall and Medium Enterprises As A Base For Restructuring Serbian EconomyNeko PlusNo ratings yet
- EfficiencyDocument71 pagesEfficiencyhahahasanNo ratings yet
- Economies of Scale: Lower Costs from Increased Production SizeDocument5 pagesEconomies of Scale: Lower Costs from Increased Production SizeRaiaana SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Enterprenurship Sumanta SharmaDocument6 pagesEnterprenurship Sumanta SharmaSarita PatidarNo ratings yet
- Multinational Financial Management 9th Edition Shapiro Solutions ManualDocument9 pagesMultinational Financial Management 9th Edition Shapiro Solutions ManualAlyssaCooksNo ratings yet
- Global Operations StrategiesDocument14 pagesGlobal Operations StrategiesJemimah Joy OriendoNo ratings yet
- Economies & Diseconomies of Scale ExplainedDocument5 pagesEconomies & Diseconomies of Scale ExplainedsamNo ratings yet
- Economies of ScaleDocument14 pagesEconomies of Scalemandeepsingh6432No ratings yet
- Business Studies New 2016 NotesDocument7 pagesBusiness Studies New 2016 Notesamr ahmedNo ratings yet
- 2008 TPJC H2 Economics Prelim Exam AnswersDocument53 pages2008 TPJC H2 Economics Prelim Exam AnswersChristabel TanNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance Models and GoalsDocument6 pagesCorporate Governance Models and GoalsWasim DawarNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Large Scale OrganizationsDocument36 pagesBenefits of Large Scale OrganizationsKatie Bell100% (1)
- EfeDocument41 pagesEfeKarthikeyaNo ratings yet
- H2 Econs Essay 1Document7 pagesH2 Econs Essay 1jjnaseemNo ratings yet
- Role of IRDA in regulating India's insurance sectorDocument9 pagesRole of IRDA in regulating India's insurance sectorSakshi BorkarNo ratings yet
- Efe I Ii UnitsDocument17 pagesEfe I Ii UnitsKarthikeyaNo ratings yet
- Efe I Ii UnitsDocument18 pagesEfe I Ii UnitsKarthikeyaNo ratings yet
- EfeDocument41 pagesEfeKarthikeyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 19: Dvantages and Isadvantages of Large and Small FirmsDocument11 pagesChapter - 19: Dvantages and Isadvantages of Large and Small Firmsshamawail hassanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Types of FirmsDocument10 pagesUnit 3 Types of FirmsHemalsha TashiyaNo ratings yet
- POB - Lesson 5 - Cottage industries sizes of organizations and MISDocument4 pagesPOB - Lesson 5 - Cottage industries sizes of organizations and MISAudrey RolandNo ratings yet
- MBA-4TH SEMESTER STRATEGY SUBJECTDocument7 pagesMBA-4TH SEMESTER STRATEGY SUBJECTAnonymous UFaC3TyiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Economics Is The Study of FirmsDocument3 pagesIndustrial Economics Is The Study of FirmsRaheel HusainNo ratings yet
- Scale of ProductionDocument9 pagesScale of ProductionOnindya MitraNo ratings yet
- Anjuman-I-Islam'S: Allana Institute of Management StudiesDocument30 pagesAnjuman-I-Islam'S: Allana Institute of Management StudiesAditya DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Economies of Scale 1Document38 pages1.6 Economies of Scale 1Ayaan HusainNo ratings yet
- Tut2TR18 Group5 VingroupandMasanDocument10 pagesTut2TR18 Group5 VingroupandMasanNhật Hoàng MinhNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Financial Sector ReformsDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Financial Sector Reformsafeawjjwp100% (1)
- ELearning (The Engine of The Knowledge Economy)Document109 pagesELearning (The Engine of The Knowledge Economy)EmajlanosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Management Accounting Defined, Described, and Compared To Financial Accounting PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Management Accounting Defined, Described, and Compared To Financial Accounting PDFfrieda20093835No ratings yet
- Chapter One "Foundations of Business and Economics" Q1: AnsDocument5 pagesChapter One "Foundations of Business and Economics" Q1: AnsFU.NahianNo ratings yet
- Implementing Target CostingDocument31 pagesImplementing Target Costingenypurwaningsih100% (1)
- Supply Theory-Benefits of Large FirmsDocument3 pagesSupply Theory-Benefits of Large FirmsMensonNo ratings yet
- Economic Efficiency of Selected Air Traffic: Iveta Podoľaková Bohuslava MihalčováDocument4 pagesEconomic Efficiency of Selected Air Traffic: Iveta Podoľaková Bohuslava Mihalčovánicolae adrian DincaNo ratings yet
- Economic Environment of BusinessDocument8 pagesEconomic Environment of BusinessBhawna KhuranaNo ratings yet
- 3.3.6 Multinational CorporationsDocument32 pages3.3.6 Multinational CorporationsAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Profit Motive Motivations of Managers and Workers Economies of Scale Risk Diversification Barriers To Growth of Firms 3noDocument3 pagesProfit Motive Motivations of Managers and Workers Economies of Scale Risk Diversification Barriers To Growth of Firms 3noArfath A JisHanNo ratings yet
- Problems Faced by MSMEs and SoutionsDocument4 pagesProblems Faced by MSMEs and Soutionsmilka o4No ratings yet
- (K54CLC5) Business Serivce - Group Enough - 9Document11 pages(K54CLC5) Business Serivce - Group Enough - 9Hoang TrangNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University Academic Task - Term Paper Max. Marks: 40 Course Code: ACC356Document2 pagesLovely Professional University Academic Task - Term Paper Max. Marks: 40 Course Code: ACC356Sai Ram BachuNo ratings yet
- BCG ReportDocument10 pagesBCG ReportGirinath Deshpande100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To EconomicsDocument51 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To EconomicsBhavana PrakashNo ratings yet
- DNA of Germany IndustryDocument15 pagesDNA of Germany Industrydiogo.hoppen.cfNo ratings yet
- IBM260 AssignmentDocument16 pagesIBM260 AssignmentHarjot SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three EntrepreneursDocument14 pagesChapter Three EntrepreneursSerkalm DamtewNo ratings yet
- 02 Horizontal Boundaries - AvDocument19 pages02 Horizontal Boundaries - AvDina ErtoleuNo ratings yet
- Chapter - I: Importance of ExportingDocument22 pagesChapter - I: Importance of ExportingenochcmsNo ratings yet
- Man PDFDocument12 pagesMan PDFmowiwamNo ratings yet
- Importance of International BusinessDocument4 pagesImportance of International BusinesssandilyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 1Document9 pagesAssignment 2 1api-226053416No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Industrial EconomicsDocument18 pagesLecture Notes For Industrial EconomicsJaga SwainNo ratings yet
- Experiencing Change in German Controlling: Management Accounting in a Globalizing WorldFrom EverandExperiencing Change in German Controlling: Management Accounting in a Globalizing WorldNo ratings yet
- Mastering Financial Analysis: Techniques and Strategies for Financial Professionals: Expert Advice for Professionals: A Series on Industry-Specific Guidance, #1From EverandMastering Financial Analysis: Techniques and Strategies for Financial Professionals: Expert Advice for Professionals: A Series on Industry-Specific Guidance, #1No ratings yet
- Presentation TranscriptDocument2 pagesPresentation Transcriptbhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- Economies of ScaleDocument15 pagesEconomies of Scalebhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- Economies Dis Economies of ScaleDocument17 pagesEconomies Dis Economies of ScaleMohit KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Economies of ScaleDocument15 pagesEconomies of Scalebhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- Economies of ScaleDocument18 pagesEconomies of Scalebhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- Economies of ScaleDocument16 pagesEconomies of Scalebhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- Economies of Scale AND Diseconomies of ScaleDocument21 pagesEconomies of Scale AND Diseconomies of Scalebhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- Economies of ScaleDocument16 pagesEconomies of Scalebhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- Economies Diseconomies of ScaleDocument37 pagesEconomies Diseconomies of Scalebhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- PRODUCTION ANALYSIS: SHORT-RUN ANALYSISDocument70 pagesPRODUCTION ANALYSIS: SHORT-RUN ANALYSISprabhatrcNo ratings yet
- Economies of ScopeDocument13 pagesEconomies of ScopePrabodaLakruwanRupanandaNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Cost of ProductionDocument21 pagesCH 11 Cost of Productionbhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- Economies of ScopeDocument13 pagesEconomies of ScopePrabodaLakruwanRupanandaNo ratings yet
- Economies of ScaleDocument18 pagesEconomies of Scalebhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument74 pagesProblem SolvingRamy SolimanNo ratings yet
- StudentSlides ProblemSolvingDocument38 pagesStudentSlides ProblemSolvingjuilee_bNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving and Decision MakingDocument59 pagesProblem Solving and Decision Makingbhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- Tdgs Stex BFGDocument37 pagesTdgs Stex BFGAkmal VatanshoevNo ratings yet
- Oracle Data EncryptionDocument40 pagesOracle Data EncryptionSangram BhujabalNo ratings yet
- Making Decisions & Controlling as a ManagerDocument15 pagesMaking Decisions & Controlling as a ManagerLetty SiaNo ratings yet
- HRADocument31 pagesHRABinesh RaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document58 pagesChapter 07bhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- On Kenya AirlinesDocument14 pagesOn Kenya Airlinesbhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- Business Writing Skills: ReservedDocument52 pagesBusiness Writing Skills: ReservedAlphaeusNo ratings yet
- Employee Performance Appraisal MethodsDocument23 pagesEmployee Performance Appraisal MethodsSonia WaliaNo ratings yet
- HRMDocument25 pagesHRMSampath Kumar JNo ratings yet
- 1307511501232-IT Applications in Passenger BusinessDocument22 pages1307511501232-IT Applications in Passenger Businessbhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- Oracle AppsDocument16 pagesOracle Appsbhakti_kumariNo ratings yet
- Ppts On Industrial RelationsDocument89 pagesPpts On Industrial Relationsdeep_archesh100% (2)