Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PE 2m
Uploaded by
JPR EEEOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PE 2m
Uploaded by
JPR EEECopyright:
Available Formats
POWER ELECTRONICS PART A UNIT - I 1.What is a SCR?
? A silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) is a three terminal , three-junction semiconductor device that acts as a true electronic switch. It is a unidirectional device. It control the amount of power fed to the load. Its structure and symbol are shown in figure. 2. Define break over voltage of SCR. Break over voltage is defined as the minimum forward voltage (gate being open) at which the SCR starts conducting heavily. 3. Draw the two transistor model of a SCR and mention its applications.
List the applications of SCR . (i) It can be used as a speed controller in DC and AC motors (ii) It can be used as inverter. (iii) It can be used as converter. (iv) It is used in battery charges. (v) It is used for phase control and heater control. (vi) It is used in light dimming control circuits. 4. Draw the VI characteristics of a SCR and mark important points.
5. What is meant by latching current & holding current? Latching current is the minimum anode current required to maintain the thyristor in the on state immediately after a thyristor has been turned on and gate signal has been removed. Holding current is the minimum anode current to maintain the thyristor in the on state. 6. Draw the two transistor analogy of a SCR
7. Mention the various firing circuits for SCR? (i) Simple R and RC triggering circuits. (ii) UJT pulse triggering circuit. (iii) Digital firing scheme. 8.. If the latching current in the circuit is 5mA. Obtain the minimum width of the gating pulse required to properly turn on the SCR
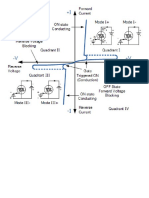
9. What is a Triac? Triac is a three terminal bi-directional semiconductor-switching device. It can conduct in both the directions for any desired period. In operation it is equivalent to two SCRs connected in antiparallel. Next to SCR it is the widely used device for power control. 10. Draw the volt-ampere characteristic of a Triac.
11. Why Triac not popular compared to SCR? commutation of Triac in inductive load is difficult when compared to SCR. Hence it is not popular 12. .Distinguish between SCR and TRIAC. S. No 1. 2. 3. 4. SCR It is unidirectional semiconductor device. It has fast turn-off time. It can be used to switch AC supply frequencies up to few KHz. It is triggered by positive voltage applied to the gate. Triac It is a bi-directional semiconductor device. It has a comparatively longer turn -off time. It can be used to switch AC supply frequencies up to 40Hz only. It is triggered by either positive or negative voltage applied to the gate.
13. Draw the construction, equivalent circuit and symbol of Triac.
14. What is power MOSFET? A power MOSFET is a voltage-controlled device and requires only a small input current. The switching speed is very high and the switching times are of the order of nanoseconds. 15..Explain the importance of threshold voltage in gate circuit when the voltage Vgs is increased beyond threshold voltage, the device starts to conduct and the current will be increased from zero . 16. Draw the circuit model of power MOSFET in active and ohmic region
17. list the driving circuits for power MOSFETS i) driving the mosfet from TTL ii) driving the mosfet from cmos iii)driving the mosfet from linear circuit iv)isolated gate circuits 18. What is the common method used for di / dt protection? The value of the di / dt Can be maintained below acceptable limit by using a small inductor called di / dt inductor in series with the anode circuit.
19. Compare the transistor and thyristor S.NO 1. 2. 3. TRANSISTOR Transistor is a three layer , two junction device Commutation circuitry which is costly and bulky, is not required To keep a transistor in the conducting state, a continuous base current is required THYRISTOR Thyristor is a four layer, three junction device Commutation circuit is required Thyristors require a pulse to make it conducting and thereafter it remain conducting
20. What is an IGBT? Insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) combines the advantages of BJT and MOSFET. Therefore it has low switching times as well as low power losses. 21What are the types of IGBT? 1. punch through IGBT 2. non punch IGBT 22. What are the advantages of IGBTs? i. They have high input gate impedance. ii. They have low conduction loss. iii. They have fast switching characteristics. iv. They have very high operating frequency. 23. List the applications of IGBTs. (i) They are used in low noise, high performance power supplies. (ii) They are used in inverters. (iii) They are used in motor speed controls. UNIT - II 1. What is a controlled rectifier? The output voltage of thyristor rectifier is varied by controlling the delay or firing angle of thyristors. Therefore thyristor rectifiers are called as controlled rectifiers. 2. Define delay angle or firing angle. Delay angle or firing angle is defined as the time after the input voltage starts to go positive until the thyristor is fired at cot = . 3. Define the effect of freewheeling diode. i ) It prevents reversal of load voltage except for a small voltage drop ii) It transfers the load current away from the main rectifier, thereby allowing all of its thyristor to regain its blocking states 4. Mention application of phase controlled rectifier 5
i) battery charges ii)DC drives iii) DC power supplies 5. Mention two functions of freewheeling diode (a) Reduction of ripple voltage in d.c terminals (b) Prevents reversal of load voltage except for small diode voltage-drop (c) It transfers the load current away from the main rectifier, thereby allowing all of its thyristors to regain their blocking states. 6. What is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric semiconductor configuration? In symmetric semiconductor, each leg contains one SCR and one diode. In asymmetric semi converter, one leg contains two SCRs and the other leg contains two diodes 7. Draw the power circuit diagram of half controlled thyristor rectifier.
8. compare continuous and discontinuous conduction CONTINUOUS DISCONTINUOUS =+ <+ Inductance value is very Inductance value is large very small 9. Explain about the two quadrant operation? A full converter is a two -quadrant converter and the polarity of its output voltage can be either positive or negative. 10. Define form factor and ripple factor form factor ff = Erms / Edc ripple factor = ( ff2 1)1/2 11. Explain the inversion mode of fully controlled bridge rectifier? 6 S.NO 1. 2.
When firing angle is greater than 90 , then the voltage is maximum in negative is called inversion mode 12. Define the input power factor P. f = ( IS1 / ISrms) cos IS1 = fundamental current ISrm = rms current 13. Mention the effect of source inductance in converters. The source inductance causes the outgoing and incoming SCRs to conduct together .When the source inductor increases, the overlap angle increases and as a consequence the average output voltage decreases. 14. Why 3-pulse converter is not much used? The 3-pulse converter requires special types of converter transformer to prevent DC magnetization. Therefore they are not much used. 15. compare single phase converter and three phase converter S.no 1. 2. 3. 4. parameter Ripple content in output Supply current waveform Control & complexity Single phase more Square wave Less complex & easy control Three phase Less Quasi square wave Complex control & implementation Less
Supply & load Higher derating 16. Express the average output voltage of 3 semi converter
17. compare half controlled and fully controlled rectifier Half controlled converter Fully controlled converter It uses one thyristor. It uses four thyristor One quadrant converter Two quadrant converter At time one thyristor is At a time two thyristor are conducting conducting 18. Why is circulating current mode prepared over non - circulating current mode in S .No 1. 2. 3.
dual converter? The circulating current mode is preferred over non - circulating current mode in Dual converter due to the following advantages. (a) Both converters are in operation continuously. The time response to change the operation from one quadrant to the other is faster. (b) One converter is always working as rectifier and the other as inverter. Therefore power flow can be in either direction at any time. (c) The circulating current helps in maintaining continuous conduction on both converters irrespective of load. UNIT III 1. What is meant by time ratio (duty cycle) of a DC chopper? The ratio of a period to the total time period is known as time control ratio (or) duty ratio. It is given by. 2. What is the effect of load inductance on the load current waveforms in the case of DC chopper? If load inductance is high, it will reduce the ripple in the output currents waveforms. Load current becomes continuous. 3. What is PWM voltage control of output of a chopper? In PWM, the frequency is kept constant and output voltage is varied by varying Ton and T off. 4. Differentiate between single quadrant and two quadrant and two quadrant DC chopper. S. No 1. 2. Single quadrant Load current flows from source to load. Both voltage and current are positive. Two quadrant Load current flows from load to source. Voltage is positive, current is either positive or negative.
6. What is the principle of on-off control? Thyristor switch connects the AC supply to load for a time ton, the switch is turned off by a gate pulse inhibiting for time t off. 7. What is the principle of step - up DC chopper? A constant voltage is applied to the inductor. Hence the current through the inductor increases linearly during the period T on. After the SCR is turned off, the energy in the inductor is transferred to the load along with supply voltage. 8. What is the function of free wheeling diode in a chopper?
(i) It protects SCR from high voltage that may be induced when the inductive circuits is interrupted. (ii) It helps to maintain constant current though the load. (iii) It helps to commutate main SCR. 9. Which power electronic circuits is DC equivalent of transformer? DC chopper connects fixed DC to variable DC. Autotransformer connects fixed AC in to variable AC. 10. What are the applications of DC Chopper? (i) Electric locomotives (ii) Battery operated cars. (iii) Power supplies. 11. What are the advantages of DC choppers? (i) Flexible (ii) Easy to control & compact (iii) Closed loop control can be implemented 12. What is the disadvantages of frequency modulated chopper? Design of filter is difficult, interference with commutation signals. 13. What is Time ratio control? The Time ratio control () is the ratio between t on to the total time period (T) i.e = ton T By varying the ton period the output voltage can be controlled and this sis Called as time ratio control. 14. Why thyristor are not preferred for inverter and choppers? Inverters operating at high frequencies require fast acting switch. Thyristor Is not preferred since it can operate at a low switching frequency of 2KHz. Thyristors require forced commutation circuits. 15. What is meant by step down and step up chopper? If chopper output voltage is less than input voltage it is called step down chopper. If chopper output voltage is greater than input voltage it is called step up chopper. 16. Write down the expression for average output voltage for step down chopper. Average output voltage for step-down chopper V0 = Vs. is the duty cycle.
17. What is meant by duty cycle? Duty cycle is defined as the ratio of the on time of the chopper to the total time period of the chopper. It is denoted by . 18. What are the two types of control strategies?
a. time ratio control b. current limit control 19. What are the two types of TRC? a. constant frequency control b. variable frequency control
20. Compare between linear & switched mode regulator. S.no 1. 2. 3. 4. Parameter swihching Losses RFI\EMI Efficiency Size & cost linear regulator zero Absent Low High switched mode High High High High
21. Write advantages of buck-boost regulator? a. provides inverted output b. high efficiency c. Both Buck\boost operation simulation d. short circuit protection can be easily implemented e. 22. Write the disadvantages of boost regulator a. High peak current through device b. Output voltage is highly sensitive to change in duty cycle c. Large inductance & capacitance are required 23. Write the expression of Imax, Imin The expressions of Imax, Imin are Vs (1 e Ton \Ta ) E Im ax = R (1 e Ton \Ta ) R Im in = 24. Vs (e Ton \Ta 1) E R (e Ton \Ta 1) R
Write the expression of p.u. ripple current. Im ax Im in = Vs (1 e Ton \Ta )(1 e (1 )T \Ta ) R (1 e Ton \Ta )
25.
Write the output voltage expression of step up\step down chopper.
26.
Vs (1 ) Write the output voltage expression of step up chopper.
Vo =
10
Vo =
1 Vs (1 )
UNIT IV 1. How the output frequency is varied in the case of an inverter? Output frequency is varied by varying switching frequency. 3. State the necessity of return current diodes in inverter. If the load connected to the inverter is inductive, then high voltages occur Across the thyristor when it is switched off. This will damage the thyristor if there is no path for diverting the current. Feedback diodes (or) return current diodes are connected across each thyristor in antiparallel. The feed back diode which is connected across the thyristors feeds the reactive power to the supply. 4. State one application for series inverter. Variable speed AC motor drives. Induction heating Standby power supplies UPS 5. Mention the advantages of current source inverter over voltage source inverter. Commutation circuit is simple since it requires only capacitors. Slow response to load changes. No feedback diodes are required Utilize thyristors very effectively. Inherent regeneration failure. 6. How to change the output voltage of a square wave inverter? By using the PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) techniques, the output voltage of an inverter can be varied. 7. What is the necessity of isolation between power circuit and control circuit? It is preferred to have separate grounds for power circuit and control circuit.If the round of power circuit is connected to the ground of control circuit, there is no isolation. If a wise of power circuit touches control circuit, largecurrent flows through the control circuit and it get damaged. Hence isolation is required between power circuit and control circuit.
8. What are the difference between return current diodes and freewheeling diodes?
11
Freewheeling diode A single diode is used. Connected across the load. It provide path to ensure continuous conduction.
Return current diode Many diodes are connected across the thyristor. Connected across each thyristor in antiparallel. It feeds the reactive power to the source.
10 What are the difference between VSI and CSI? VSI CSI Uses voltage source. Uses current source. Uses current commutation. Uses voltage commutation Diodes are connected in parallel. Diodes are connected in series. Can be used for only 1208 and Can be used for only 1208 1808 Output voltage is quasi square Output current is quasi square wave. wave. 11. What are the limitations of series inverter? It cannot be used for low frequency. Output frequency has to be less than resonant frequency. Pure sinewave cannot be obtained due to dead band. 12. Define harmonic distortion factor? Harmonic distortion factor is the harmonic voltage to the fundamental voltage. 13. What is the difference between voltage commutation and current commutation. S. No Voltage commutation Current commutation 1. Precharged capacitor pumps In current commutation, Llarge current though SCR C circuit pumps smooth and turn it off. SCR and turn off. 2. Capacitor applies reverse Diode applies reverse bias bias to the outgoing SCR. to the outgoing SCR. 14. What is the necessity of PWM within an inverter? To control voltage and harmonics PWM is used. In PWM, output voltage is controlled by varying the width of pulse. Percentage harmonic can be controlled by changing number of pulse per half cycle. 15. What are the methods of voltage control in Inverters? External control of AC output voltage. External control of DC input voltage. Internal control of inverter. 16. What type of Inverter load requires feedback diodes? Inductive load.
12
17. How is third harmonic eliminated at the output of single-phase bridges inverter? By having a transformer connection in the output. 18. How does a thyristor commutate in series inverters? By self- commutation. 19. What is the order of output frequencies of series inverters? 5KHz to 30 KHz 20. What is meant by line commutated inverter? Phase-controlled converters, when operated in the inverter mode, are called linecommutated inverters. 22. Mention any one demerit of a current source inverter. It requires a relatively large reactor to exhibit current-source characters and an extra converter state to control the current. The dynamic response is slower. Due to current transfer from one pair of switches to another, an output filter is required to suppress the output voltage spikes. 23. How do you select SCR for inverter? o Turn-off time should be minimum. Use inverter grade SCRs for low frequency application. Use BJT or MOSFET for high frequencies. o Use devices with high dt \ dt ratings. o Use factor of safety of 2 to 3. 24. What is the function of feedback diodes in bridge inverter? Feedback diodes pump reactive current to the DC source. 25. What is the simplest method of eliminating 3rd harmonic in a 3- inverter? Use 1200 mode or connect the system in star. 26. List the advantages and disadvantages of transistor inverter over thyristor inverter. Advantages: Disadvantages: It requires a driving circuit. Continuous base pulse should be applied since BJT does not have self latching property.
27. State and explain the merits and demerits of CSI over VSI. Merits: 13
Regeneration is possible with CSI. Simple power circuit. Demerits: Large filter inductor is required in the DC line. Power factor of the source and converter is poor at higher values of . 28. What is meant by total harmonic distortion (THD)? The total harmonic distortion; which is a measure of closeness in shape between a waveform and its fundamental component, is defined as 29. What is meant by lowest order harmonic (LOH)? The lowest-order harmonic is that harmonic component whose frequency is closest to the fundamental one, and its amplitude is greater than or equal to 3% of the fundamental component. 30. What are the various methods of harmonic control? Tap changing Transformer connections Filters PWM. UNIT V 1. What is an AC voltage regulator? An AC voltage regulator is an AC to AC converter. It converts a constant AC voltage into a variable AC voltage of the same frequency. 2. What are the two types of control normally used in AC voltage controller? i. On-off control ii. Phase angle control
3.
What is the difference between on-off control and phase angle control? In on-of control, thyristor switches connect the load to the AC source for a few cycles of input voltage and then disconnect it for another few cycles. In phase angle control, thyristor switches connect the load to the AC source for a portion of each cycle of input voltage. Why is half wave AC voltage regulator not used? Single-phase half wave voltage regulator consists of a Thyristor and a diode in anti parallel. Therefore control is possible only in positive half cycle. The output waves are very much distorted. Therefore half wave regulator is not used. 4.
5.
Draw the circuit diagram of single-phase half wave AC voltage controller.
14
6.
Draw the circuit diagram of single phase full wave AC voltage regulator.
7.
Which method of commutation is used in AC voltage regulators? Line commutation is used in AC voltage regulator. i.e the thyristor will get turned off when the current through it falls below the holding current value because of the nature of the source itself. Define duty cycle of AC voltage controller. Duty cycle = n / n + m Where n = number of on-cycles m = number of off-cycles
8.
9.
Explain the term sequence control of ac voltage regulators. Sequence control of a.c regulators means the use of two or more stages of voltage controllers in parallel for the regulation of output voltage. The voltage controllers in parallel are triggered in proper sequence one after the other so as to obtain a vaiable output with low harmonic content.
10. What are the advantages of sequence control of AC voltage regulators?
15
The advantages of sequence control are 1) the reduction of harmonics in the load voltages and line currents 2)Improvement of power factor. 11. Name some applications of AC regulator. AC regulators are used in industries heating, illumination level controller on load transformer tap changing, speed control of induction motor etc., 12. What is a Cycloconverters? A Cycloconverter is a direct-frequency changer that converts ac power at one frequency to ac power at another frequency by ac-ac conversion, without an intermediate conversion link. 13. List the applications of cycloconverter. Cycloconverters are used in i. Variable speed AC motors. ii. Induction heating iii. Electric traction iv. Static var systems etc. 14. List the advantages of cycloconverters. i. Freqency conversion in single stage is possible ii. Both frequency and voltage are controllable. iii. Natural commutation is used. Hence commutation circuits are not needed. iv. THD is lesser than d.c link converters. v. Isolation of a defective SCR does not require the cycloconverters to be switched off. vi. The power transfer is bidirectional 15. List the disadvantages of cycloconverters. i. Cyclocoverter operation is possible only for frequencies less than half of the input frequency. ii. Number of SCRs required is more than that for d.c link converters. iii. Complex control circuitry. iv. At smaller load currents, the cycloconverters may create problem in firing delay control. 16. What are the factors affecting the harmonics in cycloconverters? i. Number of pulses per cycle ii. Circulating or non-circulating mode of operation iii. Continuous or discontinuous conduction iv. Effect of overlap v. Effect of load power factor vi. Control methods
17. Why the output frequency of a cycloconverter is significantly lower than the input
16
frequency? Since the cycloconverter is a phase controlled AC-AC converter producing the desired output AC voltage by selecting segments of the input voltage utilizing natural commutation, the output frequency becomes significantly lower than the input frequency. 18. What is a matrix converter? The matrix converter is a single-stage converter. It uses bi-directional fully controlled switches for direct conversion from ac to ac. It is an alternative to the double sided PWM voltage rectifier-inverter. 19. What are the advantages of matrix converters? i. Inherent bidirectional power flow ii. Sinusoidal input-output waveforms with moderate switching frequency. iii. Possibility of compact design due to absence of dc-link reactive components iv. Controllable input powerfactor. 20. What are the bottlenecks of matrix converters? i. Non-availability of the bilateral fully controlled switches capable of highfrequency operation. ii. Complex control law implementation iii. An intrinsic limitation of the output-input voltage ratio iv. Commutation and protection of the switches. 21. What are types of control of matrix converters? i. Venturini method that is based on a mathematical approach of transfer function analysis ii. PWM iii. Space vector Modulation. 22. Differentiate step-down cycloconverter and step-up cycloconverter. S.No 1 2 Step-down cycloconverter It gives an output whose frequency is lower than that of output. It uses line or natural commutation Step-up cycloconverter It gives an output whose Frequency is higher than that of output. It requires force commutation
23. Classify Cycloconverters. Single phase to single-phase cycloconverter. Three phase to single phase cycloconverter. Three-phase to three-phase cycloconverter. Cycloconverters can also be classified as Step-down cycloconverter Step-up cycloconverter 24. Draw the circuit diagram of three phase to single phase bridge configuration of cycloconverter. 17
25. Explain the purpose of IGR in cycloconverter. If by any chance both of the converters are enabled, then the supply is shortcircuited. To avoid this short circuit, an intergroup reactor (IGR) can be connected between the converters as shown in Fig.
With IGR cycloconverters can be operated in circulating current mode. 26. What is meant by blocked group operation? In a cycloconverter if the two groups of thyistors conduct together, the supply is short circuited. When the operation is to be shifted from one group to the other an open circuit exists across the load. This is because of the reason that thyristors need a finite time to turn off. To avoid the possibility of short circuit it is necessary to block the turning on of one group when the other group is conducting. The firing schemes of both the groups are so designed that any group can not be triggered till the current of the other group becomes zero. This is known as blocked group operation.
18
You might also like
- OOPS Prev. QPDocument2 pagesOOPS Prev. QPJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Class: III EEE Subject Code: CS2311 Subject: Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument35 pagesClass: III EEE Subject Code: CS2311 Subject: Object Oriented ProgrammingJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Nov Dec 2011Document2 pagesNov Dec 2011JPR EEENo ratings yet
- List of Questions LabDocument1 pageList of Questions LabJPR EEENo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 NotesDocument38 pagesUNIT 1 NotesJPR EEENo ratings yet
- QB 2Document3 pagesQB 2JPR EEENo ratings yet
- ProgramsDocument3 pagesProgramsJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Oops Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesOops Important QuestionsJPR EEE100% (1)
- Explicit ConstructorsDocument3 pagesExplicit ConstructorsJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Oops - FilesDocument14 pagesOops - FilesJPR EEENo ratings yet
- OopsDocument14 pagesOopsJPR EEENo ratings yet
- CS1015 QBDocument4 pagesCS1015 QBdivyamk02No ratings yet
- AnnaDocument7 pagesAnnaJPR EEENo ratings yet
- CS1204 Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument59 pagesCS1204 Object Oriented ProgrammingNaleena SaravananNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.3Document19 pagesUnit 2.3JPR EEENo ratings yet
- Unit 2.2Document16 pagesUnit 2.2JPR EEENo ratings yet
- Unit 2.2Document16 pagesUnit 2.2JPR EEENo ratings yet
- Eee Nov 2012 Timetable CompleteDocument3 pagesEee Nov 2012 Timetable CompleteJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document44 pagesUnit 5JPR EEENo ratings yet
- Unit 2.4Document8 pagesUnit 2.4JPR EEENo ratings yet
- Power Flow Through Transmission LinesDocument9 pagesPower Flow Through Transmission LinesJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Inductance of 3-Phase Transmission LinesDocument14 pagesInductance of 3-Phase Transmission LinesJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document54 pagesUnit 1JPR EEENo ratings yet
- Performance of Transmission LineDocument10 pagesPerformance of Transmission LineJPR EEE100% (2)
- Generalized Circuit ConstantsDocument10 pagesGeneralized Circuit ConstantsJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Unit 1.2Document26 pagesUnit 1.2JPR EEENo ratings yet
- Interference With Communication CircuitsDocument11 pagesInterference With Communication CircuitsJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Medium Transmission LinesDocument8 pagesMedium Transmission LinesJPR EEENo ratings yet
- CoronaDocument14 pagesCoronaJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Cables For 3 Phase ServiceDocument22 pagesCables For 3 Phase ServiceJPR EEENo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Dimmer CircuitDocument10 pagesDimmer CircuitMd. Azizul Haque 180235No ratings yet
- SGS Thomson DB3-DB4-DC34 Diode Data SheetDocument5 pagesSGS Thomson DB3-DB4-DC34 Diode Data SheethoahlukeNo ratings yet
- WT8072Document5 pagesWT8072hectcandNo ratings yet
- HDL-MHRCU.433 RCU Room Control Unit: DatasheetDocument2 pagesHDL-MHRCU.433 RCU Room Control Unit: DatasheetDavidChicaisaNo ratings yet
- TIC226Document4 pagesTIC226TestronicpartsNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument41 pagesPower Electronics Lab ManualZzzzzzNo ratings yet
- ABB Single Phase MotorsDocument30 pagesABB Single Phase MotorsErvin BošnjakNo ratings yet
- Electronic Semister 2 MCQDocument75 pagesElectronic Semister 2 MCQNikesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Bcr1am 12Document6 pagesBcr1am 12Enrique TrascastroNo ratings yet
- Automatic Temperature Controlled FanDocument27 pagesAutomatic Temperature Controlled Fankannan100% (2)
- Power Electronics Devices and Circuits Second Edition PDFDocument383 pagesPower Electronics Devices and Circuits Second Edition PDFRuben Ignacio Salazar Baez100% (7)
- What Is A DIAC - TutorialDocument4 pagesWhat Is A DIAC - TutorialImtiax LaghariNo ratings yet
- Discontinued Products and Service Parts (NND)Document7 pagesDiscontinued Products and Service Parts (NND)RudyXPNo ratings yet
- BCR8PMDocument6 pagesBCR8PMJose CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Triac Z3MDocument6 pagesTriac Z3MTanja IkalovicNo ratings yet
- 3361702Document7 pages3361702josephNo ratings yet
- BTA40 and BTA/BTB41 Series: 40A TriacDocument6 pagesBTA40 and BTA/BTB41 Series: 40A TriacAank Anggun PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Komponen PCB MainDocument6 pagesKomponen PCB MainMohammad RofiiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Manual of 4th Sem EEEDocument32 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual of 4th Sem EEETusshar Kamath0% (1)
- PE & S Lab Manual (Student Copy)Document67 pagesPE & S Lab Manual (Student Copy)Chunduri Rambabu100% (4)
- Ai-719 Artificial Intelligence Industrial ControllerDocument46 pagesAi-719 Artificial Intelligence Industrial ControllerFabio SilvaNo ratings yet
- Triac QuadrantDocument15 pagesTriac QuadrantJohn Paul BaquiranNo ratings yet
- Surface Mount Triac: SOT223 (Plastic)Document4 pagesSurface Mount Triac: SOT223 (Plastic)Mike BrdnNo ratings yet
- Yudian Ai708 PDFDocument30 pagesYudian Ai708 PDFEhitishamNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Power ElectronicsDocument23 pagesLab Manual: Power Electronicsprakhar yadavNo ratings yet
- DET40073 - Topic 1Document54 pagesDET40073 - Topic 1KuhaanProNo ratings yet
- CRM-91H 93H 9S Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesCRM-91H 93H 9S Datasheet PDFMesko MehmedovicNo ratings yet
- Triacs BT139 Series: General Description Quick Reference DataDocument6 pagesTriacs BT139 Series: General Description Quick Reference DataJose Luis SabinoNo ratings yet
- Arm Cortex (LPC 2148) Based Motor Speed ControlDocument25 pagesArm Cortex (LPC 2148) Based Motor Speed ControlUday Wankar100% (1)
- Power 1Document6 pagesPower 1john enockNo ratings yet