Professional Documents
Culture Documents
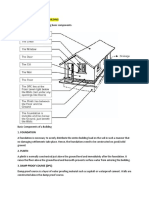
Types of Roofing
Uploaded by
Farrah Ruiz PahimalanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Roofing
Uploaded by
Farrah Ruiz PahimalanCopyright:
Available Formats
Gable Roofing - This type of roofing is the most common ceiling style that you see in most houses.
This has 2 upward slopes meeting at the ridge, the typical proportioned triangle style of roofing. The good thing about gable roofing is that it easily ran off water.
Flat Form - This type of roofing does not have much of a slope. Although some has a slight slope, most are totally horizontal. This type of roofing is layered in trays with joints. This type of roofing is common for some modern westernized designs of homes. Hipped Form - Hipped forms have a trapezoidal side. With four faces, it often have slanted sides and the gutter is fitted all around. Constructing this type of roofing is kind of complex compare to gable and flat forms. But the good side about this is that it evenly distributes the load of the roof to each walls. This type of roofing is all very common in some modern house in the Philippines as these are proven solid, comfortable and more classy.
Architectural Roof Types
Click For Larger View
Some houses have large, prominent roofs; some have virtually no roofline at all. The roofline of your home will influence your selection of roofing materials. There are three basic roof forms: gable, hipped, and shed. More-specialized roof types, such as mansard, gambrel, and flat, are variations of the basic three. Each type displays a different amount of roofing material and exerts a major influence on the appearance of a house. Each roof has a certain pitch the degree of slope in the roof. Pitch is expressed as an equation that describes how many inches the roof rises vertically for every 12 inches of horizontal measurement. A 6-in-12 roof pitch means the roof rises 6 inches for every 12 inches of horizontal span. A 12-in-12 roof rises 12 inches for every horizontal foot. If you draw a 12-in-12 roofline on paper, youll see the roof is at a 45-degree angle a very steep roof indeed. Pitch affects the appearance of a home and helps determine the types of roofing materials that may be used. In general, the flatter the pitch, the more specialized the roofing materials must be. Most common roofing materials are not recommended for roofs with a pitch of less than 3-in-12, because water does not fall off quickly and the possibility exists that wind will force rain or melted snow up under the bottoms of the shingles. Nearly flat and completely horizontal rooftops (such as those on mansards) are best protected by a continuous, seamless membrane.
Detail Engineering Design Structure Type Roof Architecture
Standard procedure before build roof structure must be defined and planning on Detail Engineering Design (DED) what roof type that will be chosen to cover top of the house. There is so many roof type and roof architecture which can be use todesign house roof. Roof architecture, roof shapes, and roof tile or slates type that used for roof design has greatest influence on the appearance and effect of the house or building as a whole. Basically roof type was grouped as: Hip Roof: A type of roof structure containing sloping planes of the same pitch on each of four sides without gables. Gable Roof: Roof type structure containing sloping planes of the same pitch on each side of the ridge, a gable roof typically contains a gable at each end. Gable: The upper portion of a sidewall that comes to a triangular point at the ridge of a sloping roof. Dutch Gable: Is a combination of a Hip roof with a small Gable at the top and a sloping roof below. Gambrel roof: roof type containing two sloping planes of different pitch on each side of the ridge. The lower plane has a steeper slope than the upper. A gambrel roof usually contains a gable at each end, just like a standard gable roof.
Skillion Roof: A Skillion Roof slopes from one side of the building to the other in a single span and no ridge. As a result the external walls are of varying heights. Lean-to Roof: A roof with one slope only that is built against a higher wall. Mansard roof: A type of roof containing two sloping planes of different pitch on each of four sides. The lower plane has a much steeper pitch than the upper, often approaching vertical. It contains no Gables. Jerkinhead Roof: Consists of a Gable Roof with a truncated Hip Roof section atthe top to reduce the height of the Gable. Gazebo Roof: usually roof type with Often Hexagonal or Octagonal but frequently symmetrical in their design. After structure and function have been taken into roof type choice, DetailEngineering Design of the roof may be modified by other considerations, such asweathering and aesthetics. Roof structural frame or truss must be designed according to standard roofing construction to ensure safety the occupant. Truss frame can be build from any materials such as wood, weight steel, light steel, or combination wood and steel. Here we have some examples pictures of the variety roof shape, roof type, and truss type which can be used to design a roof, but actually there is so many more combinations are possible which not include in this roof example.
You might also like
- Types of RoofDocument37 pagesTypes of RoofBRAIN OF AN ARCHITECT100% (1)
- Types of Roof For TLEDocument31 pagesTypes of Roof For TLEJenmarie Hermoso DullenteNo ratings yet
- 21 Different Types of Light FixturesDocument51 pages21 Different Types of Light FixturesVictor Rosales100% (1)
- 1 Building Const 2Document89 pages1 Building Const 2Iyan Kenet HerodicoNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 - Doors and WindowDocument45 pagesLecture - 3 - Doors and WindowGanesh.Rajan100% (2)
- Construction Tools and Their UsesDocument20 pagesConstruction Tools and Their UsesMarsheil Bawaan80% (5)
- Structural Engineering Building Construction Part IDocument55 pagesStructural Engineering Building Construction Part IHung Leung Sang EddyNo ratings yet
- Construction Technology Diploma 3rd SemDocument19 pagesConstruction Technology Diploma 3rd SemToby My GantzNo ratings yet
- Fabricate and Install Wooden CABINETDocument30 pagesFabricate and Install Wooden CABINETsam jeaNo ratings yet
- RoofDocument55 pagesRoofRosele LabarreteNo ratings yet
- Types of Glass FinishesDocument24 pagesTypes of Glass FinishesHitesh MalekarNo ratings yet
- Brochure Architectural Collection A e Series Window Door 9064702Document68 pagesBrochure Architectural Collection A e Series Window Door 9064702Alejandra100% (1)
- Plumbing Tools: Professor: Arch. Flynn B. Arana, Uap, RMPDocument12 pagesPlumbing Tools: Professor: Arch. Flynn B. Arana, Uap, RMPMherlieNo ratings yet
- Different Types of WoodDocument1 pageDifferent Types of WoodJessAntonioNo ratings yet
- Design ControlDocument59 pagesDesign ControlAldrin SerranoNo ratings yet
- 01 AutoCAD Intoduction and The AutoCAD InterfaceDocument10 pages01 AutoCAD Intoduction and The AutoCAD InterfaceErline Grace E. DatocNo ratings yet
- Terms Used in RoofDocument2 pagesTerms Used in Roofrahul_5587_265238786No ratings yet
- 04 MasonryDocument34 pages04 MasonrySajay PajarillagaNo ratings yet
- Drafting Foundation PlanDocument24 pagesDrafting Foundation Planerol bancoroNo ratings yet
- Types and Materials Used For FormworkDocument17 pagesTypes and Materials Used For FormworkAshrutha Harshini100% (1)
- Make A Plaid Cutting Board: InstructablesDocument8 pagesMake A Plaid Cutting Board: InstructablesRod Hyatt100% (1)
- Cement Lining Specs EilDocument15 pagesCement Lining Specs EilstegenNo ratings yet
- Types of StairsDocument46 pagesTypes of Stairsplayquiditch100% (1)
- PD 1096 - The National Building Code of The Philippines: Prepared By: Cristobal TardoDocument47 pagesPD 1096 - The National Building Code of The Philippines: Prepared By: Cristobal Tardoanon_2765746230% (1)
- Roof CoveringDocument30 pagesRoof CoveringDipal ParakhNo ratings yet
- Roofing Plans PDFDocument18 pagesRoofing Plans PDFAilyn TanNo ratings yet
- Foundation PlanDocument62 pagesFoundation PlanLhen Mediante AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Defects of TimberDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Defects of TimberKrishnaSah0% (1)
- Construction ToolsDocument43 pagesConstruction ToolsThe Truth. IndNo ratings yet
- Condominium GuidelinesDocument12 pagesCondominium GuidelinesJem GarciaNo ratings yet
- 19 Parts of A Roof On A House and Types of RoofDocument41 pages19 Parts of A Roof On A House and Types of RoofCaryl Louise ObcianaNo ratings yet
- DK CHING SUMMARY NOTES - Building Construction IllustratedDocument70 pagesDK CHING SUMMARY NOTES - Building Construction IllustratedManny InocencioNo ratings yet
- Architectural SymbolsDocument17 pagesArchitectural Symbolsjovan kusumaNo ratings yet
- Agreement For The Renovation of Guiguinto Store: Know All Men by This PresentsDocument2 pagesAgreement For The Renovation of Guiguinto Store: Know All Men by This PresentsluckyNo ratings yet
- Building TechnologyDocument96 pagesBuilding Technologynickdash09100% (1)
- Walls Structure Walls StructureDocument32 pagesWalls Structure Walls StructureNor Alia Shafia100% (1)
- Angles, Slope or PitchDocument12 pagesAngles, Slope or PitchReyamrk RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety and Fire Protection Engineering: Philippine Society of Mechanical Engineers, IncDocument116 pagesFire Safety and Fire Protection Engineering: Philippine Society of Mechanical Engineers, IncLister NambatacNo ratings yet
- Basic Components of A BuildingDocument13 pagesBasic Components of A Buildingkhim zukami100% (1)
- B TschumiDocument63 pagesB TschumiHarshita MittalNo ratings yet
- Parts of The BuildingDocument16 pagesParts of The BuildingAkshaya Dheer MadugulaNo ratings yet
- Composites India Expo 2012Document5 pagesComposites India Expo 2012Swati SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Roof CoveringDocument39 pagesCH 9 Roof CoveringEyoatem TeferiNo ratings yet
- Masonry ToolsDocument6 pagesMasonry ToolsJade Marielle DugeniaNo ratings yet
- Types of WindowDocument30 pagesTypes of WindowRod AquinoNo ratings yet
- Building Construction Lecture Note.Document31 pagesBuilding Construction Lecture Note.Umar Bello NuhuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 RoofingDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Roofingrichard.peterson100% (1)
- Roofing Materials 1Document53 pagesRoofing Materials 1Melvin QuidongNo ratings yet
- Openings in WallsDocument18 pagesOpenings in WallsCaroline Mugure50% (2)
- Layers of A Floor - Anatomy, and Parts (Illustrated)Document8 pagesLayers of A Floor - Anatomy, and Parts (Illustrated)Melaine A. FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Roof Types1Document34 pagesRoof Types1Shah Swara100% (1)
- Wall FinishesDocument21 pagesWall FinisheslavekushNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - Glass and Glazing PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 24 - Glass and Glazing PDFpokemonNo ratings yet
- Finishing Materials PDFDocument40 pagesFinishing Materials PDFEdon PiperkuNo ratings yet
- 08 - Lecture 08 - Building Materials and Construction IIDocument30 pages08 - Lecture 08 - Building Materials and Construction IIYohans EjiguNo ratings yet
- SNT MRDocument35 pagesSNT MRElla DasigNo ratings yet
- I. Module 1 Title: Glass and Glazing Building TechnologyDocument9 pagesI. Module 1 Title: Glass and Glazing Building Technologydee jayNo ratings yet
- Ale Building Technology and MaterialsDocument2 pagesAle Building Technology and MaterialsiloilocityNo ratings yet
- April 2005 BLDG Cons T 1Document55 pagesApril 2005 BLDG Cons T 1Rabbit Preacher100% (1)
- Technical CAPS Civil Technology With SpecialisationDocument122 pagesTechnical CAPS Civil Technology With SpecialisationqanaqNo ratings yet
- Soil Erosion Solutions Case StudiesDocument20 pagesSoil Erosion Solutions Case StudiesMaribel Bonite PeneyraNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities IIDocument9 pagesBuilding Utilities IILeonard MalateNo ratings yet
- ABE Lecture 2Document40 pagesABE Lecture 2Lineth DomingoNo ratings yet
- Finishing CarpentryDocument25 pagesFinishing CarpentryKevin Fernandez MendioroNo ratings yet
- Upper FloorsDocument31 pagesUpper FloorsAnySika100% (1)
- Floor and Roof Connections To Masonry WallsDocument4 pagesFloor and Roof Connections To Masonry WallsChris FindlayNo ratings yet
- Different Types of RoofsDocument6 pagesDifferent Types of RoofsSanderNo ratings yet
- Structures 2B - Lecture Notes 03 - Roof and Skylight TypesDocument34 pagesStructures 2B - Lecture Notes 03 - Roof and Skylight TypesLawrence OgunsanyaNo ratings yet
- Knauf Moisture Resistant Gypsum BoardsDocument2 pagesKnauf Moisture Resistant Gypsum Boardssr2011glassNo ratings yet
- Uck Id Case Study 1 Sem4Document14 pagesUck Id Case Study 1 Sem4Utkarsha KolheNo ratings yet
- Aquaponic ModelDocument9 pagesAquaponic ModelSalfate ProductoresNo ratings yet
- Shaker Broom ViseDocument4 pagesShaker Broom Visejohnjohanson11No ratings yet
- BXUV7.GuideInfo - Fire-Resistance Ratings - CAN - ULC-S101 Certified For Canada - UL Product IqDocument2 pagesBXUV7.GuideInfo - Fire-Resistance Ratings - CAN - ULC-S101 Certified For Canada - UL Product IqEmanuel Ciprian CiucurNo ratings yet
- War Butuan 15Document4 pagesWar Butuan 15MilesNo ratings yet
- Zaha HadiddDocument25 pagesZaha Hadiddheygirlhey100% (1)
- D Eugp1 TPT G 000 Gen FWG 001 R01Document1 pageD Eugp1 TPT G 000 Gen FWG 001 R01debapriyoNo ratings yet
- Window Sizes HOutDocument11 pagesWindow Sizes HOutAustine MakateNo ratings yet
- BAND 675 North RD - Mechanical IFC - 2023-11-15Document162 pagesBAND 675 North RD - Mechanical IFC - 2023-11-15Hakar Qadir GardiNo ratings yet
- Roofing Terminology: S&K Roofing, Siding and Windows Aims To Be Your Roofing Resource in MD & VADocument2 pagesRoofing Terminology: S&K Roofing, Siding and Windows Aims To Be Your Roofing Resource in MD & VAOnuoha ChiemezieNo ratings yet
- Basement Cost CalculatorDocument19 pagesBasement Cost CalculatorBrian MenzieNo ratings yet
- M3 Fender Attachment BracketsDocument14 pagesM3 Fender Attachment BracketsĐông NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 50-0RG2N-DD-021 Data Sheet For Ad-306001 (Bit)Document3 pages50-0RG2N-DD-021 Data Sheet For Ad-306001 (Bit)RajaramNo ratings yet
- BW - Plan Booklet - VTP Bellissimo - 2022-05-10Document37 pagesBW - Plan Booklet - VTP Bellissimo - 2022-05-10Ninad KhandagaleNo ratings yet
- Metro System in India: (Elevated Rail Corridor Civil Works)Document41 pagesMetro System in India: (Elevated Rail Corridor Civil Works)Ajinkya MahajanNo ratings yet
- DR - Majid Albana SCHOOL CONSTRUCSION - 1Document11 pagesDR - Majid Albana SCHOOL CONSTRUCSION - 1ALINo ratings yet
- Slips and Trips Mapping Tool: An Aid For Safety RepresentativesDocument4 pagesSlips and Trips Mapping Tool: An Aid For Safety RepresentativesIoana UrsanNo ratings yet
- Papier MacheDocument10 pagesPapier MacheKiraNo ratings yet
- Alccocrete (HS)Document2 pagesAlccocrete (HS)Siddhesh Kamat MhamaiNo ratings yet
- Silverado 2008 - Plastic PanelsDocument7 pagesSilverado 2008 - Plastic PanelsBaltazar DiazNo ratings yet
- Hilti HIT HY70 Injection Mortar For Masonry PDFDocument26 pagesHilti HIT HY70 Injection Mortar For Masonry PDFfkh3dNo ratings yet