Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial
Uploaded by
Mat UsoppOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial
Uploaded by
Mat UsoppCopyright:
Available Formats
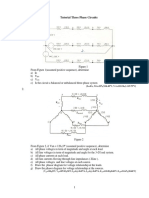
TUTORIAL FUNDAMENTALS OF AC THEORY 1. A load draws 1000 kVA at a power factor 0.8 lagging.
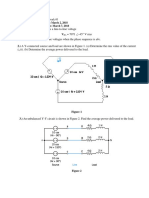
Calculate the real and reactive power of the system. [800 kW, 600 kVar] 2. For the given voltage and current below, calculate the complex power, apparent power, real and reactive power. Then, determine whether the power factor obtained is leading or lagging. V = 240 30, I = 5 60 [1200 30 VA, 1200 VA, 1.04 kW, 600Var, 0.87 leading] 3. An inductive load consisting of R and X feeding from a 2400 V rms supply absorbs 288 kW at a lagging power factor of 0.8. Determine R and X if a. R and X in series b. R and X in parallel [a. 12.8 , 9.6 b. 20 and 26.7 ] 4. Two impedances, Z1 = 0.8 + j 5.6 and Z2 = 8 j 16 and a single-phase motor are connected in parallel across a 200 V, 60 Hz supply. The motor draws 5 kVA at 0.8 power factor lagging. a. Find the complex power S1, S2 for the two impedances and S3 for the motor. b. Determine the total power taken from the supply, the supply current and the overall power factor. c. A capacitor is connected in parallel with the loads. Find the capacitance in F to improve the overall power factor to unity. [a. 7.071 81.87 kVA, 2.236 63.43 kVA, 5 36.87 kVA b. 10 53.13 kVA, 50 53.13 A, 0.6 lagging c. 530.5 F] 5. Three impedances of 4 + j 3 are -connected and tied to a three-phase 208-V power line. Find I, IL, P, Q, S, and the power factor of this load. [41.6 A, 72.05 A, 20.77 kW, 15.58 kVar, 25.96 kVA, 0.8 lagging] 6. Figure 1 shows a three-phase power system with two loads. The -connected generator is producing a line voltage of 480 V, and the line impedance is 0.09 + j 0.16 . Load 1 is Y-connected, with a phase impedance of 2.536.87 and load 2 is -connected, with a phase impedance of 5-20 . a. What is the line voltage of the two loads? b. What is the voltage drop on the transmission lines? c. Find the real and reactive powers supplied to each load. d. Find the real and reactive power losses in the transmission line. e. Find the real power, reactive power, and power factor supplied by the generator. [a. 439 7.3 V b. 41.3 52 V c. 61.6 kW, 46.2 kVar; 108.4 kW, 39.5 kVar d. 13.7 kW, 24.3 kVar e. 183.7 kW, 31 kVar, 0.986 lagging]
Figure 1
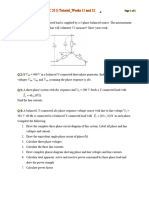
7. The figure2 below shows a one-line diagram of a simple power system containing a single 480 V generator and three loads. Assume that the transmission lines in this power system are lossless, and answer the following questions. a. Assume that Load 1 is Y-connected. What are the phase voltage and currents in that load? b. Assume that Load 2 is -connected. What are the phase voltage and currents in that load? c. What real, reactive, and apparent power does the generator supply when the switch is open? d. What is the total line current L I when the switch is open? e. What real, reactive, and apparent power does the generator supply when the switch is closed? Assume that Load 2 is -connected. f. What is the total line current L I when the switch is closed?
Figure 2 [a. 277 V, 133.7 25.84 A b. 480 V, 55.56 36.87 A c. 164 kW, 96.4 kVar, 189.2 kVa d. 228.8 A e. 244 kW, 46.8 kVar f. 298.8 10.87 A] 2
You might also like
- 1710-EET2166 Tutorial - Three Phase CircuitsDocument4 pages1710-EET2166 Tutorial - Three Phase CircuitsLucas LeeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Ahtasham ArshadNo ratings yet
- Assin3 PDFDocument3 pagesAssin3 PDFRishav ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTutorial 1Muhammad Firdaws100% (1)
- EPE491 AC Circuits Power TutorialDocument3 pagesEPE491 AC Circuits Power TutorialMohdFirdausNo ratings yet
- EE-301Tutorial 1Document2 pagesEE-301Tutorial 1Abhishek MeenaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Varun TandonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Hilman AbdullahNo ratings yet
- EPE491 Three Phase Circuits TutorialDocument2 pagesEPE491 Three Phase Circuits TutorialMohdFirdausNo ratings yet
- EE229/EEE223/GEE202 - 3-Phase Systems Problem SheetDocument1 pageEE229/EEE223/GEE202 - 3-Phase Systems Problem SheetlordeinstNo ratings yet
- BEEI 2383 TutorialDocument3 pagesBEEI 2383 TutorialAIMAN DANIAL BIN SULONGNo ratings yet
- Assignment On 3-Phase - 2Document1 pageAssignment On 3-Phase - 2Vachist WangelNo ratings yet
- ET Tutorial Sheet 3Document4 pagesET Tutorial Sheet 3Nick FuryNo ratings yet
- Polyphase Circuits Problems and SolutionsDocument3 pagesPolyphase Circuits Problems and SolutionsJohn Eduard Felix BetuinNo ratings yet
- Polyphase SystemDocument2 pagesPolyphase SystemChocomalteeChocomaltee100% (1)
- Circuits 3 ProblemDocument5 pagesCircuits 3 ProblemraramalazaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7Document3 pagesTutorial 7Dhivya NNo ratings yet
- EE103 Homework 5Document2 pagesEE103 Homework 5Hubert Semeniano0% (1)
- Machines Tutorial Sheet #1Document4 pagesMachines Tutorial Sheet #1Shruthi reddyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 6 PDFJagtar SinghNo ratings yet
- EE Refresher 1Document3 pagesEE Refresher 1giophilipNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3Spring RollsNo ratings yet
- Advanced Power System AssinmentDocument3 pagesAdvanced Power System AssinmentJara FeyisaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PsDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 PsAmin RafidNo ratings yet
- Iee Assignment-2Document4 pagesIee Assignment-2220112034No ratings yet
- Tuto 4 PuDocument3 pagesTuto 4 PuVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesNo ratings yet
- Electrical Question BankDocument4 pagesElectrical Question BankAmar Wali0% (1)
- TUTO 3 3 PhsDocument5 pagesTUTO 3 3 PhsVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesNo ratings yet
- Where Do You Need This?: 1.maintenance Engineer 2.energy Management System 3.energy ManagerDocument31 pagesWhere Do You Need This?: 1.maintenance Engineer 2.energy Management System 3.energy Managerconference RequirementsNo ratings yet
- Series Resonant Circuit Tutorial ProblemsDocument3 pagesSeries Resonant Circuit Tutorial ProblemsShirshak BajgainNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Tirupati EE3103 - Electrical MachinesDocument5 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Tirupati EE3103 - Electrical MachinesHarshaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Technology AssignmentDocument3 pagesBasic Electrical Technology AssignmentSaquib FarazNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document7 pagesProblem Set 2Jomari MoralesNo ratings yet
- Pse Problems Group AssignmentDocument14 pagesPse Problems Group AssignmentSajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Review Class Circuits 2 Basic Electrical Engineering Knowledge Review QuestionsDocument16 pagesReview Class Circuits 2 Basic Electrical Engineering Knowledge Review QuestionsCristele Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Generator Tutorial: Per-Phase Equivalent Circuit and Power EquationDocument11 pagesSynchronous Generator Tutorial: Per-Phase Equivalent Circuit and Power EquationSimon LarssonNo ratings yet
- Bee Worksheet No-2 (2018-19)Document5 pagesBee Worksheet No-2 (2018-19)vikhli sallagargiNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies: Weekly Test - 7/SEM-2Document3 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies: Weekly Test - 7/SEM-2rohitarya27No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Syed Faras HaiderNo ratings yet
- Basic Ee Exp 5Document10 pagesBasic Ee Exp 5Faye Ann Rose Rivera-BagtasosNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document4 pagesTutorial 3DavidNo ratings yet
- Lab PlotsDocument3 pagesLab PlotsSrinivasa Rao DNo ratings yet
- Problems in 3 Phase CircuitsDocument1 pageProblems in 3 Phase CircuitsSiddharth Kumar100% (1)
- Ee2351 Psa Im 2013Document11 pagesEe2351 Psa Im 2013ZARGHAM KHAN100% (1)
- IGEE 402 - Power System Analysis Final Examination - Sample Fall 2004Document28 pagesIGEE 402 - Power System Analysis Final Examination - Sample Fall 2004Akinbode Sunday OluwagbengaNo ratings yet
- EE QuestionDocument2 pagesEE QuestionLeng A. PradoNo ratings yet
- EEET2263 1phs AC NetworksDocument2 pagesEEET2263 1phs AC Networkslam koNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Weeks 11 and 12 Power SystemsDocument2 pagesTutorial - Weeks 11 and 12 Power Systemsvinaykumarm810No ratings yet
- Review Questions Single Phase Circuits - v2 TestDocument4 pagesReview Questions Single Phase Circuits - v2 TestSri NisshaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power SystemsDocument4 pagesElectrical Power SystemsAnnie CocatanaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Short Questions (2 & 3 Marks)Document6 pagesUnit - 1 Short Questions (2 & 3 Marks)Sujit KumarNo ratings yet
- PSA SolutionDocument5 pagesPSA SolutionviswaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Three-Phase Watts, Vars, and Volt-Amperes - Power Circuit - PP216Document8 pages2 - Three-Phase Watts, Vars, and Volt-Amperes - Power Circuit - PP216Khawla AlameriNo ratings yet
- T 4Document2 pagesT 4Stone WangNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document3 pagesTutorial 3Afie Fahry AdzmiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Rajath Sharma100% (1)
- Problem SetsDocument2 pagesProblem Setsesrom adlawanNo ratings yet
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Test 104Document45 pagesTest 104Rinalyn-Oscar Gamboa Magtibay56% (9)
- LG Kg270, Mg160 Service ManualDocument125 pagesLG Kg270, Mg160 Service ManualHasnat BugviNo ratings yet
- Short Questions Power System For Competitive Exams Prepared by Venkatesh, Siddhartha Engineering CollegeDocument15 pagesShort Questions Power System For Competitive Exams Prepared by Venkatesh, Siddhartha Engineering Collegevenki249100% (11)
- Caracteristicas SemiconductorsDocument146 pagesCaracteristicas SemiconductorsEdgardo MarroquínNo ratings yet
- Optical Sources DetectorsDocument72 pagesOptical Sources DetectorsDivyank BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Program BrochureDocument11 pagesCloud Computing Program BrochureKartik RavirajNo ratings yet
- 8253 Programmable Interval Timer - Free 8085 Microprocessor Notes PDFDocument4 pages8253 Programmable Interval Timer - Free 8085 Microprocessor Notes PDFMary HelenNo ratings yet
- Generator ProtectionDocument10 pagesGenerator ProtectionVirendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current (AC) Semiconductor (Amplifier) Circuits Ohm's Law Series/parallel AnalysisDocument3 pagesAlternating Current (AC) Semiconductor (Amplifier) Circuits Ohm's Law Series/parallel AnalysisInsik Agir ZernaNo ratings yet
- 2.3. Periodic Table and Trends NotesDocument12 pages2.3. Periodic Table and Trends Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- SHT31 PDFDocument21 pagesSHT31 PDFJhony UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Solar Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging SystemDocument7 pagesSolar Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging SystemMANISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- TL 082Document50 pagesTL 082pacoNo ratings yet
- MemsAccelerometer-151 ResearchgateDocument7 pagesMemsAccelerometer-151 ResearchgateJ. AbhiraajNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen ProductionDocument59 pagesHydrogen ProductionIndra Maulana100% (1)
- SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATADocument6 pagesSEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATASimeon PetkovNo ratings yet
- Bizgram Export FileDocument58 pagesBizgram Export FileBizgram Asia0% (1)
- HP ProBook 450 G3 Notebook PC (Y1S96PA) Rs.60,000Document4 pagesHP ProBook 450 G3 Notebook PC (Y1S96PA) Rs.60,000pankajNo ratings yet
- Pe Notes PDFDocument197 pagesPe Notes PDFKartikNo ratings yet
- Op467 PDFDocument20 pagesOp467 PDFCelvin DiagustaNo ratings yet
- Psim Interface Opal RTDocument33 pagesPsim Interface Opal RTtvs_krishnavarmaNo ratings yet
- CTS Session 01 BasicDocument25 pagesCTS Session 01 BasicDavid TanadiNo ratings yet
- Basics of PVDocument117 pagesBasics of PVJay SinghNo ratings yet
- 6.02 Nitride-Based LEDs and Superluminescent LEDsDocument73 pages6.02 Nitride-Based LEDs and Superluminescent LEDsfojxNo ratings yet
- Season Based Street Light Switching Based On SensorsDocument54 pagesSeason Based Street Light Switching Based On SensorsVenkatesh YekkaluriNo ratings yet
- MT 48lc2m32b2 - 64mb x32 SdramDocument53 pagesMT 48lc2m32b2 - 64mb x32 SdramJannik SvenssonNo ratings yet
- DS1621 Digital Thermometer and Thermostat GuideDocument16 pagesDS1621 Digital Thermometer and Thermostat GuideAnassFouadNo ratings yet
- Web Links MP FinalDocument11 pagesWeb Links MP FinalVidhya DharanNo ratings yet
- BJT ManufacturingDocument36 pagesBJT ManufacturingM. AhmedNo ratings yet