Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.4 IQM Suggested Answers
Uploaded by
Collen MahamboOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.4 IQM Suggested Answers
Uploaded by
Collen MahamboCopyright:
Available Formats
The Association of Business Executives
Certificate
Introduction to Quantitative Methods
June 2011
Suggested Answers
1.4 IQM
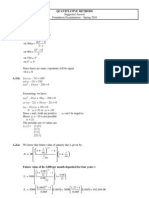
Q1.
(a)
(i)
3
1
1
8
3
1
2
1
2
|
.
|
\
|
=
3
4
8
11
2
5
|
.
|
\
|
=
3
4
8
11
8
20
|
.
|
\
|
=
3
4
8
9
=
24
36
=
2
1
1
(ii)
2
4
2
64
36
|
.
|
\
|
=
16
4
8
6
=
4
16
8
6
=
32
96
= 3
(b)
(i) ln 5.98 = 1.78842 = 1.79
(ii) e
0.58
= 1.78603 = 1.79
(c)
(i) 1.061208 10
2
(ii) 106.1
(d)
(i)
4
6
=
2
3
=
2
1
1
(ii)
4
6
=
1
100
4
6
= 150%
(iii)
4
6
= 1.5
(e) Petrol cost = 20 . 1
15
285
= 22.80
Q2.
(a)
(i) 000 , 500
12 8 5
5
+ +
= 100,000
(ii) 000 , 40
12 8 5
8
+ +
= 12,800
(iii)
1
100
8
5
= 62.5%
(iv)
1
100
000 , 500
12 8 5
12
000 , 40
12 8 5
12
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
= 8%
(v) Freddie would increase his investment by 60% (i.e. 60,000):
= (5 1.6):8:12 = 8:8:12 = 2:2:3
(b)
(i) US$ 500 converted into Yen = 500 78.1 = 39,050 Yen
Less amount spent: = 39,050 8,690 = 30,360 Yen
Yen converted back into US$: =
5 . 82
360 , 30
= US$ 368
(ii) US$ 500 converted into Yen = 500 78.1 0.975 = 38,073.75 Yen
Less amount spent: = 38,073.75 8,690 = 29,383.75 Yen
Yen converted back into US$: = 975 . 0
5 . 82
29,383.75
= US$ 347.26
Reduction in US$ Dollars: = 368.00 - 347.26 = US$ 20.74
= US$ 21
Q3.
(a) Total interest received on investment = 6,600 5,000 = 1,600
Annual simple interest received = 5,000
100
4
= 200
Number of years investment made =
200
600 , 1
= 8 years
(b)
(i) Total annually compounded interest earned:
= 20,000
10
100
0 . 6
1 |
.
|
\
|
+ 20,000
= 15,817
(ii) Total quarterly compounded interest earned:
= 20,000
4 10
4
0 . 6
100
1
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ 20,000
= 16,280
(c)
(i) Initial cost: 200,000
Depreciation: 18,000 4 = 72,000
Value of machine after four years: 200,000 72,000 = 128,000
(ii) The value at the end of each year is 90% of the value at the beginning of the year:
Value at the end of year 1: 200,000.00 91% = 182,000.00
Value at the end of year 2: 182,000.00 91% = 165,620.00
Value at the end of year 3: 165,620.00 91% = 150,714.20
Value at the end of year 4: 150,714.20 91% = 137,149.92
= 137,150
Q4.
(a)
(i) 4x + 2(x y) = 4x + 2x 2y
= 6x 2y
(ii) a(b c) b(c a) = ab ac bc + ab
= 2ab ac bc
= 2ab c(a + b)
(b)
(i) ( )( ) c b a c b a + + 3 2 2 = ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 1 1 2 3 1 2 1 2 + +
= ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 1 1 6 2 2 + +
= ( ) ( ) 4 10
= 40
(ii)
a c
b a
4 6
3
+
=
( )
( ) ( ) 1 4 2 6
1 3 1
+
=
( )
( ) ( ) 4 12
3 1
+
=
16
4
= 25 . 0
= 0.5
(c)
(i)
4
x
+
2
x
=
10
6
4
x
+
4
2x
=
10
6
4
3x
=
10
6
x =
3
4
10
6
x =
30
24
x =
5
4
or 0.8
(ii) 9x
2
+ 12x + 4 = 0, using factorisation:
(3x + 2)(3x + 2) = 0
either:
3x + 2 = 0 or 3x + 2 = 0
so:
3x = 2 or 3x = 2
x = 0.667 or x = 0.667
(iii) 5x
2
8x + 2 = 0, using the quadratic formula
5 2
) 2 5 4 ( 8 ) 8 (
2
= x
so:
10
40 64 8
= x
10
24 8
= x
10
89898 . 4 8
= x
so:
x = 1.29 or x = 0.31
Q5.
(a)
(i) Line A: x = 1, y = 2 and c = 2
Thus: 2 = (m 1) 2 m = (2) 2 m = 4
y = 4x 2
(ii) Line B: x = 1, y = 0 and m = 3
Thus: 0 = (3 (1)) + c c = (3) 0 c = 3
y = 3x + 3
(iii) Line C: x = 3, y = 4 and x = 1, y = 2
Thus: m =
) 1 ( 3
2 4
=
4
2
= 0.5
4 = (0.5 3) + c c = (1.5) 4 c = 2.5
y = 0.5x + 2.5
(b) Let: x = cost of bananas per kg
y = cost of apples per kg
then:
11x + 6y = 17.30 (i)
6x + 11y = 13.30 (ii)
to eliminate x, multiply by:
6 66x + 36y = 103.80 (i)
11 66x + 121y = 146.30 (ii)
subtract (i) from (ii):
85y = 42.50 so y = 0.50
substituting for y in (i) we get:
11x + (6 0.50) = 17.30
11x + 3 = 17.30
x =
11
3 30 . 17
so x = 1.30
Therefore: the cost of bananas is 1.30 per kg
the cost of apples is 0.50 per kg.
(c) Using the rule: log (p q) = log p + log q:
log (x) + log (x2) = log (x (x - 2))
= log (x
2
- 2x)
Q6.
(a)
(i) mode = 5 hours
(ii) median =
2
7 6 +
= 6.5 hours
(iii) mean =
12
84
= 7 hours
(iv) range = 12 3 = 9 hours
(v) standard deviation =
2
12
84
12
680
|
.
|
\
|
( )
2
7 67 . 56
= 67 . 7 = 2.77 hours
(b)
Stem and leaf diagram to show weight in grams of 18 airmail letters
21 6
22 4, 5
23 2, 2, 2, 8, 9
24 1, 1, 4, 6
25 5, 6, 7, 7
26 4, 6
Key 216 means 21.6 g
(c) Scatter diagrams are used as a visual aid to examine potential relationships between
two sets of (quantitative) variables, rather than simply providing a visual summary of
one (or more) set of variables.
Specifically, scatter diagrams are the appropriate method of presenting data when you
want to examine the relationship between two continuous variables, such as the
relationship that may exist between sales revenue and the level of advertising
expenditure.
Q7.
(a)
(i) Qualitative
(ii) Quantitative
(iii) Quantitative
(iv) Quantitative
(v) Qualitative
(vi) Qualitative
(b)
(i)
Examination marks Frequency
31 to 40 2
41 to 50 12
51 to 60 23
61 to 70 10
71 to 80 7
81 to 90 4
91 to 100 2
(ii)
0
5
10
15
20
25
41 51 61 71 81 91 100
Frequency
Examination marks
Histogram of examination marks
awarded to business studies students
65.6
(iii) From the histogram, the most likely value of the mode is 65.6 marks
(iv) Measures of dispersion include: standard deviation and range
(v) The distribution of the students examination marks is not normally distributed as
the histogram is positively skewed.
Q8.
(a)
(i) P(scoring < 4) =
6 6
3
=
36
3
=
12
1
or 8.3%
(ii) Expected profit = (100 1) (100
12
1
5) = 58
(b)
(i) P(X < 960) = P(Z <
80
1000 960
)
= P(Z < 0.5)
= 0.3085 = 30.85%
(ii) P(X > 1124) = P(Z >
80
1000 1124
)
= P(Z > 1.55)
= 0.0606 = 6.06%
(iii)
P(X < 960)
P(X > 1124)
You might also like
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Let The Required Sales Quantity Be X: Quantitative MethodsDocument8 pagesLet The Required Sales Quantity Be X: Quantitative MethodsUmer RehmanNo ratings yet
- Jawapan PPT Math Ting 3 (Modul 2)Document6 pagesJawapan PPT Math Ting 3 (Modul 2)Yan WahabNo ratings yet
- Icse Class VI Mathematics Sample Paper 1 - Solution Time: 2 HR 30 Min Total Marks: 80Document8 pagesIcse Class VI Mathematics Sample Paper 1 - Solution Time: 2 HR 30 Min Total Marks: 80Pappu Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Ak Fe SQP Math G8 2023 24Document4 pagesAk Fe SQP Math G8 2023 24jj7m2vjg52No ratings yet
- Credit Past Paper Questions - SolutionsDocument28 pagesCredit Past Paper Questions - SolutionsknoxmathsNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Paper 1Document9 pagesMathematics Paper 1James LusibaNo ratings yet
- G Cen Tre: SSC Mock Test - 102 (Solution)Document8 pagesG Cen Tre: SSC Mock Test - 102 (Solution)Mayank GuptNo ratings yet
- Top Gain - Maths f4Document48 pagesTop Gain - Maths f4Menaka SundramNo ratings yet
- CE Maths 2009 Paper1 (ANS)Document5 pagesCE Maths 2009 Paper1 (ANS)Mok Sze Nga100% (1)
- Revision - Final Exam Math 4Document14 pagesRevision - Final Exam Math 4Shahnizam SamatNo ratings yet
- 2014 S4 MYE IM1 Solutions: MX N yDocument2 pages2014 S4 MYE IM1 Solutions: MX N ymiaowNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Higher Tier Mathematics 4H June 2010Document6 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Higher Tier Mathematics 4H June 2010PainKillerNo ratings yet
- Jawapan PPT Add Maths 2 f5 2016 Kertas 2Document12 pagesJawapan PPT Add Maths 2 f5 2016 Kertas 2yenLee IOIINo ratings yet
- Linear ProgrammingDocument5 pagesLinear ProgrammingSyed NazmiNo ratings yet
- Solution of Engineering MatgematicsDocument119 pagesSolution of Engineering MatgematicsEng W Ea100% (2)
- KPS Chap 2Document14 pagesKPS Chap 2mbaskar57No ratings yet
- 6th Class Maths Track - A, Ratioonal NumbersDocument13 pages6th Class Maths Track - A, Ratioonal NumbersSamhithaReddy100% (1)
- Linear Programming: y X 3 y y X + 1 y 2xDocument5 pagesLinear Programming: y X 3 y y X + 1 y 2xShwe WenNo ratings yet
- ICSE - Mathematics Sample Paper-1-solution-Class 10 Question PaperDocument19 pagesICSE - Mathematics Sample Paper-1-solution-Class 10 Question PaperFirdosh KhanNo ratings yet
- 21 Linear Programming: y X 3 y y X + 1 y 2xDocument4 pages21 Linear Programming: y X 3 y y X + 1 y 2xSeanNo ratings yet
- R R A S: Quantitative MethodsDocument9 pagesR R A S: Quantitative MethodsMehmoodulHassanAfzalNo ratings yet
- bbmp1103 Sem 2Document13 pagesbbmp1103 Sem 2irisardellaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Group5Document27 pagesCalculus Group5VictoriaReyes_No ratings yet
- Perfect Score Add Maths 2011 Ans Module 1 - Module 5Document16 pagesPerfect Score Add Maths 2011 Ans Module 1 - Module 5Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- SSC (Tier-II) - 2013 (Mock Test Paper - 1) (SOLUTION) : Centres atDocument11 pagesSSC (Tier-II) - 2013 (Mock Test Paper - 1) (SOLUTION) : Centres atgauravkakkar28No ratings yet
- Appendix A - Solutions To ExercisesDocument48 pagesAppendix A - Solutions To Exerciseswanda MdluliNo ratings yet
- PY Answers 202305Document6 pagesPY Answers 202305tanjx-pm23No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document39 pagesChapter 4Hamza KahemelaNo ratings yet
- DiagnosticDocument5 pagesDiagnosticsindy syahilla100% (1)
- Ceodelhi - Gov.in OnlineErms VoterSlipDocument8 pagesCeodelhi - Gov.in OnlineErms VoterSlipsumitchintuNo ratings yet
- 2022 Set 03 SLE (Solution)Document9 pages2022 Set 03 SLE (Solution)BooNo ratings yet
- Jawapan PPT Math Ting 3 2023Document6 pagesJawapan PPT Math Ting 3 2023Yan WahabNo ratings yet
- O-Levels Mathematics 2006 AnswersDocument13 pagesO-Levels Mathematics 2006 AnswersKuziva MbeuNo ratings yet
- Solution SSC Mock Test 40 PDFDocument9 pagesSolution SSC Mock Test 40 PDFUday KiranNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual For Business Statistics 3e by Norean D Sharpe 0133866912Document13 pagesSolutions Manual For Business Statistics 3e by Norean D Sharpe 0133866912TimothyHilldpgoa100% (76)
- SSC Mains (Maths) Mock Test-8 (Solution)Document13 pagesSSC Mains (Maths) Mock Test-8 (Solution)Ravinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Math 1ZC3 Custom Courseware 2012Document121 pagesMath 1ZC3 Custom Courseware 2012Vytautas StasiuleviciusNo ratings yet
- Ebook Elementary Statistics 2Nd Edition Navidi Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesEbook Elementary Statistics 2Nd Edition Navidi Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDouglasRileycnji100% (12)
- Elementary Statistics 2nd Edition Navidi Solutions ManualDocument22 pagesElementary Statistics 2nd Edition Navidi Solutions Manualberthakha3lw100% (31)
- STUDENT ID: C0796526: Name: Paritosh SharmaDocument9 pagesSTUDENT ID: C0796526: Name: Paritosh SharmaDeepika DhimanNo ratings yet
- AS Exercise Solution 2021Document51 pagesAS Exercise Solution 2021Pik ki WongNo ratings yet
- Zimsec June 2020 O'Level Maths Marking Scheme: 0774236872 SYTECH LEARNING ACADEMY Https://sytech - Co.zwDocument5 pagesZimsec June 2020 O'Level Maths Marking Scheme: 0774236872 SYTECH LEARNING ACADEMY Https://sytech - Co.zwBrãñdøn Dzîñgáí100% (3)
- QT 1 Tutorial 1-6Document16 pagesQT 1 Tutorial 1-6Hui Kee0% (1)
- Core Sample Worked SolutionsDocument10 pagesCore Sample Worked SolutionsAli HassanNo ratings yet
- A+ Blog-Sslc-Maths-Second Term 2023-24-Ans Key emDocument8 pagesA+ Blog-Sslc-Maths-Second Term 2023-24-Ans Key emmuyeenuswabiriNo ratings yet
- (MAI 4.1-4.3) DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS - SolutionsDocument12 pages(MAI 4.1-4.3) DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS - Solutionsrania.kerrouchNo ratings yet
- MT k2 Marking Scheme 2010Document8 pagesMT k2 Marking Scheme 2010Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Answer SPM Trial Add Math 2015Document9 pagesAnswer SPM Trial Add Math 2015YAUNo ratings yet
- Math 5 Pmdas&gmdasDocument2 pagesMath 5 Pmdas&gmdasAnaliza Dequinto BalagosaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Algebraic Expressions and Identities Exercise 9.5Document8 pagesNCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Algebraic Expressions and Identities Exercise 9.5Varsha RaiNo ratings yet
- Answer: C Answer: D: The Two Zeros Are Not Counted As Signifi Cant Fi GuresDocument9 pagesAnswer: C Answer: D: The Two Zeros Are Not Counted As Signifi Cant Fi GurescikcinonetNo ratings yet
- G12 Maths Paper 1 2018 GCE Marking Scheme 1Document30 pagesG12 Maths Paper 1 2018 GCE Marking Scheme 1pailot kanyadzoNo ratings yet
- Paper 1: FOJ 180° 40° 40° Answer: DDocument9 pagesPaper 1: FOJ 180° 40° 40° Answer: Dsherlyn may lolNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Further TransDocument4 pagesTutorial Further TransGileShopping CrewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Binomial ExpansionDocument4 pagesChapter 6 - Binomial ExpansionSyeda Asra AkhterNo ratings yet
- Compan Y Cars (X) Revenue (Y) XY: AnswersDocument2 pagesCompan Y Cars (X) Revenue (Y) XY: AnswersJohnNo ratings yet
- FP1 Mathematics AlevelDocument172 pagesFP1 Mathematics AlevelJohn100% (7)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Liquidity Management in BanksDocument11 pagesLiquidity Management in BanksPoonam SannakeNo ratings yet
- 01 Long QuizDocument6 pages01 Long Quizgiana riveraNo ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument80 pagesWorking Capital ManagementRaghavendra yadav KMNo ratings yet
- Bebchuk Cohen and Ferrell (2009) RFSDocument45 pagesBebchuk Cohen and Ferrell (2009) RFSktsakasNo ratings yet
- Perkins v. Haines - Initial BriefDocument84 pagesPerkins v. Haines - Initial BriefFloridaLegalBlogNo ratings yet
- Report On EicherDocument65 pagesReport On EicherJeet Mehta100% (1)
- Oracle HCM FreeLancer Consulting Manager Hamdy Mohamed CV2Document10 pagesOracle HCM FreeLancer Consulting Manager Hamdy Mohamed CV2Joseph CohenNo ratings yet
- BBDO KNOWS Banking Industry Challenges Part OneDocument32 pagesBBDO KNOWS Banking Industry Challenges Part OneDigital LabNo ratings yet
- CVIF Monthly FebDocument6 pagesCVIF Monthly FebvictoruhNo ratings yet
- Utkarsh Project ReportDocument47 pagesUtkarsh Project ReportKaran BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Working Capital TheoryDocument24 pagesWorking Capital TheoryDivya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Walt DisneyDocument56 pagesWalt DisneytaiNo ratings yet
- Ben & Jerry Case StudyDocument38 pagesBen & Jerry Case Studyjennifah_noordin442394% (18)
- (FreeCourseWeb - Com) 2019-12-01.money - AustraliaDocument148 pages(FreeCourseWeb - Com) 2019-12-01.money - AustraliaaerqwerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Entrepreneurship New Ventures and Business OwnershipDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Entrepreneurship New Ventures and Business OwnershipMhmd KaramNo ratings yet
- Course: Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument40 pagesCourse: Introduction To Operations ManagementShan MalikNo ratings yet
- Breakeven Analysiscase StudyDocument7 pagesBreakeven Analysiscase StudyAlkadir del AzizNo ratings yet
- Managerial AccountingDocument39 pagesManagerial Accountingnerurkar_tusharNo ratings yet
- Capital Structure and Profitability: A Correlation Study of Selected Pharmaceutical Companies of IndiaDocument5 pagesCapital Structure and Profitability: A Correlation Study of Selected Pharmaceutical Companies of IndiaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- 5.E - Conv07 - Paper - Lurie - Actuarial Methods in Health Insurance PricingDocument23 pages5.E - Conv07 - Paper - Lurie - Actuarial Methods in Health Insurance PricingJeezNo ratings yet
- c914 - 2016 Updates On DOSRI Rule PDFDocument19 pagesc914 - 2016 Updates On DOSRI Rule PDFJoey SulteNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship ProjectDocument25 pagesSummer Internship ProjectMegha PatelNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2: Single-Step Income StatementDocument3 pagesExercise 2: Single-Step Income StatementSalman IslamNo ratings yet
- A Study of Capital Structure in Extremely Different EnvironmentsDocument101 pagesA Study of Capital Structure in Extremely Different EnvironmentsSandeep BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Co Variance ShrinkageDocument9 pagesCo Variance ShrinkageEttore TruccoNo ratings yet
- DG Khan CementDocument47 pagesDG Khan CementDebbie JacobsonNo ratings yet
- University of Pune Oct - 2005, Mba III Sem - Question PaperDocument40 pagesUniversity of Pune Oct - 2005, Mba III Sem - Question PaperSonali BangarNo ratings yet
- Ross Hart Maiden SpeechDocument16 pagesRoss Hart Maiden SpeechThe ExaminerNo ratings yet
- 11.30 Michel Folliet, International Finance CorporationDocument11 pages11.30 Michel Folliet, International Finance CorporationMohd AliNo ratings yet
- The Beneficial OwnerDocument15 pagesThe Beneficial OwnerDevaughn Immanuel Corrica-El100% (1)