Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Safety Zone Classification
Uploaded by
rajeshdubey7Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Safety Zone Classification
Uploaded by
rajeshdubey7Copyright:
Available Formats
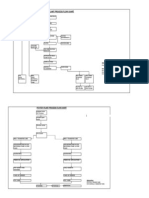
Divisions or zones (gases, vapors and dust.
)
In an industrial plant such as a refinery or chemical process plant, handling of large quantities of flammable liquids and gases creates a risk of leaks. In some cases the gas, ignitable vapor or dust is present all the time or for long periods. Other areas would have a dangerous concentration of flammable substances only during process upsets, equipment deterioration between maintenance periods, or during an incident. Refineries and chemical plants are then divided into areas of risk of release of gas, vapor or dust known as divisions or zones. The process of determining the type and size of these hazardous areas is called area classification. Guidance on assessing the extent of the hazard is given in the NFPA 497 Standard, or API 500 and according to their adaptation by other areas gas zones is given in the current edition of IEC 60079.10. For hazardous dusts, the guiding standard is IEC 61421.10. Typical gas hazards are from hydrocarbon compounds, but hydrogen and ammonia are common industrial gases that are flammable. Safe area An area such as a residence or office would be classed as safe area, where the only risk of a release of explosive or flammable gas would be such things as the propellant in an aerosol spray. The only explosive or flammable liquid would be paint and brush cleaner. These are classed as very low risk of causing an explosion and are more of a fire risk (although gas explosions in residential buildings do occur). Safe area on chemical and other plant are present where the hazardous gas is diluted to a concentration below 25% of its lower flammability limit (or lower explosive limit (LEL)). Division 2 or Zone 2 area This is a step up from the safe area. In this zone the gas, vapor or mist would only be present under abnormal conditions (most often leaks under abnormal conditions). As a general guide for Zone 2, unwanted substances should only be present under 10 hours/year or 00.1% of the time[2]. Division 1 or Zone 1 area Gas, vapor or mist will be present or expected to be present for long periods of time under normal operating conditions. As a guide for Zone 1, this can be defined as 101000 hours/year or 0.110% of the time. Zone 0 area Gas or vapor is present all of the time. An example of this would be the vapor space above the liquid in the top of a tank or drum. The ANSI/NEC classification method consider this environment a Division 1 area. As a guide for Zone 0, this can be defined as over 1000 hours/year or >10% of the time.
You might also like
- Dust Explosion and Fire Prevention Handbook: A Guide to Good Industry PracticesFrom EverandDust Explosion and Fire Prevention Handbook: A Guide to Good Industry PracticesNo ratings yet
- Sis & SilDocument65 pagesSis & SilGecNo ratings yet
- Electrical Equipment in Hazardous Areas - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 pagesElectrical Equipment in Hazardous Areas - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMrNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture and Storage: The Legal Landscape of Climate Change Mitigation TechnologyFrom EverandCarbon Capture and Storage: The Legal Landscape of Climate Change Mitigation TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Equipment in Hazardous AreasDocument10 pagesElectrical Equipment in Hazardous Areasperumal1312No ratings yet
- Gas Sweetening and Processing Field ManualFrom EverandGas Sweetening and Processing Field ManualRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- Hazardous Area Classification - JacobsDocument53 pagesHazardous Area Classification - Jacobskarthikraja21No ratings yet
- Storage Tanks Selection, Design, Testing, Inspection, and Maintenance: Emission Management and Environmental Protection: Emission Management and Environmental ProtectionFrom EverandStorage Tanks Selection, Design, Testing, Inspection, and Maintenance: Emission Management and Environmental Protection: Emission Management and Environmental ProtectionNo ratings yet
- Electrical Equipment in Hazardous AreasDocument7 pagesElectrical Equipment in Hazardous Areasaling alingNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument13 pagesManualkenoly123No ratings yet
- Hazardous Area ClassificationDocument4 pagesHazardous Area ClassificationmkkamarajNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Classification - JacobsDocument53 pagesHazardous Area Classification - JacobsPedro Luis Choque Mamani100% (1)
- 00 Feam Gioi ThieuDocument12 pages00 Feam Gioi ThieuthanhlangdaiNo ratings yet
- Fire ZoneDocument8 pagesFire ZoneKannan NNo ratings yet
- Hac BasicDocument3 pagesHac BasicLuqman OsmanNo ratings yet
- Chap 03Document11 pagesChap 03megahedmNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area PresentationDocument98 pagesHazardous Area PresentationcamspsNo ratings yet
- SA+ Waste-Water Industry Application NoteDocument2 pagesSA+ Waste-Water Industry Application NoteKVRamananNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Classification PDFDocument5 pagesHazardous Area Classification PDFAnna Yunita Sitompul100% (2)
- General Principles For Hazrdous Area ClassificationDocument13 pagesGeneral Principles For Hazrdous Area ClassificationwaheedNo ratings yet
- Confined Safety Entry: NtroductionDocument10 pagesConfined Safety Entry: NtroductionSteve manicsicNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area ClassificationDocument2 pagesHazardous Area ClassificationRatnakar Pai100% (1)
- Hazardous Area ClassificationDocument48 pagesHazardous Area ClassificationRakesh suvarnaNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area ClassificationDocument36 pagesHazardous Area Classificationvenkeeku100% (1)
- API 500 505 PresentationDocument51 pagesAPI 500 505 Presentationtharun venkatNo ratings yet
- 01 Feam Introduzione EngDocument12 pages01 Feam Introduzione EngTh NattapongNo ratings yet
- Electrical Equipment in Hazardous AreasDocument8 pagesElectrical Equipment in Hazardous AreasMehulkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Estellito - Area ClassificationDocument7 pagesEstellito - Area ClassificationRoadieNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Classification & Intrinsic SafetyDocument35 pagesHazardous Area Classification & Intrinsic SafetyMukesh C ChavanNo ratings yet
- Is 5572Document21 pagesIs 5572MD Parthi100% (2)
- Area ClassificationDocument28 pagesArea ClassificationborrowmanaNo ratings yet
- Ha Elec InspectDocument16 pagesHa Elec InspectDebajit BurhagohainNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area ClassificationDocument9 pagesHazardous Area ClassificationyogitatanavadeNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Classification and Control of Ignition SourcesDocument9 pagesHazardous Area Classification and Control of Ignition SourcesKHALID HUBBAHNo ratings yet
- Electrical Area ClassificationDocument10 pagesElectrical Area Classificationlisaparker45No ratings yet
- Hazardous Location LightingDocument4 pagesHazardous Location LightingwahyuNo ratings yet
- Zone Classification: Doc. No. 50068905 Ver.1.0Document23 pagesZone Classification: Doc. No. 50068905 Ver.1.0mkpasha55mp100% (1)
- Electrical Equipment in HazardousDocument17 pagesElectrical Equipment in HazardousZen LohNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Classification and Control of Ignition SourcesDocument10 pagesHazardous Area Classification and Control of Ignition SourcesS.KalatheeswaranNo ratings yet
- Cold Venting As API 521 To Discharge HCDocument4 pagesCold Venting As API 521 To Discharge HCkenoly123100% (1)
- Electrical Safety Week - HAC & EEQ 2022Document62 pagesElectrical Safety Week - HAC & EEQ 2022SanjayNo ratings yet
- Brochure Explosion Protection enDocument45 pagesBrochure Explosion Protection enpramodtryNo ratings yet
- DesignGuide enDocument103 pagesDesignGuide enpptmnltNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Classification and DivisionDocument51 pagesHazardous Area Classification and DivisionK LandryNo ratings yet
- Pocket ManualDocument21 pagesPocket Manualakhilesh_kabra17100% (1)
- Hvac Oil GasDocument8 pagesHvac Oil GasManuelNo ratings yet
- Safety: Terms and DefinitionsDocument8 pagesSafety: Terms and DefinitionsAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Classification of Large Scale PlantsDocument13 pagesHazardous Area Classification of Large Scale PlantsAl Faruq Shinaga100% (2)
- I Ec StandardsDocument4 pagesI Ec StandardsAhmad Adel El TantawyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HacDocument51 pagesIntroduction To HacYuliyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HacDocument51 pagesIntroduction To HacYuliyaNo ratings yet
- At Ex Explosion GuidelinesDocument16 pagesAt Ex Explosion GuidelinesjovanivanNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area Hazardous Area ClassificaDocument106 pagesHazardous Area Hazardous Area ClassificaHedi Ben MohamedNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Area ClassificationDocument63 pagesHazardous Area Classificationhtetwin100% (3)
- AtexDocument60 pagesAtexWendi Junaedi100% (1)
- CA-4079 - Hand Book - 02062018Document49 pagesCA-4079 - Hand Book - 02062018Mohamed RizwanNo ratings yet
- The Technical Times: Heating Equipment in Hazardous (Classified) LocationsDocument4 pagesThe Technical Times: Heating Equipment in Hazardous (Classified) LocationslymacsausarangNo ratings yet
- Appendix 20 Electrical Installation Requirements: Hazardous Area ClassificationsDocument12 pagesAppendix 20 Electrical Installation Requirements: Hazardous Area ClassificationsNaveedNo ratings yet
- Sec13 - Hazardous (Classified) LocationsDocument11 pagesSec13 - Hazardous (Classified) LocationsYusufNo ratings yet
- BurstingDocument3 pagesBurstingrajeshdubey7No ratings yet
- Measurement of Spin Finish On Polyester Filament (NMR) : Calibration and ResultsDocument3 pagesMeasurement of Spin Finish On Polyester Filament (NMR) : Calibration and Resultsrajeshdubey7No ratings yet
- Measurement of Spin Finish On Polyester Filament (NMR) : Calibration and ResultsDocument3 pagesMeasurement of Spin Finish On Polyester Filament (NMR) : Calibration and Resultsrajeshdubey7No ratings yet
- Spin Finish PDFDocument4 pagesSpin Finish PDFrajeshdubey7No ratings yet
- Meditation PDFDocument30 pagesMeditation PDFrajeshdubey7No ratings yet
- Procedure of Filter Element Candle Cleaning - Polyester SoiledDocument4 pagesProcedure of Filter Element Candle Cleaning - Polyester Soiledrajeshdubey7No ratings yet
- Flow Chart Continous Polymerization and Direct Melt SpinningDocument2 pagesFlow Chart Continous Polymerization and Direct Melt Spinningrajeshdubey7100% (1)
- Hvac CalDocument2 pagesHvac Calrajeshdubey7No ratings yet
- Child PsychologyDocument3 pagesChild Psychologyrajeshdubey7No ratings yet
- Savings Assurance PlanDocument1 pageSavings Assurance Planrajeshdubey7No ratings yet
- 60fire SAFETY PreventionDocument23 pages60fire SAFETY PreventionCarlos Roberto Danker100% (1)
- Smart Target and Goal SettingDocument4 pagesSmart Target and Goal Settingrajeshdubey7No ratings yet
- Electron Photon and X RayDocument21 pagesElectron Photon and X RayJuniordr_ZHNo ratings yet
- Kaia Pelkey - Science Fair Research Paper Rough DraftDocument6 pagesKaia Pelkey - Science Fair Research Paper Rough Draftapi-535479836No ratings yet
- GR 4 Science Reviewer - Water & States of MatterDocument2 pagesGR 4 Science Reviewer - Water & States of MatterQuake Garen100% (13)
- s6 Physics p1 BugandaDocument7 pagess6 Physics p1 BugandaWafula EricNo ratings yet
- Valtam DataDocument2 pagesValtam DataSantosh ZunjarNo ratings yet
- GEOTHERMAL POWER PLANT. CastilloxbachillerDocument33 pagesGEOTHERMAL POWER PLANT. CastilloxbachillerCastillo MiraNo ratings yet
- Final Exam in DRRR 2020Document4 pagesFinal Exam in DRRR 2020Ryan San LuisNo ratings yet
- 2004 Physical Geology 1st Exam SampleDocument9 pages2004 Physical Geology 1st Exam SampleShadi GarmaNo ratings yet
- EET416 Problem Set 2 SolutionDocument8 pagesEET416 Problem Set 2 SolutionAbdallah E. Abdallah100% (1)
- AITS Schedule 2023Document2 pagesAITS Schedule 2023Pushpanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- 5G Power Outdoor Series-MTS9304A-HX10A1 (01075308-002) Datasheet 2019101...Document3 pages5G Power Outdoor Series-MTS9304A-HX10A1 (01075308-002) Datasheet 2019101...elesoporte100% (1)
- GC2 Q3 Week-1a-1Document5 pagesGC2 Q3 Week-1a-1Gerrylie GallardoNo ratings yet
- HMTDocument2 pagesHMTKarthiNo ratings yet
- Wind AssesmentDocument16 pagesWind AssesmentMuluken TemesgenNo ratings yet
- Make The Grade As and A2 Chemistry Chemistry Revision Guide Edexcel As A2 Modular Nelson Advanced ScienceDocument147 pagesMake The Grade As and A2 Chemistry Chemistry Revision Guide Edexcel As A2 Modular Nelson Advanced Scienceareyouthere92100% (3)
- .Urp 203 Note 2022 - 1642405559000Document6 pages.Urp 203 Note 2022 - 1642405559000Farouk SalehNo ratings yet
- KRSD CompressorDocument7 pagesKRSD CompressorMohit PanchalNo ratings yet
- Waste Management in The PhilippinesDocument35 pagesWaste Management in The PhilippinesJunKarrenV.CaparosoNo ratings yet
- Remedies Against Natural CalamitiesDocument16 pagesRemedies Against Natural CalamitiesSyed Hamdan100% (1)
- CCS in The Cement IndustryDocument19 pagesCCS in The Cement IndustryJohn Giannakopoulos100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Section 1 OutlineDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Section 1 Outlineapi-263455062No ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument13 pagesThermodynamicssingh.aaradhya2007No ratings yet
- ID167 Valentine Chandra Component 2Document7 pagesID167 Valentine Chandra Component 2Audrey Patricia GunawanNo ratings yet
- Fungi Are Key Players in Extreme Ecosystems: Ecology & EvolutionDocument12 pagesFungi Are Key Players in Extreme Ecosystems: Ecology & Evolutiondanna murilloNo ratings yet
- Toyoshima, Miyahara - 1975 - Catalysis and Coordinative Active Sites On Sulfurated Unsaturation ofDocument7 pagesToyoshima, Miyahara - 1975 - Catalysis and Coordinative Active Sites On Sulfurated Unsaturation ofDOUGLAS RAMON RODRIGUEZ ORDOÑEZNo ratings yet
- Product Fiche: P/NO: MBM38202935 (1411-REV11) Printed in KoreaDocument2 pagesProduct Fiche: P/NO: MBM38202935 (1411-REV11) Printed in KoreaCaraman ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Algae Water Flea Stickleback: ProtoctistsDocument2 pagesAlgae Water Flea Stickleback: Protoctistsghadeer alkhayatNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry NotesDocument7 pagesGeneral Chemistry NotesIrish Angel VicencioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Inorganic Chemistry - Part 1Document5 pagesIntroduction To Inorganic Chemistry - Part 1Mohamad AzaniNo ratings yet
- Q1 - L2-Risk Factors Underlying DisastersDocument15 pagesQ1 - L2-Risk Factors Underlying DisastersJennilyn FelicianoNo ratings yet
- The Design Thinking Playbook: Mindful Digital Transformation of Teams, Products, Services, Businesses and EcosystemsFrom EverandThe Design Thinking Playbook: Mindful Digital Transformation of Teams, Products, Services, Businesses and EcosystemsNo ratings yet
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchFrom EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelFrom EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Articulating Design Decisions: Communicate with Stakeholders, Keep Your Sanity, and Deliver the Best User ExperienceFrom EverandArticulating Design Decisions: Communicate with Stakeholders, Keep Your Sanity, and Deliver the Best User ExperienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- Laws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesFrom EverandLaws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Analog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceFrom EverandAnalog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceNo ratings yet
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataFrom EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- The Art of Welding: Featuring Ryan Friedlinghaus of West Coast CustomsFrom EverandThe Art of Welding: Featuring Ryan Friedlinghaus of West Coast CustomsNo ratings yet
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationFrom EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Lean vs Agile vs Design Thinking: What You Really Need to Know to Build High-Performing Digital Product TeamsFrom EverandLean vs Agile vs Design Thinking: What You Really Need to Know to Build High-Performing Digital Product TeamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Design for How People Think: Using Brain Science to Build Better ProductsFrom EverandDesign for How People Think: Using Brain Science to Build Better ProductsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- The Jobs To Be Done Playbook: Align Your Markets, Organization, and Strategy Around Customer NeedsFrom EverandThe Jobs To Be Done Playbook: Align Your Markets, Organization, and Strategy Around Customer NeedsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Heat Exchanger Design Guide: A Practical Guide for Planning, Selecting and Designing of Shell and Tube ExchangersFrom EverandHeat Exchanger Design Guide: A Practical Guide for Planning, Selecting and Designing of Shell and Tube ExchangersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tFrom EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Understanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveFrom EverandUnderstanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (16)
- The Maker's Field Guide: The Art & Science of Making Anything ImaginableFrom EverandThe Maker's Field Guide: The Art & Science of Making Anything ImaginableNo ratings yet