Professional Documents
Culture Documents
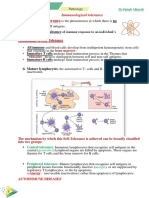
Immunology Mscbi-1 Preuniversity Examination: Part A
Uploaded by
Dipankar RotOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Immunology Mscbi-1 Preuniversity Examination: Part A
Uploaded by
Dipankar RotCopyright:
Available Formats
Immunology MScBI-1 PreUniversity Examination
Dated: 23.01.09. PART A: 1. Epitope is situated in ______. A. Antibody B. MHC complex. C. Antigen surface. D. In association with Hapten. Ans: C 2. Memory B cells and Plasma cells are associated with _______. A. Innate Immunity. B. Humoral Immunity. C. B lymphocyte. D. Both B. and C. Ans: D 3. All living organisms are naturally gifted with an ability to resist the invasion of any kind of foreign materials, and this natural mechanism is known as ________. A. Acquired immunity. B. Innate immunity. C. Natural immunity. D. Both B and C. Ans: D 4. Foreign entity is associated with the following specific immunological activity ________. A. Autoimmunity. B. Non-self immunity. C. Non-self recognition. D. Both B and C. Ans: D 5. _______ recognizes changes on virus-infected cells and destroy them by an extracellular killing mechanism. A. Plasma cells.
B. Helper cells. C. Natural killer cells D. Memory cells. Ans: C. 6. Opsonization is a process associated with ----------A. Phagocytosis involving coating of microorganism with C3b. B. Pinocytosis. C. Both a. and b. D. Recognition of the antigen presented by microorganism. Ans: A 7. Natural killer (NK) cells are associated with the releasing of _______ molecules. A. toxin B. toxic C. cytotoxic D. pus Ans: C 8. A specific component (C3b) formed during the process of activation of complement system, facilitate the phagocytic uptake of target materials by macrophages and neutrophils a phenomenon known as __________. A. Interferons. B. Acute phase proteins. C. Complement. D. Opsonophagocytosis. Ans: D. 9. Another name for an antigenic determinant is ______ A. Paratope B. Carriers C. Epitope D. Antigen Ans: C. 10.The sites in or on antigens with which antibodies react are called. A. Haplotypes B. Isotypes C. Epitopes D. Idiotypes Ans: C. 11._________ are produced in the red bone marrow by the process of hematopoiesis.
A. B. C. D.
Lymphocytes Plasma cells Cytokine cells Memory B cells.
Ans: A 12.______ is active mostly against the invaded bacteria, bacterial toxins and viruses. A. cell-mediated immunity B. antibody-mediated humoral immune response. C. Antigen-presenting cells. D. Phagocytic cells. Ans: B. 13.The rapid rise, elevated level, and prolonged production of antibody that follows a second exposure to antigen is known as the A. Delayed hypersensitivity reaction. B. Autoimmune response C. Anamnestic response D. Conditioned response. Ans: C. 14.The monokines that is intimately involved in the immune response is ______. A. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) B. IL-2. C. IL-3 D. Macrophage-activating factor (MAF). Ans: A 15.One of the characteristics of the secondary immune response is that it _________ A. is mainly IgM antibody. B. requires a low dose of immunogen for induction. C. has low-affinity antibodies. D. Has a short duration of antibody synthesis. Ans: B. 16. A _______ is a subpopulation of T lymphocyte that aids in presentation of T-dependent antigens. A. T-plasma cells. B. T-memory cells. C. T-helper cell. D. None of the above. Ans: C
18.
17. There are a large number of antigens presenting cells in the body and almost all of them constitutively express __________. A. MHC class I molecule. B. MHC class II molecule. C. Both MHC class I and II molecules. D. None of the above. Ans: B. The antigen presenting cell releases a cytokine which is called----A. Interleukin-2 B. Interleukin-1 C. Interleukin-6 D. None of the above. Ans: B. 19. The basic unit of all immunoglobulins is constructed out of four polypeptides. The two light chains are identical, as are the two heavy chains. Each L chain is attached to an H chain by ________. A. covalent bonds. B. Van der waals attraction. C. dipole-dipole attraction. D. disulfide bridge linking cysteine residues and also by the mutual attraction of some of their hydrophobic amino acids. Ans: D 20 In most classes of antibody molecules, a small region rich in proline is present between _______. A. VH and CH. B. CH1 and CH2 domains of each heavy chain. C. Kappa and lambda. D. None of the above. Ans: B 21. Immunoglobulin, which plays a major role in protecting the surface tissues against infectious microorganisms such as viruses, bacteria, and protozoan parasites by formation of an immune barrier is called _______. A. IgA. B. IgG C. IgM D. IgE Ans: A
22. _______ within an antibody molecule is produced by the complementary determining regions (CDRs) of the light and heavy chains generating a specific three-dimensional shape. A. Hapten. B. MHC complex. C. Paratope. D. None of the above. Ans: C 23. _________ are produced when any light chain join with any heavy chain. A. Different paratopes. B. Epitopes. C. MHC complex. D. Hapten. Ans: A 24. Activated helper T cells secrete gamma interferon (IFN-), which act as an activator of _______. A. Cytokine cells B. Macrophage cells. C. Interleukins. D. Natural killer cells Ans: B. 25. The thymus is a flat bilobed organ situated above the ______. A. Lungs. B. Kidney C. Stomach D. Heart. Ans: D. 26. T cells after entering the thymus they are found to multiply within the _______. A. Medulla B. Cortex. C. Both Cortex and Medulla. D. None of the above. Ans: B. 27. Thymic epithelial cells synthesize a group of thymic hormones, namely _____ A. Thymulin. B. Thymulin, -thymosin, -4 thymosin and thymopoietin. C. -thymosin.
D. thymopoietin Ans: B. 28. Spleen is an ovoid secondary lymphoid organ situated in the ________. A. Liver. B. Brachial artery. C. Left abdominal cavity. D. duodenal region Ans: C. 29. Spleen is an encapsulated structure which is compartmentalised into red pulp and white pulp by the _________. A. trabeculae of outer membrane. B. trabeculae of the capsule. C. trabeculae made up of connective tissue. D. trabeculae separating cortex and medulla. Ans: B. 30. Treatment of the IgG monomer with papain splits it into _____. A. One F(ab)2 fragment and one Fc fragment. B. two Fab fragments and one Fc fragment C. two Fd fragments . D. two Fc fragments. Ans: B. 31. The major antibody in immune globulin is _______. A. IgA B. IgD C. IgE D. IgG Ans: D 32. Immunodeficiency resulting in increased susceptibility to viral and fungal infections is due primarily to a deficiency in ________. A. Macrophage. B. B cells C. T cells D. Neutrophil. Ans: C. 33. All of the following cell types participate in a humoral immune response to a thymus-independent antigen EXCEPT the A. T cell B. B cell C. macrophage.
D. antigen-presenting cell Ans: A 34. Macrophage engage in all of the following activities EXCEPT A. processing antigen. B. production of interleukin-2 (IL-2). C. presenting of antigen. D. Phagocytosis Ans: B 35. Immunoglobulin molecules contain all of the following structures EXCEPT A. Heavy (H) and Light (L) chains. B. Constant (C) domains. C. Variable (V) domains D. J chains Ans: D. 36. ______ are of particular importance in relation to intestinal parasite. A. IgG and IgM B. IgE and IgA C. IgD and IgA D. Ig E and Ig M Ans: B. 37. ____ cross link IgE on the surface of mast cells and cause degranulation followed by attraction of eosinophils. A. Parasite antigens B. Parasite surface molecule. C. Toxin released by parasite. D. Opsonins. Ans: A. 38. Parasitic infection evokes ______ immune responses. A. Humoral-mediated immune response. B. Cell-mediated immune responses C. Both Humoral as well as cell-mediated immune responses. D. None of the above. Ans: C. 39. Trypanosoma cruzi can be killed by _________. A. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity mechanisms B. Macrophage-dependent cell-mediated immune system. C. Platelets D. Tumor necrosis factor. Ans: A.
40. Individuls with sickle cell trait are resistant to ________. A. Filiariais. B. Schistosomiasis C. Malaria. D. Sleeping sickness. Ans: C. 41. Antigens from sites of infection reach lymph nodes via: A. Afferent lymphatic vessels. B. Efferent lymphatic vessels. C. Lymph node arteries. D. Lymph node veins. Ans: A. 42. Which of the following statements regarding epitopes is NOT TRUE? A. An antigen can contain many different epitopes. B. An epitope can be made of a continuous stretch of amino acids. C. A given epitope can be found on different antigens. D. An epitope is always immunogenic. Ans: D 43. Which of the following human immunoglobulin molecules has four heavy chain constant region domains? A. IgM B. IgD C. IgG1 D. IgA Ans: A 44. Which of the following class(es) of immunoglobulin utlilize(s) the J chain in forming multimeric Ig complexes? A. IgD B. IgG C. IgM D. IgE Ans: A
Part B: 45. Which substance helps to activate immune system? i) Antigen. ii) Epitope. iii) Haptens iv) Antigenic determinants. A. Only (i), (ii), and (iv) B. Only (ii), (iii) and (i). C. Only (ii), (iii) and (iv). D. None of the above. Ans: A. 46. When an antigen is introduced into an organism, the degree of its immunogenicity depends on how much greater the phylogenetic distance between two species. If this is true then which of the following are known to exhibit immunogenicity? i) Bovine serum albumin (BSA) when injected into a rabbit. ii) BSA when injected in a goat. iii) BSA when injected in a chicken iv) BSA when injected in Cow. A. Only (ii), (iii), and (iv). B. Only (i), (ii), and (iii). C. Only (iii) and (ii) D. All of the above. Ans: C. 47. _______ are those which soluble in the body fluids. Particulate antigens. Soluble antigens. Exotoxins. Endotoxins. A. (i) B. (i) and (ii). C. (ii) and (iv). D. (ii) and (iii) Ans: D. 48. Most Gram-negative bacteria have lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the outer membrane of their cell wall that is toxic to hosts under certain circumstances. This LPS is called ______. Exotoxins. Endotoxins.
i) ii) iii) iv)
B. C. D.
Toxic proteins. Toxin. A. (ii), (iii) and (iv) (i) and (iii) (ii) and (iv) (ii) Ans: A. 49. The key features of all antigen presenting cells include -----i) their intrinsic ability to ingest and process the antigen to varying extent. ii) To display a selected part of the antigen on cell surface together with MHC class II molecules essential for its presentation to CD4+T-cells. iii) To degrade the ingested antigen. iv) Select an appropriate antigen fragment recognizable by + CD4 T cells for expression on their surface. A. (i) B. (i) and (iv) C. All of them. D. (ii) and (iii). Ans: C. 50. __________ may activate C1 component of the complement without the involvement of antibody or induces conformational changes in the Fc portion of IgM or IgG molecule that expose a binding site for the C1 component of the complement system. (i) Binding of antigen presenting cell with B-lymphocyte. (ii)The complexing of antibody with antigen, (iii) Some microbial products (Lipid A of endotoxin and Staphylococcal protein A) or plasmin (a proteolytic enzyme that dissolves the fibrin of blood clots). (iv) Binding of epitope region of the antigen and paratope region of antibody. A. only (i). B. (iii) and (i). C. (iii), (ii) and (iv) D. (ii) and (iv) Ans: C
51. Antibodies are group of ________. i) Alpha-globulins. ii) Gamma-globulins. iii) Beta-globulins. iv) Glycoproteins. A. only (i) B. (i) and (iii). C. (iii) only D. (ii) and (iv) Ans: D. 52. The complexing of antibody with antigen induces conformation changes in the Fc portion of the IgM or IgG molecule that expose a binding site for the C1 component of the complement system, which in serum is ________. i) C1q sub-component. ii) C1r iii) C1s iv) a molecular complex consisting of C1q and two molecules each of C1r and C1s held together in a complex (C1qr2s2). A. (i) only B. (ii) and (iii) C. (iv) only. D. (i) and (ii) Ans: C 53. Alternative pathway of complement activation involves ______ i) C3. ii) Factor B iii) Factor D iv) Properdin A. (i) only B. (ii) and (iii) C. (iii) and (i) D. (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) Ans: D 54. Which of the following are not involved in phagocytosis? i) Attachment of the bacterium or particulate matter to the long membrane evaginations called pseudopodia. ii) Ingestion of bacterium to form a phagosome.
iii) Bacterium are killed by the some cytotoxic factors. iv) Fusion of phagosome and lysosome forms phagoglysosome and lysosomal enzymes are released into the phagosome. A. only (iii) B. only (i) C. Only (ii) and (iii) D. Only (i), (ii), and (iv). Ans: A. 55. Tissue damage caused by a wound or by an invading pathogen leads to the induction of a complex sequence of events collectively known as the inflammatory response, which shows _____. i) Redness, heat, itching, and pain sensation in some portion of the body. ii) Redness and burning sensation spreaded over wide region of the body. iii) Redness, heat, swelling, pain and loss of function within a localized region. iv) Redness and itching sensation. A. only (i) B. Only (ii) C. Only (iii) D. Only (iv) Ans: C. 56. Monocyte on entering the tissues differentiate into _______. i) Cytotoxic cells ii) Natural killer cells iii) Macrophage cells. iv) Phagocytic cells. A. Only (i) B. Only (ii) and (iii) C. Only (iii) and (iv) D. Only (iii). Ans: C. 57. Effector components of cellular immune system constitute _______. (i) T and B lymphocytes. (ii) Macrophages, mast cells, killer cells, natural killer cells. (iii) Neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. iv) Antigen presenting cells. A. only (i). B. Only (ii) and (iii)
iii) iv)
(iv)
C. All of the above. D. None of the above. Ans: C 58. T cell can attack ______. i) Host cells that have been parasitized by pathogens. ii) Tissue cells that have been transplanted from one host to another. Cancer cells. cell undergoing autoimmunity. A. only (i) and (ii). B. Only (ii) and (iii). C. Only (iii) and (iv) D. Only (i) ,(ii) and (iii). Ans: D. 59. Macrophages releases a number of complement components and cytokines such as _______. (i) Interleukin-1. (ii) Free Radicals (iii) Interferons. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF). A. Only (i) and (ii) B. Only (ii) and (iii) C. Only (i), (iii) and (iv). D. Only (iii) and (iv). Ans: C. 60. Antibodies secreted out by plasma cells are a group of _____ present in the gamma globulin fraction of blood serum, tissue fluids and on the surface of B cells. (i) Glycoproteins. (ii)Lipopolysaccharides. (iii) Sphingosine. (iv) Lipoproteins. A. Only (i) B. Only (ii) C. Only (iii) D. Only (iv). Ans: A. 61. Gamma-interferons are secreted by _______. i) TH cells ii) Tc cells. iii) Both TH and Tc cells.
iv) Interleukins. A. (i) B. (ii) C. (iii) D. None of the above. Ans: A. Part C: 62. Match the following in the Set I with their appropriate match in the Set II: Set I: 1. The CD8+ T-cell kills the target cell. 2. armed T-cell 3. Lymphokine 4. Interferon- Set II: a. kills the target cell by inducing apoptosis. b. Released by TH cells c. Produced by TH cells d. Some of them become memory T-cells. A. 1-a, 2-d, 3-b, 4-c. B. 1-b, 2-a, 3-c, 4-d C. 1-c, 2-b, 3-d, 4-a D. 1-d, 2-c, 3-a, 4-b Ans: A 63. Match the following in the Set I with their appropriate match in the Set II. Set I: 1. Dust cells 2. Histocytes 3. Osteoclasts 4. Kuppfer Set II: a. Liver b. Lung c. Connective tissue d. Bone A. 1-a, 2-d, 3-b, 4-c
B. 1-b, 2-c, 3-d, 4-a C. 1-c, 2-b, 3-a, 4-d D. 1-d, 2-a, 3-c, 4-b Ans: B 64. Match the following in the Set I with their appropriate match in the Set II. Set I: 1. Neutrophil 2. Eosinophil 3. Basophil 4. Mast cell Set II: a. phagocytic granulocyte, which take basic dyes only. b. bears Fc receptor for IgE c. multilobed phagocytic granulocytes, which take both acid and basic dyes d. bilobed phagocytic granulocytes, which are take acid dye only and are capable of migrating from the blood into the tissue spaces. A. 1-b, 2-a, 3-d, 4-c B. 1-d, 2-c, 3-b, 4-a C. 1-c, 2-d, 3-a, 4-b D. 1-a, 2-b, 3-c, 4-d Ans: C.
You might also like
- Immunology Practice QuestionsDocument52 pagesImmunology Practice QuestionsBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Interesting Q&A in Immunology - Part IIIDocument21 pagesInteresting Q&A in Immunology - Part IIIVytheeshwaran Vedagiri100% (14)
- Practice Final Exam 19Document8 pagesPractice Final Exam 19Bira maroNo ratings yet
- Immunology Questions 1903Document4 pagesImmunology Questions 1903microkannan100% (5)
- Microbiology 1st Semeter BSN Mcqs by RCN, Educational PlatformDocument10 pagesMicrobiology 1st Semeter BSN Mcqs by RCN, Educational PlatformPrince Masroor Ali AbroNo ratings yet
- Immunology MCQ DrNaeem PDFDocument163 pagesImmunology MCQ DrNaeem PDFA-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia ExamDocument9 pagesNeoplasia ExamYheng Gaosaii100% (1)
- QUIZ RESULTS HematologyDocument12 pagesQUIZ RESULTS HematologyfadyaNo ratings yet
- McqsDocument21 pagesMcqsOsama Bakheet100% (2)
- Essay, How Microscopes Have Contributed To Our Understanding of Living OrganismsDocument2 pagesEssay, How Microscopes Have Contributed To Our Understanding of Living Organismslinanqikiki82% (11)
- Astm E1975 - 1 (En)Document17 pagesAstm E1975 - 1 (En)Dinesh Sai100% (1)
- Craig - 4353 TX CobraDocument3 pagesCraig - 4353 TX CobraJorge ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Tions Answer The Following Ques: - LymphocytesDocument9 pagesTions Answer The Following Ques: - LymphocytesMarina AshrafNo ratings yet
- Immunology Midterm Exam Multiple Choice Questions: Choose The One Best AnswerDocument8 pagesImmunology Midterm Exam Multiple Choice Questions: Choose The One Best AnswerIceBearNo ratings yet
- Immunology ReviewDocument83 pagesImmunology ReviewMarianne Paed100% (1)
- اهم اسئلة 2Document32 pagesاهم اسئلة 2Adam JerusalemNo ratings yet
- Sample Exams To Post 2019 PDFDocument32 pagesSample Exams To Post 2019 PDFDustin SuttonNo ratings yet
- 2005719194923738Document10 pages2005719194923738DenizDerenNo ratings yet
- Immunology Final X 2021Document491 pagesImmunology Final X 2021nNo ratings yet
- Microbiology (Chapter - Immunology) Solved MCQs (Set-1)Document5 pagesMicrobiology (Chapter - Immunology) Solved MCQs (Set-1)خلطة علومNo ratings yet
- ImmunologieDocument15 pagesImmunologieHaixing WangNo ratings yet
- Immunology Qs - Part #2 M.TawalbehDocument15 pagesImmunology Qs - Part #2 M.TawalbehMohamed Tawalbe100% (6)
- AP Bio Unit 7 Study Guide Chapter 43Document7 pagesAP Bio Unit 7 Study Guide Chapter 43Huma KhanNo ratings yet
- Immunology-1st Master Q&ADocument20 pagesImmunology-1st Master Q&AIslam Fathy El NakeepNo ratings yet
- CALIBRATE IMSE Answer Key by Sir CarlDocument5 pagesCALIBRATE IMSE Answer Key by Sir CarlMark Justin OcampoNo ratings yet
- Kuis Imun UTSDocument8 pagesKuis Imun UTSichiNo ratings yet
- Immunology Practice QuestionsDocument13 pagesImmunology Practice QuestionsAishwariya RaiNo ratings yet
- Immunology Mid-ExamDocument11 pagesImmunology Mid-ExamNgMinhHaiNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Mcqs 1Document9 pagesMicrobiology Mcqs 1Patricia Denise OrquiaNo ratings yet
- MD3 Immunology Final Exam ReviewDocument28 pagesMD3 Immunology Final Exam Reviewdavid100% (1)
- Immunology QuizDocument29 pagesImmunology QuizRa A GulNo ratings yet
- Immunology MCQ SampleDocument4 pagesImmunology MCQ SampleNissin CupNoodlesNo ratings yet
- Immunology MCQ BY: Dr. AlgassimDocument4 pagesImmunology MCQ BY: Dr. AlgassimmohamedNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin Determination: Cyanmethemoglobin MethodDocument31 pagesHemoglobin Determination: Cyanmethemoglobin Methodبراءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- Autoimmunity and Tolerance MCQsDocument2 pagesAutoimmunity and Tolerance MCQsMahi Shafique100% (1)
- IMMUNOLOGY AND SEROLOGY Exam Finalsb PDFDocument8 pagesIMMUNOLOGY AND SEROLOGY Exam Finalsb PDFMarcelino CalataNo ratings yet
- 130 Immunology Questions and AnswersDocument41 pages130 Immunology Questions and AnswersAymen OmerNo ratings yet
- Career Point:, CP Tower, IPIA, Road No.1, Kota (Raj.), PH: 0744-3040000 Immunity and DiseaseDocument25 pagesCareer Point:, CP Tower, IPIA, Road No.1, Kota (Raj.), PH: 0744-3040000 Immunity and DiseaseSonika AlohiyaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Immunology BasicDocument71 pagesMCQ Immunology BasicMatthew HallNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument1 pageImmunologySenthilkumar PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Old Immunology Exam(s)Document16 pagesOld Immunology Exam(s)Ham Mad0% (1)
- MCQ On Hypersensitivity PDFDocument2 pagesMCQ On Hypersensitivity PDFFathima Siyad100% (2)
- Immunology ExamDocument9 pagesImmunology ExamNICHOLAS KAUMBANo ratings yet
- Revision MCQsDocument37 pagesRevision MCQsaNo ratings yet
- Rbcs Modifie 2Document6 pagesRbcs Modifie 2Habib UllahNo ratings yet
- Immune System REVISION AnswersDocument22 pagesImmune System REVISION Answersinder191100% (1)
- Select The Single Best Answer of The Following:: B. Non-ImmunogenicDocument14 pagesSelect The Single Best Answer of The Following:: B. Non-ImmunogenicAdel AlomarNo ratings yet
- Bacteria MCQDocument20 pagesBacteria MCQEbenizer Desta100% (2)
- Immunopathology Lec 4Document11 pagesImmunopathology Lec 4zaharNo ratings yet
- Immunology QuestionsDocument41 pagesImmunology QuestionsNazima Nasrullah100% (1)
- Acute and Chronic Inflammation MCQDocument2 pagesAcute and Chronic Inflammation MCQPrahul100% (1)
- MCQ Adaptive and Innate Immunity SET-ADocument4 pagesMCQ Adaptive and Innate Immunity SET-AParvathy Sarma100% (1)
- Acute Leukemia - Multiple Choice Questions - Laboratory HubDocument14 pagesAcute Leukemia - Multiple Choice Questions - Laboratory HubAssssssNo ratings yet
- 130 Immunology Questions and AnswersDocument44 pages130 Immunology Questions and AnswersEbenizer DestaNo ratings yet
- MCQ On ErythropoiesisDocument6 pagesMCQ On ErythropoiesisIrekton GGNo ratings yet
- Tropical MCQS: C. Visceral LeishmaniasisDocument29 pagesTropical MCQS: C. Visceral Leishmaniasisساره ابوالقاسمNo ratings yet
- REVIEW Cell Adaptation, Injury and DeathDocument101 pagesREVIEW Cell Adaptation, Injury and DeathandiariansyahNo ratings yet
- 4 2 PDFDocument9 pages4 2 PDFMahtab KhalifpourNo ratings yet
- Pre-Board Examination in Immunology-Serology and Blood Banking (Part 2)Document5 pagesPre-Board Examination in Immunology-Serology and Blood Banking (Part 2)Christyl JoNo ratings yet
- Part1ISBB 1Document5 pagesPart1ISBB 1Christyl Jo0% (1)
- Chapter 43 The Immune SystemDocument13 pagesChapter 43 The Immune System蔡旻珊No ratings yet
- Immunology-1st Master QDocument20 pagesImmunology-1st Master QIslam Fathy El NakeepNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Lecture Exam 2 Biol 1407 03.12.2010Document50 pagesStudy Guide For Lecture Exam 2 Biol 1407 03.12.2010Erica MizzIndependent BubuchuNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells PDFDocument4 pagesAnimal Cells PDFFalah HabibNo ratings yet
- Microbiology QuestionsDocument5 pagesMicrobiology QuestionsNaeem AminNo ratings yet
- Hostel B Menu From 16 March To 31 March'2024Document4 pagesHostel B Menu From 16 March To 31 March'2024govindkauNo ratings yet
- EN 14103 - ThermoDocument4 pagesEN 14103 - ThermoLuciana TrisnaNo ratings yet
- Designing New Vanillin Schiff Bases and Their Antibacterial StudiesDocument4 pagesDesigning New Vanillin Schiff Bases and Their Antibacterial StudiesAvinash PurohitNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report: Gass/Mfo Success Indicators Actual Accomplishments RemarksDocument1 pageAccomplishment Report: Gass/Mfo Success Indicators Actual Accomplishments RemarksGlenn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Water Heater: The Ecological Revolution MADE IN ITALYDocument4 pagesPhotovoltaic Water Heater: The Ecological Revolution MADE IN ITALYDani Good VibeNo ratings yet
- By Beholding We Are ChangedDocument2 pagesBy Beholding We Are ChangedAdrian EbensNo ratings yet
- Clover by The RiverDocument24 pagesClover by The RiverE. PoornimaNo ratings yet
- List Lagu EnglishDocument7 pagesList Lagu EnglishRyn ZulfanNo ratings yet
- Our School Broke Up For The Winter VacationsDocument7 pagesOur School Broke Up For The Winter VacationsprinceNo ratings yet
- What Is MetaphysicsDocument24 pagesWhat Is MetaphysicsDiane EnopiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 Area MethodDocument14 pagesChapter 34 Area Methodthorgod941500% (1)
- Kyocera Mita KM1505 1510 1810 Series ELITEC EssentialsDocument6 pagesKyocera Mita KM1505 1510 1810 Series ELITEC EssentialsJaime RiosNo ratings yet
- Underground-Sprayed Concrete BrochureDocument12 pagesUnderground-Sprayed Concrete BrochureEngTamerNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Results ReportingDocument7 pagesInterpretation of Results ReportingMerill Harrelson LibanNo ratings yet
- Balance Diet and NutritionDocument9 pagesBalance Diet and NutritionEuniceNo ratings yet
- INERT-SIEX 200-300 IG-100: Design ManualDocument54 pagesINERT-SIEX 200-300 IG-100: Design ManualSaleh Mohamed0% (1)
- Fisher N551 ESVDocument2 pagesFisher N551 ESVWynn ChoNo ratings yet
- Unidajump2019,+5 +31-42+JP+9 (1) +April+2018+AminullahDocument12 pagesUnidajump2019,+5 +31-42+JP+9 (1) +April+2018+AminullahSatria MandalaNo ratings yet
- Taenia SoliumDocument40 pagesTaenia SoliumBio SciencesNo ratings yet
- Elementary Graph Theory: Robin Truax March 2020Document15 pagesElementary Graph Theory: Robin Truax March 2020Jefferson WidodoNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Budget 2013-14Document33 pagesAgriculture Budget 2013-14Ajay LimbasiyaNo ratings yet
- 14 Parabola Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument9 pages14 Parabola Formula Sheets QuizrrChandanNo ratings yet
- Weekly Reminder August 18, 2014Document4 pagesWeekly Reminder August 18, 2014PauldingProgressNo ratings yet
- MiniNova GuideDocument41 pagesMiniNova GuideBob FredNo ratings yet
- A. Questions: Conversation Activities - TravelDocument11 pagesA. Questions: Conversation Activities - TravelkicsirekaNo ratings yet