Professional Documents
Culture Documents
International Finance Assignment Report
Uploaded by
NaveenkalburgiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
International Finance Assignment Report
Uploaded by
NaveenkalburgiCopyright:
Available Formats
INTERNATIONAL FINANCE ASSIGNMENT REPORT
Submitted By: Naveen K.N 5th SEM A
Activity 1: case study Answers
i.
What was the goals of the policies that the IMF and World Bank adopted towards Zaire? Do you think these policies were appropriate for an impoverished nation? In what ways may IMF policies have contributed to the economic problems in Zaire?
The Democratic Republic of the Congo, formerly known as Zaire, gained its independence from Belgium in 1960. The central African nation, rich in natural resources such as copper, seemed to have a promising future. Policies adopted by IMF and World Bank towards Ziare: Devaluation of Zaires currency in order to boost exports and reduce imports. Taxes were hiked in order to balance Zaires budget The government subsidies were substantially reduced on the advice of IMF and World Bank The increase in taxation appeared to be disincentive to the workers, as a result the government revenue reduced and the budget deficit widened which again resulted in the government failing to meet its debt obligation. The policies used by these institutions were inappropriate for an impoverished nation like Zaire at a time when the country had its own internal problems and the civil war in the late 90s. Despite the country's vast resources, Mobutu's rule by theft impoverished most Congolese, forcing many to engage in corrupt practices. Just providing the country with monetary support is not enough, we should also look into how that money has been used and for what purposes.
ii.
Do you think the IMF and World Bank should lend money to countries such as Zaire where there is systematic evidence of widespread government corruption?
Every country requires external funding in some way or the other. The underdeveloped countries meet most of its requirements with the help of external funding. These may be in the form of grants, loans etc. IMF was setup to look into the matters of international monetary system and World bank to help underdeveloped and developing countries to promote general economic development. Therefore it is necessary that these institutions help the poorer countries in their quest for development. These countries are suffering from higher rate of inflation, majority of the people are below the poverty line, no proper infrastructure facilities, the children are undernourished and most importantly we can see widespread corruption at all levels. Every country requires external funding in some way or the other. The underdeveloped countries meets most of its requirements with the help of external funding. These may be in the form of grants, loans etc. IMF was setup to look into the matters of international monetary system and World bank to help underdeveloped and developing countries to promote general economic development. Therefore it is necessary that these institutions help the poorer countries in their quest for development. These countries are suffering from higher rate of inflation, majority of the people are below the poverty line, no proper infrastructure facilities, the children are undernourished and most importantly we can see widespread corruption at all levels.
iii.
What alternative policies could the IMF and World Bank have adopted in Zaire? How might these policies have helped the country avert the economic and political chaos of the 1990s, which included a prolonged civil war and economic disintegration?
The IMF and World Bank were major donors to post independence Zaire. The IMFs involvement with Zaire dates to 1967, when the IMF approved Zaires first economic stabilization plan, backed by a $27 million line of credit. About the same time, the World Bank began to make low-interest infrastructure loans to the Government of Mobutu Sese Seko.
Despite all this help, Zaires economy continued to deteriorate. By 1982, 15 years of IMF assistance, Zaire had a lower GNP than in 1967 and faced default on its debt. IMF and World Bank acted irresponsibly by lending money to the Government of Mobutu Sees Seiko even after knowing about the presence of excessive corruption. All these resulted in the further deterioration of Zaires economy.
Providing support to set up ancillary units in the copper industry would have provided means of livelihood to a large no of people.
Activity 2: Summary of balance of payment from 2001-2006
Summary of balance of trade of U.S from 2001 to 2011
Summary of BOP of INDIA from 2006-2012
I.
Analysis of various accounts that swing BOP of India from 2001-20011
1) Trade Balance Trade balance was in deficit throughout the period shown in the table as imports always exceeded the exports. Within the imports the POL items constituting a sizeable position continued to increase throughout. Exports did not achieve the required growth rate. Trade deficit in 2010-2011 stood at $ -85765 billion US $. And hence indicates how India and been importing many goods than its exporting to other countries and hence there is always a deficit for the period. The above balance of trade of US shows that Europe is one major Exporter of goods to US and it also shows how it is one of major exporter of their service to the Europeans countries and the balance of trade of goods of US shows it has always been in deficit from right 2001 to 2012. And other hand services of us has always been in surplus and put them in a new benchmark and 2. Current Account Current account balance includes visible items (trade balance) and invisible is in a more encouraging position. It declined to $ -2,666 million in 2000-01 from $-9680 million in 199091 and recorded a surplus in 2003-04 to the extent of $ 14,083 million. In 2005-06, once again there was a deficit of $ 9,186 million. Since then the Indian current account balance is in deficit and now in 2011-2012 the deficit has increased unto $-32840 because very less growth in the invisibles .The main reason for the improvement during 2001-05 was the success of invisible items.
3. Invisible The impressive role placed by invisibles in covering trade deficit is due to sharp rise invisible receipts. The main contributing factor to rise in invisible receipts is non factor receipts and private transfers. As far as non factor services receipts are concerned the main development has been the rapid increase in the exports of software services. As far as private transfers are concerned their main constituent is workers remittance from abroad. During this period the private transfer receipts also increased from $ 2,069 million in 1990-91 to $ 24,102 million in 2005-06. And the invisibles moved on surplus still 2009 but India faced it deficit in invisibles in year 2010-2011 to $-39283 million because of the recession hitting India badly and now however it is trying to regain The current trend of outsourcing a number of jobs by the developed countries to the developing ones is also helping us to get more jobs and earn additional foreign exchange.
4. Capital Account Capital account has been positive throughout the period. NRI deposits and foreign investment both portfolio and direct have helped to a great extent. The main reasons for huge increase in capital account is due to large capital inflows on account of Foreign direct investment (FDI); Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) investment on the stock markets and also by way of Euro equities raised by Indian firms. The Non-resident deposit also forms a part of capital account which has made the capital account of India always at a surplus.2001 it was deficit of $-8068 million dollar and now the capital account balance of India as on 2011- 2012 is at $41061 million dollar. This shows how India has been able to increase its FDI and FII over years and how MNC are willing to enter the Indian market.
5. Reserves Reserves have changed during this period depending on a balance between current and capital account. An increase in inflow under capital account has helped us to build up our foreign exchange reserve making the country quiet comfortable on this count. In April 2007 we had $ 203 billion foreign exchange reserves. The year 2005-06 registered the highest trade deficit so far running into $ 51,841 million, because of rising Oil prices; As a result despite impressive positive earnings of as much as $ 42,655 million from invisibles, the current account deficit in this year was $ 9,189 million which is 1.1% of GDP. Further the reserves of India goes surplus in the year 2007-2008 to extent of $-92164 million dollars which was highest till date and today the reserves of India as on 2011-2012 is $-5719 million dollars which is very less compared to 2008. And hence the reserves of India are in decline stage.
II.
Relationship of change between the current account balance and savings and investments of
According to the Chart the relationship between the current account and the investments are as follow
In this chart it directly understandable that your investment such as FDI and FII has direct Impact on balance of trade and it shows how the investments and savings has its it role in increase or decrease of Reserves of India
In 2009-2010 it shows that the current account balance of India stood as deficit of 38.2 as imports of country was much higher than the exports and hence had deficit still date. Whereas the FDI and FII and portfolio investments and saving and after deduction amounted to surplus of 13.4 dollars which led to decrease in reserves of $- 27.1 of reserve due to less people investing in country and more amount of imports and increase in imports leads to direct decrease in value of reserves. Similarly the deficit has been reducing year by year and now in 20112012 it is $-6.7 million us dollars
And By this way the current account and the investments and savings are directly related and will lead to surplus or deficit of the reserves in the BOP of the India.
III.
Relation between government budget of India and US with current account balance and savings and investments.
Activity 3:
The Big Mac index of 2012 is represented in following diagram which is as follows
According to the Chart the Big Mac index can be analysed as follows Countries with lower purchasing parity India Sri Lanka China UAE Singapore Peru Big Mac index $ (PPP Rate) -1.82 -2.56 -2.64 -3.27 -3.75 -3.71 Currency of the country INR- Indian rupees LKR-Sri Lankan rupees CNY-Chinese Yuan AED -Dirham SGD-Singapore dollar PEN-Peruvian Nuevo sol
Countries with higher Purchasing power parity Switzerland Norway Brazil Australia
Big Mac index $ (PPP Rate) + 6.81 +6.71 +5.68 +4.94
Currency of the country CHF-Swiss franc NOK-Norwegian Krone BRL-Brazilian real AUD-Australian dollar
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Module 6 ChapterDocument10 pagesModule 6 ChapterNaveenkalburgiNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Module 6 ChapterDocument10 pagesModule 6 ChapterNaveenkalburgiNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- It 2 AssignmentDocument7 pagesIt 2 AssignmentNaveenkalburgiNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- RM FinalDocument36 pagesRM FinalNaveenkalburgiNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Business Communication Synopsis ON "Organisation Structure ofDocument20 pagesBusiness Communication Synopsis ON "Organisation Structure ofNaveenkalburgiNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- ID Number Full Name Phone Number Date of BirthDocument6 pagesID Number Full Name Phone Number Date of BirthThái TranNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Póliza de RC T77 y NAODocument53 pagesPóliza de RC T77 y NAODavid Manuel Choque ValdiviezoNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Retail Bonds Trading Turnover and Trades 2015Document329 pagesRetail Bonds Trading Turnover and Trades 2015Sorken75No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- سياسات بنك السودان المركزي للعام 2022مDocument12 pagesسياسات بنك السودان المركزي للعام 2022مAhmed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Econ 90 - Chapter 9 ReportDocument11 pagesEcon 90 - Chapter 9 ReportAnn Marie Abadies PalahangNo ratings yet
- Ila IBAN Letter BH60 ABCO 5461 2669 1010 01Document1 pageIla IBAN Letter BH60 ABCO 5461 2669 1010 01masud alamNo ratings yet
- 60 TL To Eur - Pesquisa GoogleDocument1 page60 TL To Eur - Pesquisa GoogleRafael Filipe Fernandes Reino AlunoNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Balance of Payments and Sri Lanka Case StudyDocument14 pagesBalance of Payments and Sri Lanka Case StudyAkshay khóseNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Understanding the Key Concepts of International EconomicsDocument19 pagesUnderstanding the Key Concepts of International EconomicsUJJWAL SHARMANo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Pakistani Rupee Exchange Rate Chart 1998-2012 vs. US DollarDocument2 pagesPakistani Rupee Exchange Rate Chart 1998-2012 vs. US DollarGENIUS1507No ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- GFI 2019 IFF Update Report 1.29.18Document56 pagesGFI 2019 IFF Update Report 1.29.18Abdoulahi Y MAIGANo ratings yet
- Trade Policy in Developing CountriesDocument26 pagesTrade Policy in Developing CountriesAlice AungNo ratings yet
- Alhambra, Vincent Leonard V. AC102Document7 pagesAlhambra, Vincent Leonard V. AC102Vincent AlhambraNo ratings yet
- International TradeDocument11 pagesInternational TradeFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Vol 1, Issue 2, Apr-June, 2023Document122 pagesVol 1, Issue 2, Apr-June, 2023Vishakha SankhalaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- International Business AssignmentDocument5 pagesInternational Business AssignmentCeline cheahNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Special Drawing RightDocument12 pagesSpecial Drawing RightrirannaNo ratings yet
- Reasons for International Trade: Benefits and DrawbacksDocument4 pagesReasons for International Trade: Benefits and DrawbacksDrNadia ZubairNo ratings yet
- Manmgt3 1 PDFDocument29 pagesManmgt3 1 PDFWilsonNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Namma Kalvi Economics Unit 8 Surya Economics Guide emDocument28 pagesNamma Kalvi Economics Unit 8 Surya Economics Guide emAakaash C.K.No ratings yet
- WWW Tribology Abc Com Calculators Iso - Holes HTM PDFDocument1 pageWWW Tribology Abc Com Calculators Iso - Holes HTM PDFdilipNo ratings yet
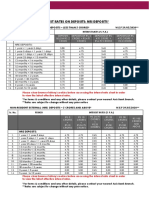
- Rate Chart Nre Nro FCNR RFC Deposit - Wef 29 05 2020Document3 pagesRate Chart Nre Nro FCNR RFC Deposit - Wef 29 05 2020Manveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Big Mac IndexDocument3 pagesBig Mac IndexpjftavaresNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- L02 - Mundell Fleming ModelDocument39 pagesL02 - Mundell Fleming ModelanufacebookNo ratings yet
- Foreign Trade and Trade Policy: Group - 7Document16 pagesForeign Trade and Trade Policy: Group - 7Ashutosh BiswalNo ratings yet
- 3 and 4. Trade TheoriesDocument26 pages3 and 4. Trade TheoriesZohaib Jamil WahajNo ratings yet
- International Finance Chapter 7 Part 1Document11 pagesInternational Finance Chapter 7 Part 1Rohil ChitrakarNo ratings yet
- World Trade OrganizationDocument9 pagesWorld Trade OrganizationNerish PlazaNo ratings yet
- Anthropology of GlobalizationDocument147 pagesAnthropology of GlobalizationsucoutinhoNo ratings yet
- Bretton Woods SystemDocument15 pagesBretton Woods SystemRahul KambleNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)