Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Breast Reconstruction
Uploaded by
Darren FranceyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Breast Reconstruction
Uploaded by
Darren FranceyCopyright:
Available Formats
in the operating theatre:
MeThodS of ReconSTRUcTIon
Implant-based reconstruction is a popular choice that uses an implant to rebuild the breast. A deflated, expandable implant is placed under the chest muscle and small amounts of a salt water solution are injected every few weeks until the desired breast size is reached. A second surgery removes the expandable implant and replaces it with a permanent one, either silicone or saline. Small-breasted women with little abdominal fat are the best candidates for this type of reconstruction. Women who have had radiation therapy on their chest are usually not good candidates, as the skin can be too damaged to stretch.
Autologous reconstruction uses skin, fat and muscle from the body; includes DIEP, SGAP, TRAM and TUG
dIeP flap The Deep Interior Epigastric Perforator flap is microsurgery suitable for patients with sufficient stomach fat 3. New skin flap is attached to internal mammary vessels, which will nourish the flap.
1. Skin, fat and blood vessels removed from the abdomen, leaving the muscle in place to preserve abdominal strength and speed up recovery time. SGAP or IGAP flap spare the muscle, using only skin, fat and blood vessels from the upper or lower buttock to build a new breast. A surgeon uses a microscope to reconnect even the tiniest blood vessels. SGAP uses tissue from the upper part of the buttock, while IGAP uses tissue from the lower buttock.
2. The DIEP flap transports the deeper blood vessels that run below and within the abdominal muscle.
New nipple and areola created at a later stage
TUG flap is microsurgery which uses skin, fat, blood vessels and some muscle from the patients inner thigh to create a new breast.
TRAM flap surgery uses muscle, skin, fat and blood vessels from the abdomen. The procedure can either be a pedicled flap, where the tissue is tunnelled under the abdominal skin to the chest and keeps its original blood supply, or a free flap, where the tissue is completely removed and reconnected through microsurgery.
Latissimus dorsi flap uses muscle, fat and skin from the patients back to create a new breast. If the patient has large breasts, the surgeon may use an implant as well to more closely match the size of the remaining healthy breast. Women who arent candidates for the TRAM and DIEP flap are the best candidates. However, active women who take part in activities using the shoulder muscles, like swimming, tennis, or rowing are not good candidates.
Illustrations courtesy Center for Restorative Breast Surgery Graphic: Darren Francey, Calgary Herald
You might also like
- Cyber Safety ActDocument2 pagesCyber Safety ActDarren FranceyNo ratings yet
- Special Report 2009Document7 pagesSpecial Report 2009Darren FranceyNo ratings yet
- SHC Project Charter 2008Document4 pagesSHC Project Charter 2008Darren FranceyNo ratings yet
- BC Submission To NGP JointReviewPanel 130531Document99 pagesBC Submission To NGP JointReviewPanel 130531National PostNo ratings yet
- Boston ManhuntDocument1 pageBoston ManhuntDarren FranceyNo ratings yet
- Recommendations 2005Document12 pagesRecommendations 2005Darren FranceyNo ratings yet
- CHR Revisions 2008Document4 pagesCHR Revisions 2008Darren FranceyNo ratings yet
- CHR Budget 2007Document7 pagesCHR Budget 2007Darren FranceyNo ratings yet
- CHR Revised Budget 2007Document4 pagesCHR Revised Budget 2007Darren FranceyNo ratings yet
- Worst Industrial AccidentsDocument1 pageWorst Industrial AccidentsDarren FranceyNo ratings yet
- Blasts Hit Boston MarathonDocument1 pageBlasts Hit Boston MarathonDarren FranceyNo ratings yet
- Map: Scene of Boston Marathon Attack BombsDocument1 pageMap: Scene of Boston Marathon Attack BombsThe State NewspaperNo ratings yet
- AHS Letter To DoctorsDocument1 pageAHS Letter To DoctorsDarren FranceyNo ratings yet
- Temporary Foreign Worker ApprovalsDocument93 pagesTemporary Foreign Worker ApprovalsDarren FranceyNo ratings yet
- Injecting A Sense of UrgencyDocument33 pagesInjecting A Sense of UrgencyDarren FranceyNo ratings yet
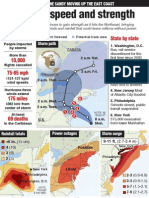
- Hurricane SandyDocument1 pageHurricane SandyDarren FranceyNo ratings yet
- Arming The PacificDocument1 pageArming The PacificDarren FranceyNo ratings yet
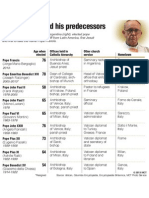
- Pope HistoryDocument1 pagePope HistoryDarren FranceyNo ratings yet
- Shooting TimelineDocument1 pageShooting TimelineDarren FranceyNo ratings yet
- Hostage Crisis in AlgeriaDocument1 pageHostage Crisis in AlgeriaDarren FranceyNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- الطبيعة القانونية للمسؤولية المدنية المترتبة عن الجراحة التجميليةDocument17 pagesالطبيعة القانونية للمسؤولية المدنية المترتبة عن الجراحة التجميليةAs SsNo ratings yet
- Reusable & Disposable Pencils: A B C DEDocument6 pagesReusable & Disposable Pencils: A B C DE莫明No ratings yet
- Breast Reconstruction and MastectomyDocument3 pagesBreast Reconstruction and Mastectomysina bayat shahbaziNo ratings yet
- Speakers & TrainersDocument23 pagesSpeakers & Trainersuser656615166No ratings yet
- Cervicoplastia: Mauricio Rodriguez Urrea Cirugía Plástica, Reconstructiva y EstéticaDocument74 pagesCervicoplastia: Mauricio Rodriguez Urrea Cirugía Plástica, Reconstructiva y EstéticaVanessaGGSNo ratings yet
- Internalfit: Simplicity Made AccessibleDocument2 pagesInternalfit: Simplicity Made AccessibleCris GshsuwNo ratings yet
- Review of retentive aids in maxillofacial prosthesesDocument4 pagesReview of retentive aids in maxillofacial prosthesesmaha mohNo ratings yet
- Curs Postuniv Reconstructie SiniDocument82 pagesCurs Postuniv Reconstructie Sinithanos bakourasNo ratings yet
- Azurite PricingDocument3 pagesAzurite Pricingtrina azuriteNo ratings yet
- Isaps Global Survey 2021Document57 pagesIsaps Global Survey 2021abigail juaricoNo ratings yet
- MastopexyDocument15 pagesMastopexyLuiggi FayadNo ratings yet
- Speakers & TrainersDocument22 pagesSpeakers & Trainersuser656615166No ratings yet
- Canniesburn Flap Course AdvertDocument4 pagesCanniesburn Flap Course AdvertplastaukNo ratings yet
- Return Invoice 231.8.2023Document2 pagesReturn Invoice 231.8.2023ahmed.zulkhaireNo ratings yet
- Gambhir Cosmetic Medicine Philadelphia, Exton, King of Prussia, PA.Document20 pagesGambhir Cosmetic Medicine Philadelphia, Exton, King of Prussia, PA.Dr GambhirNo ratings yet
- 020827-181217 Product Catalog 1419Document13 pages020827-181217 Product Catalog 1419Igor GrisendiNo ratings yet
- Rev C Catalog Mentor PerouseDocument34 pagesRev C Catalog Mentor PerouseDona MeyerNo ratings yet
- Implant Connections Website enDocument13 pagesImplant Connections Website enCatalin PopescuNo ratings yet
- A New Simple Technique For Neoumbilicoplasty: Vertical Incision and Partial Skin GraftDocument5 pagesA New Simple Technique For Neoumbilicoplasty: Vertical Incision and Partial Skin GraftJorge Luis MarcosNo ratings yet
- Inked Magazine 2011-05Document100 pagesInked Magazine 2011-05giogio29100% (2)
- 2020 Cement in Hip Knee ArthroplastyDocument15 pages2020 Cement in Hip Knee ArthroplastyJD2750No ratings yet
- First Announcement ISWAM 2023 (1) - CompressedDocument11 pagesFirst Announcement ISWAM 2023 (1) - CompresseddominiqwicNo ratings yet
- Hyderabad: Cortico-Basal Implantology CourseDocument6 pagesHyderabad: Cortico-Basal Implantology CourseYousuf AdamNo ratings yet
- ISAPS 2017 International Study Cosmetic Procedures NEWDocument73 pagesISAPS 2017 International Study Cosmetic Procedures NEWEva Marie NejarNo ratings yet
- Cardioxyl GBDocument5 pagesCardioxyl GBHuy Trần ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Augmentation Mammoplasty:MastopexyDocument12 pagesAugmentation Mammoplasty:MastopexyfumblefumbleNo ratings yet
- POLYTECH Implantaty Produktovy KatalogDocument31 pagesPOLYTECH Implantaty Produktovy KatalogSzilviaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Surgery - Taboo TopicsDocument2 pagesPlastic Surgery - Taboo TopicsSahil MohammadNo ratings yet
- AmputationDocument7 pagesAmputationAsma SaleemNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents - NeliganDocument9 pagesTable of Contents - NeliganStephanie LopezNo ratings yet