Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Automatic Climate Control System
Uploaded by
Syahiran SharifOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Automatic Climate Control System
Uploaded by
Syahiran SharifCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction The automatic climate control system, also known as the auto climate control is a system that monitors,
analyzes and controls your cars air conditioning system so that the optimal temperature is set within your car. You would find this feature incorporated in most of the new cars that are being produced today, as car manufacturers are using this feature as a pulling factor to boost sales figures of their vehicles. If you have auto climate control in your car, you would not need to manually adjust your temperature or blowing capability, instead it would be done automatically for you. Nevertheless if you want to, you could still override the system and manually adjust your air conditioning system if you feel the need to. For the record, auto climate control was firstly introduced in vehicle back in the early 1960s, and the technology has grown by leaps and bounds to what you find in the modern cars today. As you are able to manage the temperature of your cars interiors based on your ambient temperature, the main benefit of this system is the ability to standardize the temperature inside your vehicle to provide you with better drive comfort. Once the temperature is set, your regulator would then proceed to monitor and adjust the internal temperature through the climate control system, that would define how best to maintain the current environment within the car to give you the best possible comfort levels. Before cars used the auto climate control system, your cooling system could only be activated by manually triggering the air-conditioning system. And you would have to manually adjust the temperature as well in accordance to what you need, something that has changed completely with the introduction of the auto climate control system. This system has undoubtedly increased the comfort levels of vehicle users without the hassle of having to
manually adjust your cooling system from time to time.
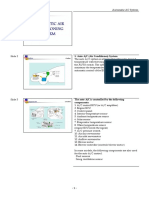
Operation Component
1. Automatic climate control unit
2. Indoor temperature sensor 3. Solar sensor 4. Outside temperature indication ACC I - Sensor located on blower motor housing ACC II - Temperature signal received from ECU
5. Rear door fans 6. Rear window heater 7. Outside mirror heaters
8. Mixed air temperature sensor 9. Air distribution motor 10. 11. 12. Temperature control motor Recirculation motor Ventilation fan motor
Inputs components
The temperature indication signals from the indoor and mixed air temperature sensors are DC signals proportional to temperature. Power is sent to the indoor temperature sensor for a small fan which moves air through the sensor. On ACC I the outside temperature signal is calculated via voltage drop across a PTC resistor mounted on the main blower motor housing. On ACC II, the solar sensor input is also an output since it is a serial data link providing 2-way communication between the microprocessors used in the solar sensor and ACC unit. On ACC II the ECU processes a signal from the sensor mounted below the front bumper, converts it to digital pulses and transmits it to the ACC. The battery supply provides the main power for the unit and the +54 ignition supply is used to switch on the unit.
The rheostat supply is used for the push button lamps and during darker conditions also supplies the LED indicators. Output components
The AC output and the output to the rear window and mirror heater are 12V signals to operate relays. On ACC II, the Intelligent Saab tester (ISAT) output and input provides the communication between the ACC and ISAT microprocessors. The remaining outputs are all motor drives as follows: a. Ventilation fan: Variable 0 to 5V DC signal to the fan speed controller. The fan feedback signal is a 1 to 12V DC signal proportional to the speed of the fan. b. Air recirculation flap: Reversible constant speed DC drive.
c. Temperature control flap:
ACC I - Reversible DC motor with a built in variable resistor to feedback door position information to the ECU ACC II - A pulsed power signal to operate the stepper motors. By counting the number of pulses the ECU can determine flap position.
d. Air distribution flap:
ACC I - Reversible DC motor with a built in variable resistor to feedback door position information to the ECU
ACC II - A pulsed power signal to operate the stepper motors. By counting the number of pulses the ECU can determine flap position.
e. Rear door fans:
ACC 2 - Variable voltage supply from 7-11 VDC proportional to cabin blower speed ACC 1 - Not controlled by ACC, two speed rocker switch on the console.
Wiring diagram
No 1 2 3 4 5 6
PCM A/C relay Refrigerant pressure switch Magnetic clutch Climate control unit A/C amplifier/thermoswitch
No 7 8 9 10 11
A/C switch Fan switch Blower resistor Blower motor Blower relay
Advantages of Auto climate control 1. Increases comfort of occupants by allowing the perfect in-car temperature to be selected and maintained. 2. Improved screen and window visibility, especially during winter, when the external climate is damp, air conditioning works in conjunction with the heating system to provide rapid and continued demisting of the windows. 3. Prevents drowsiness and enhances driver awareness, allowing the driver to stay alert and fresh. 4. Protects from pollution, smog and traffic fumes. 5. Constantly filters air-borne pollutants like pollen and dust from entering the car. 6. By allowing car windows to be kept closed, the car's aerodynamics remains unaltered, lowering external noise and increasing passenger safety and comfort. 7. Enjoy warmth without stuffiness in winter. 8. Clean fresh air even in the heaviest traffic. 9. Remain cool, calm and collected regardless of the external temperature or humidity. Disadvantages of Auto climate control system 1. Cost higher than conventional air conditioning system 2. Complicated wiring, switches and components. 3. Higher maintenance since using more components and switches.
4. Very occasionally used in permanent hot climate region, so the
implement of auto climate control system in vehicles would be irrelevant.
Conclusion The advancement of the auto climate control system has now reached such heights that you now have zone-based climate control system available. This means that each passenger or occupant in the car would have the ability to adjust the temperature of each seating area individually. This is made possible by the separate climate control sensors that are located within each individual area. For the record a central computing unit would monitor and control factors such as fan speed, air compressor engagement, air temperature and other related factors of the system. To conclude, the arrival of the auto climate control system for your vehicle is indeed something that is beneficial in terms of comfort while you drive!
Reference
1. SAAB ACC system e-book
2. Mazda 6 ACC wiring diagram 3. Yahoo! Answer
You might also like
- Practical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneFrom EverandPractical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneNo ratings yet
- ACC - Automatic Climate ControlDocument18 pagesACC - Automatic Climate ControlDmitrij BelovNo ratings yet
- Full Report Control EngineeringDocument14 pagesFull Report Control EngineeringJoshua ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- Practical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part TwoFrom EverandPractical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part TwoNo ratings yet
- Infotronics Answer KeyDocument14 pagesInfotronics Answer Keydhruv royNo ratings yet
- Automotive Electronic Diagnostics (Course 2)From EverandAutomotive Electronic Diagnostics (Course 2)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- SSP 271 PDFDocument76 pagesSSP 271 PDFDaniel TrutaNo ratings yet
- SSP 271 Phaeton Heating & ACDocument76 pagesSSP 271 Phaeton Heating & ACภูเก็ต เป็นเกาะNo ratings yet
- Engine Vehicle Management SystemsDocument92 pagesEngine Vehicle Management Systemsprabahar jeevanandamNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15From EverandIntroduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15No ratings yet
- Automatic Ventilation SystemDocument69 pagesAutomatic Ventilation SystemGurram SaiTejaNo ratings yet
- Specific Features of IoT Electric FanDocument1 pageSpecific Features of IoT Electric Fansoteriovincent941No ratings yet
- SSP 25 Octavia ClimatronicDocument42 pagesSSP 25 Octavia Climatronicahmedsalehawad100% (1)
- Automotive Air Conditioning SystemsDocument14 pagesAutomotive Air Conditioning SystemsBekalu DanielNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of The Automotive Cabin Climate Control SystemDocument6 pagesFundamentals of The Automotive Cabin Climate Control SystemSeddik MaarfiNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning System For Your CarDocument9 pagesAir Conditioning System For Your CarSanjeev GuptaNo ratings yet
- 20 Comfort and convenience technologyDocument22 pages20 Comfort and convenience technologyjovopavlovicNo ratings yet
- Agco Challenger Hvac Automatic Temperature Control User's Guide (Rev. C) R-9787-4 Rev.A (Agco 536450D1)Document21 pagesAgco Challenger Hvac Automatic Temperature Control User's Guide (Rev. C) R-9787-4 Rev.A (Agco 536450D1)nunyaNo ratings yet
- Hybrid 12Document22 pagesHybrid 12squishbug100% (1)
- Chapter 2 How Organizations Use ICT 1Document27 pagesChapter 2 How Organizations Use ICT 1Arpan JhaNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Electronic Control Terms 3126Document5 pagesGlossary of Electronic Control Terms 3126GerardoNo ratings yet
- Sensata Cabin Comfort PDFDocument12 pagesSensata Cabin Comfort PDFhaiderNo ratings yet
- VW Climatronic Codes Service EngDocument24 pagesVW Climatronic Codes Service Engmegatron_vf50% (2)
- Engine Cooling FanDocument4 pagesEngine Cooling FanGrizono MassimoNo ratings yet
- Automotive temperature sensing trends and applicationsDocument8 pagesAutomotive temperature sensing trends and applicationsvkmsNo ratings yet
- Suzuki F6a Engine ManualDocument202 pagesSuzuki F6a Engine ManualJongardsOllirum70% (20)
- Mechatronics Case StudyDocument7 pagesMechatronics Case Studyyogeesh_sharmaNo ratings yet
- AutoSpeed - Electronic Engine Management, Part 1 PDFDocument7 pagesAutoSpeed - Electronic Engine Management, Part 1 PDFamsouyioltzisNo ratings yet
- Engine Management MechatronicsDocument18 pagesEngine Management MechatronicsTanuj Kumar67% (3)
- HVAC System For Cars and Automotive Vehicles - USDocument96 pagesHVAC System For Cars and Automotive Vehicles - USnwg6ssdm8rNo ratings yet
- ECU Designing and Testing Using National Instruments ProductsDocument7 pagesECU Designing and Testing Using National Instruments ProductsTYu4443No ratings yet
- OBD-InsightsDocument52 pagesOBD-Insightsjayasundar100% (1)
- Data Acquisition System For A Formula SAE Race CarDocument43 pagesData Acquisition System For A Formula SAE Race CarRodrigo Bob100% (1)
- BMW E39 Integrated Automatic Heating and Air ConditioningDocument24 pagesBMW E39 Integrated Automatic Heating and Air ConditioningMario Tasev100% (8)
- Auto AppDocument8 pagesAuto Appmarran almarranyNo ratings yet
- TBMC12Document10 pagesTBMC12Joel E ValenciaNo ratings yet
- ECU Controls Engine FunctionsDocument1 pageECU Controls Engine FunctionsemmanueljosephNo ratings yet
- Electronically Controlled Diesel EngineDocument50 pagesElectronically Controlled Diesel EngineVictorIjadunminiyi100% (2)
- Introduction To Control SystemDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Control SystemSaurabh Chandra MishraNo ratings yet
- E60 AC SystemDocument57 pagesE60 AC Systemmmitev100% (9)
- 2013 EPA Compliant Trailer FTF HandbookDocument56 pages2013 EPA Compliant Trailer FTF HandbookJuan Miguel Marin Quintero100% (1)
- CH 06Document18 pagesCH 06Abdul Shokor Abd TalibNo ratings yet
- Edc System For Bs III - Bs IVDocument55 pagesEdc System For Bs III - Bs IVAparnesh Mukhopadhyay85% (170)
- Tizzy SeminarDocument12 pagesTizzy SeminarToheebdareNo ratings yet
- Tizzy SeminarDocument12 pagesTizzy SeminarToheebdareNo ratings yet
- MSA5T0123A27477Document1 pageMSA5T0123A27477Razvan MateiNo ratings yet
- Auto A/C (Air Conditioner) SystemDocument10 pagesAuto A/C (Air Conditioner) SystemDidy RobotIncorporatedNo ratings yet
- VIVAX Cool 2014 PDFDocument36 pagesVIVAX Cool 2014 PDFFeritFazliu100% (1)
- Class Notes - As Unit 3Document4 pagesClass Notes - As Unit 3aqsaleemNo ratings yet
- Climate Control System Description Ford Fiesta 1.6Document10 pagesClimate Control System Description Ford Fiesta 1.6Ismael LopezNo ratings yet
- TodayDocument3 pagesTodayCalixto AnayaNo ratings yet
- Solutions Book Activity 6.1 To 6.7Document11 pagesSolutions Book Activity 6.1 To 6.7mooNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Cooling System Automotive Air Conditioning ExperimentDocument10 pagesVehicle Cooling System Automotive Air Conditioning Experimentcfellow100% (1)
- Servomechanism Presentation MCS 1Document38 pagesServomechanism Presentation MCS 1Vipin Ramachandran PillaiNo ratings yet
- P 996 Air Conditioning DiagnosticsDocument2 pagesP 996 Air Conditioning DiagnosticsRune SteenNo ratings yet
- Control EngineeringDocument7 pagesControl Engineeringuet158No ratings yet
- Sandip Foundation Ksou ProspectDocument33 pagesSandip Foundation Ksou ProspectKannan SNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal - Haseeb - DSPDocument2 pagesResearch Proposal - Haseeb - DSPAhsan Altaf100% (1)
- Data Com HW3 MaykieDocument2 pagesData Com HW3 MaykieMaykie W.A.100% (1)
- Servo 11 2006Document84 pagesServo 11 2006xdroneNo ratings yet
- Design, Simulation and Implementation of An Adaptive Controller On Base of Artificial Neural Networks For A Resonant DC-DC ConverterDocument4 pagesDesign, Simulation and Implementation of An Adaptive Controller On Base of Artificial Neural Networks For A Resonant DC-DC Converterbacuoc.nguyen356No ratings yet
- Motivation LetterDocument2 pagesMotivation Letterbin100% (1)
- ECE Catalogue PDFDocument26 pagesECE Catalogue PDFssn100% (1)
- DSP Lab PDF 16252Document8 pagesDSP Lab PDF 16252awdfasdNo ratings yet
- 14044129-Canon Inner Finisher-B1 Inner Finisher Additional Tray-B1 Service ManualDocument100 pages14044129-Canon Inner Finisher-B1 Inner Finisher Additional Tray-B1 Service Manualvisual619100% (1)
- RCVRDocument20 pagesRCVRybas61No ratings yet
- Kenwood TK-7102 (Manual de Servicio)Document39 pagesKenwood TK-7102 (Manual de Servicio)henry3783No ratings yet
- Elements of Measurement SystemDocument13 pagesElements of Measurement SystemashishNo ratings yet
- LPBDocument6 pagesLPBalbertoNo ratings yet
- 3.power Quality Assessment Via Wavelet Transform AnalysisDocument7 pages3.power Quality Assessment Via Wavelet Transform AnalysisswatisamadhiyaNo ratings yet
- All Digital Timing Recovery and FPGA Implementation: Daniel Cárdenas, Germán ArévaloDocument6 pagesAll Digital Timing Recovery and FPGA Implementation: Daniel Cárdenas, Germán Arévalom0hmdNo ratings yet
- ProductDocument12 pagesProductPero14No ratings yet
- Readme File For Code ExampleDocument12 pagesReadme File For Code ExamplejulionbaNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Noise CancellingDocument26 pagesAdaptive Noise CancellingTütü ÖmariNo ratings yet
- Data Acquisition Catalog enDocument17 pagesData Acquisition Catalog enmsureNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Logic Control For Single Phase Multilevel InverterDocument6 pagesFuzzy Logic Control For Single Phase Multilevel InverterMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- SpaceWire PLFWI-0907 PDFDocument2 pagesSpaceWire PLFWI-0907 PDFCem OzkaptanNo ratings yet
- IAP10, IGP10, IAP20, IGP20 Pressure TransmitterDocument40 pagesIAP10, IGP10, IAP20, IGP20 Pressure TransmitterTefa SernaNo ratings yet
- 115 AllDocument8 pages115 Alljob_openings4094No ratings yet
- Temas WebDocument111 pagesTemas WebvillanucaminoNo ratings yet
- Extras: Simulink Basics Tutorial Block LibrariesDocument21 pagesExtras: Simulink Basics Tutorial Block LibrariesRaihan Fikri RoslanNo ratings yet
- M.SC - in Mechanical EngineeringDocument41 pagesM.SC - in Mechanical EngineeringIslam FattouhNo ratings yet
- Studying Digital Signal Processing On Arduino Based PlatformDocument6 pagesStudying Digital Signal Processing On Arduino Based Platformstephen562001No ratings yet
- Service Manual Prs145Document48 pagesService Manual Prs145Angel DlsgNo ratings yet
- EEE121 - Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument13 pagesEEE121 - Electric Circuit Analysisrizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- Applications of DSPDocument11 pagesApplications of DSPRajkeen ChamanshaikhNo ratings yet