Professional Documents
Culture Documents
sm5 104
Uploaded by
Sadie HnatowOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
sm5 104
Uploaded by
Sadie HnatowCopyright:
Available Formats
PROBLEM 5.
104
KNOWN: Plane wall, infinite cylinder and sphere each subjected to a constant surface heat flux.
FIND: The ratio of (i) the actual surface temperature minus the initial temperature, (T
s,act
T
i
), to (ii)
the value of this temperature difference associated with lumped capacitance behavior, (T
s,lc
T
i
), for
each of the three geometries. Criteria associated with (T
s,act
T
i
)/(T
s,lc
T
i
) s 1.1.
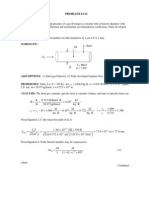
SCHEMATIC:
ASSUMPTIONS: (1) One-dimensional conduction, (2) Constant properties, (3) Fo > 0.2.
ANALYSIS: From Table 5.2b, the approximate solutions for all three geometries may be expressed
as
1
"
2
,
( )
s c
s act i c
q L kt
a b
k T T cL
(
= +
(
(1)
where L
c
= L for the plane wall, and L
c
= r
o
for the infinite cylinder and the sphere. The constants a
and b have the following values.
Geometry L
c
a b
Plane wall L 1 1/3
Infinite cylinder r
o
2 1/4
Sphere r
o
3 1/5
For the lumped-capacitance analysis with constant heat flux, we note that in general,
"
,
( )
s s s lc i
q A t cV T T = . Substituting expressions for the surface area and volume of each of the three
geometries results in the general expression,
( )
"
,
/
s lc i s c
T T aq t cL = (2)
where the constant a is the same as in the table above. Solving Eq. (1) for (T
s,act
T
i
) and dividing the
resulting expression by Eq. (2) results in
Continued
T
s
L L
x
T
i
, k, , c
T
s
q
s
r
T
i
, k, , c
r
o
q
s
r
T
i
, k, , c
r
o
q
s
q
s
Plane wall Infinite cylinder or sphere
PROBLEM C5.104 (Cont.)
( )
( )
| |
"
2
,
"
,
1
1
s c
c
s act i c
s lc i s
q L k t
a b cL
k c T T L
b
aFo b
aFo aFo T T aq t
( | |
+
( |
|
( \ .
= = + = +
(3)
Therefore, for the plane wall,
( )
( )
,
,
1
1 1
3
s act i
s lc i
T T
b
aFo Fo T T
= + = +
<
for the infinite cylinder,
( )
( )
,
,
1
1 1
8
s act i
s lc i
T T
b
aFo Fo T T
= + = +
<
for the sphere,
( )
( )
,
,
1
1 1
15
s act i
s lc i
T T
b
aFo Fo T T
= + = +
<
The preceding equations may be solved for the Fourier number associated with (T
s,act
T
i
)/(T
s,lc
T
i
) =
1.1, yielding critical Fourier numbers, Fo
c
= 3.33, 1.25 and 0.667 for the plane wall, infinite cylinder,
and sphere, respectively. Lumped capacitance behavior is exhibited at dimensionless times greater
than Fo
c
.
COMMENTS: (1) The calculated values of the Fourier number are each greater than 0.2. Hence, use
of the approximate solutions for Fo > 0.2 is justified. (2) The dimensionless time at which lumped
capacitance behavior is reached varies with the geometry.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- CH 14Document82 pagesCH 14Sadie Hnatow75% (4)
- sm9 010Document1 pagesm9 010Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 008Document1 pagesm9 008Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document82 pagesCH 14Sadie Hnatow75% (4)
- sm9 004Document1 pagesm9 004Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 001Document1 pagesm9 001Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 126Document1 pagesm8 126Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 119Document1 pagesm8 119Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 120Document1 pagesm8 120Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 123Document1 pagesm8 123Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm5 089Document2 pagessm5 089Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 125Document1 pagesm8 125Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 117Document3 pagessm8 117Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 114Document2 pagessm8 114Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 116Document2 pagessm8 116Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm5 087Document2 pagessm5 087Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm5 093Document1 pagesm5 093Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 113Document1 pagesm8 113Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm5 084Document3 pagessm5 084Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Thebault TheoremDocument5 pagesThebault TheoremBGYODANo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationMalcom MuchenjeNo ratings yet
- Shear and MomentDocument70 pagesShear and MomentDhyz Quinquilleria100% (4)
- AP Questions - Applied - Physics - Chapter - 1 - 2 - 3Document3 pagesAP Questions - Applied - Physics - Chapter - 1 - 2 - 3Harshita Sharda100% (1)
- Review On Speed Velocity AccelerationDocument29 pagesReview On Speed Velocity AccelerationLorilet OperianoNo ratings yet
- Opt Math Class X (MP 1)Document95 pagesOpt Math Class X (MP 1)Himrashmi HschoolNo ratings yet
- Spacecraft Dynamics - Final ProjectDocument11 pagesSpacecraft Dynamics - Final ProjectJames Carrillo100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document30 pagesChapter 3phanindra kumarNo ratings yet
- LP Math 3 CaDocument10 pagesLP Math 3 CaBee HiveNo ratings yet
- Plane ExtractionDocument11 pagesPlane ExtractiondanielsturzaNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument20 pagesGeometrySshivam Anand100% (1)
- Shortcuts For Ellipses and HyperBolaDocument3 pagesShortcuts For Ellipses and HyperBolaChristian Simon D. SOLINAPNo ratings yet
- Certc - Davao Diagnostic Exam: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDocument4 pagesCertc - Davao Diagnostic Exam: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- AQA IGCSE Further Maths Revision Notes: 1. NumberDocument16 pagesAQA IGCSE Further Maths Revision Notes: 1. NumberDiyaNo ratings yet
- Imc 2015 Extended PDFDocument21 pagesImc 2015 Extended PDFKhurram FawadNo ratings yet
- 01 - 02elements of VectorsDocument6 pages01 - 02elements of Vectorsshahbazalam4a5100% (1)
- Convergence in Topological Spaces. Nets.: 1 PreliminariesDocument5 pagesConvergence in Topological Spaces. Nets.: 1 PreliminariesANDRES DAVID GUEVARA MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Theorizing A New Agenda For Architecture An Anthology of Architectural Theory 1965-1995Document15 pagesTheorizing A New Agenda For Architecture An Anthology of Architectural Theory 1965-1995alexNo ratings yet
- (English) Basic Trigonometry - Sin Cos Tan (NancyPi) (DownSub - Com)Document6 pages(English) Basic Trigonometry - Sin Cos Tan (NancyPi) (DownSub - Com)Jisoo KimNo ratings yet
- 18 - Irreducible Tensor Operators and The Wigner-Eckart Theorem PDFDocument30 pages18 - Irreducible Tensor Operators and The Wigner-Eckart Theorem PDFUltrazordNo ratings yet
- Geogebra Cycloid PDFDocument20 pagesGeogebra Cycloid PDFJimNo ratings yet
- 3-Year SoW End of Term 3 Higher Test AnswersDocument5 pages3-Year SoW End of Term 3 Higher Test Answerslucas0% (2)
- STEM - Pre-Calculus CG PDFDocument5 pagesSTEM - Pre-Calculus CG PDFQuinnie Anne CarreonNo ratings yet
- Prova 1 - Cinemática - Parte IDocument6 pagesProva 1 - Cinemática - Parte IVinícius GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- EccentricityDocument7 pagesEccentricitysarveshpremiNo ratings yet
- AAUSAT-II - ACDS - Attitude Control System PDFDocument115 pagesAAUSAT-II - ACDS - Attitude Control System PDFRobin CookNo ratings yet
- The Sun, The Moon, and ConvexityDocument5 pagesThe Sun, The Moon, and ConvexityAnonymous e8BzOGqlaw100% (1)
- Autocad ShortcutsDocument7 pagesAutocad ShortcutsNayan FataniaNo ratings yet
- Area and Perimeter For SSC ExamsDocument62 pagesArea and Perimeter For SSC ExamsHema Latha100% (1)
- Eric Gjerde Origami Tessellations PDFDocument2 pagesEric Gjerde Origami Tessellations PDFmartagonzalezbordonabaNo ratings yet