Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(A4) MONTALBO DAYO - TransCebu BRT For ADB Transport Forum Nov 2012 Mijikai Nov 8
Uploaded by
Asian Development Bank ConferencesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(A4) MONTALBO DAYO - TransCebu BRT For ADB Transport Forum Nov 2012 Mijikai Nov 8
Uploaded by
Asian Development Bank ConferencesCopyright:
Available Formats
11/13/12
TransCebu: the Philippines First BRT
Cresencio Montalbo Jr., PhD.
University of the Philippines
Presentation Contents!
Project description" Why Cebu First" Best practices in Cebu BRT" Quo vadis?"
11/13/12
Cebu BRT development history
1992-94: Metro Cebu Mass Transport Study 1996: Visit to Curitiba (Brazil) 1996: Policy directives
Land use planning & transport planning cannot be separated Public transport comes first
2008: Request for World Bank funding for BRT development 2009-2011: DOTC Metro Cebu public transport strategy 2009: Cebu City BRT Pre Feasibility Study 2010: Cebu City Resolution to accept BRT 2011-2012: BRT Detailed feasibility study
Cebu BRT Pre-FS & FS
Contained within a single City Establish physical, economic and institutional feasibility Deliverability and expandability are key Studies Included: Data collection and strategic analysis of trip patterns Route appraisal - options Concept definition:
Segregation Stations Payment Information
Service & operational planning Economic & financial analysis Companion studies (PUJ industry, GHG, Institutional)
11/13/12
The BRT Project
Segregated busway: Bulacao CBD Ayala Mall BRT services operating to: SRP Talamban Tabunok/Talisay City Wide Area Traffic Control Traffic management
Why Cebu First?
Strong support from elected leaders and the public Stakeholder consulta:ve/communica:on process at an advanced stage The technical and economic viability has been established by technically sound, objec:ve studies Advanced stage of project development Included in the Country Investment Program of the Clean Technology Fund (CTF); approved by NEDA-Infracom and the CTF Board of Trustees in 2009
11/13/12
Best practices in Cebu BRT
User-focussed specic to Cebu Strong communica:ons Land use Transport Integra:on Service planning Ins:tu:onal & Opera:ons Deliverability & Sustainability
Scheme Development Based on User Needs
Focus groups with transport users all modes Mystery traveller surveys User interviews Walking survey of route Ethnographic study Policy and Technical Group Stakeholder meetings Transport groups Focus groups with PUJ drivers
11/13/12
Cebu BRT Consultation & Communications
Focus group discussions with PT and non PT users Focus group discussion in 14 Barangays Meetings with various interest groups Rolling programme of meetings in City Hall Concept testing in Ayala and SM malls Press releases Stakeholder meetings government & NGOs PUJ industry meetings and focus groups Web site & Facebook Public exhibitions: City Hall, Ayala & SM All in coordination with Cebu City Communications Committee
Service Plan
Services 1. Bulacao Talamban 2. Bulacao SRP 3. Bulacao IT Park 4. Bulacao Ayala 5. Talamban SRP 6. Talamban - Ayala 7. Ayala SRP 8. Talamban IT Park - Ayala
11/13/12
Institutional and Operations
Involvement and empowerment of existing transport providers. Engage early and consistently Public transport opportunity in BRT operations and reorganised complimentary feeder services Big opportunity for national government local government partnership
Deliverability and Sustainability
Deliverable Affordable Political will Stakeholder support Risks identification & management Sustainable Long life Reliability maintained Supportive of a developing city
11/13/12
Quo vadis?
Detailed engineering design procurement Construction to start October 2013 Operations start middle 2015 BRT in other Philippine cities Metro Manila (FS on-going) Davao?
11/13/12
Communications Strategies
Reactive media engagement answering of queries from the media and any other external parties during the conduct of the Cebu BRT FS Proactive media engagement provision of background information and briefings needed to convey the message that we have nothing to hide sensibility.
11/13/12
Busway: Typical stations
Service Plan
BRT Infrastructure Bulacao Talamban On Street: Talisay Bulacao Ayala - SM
Direct system
Feeder - Trunk system
11/13/12
The BRT Route and Network
Design Principles
Maintain appropriate road capacity Minimise land acquisition (delivery risk) Understand impact of existing utilities (drainage, electrical, water) and propose accommodation strategy Provide for competitive and reliable BRT run times Ensure pedestrian / highway safety is not compromised Ensure stations / terminals are fully accessible for all users Appreciate the need to maintain provision for u-turners / left turns Recognise the importance and cultural significance of Osmea Boulevard
10
11/13/12
BRT Stations
14 stations along the segregated corridor Road widening (land acquisition) required at each station Median stations along corridor, except on Osmea Boulevard where an asymmetrical design is proposed in order to minimise land acquisition Pedestrian access provided by At-Grade crossings Median Stations will measure approx 60 metres in length, and overall equal 150 metres when entry taper to exit taper is included Asymmetrical stations will measure 200 metres (including allowance for mid-link deviation in horizontal alignment and pedestrian access) Stations will also include facility for u-turns / left turners
Busway Typical Cross section
11
11/13/12
Busway: Typical Station Arrangement
Initial BRT
Intermediate BRT Stage II
Designated lanes/HOV lanes/queue jumper segments Additional passenger information, safety and security amenities Improved boarding accessibility and information features Extended stop distances, skip-stop and express services
Full BRT Stage IV
Exclusive alignment with full grade separation Enhanced berthing, loading and land use features Guidance, propulsion and alternative fuels features
Developing Understanding
Reference: Characteristics of Bus Rapid Transit for Decision Making August 2004 BRT is a system BRT NOT a checklist definition but a spectrum Cultural and contextual definition IS required
Components Running Ways
Stage I
Shared lanes in mixed traffic/some preferential treatment Improved shelter, signage and amenities
Stage III
Dedicated lanes and segregated facilities Enhanced station services and fare collection
Stations
Vehicles
Exterior aesthetic and ride/comfort features
Diversified vehicle sizes, materials, capacities
Service
Improved service frequency reliability
and
Regional coordination, high frequency and reliability
On/off alignment operations and convenient transfer options Flexible route options to increase one seat rides and reduce transfers Implement multi modal smart card system Vehicle location and surveillance to improve system coordination and safety/security
Route Structure
Single route with transfer connections
Multiple route operations with transfer facilities and unique identity Introduce proof of payment fare systems Passenger information to increase convenience and ridership
Integration with regional network/direct transfer options
Fare Collection
Increase pre paid fare sales
Utilise electronic collection system
fare
ITS
Signal preference enhancements to improve travel time and schedule adherence
Docking enhancements to reduce boarding times
12
You might also like
- Cebu BRT Feasibility StudyDocument35 pagesCebu BRT Feasibility StudyCebuDailyNews100% (3)
- Nicollet-Central Transit AlternativesDocument26 pagesNicollet-Central Transit AlternativesSarah McKenzieNo ratings yet
- Dayo Montalbo BRT in The Philippines For HCMC - EDocument15 pagesDayo Montalbo BRT in The Philippines For HCMC - EjpsorcererNo ratings yet
- Promoting Accessibility in Transport: MENA Region ExperiencesDocument33 pagesPromoting Accessibility in Transport: MENA Region ExperiencesÁlvaro DíazNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transportation Planning and EngineeringDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Transportation Planning and EngineeringPrabin Adhikari100% (1)
- Introduction To Highway Administration, Planning, and Design in The PhilippinesDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Highway Administration, Planning, and Design in The PhilippinesPeter John RoblesNo ratings yet
- Cresencio Montalbo - BRT in The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesCresencio Montalbo - BRT in The PhilippinesAsia Clean Energy ForumNo ratings yet
- Transportation Engineering NotesDocument9 pagesTransportation Engineering NotesAngel Jane MurilloNo ratings yet
- Madison Corridor Bus Rapid Transit StudyDocument15 pagesMadison Corridor Bus Rapid Transit StudyChs BlogNo ratings yet
- Wealth: It Is Not Which Makes Good Roads Possible - , Rather Which Makes Wealth PossibleDocument70 pagesWealth: It Is Not Which Makes Good Roads Possible - , Rather Which Makes Wealth PossiblekesharinareshNo ratings yet
- Transportation Engineering Course OutlineDocument33 pagesTransportation Engineering Course OutlineKisstar MbuyaNo ratings yet
- Traffic Engineering FundamentalsDocument24 pagesTraffic Engineering FundamentalsUmar Khan100% (1)
- July 19, 2012: City/Park Logo HereDocument18 pagesJuly 19, 2012: City/Park Logo Hereapi-63385278No ratings yet
- Introduction To Transportation Engineering 2015-2016Document19 pagesIntroduction To Transportation Engineering 2015-2016Allain DungoNo ratings yet
- Role of Transportation in Society (39Document44 pagesRole of Transportation in Society (39KingNo ratings yet
- Highway Engineering Lecturer Notes - Chapter 1&2Document77 pagesHighway Engineering Lecturer Notes - Chapter 1&2Muhammad Farhan Gul100% (8)
- Module No. 1Document5 pagesModule No. 1Mary Ann Toni N. RasonabeNo ratings yet
- Subdivision Staging Transportation Recommendations Subdivision Staging Policy Community Meeting II April 12, 2016Document36 pagesSubdivision Staging Transportation Recommendations Subdivision Staging Policy Community Meeting II April 12, 2016M-NCPPCNo ratings yet
- Highway Engineering Lecturer Notes Chapter 1 2Document77 pagesHighway Engineering Lecturer Notes Chapter 1 2dist2235No ratings yet
- BANGLADESH: Greater Dhaka Sustainable Urban Transport Project (GDSUTP) and NEPAL: Kathmandu Sustainable Urban Transport Project (KSUTP)Document17 pagesBANGLADESH: Greater Dhaka Sustainable Urban Transport Project (GDSUTP) and NEPAL: Kathmandu Sustainable Urban Transport Project (KSUTP)ADBGAD100% (1)
- Public Transport PromotionDocument59 pagesPublic Transport PromotionAndrei Slanina100% (1)
- Urban Transportation PlanningDocument107 pagesUrban Transportation Planningnobinobi845292No ratings yet
- Project Briefing: October 2007Document44 pagesProject Briefing: October 2007M-NCPPCNo ratings yet
- Council Transportation Committee December 11, 2013: Seattle Bicycle Master PlanDocument20 pagesCouncil Transportation Committee December 11, 2013: Seattle Bicycle Master PlantfooqNo ratings yet
- Movement Network Design Ceng 3431: Hawassa University Institute of TechnologyDocument24 pagesMovement Network Design Ceng 3431: Hawassa University Institute of Technologymatewos kurkaNo ratings yet
- Transport Demand ManagementDocument128 pagesTransport Demand ManagementAhmad ZulhazmiNo ratings yet
- Land Transport in Singapore OverviewDocument50 pagesLand Transport in Singapore OverviewGlen Chua100% (1)
- Module No. 3Document53 pagesModule No. 3Mary Ann Toni N. RasonabeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 2021Document50 pagesChapter 1 2021Angel YipNo ratings yet
- Integrated Transit LabDocument112 pagesIntegrated Transit LabNaresh KurubaNo ratings yet
- Site Selection CriteriaDocument5 pagesSite Selection CriteriaSahar RabadiNo ratings yet
- Rbmitem 19 HandoutDocument7 pagesRbmitem 19 HandoutMetro Los AngelesNo ratings yet
- Transit Master PlanDocument31 pagesTransit Master PlanCurtis CartierNo ratings yet
- Managed Lanes Corridor Project Feasibility StudyDocument28 pagesManaged Lanes Corridor Project Feasibility StudyDistrict Department of TransportationNo ratings yet
- Beach Corridor Alternatives - Miami Beach WorkshopDocument17 pagesBeach Corridor Alternatives - Miami Beach WorkshopNone None NoneNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study on Developing TODs along Palembang LRTDocument46 pagesFeasibility Study on Developing TODs along Palembang LRTputri arindaNo ratings yet
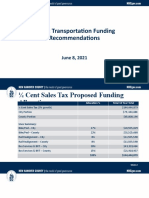
- Transportation Funding RecommendationDocument16 pagesTransportation Funding RecommendationAlexandria SandsNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To Transportation Planning: by Rei Robin Roland Tumambing, CE, RMP Elective2EDocument54 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Transportation Planning: by Rei Robin Roland Tumambing, CE, RMP Elective2ENicole De LeonNo ratings yet
- Presentation Integrated Infrastructure PlanningDocument123 pagesPresentation Integrated Infrastructure PlanningSushmitha NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Penang Integrated Transport PlanDocument76 pagesPenang Integrated Transport PlanKent KMNo ratings yet
- NTR1 Part1Document60 pagesNTR1 Part1GOATNo ratings yet
- Bus Rapid Transit System: Case Studies: at Dr. MCR HRDI, HyderabadDocument115 pagesBus Rapid Transit System: Case Studies: at Dr. MCR HRDI, HyderabadsatishsajjaNo ratings yet
- Paratransit: Jeepney-Philippines-539Document13 pagesParatransit: Jeepney-Philippines-539NURUL ATIQAH ALINo ratings yet
- Bus Terminal Design GuidedlineDocument18 pagesBus Terminal Design GuidedlinePudu Mounika100% (1)
- 2012 01 26 Transportation Progress ReportDocument13 pages2012 01 26 Transportation Progress ReportNorman OderNo ratings yet
- Revision TSM EdnaDocument4 pagesRevision TSM EdnaBASIL MAYAKANo ratings yet
- City Council Hearing 3-22-2017Document27 pagesCity Council Hearing 3-22-2017Chad ConantNo ratings yet
- PAAC Study Stakeholders 2012-06-05Document52 pagesPAAC Study Stakeholders 2012-06-05gettherepghNo ratings yet
- Transportation Facilities HandoutDocument39 pagesTransportation Facilities HandoutMj OhNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Mobility Plan GuideDocument25 pagesComprehensive Mobility Plan GuideAditya KaranNo ratings yet
- Urban Transportation Planning ProcessDocument2 pagesUrban Transportation Planning ProcessEr Khushal100% (1)
- RTS Mobility Final Report - Accessible - 2019 03 15Document134 pagesRTS Mobility Final Report - Accessible - 2019 03 15Tooba SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Transforming Commuter Corridors and Crossroads Into Sustainable PlacesDocument25 pagesTransforming Commuter Corridors and Crossroads Into Sustainable PlacesM-NCPPCNo ratings yet
- Vytilla Mobility Hub - Thesis ProposalDocument7 pagesVytilla Mobility Hub - Thesis ProposalPamarthiNikita100% (1)
- Week 11pdfDocument22 pagesWeek 11pdfÖmer faruk SilNo ratings yet
- Transportation PlanningDocument17 pagesTransportation PlanningyashaswiniNo ratings yet
- Conference Niche PaperDocument8 pagesConference Niche PaperAali PantNo ratings yet
- A Study On Traffic Management Along EDSA in Metro ManilaDocument8 pagesA Study On Traffic Management Along EDSA in Metro ManilaChinang100% (4)
- Bus Terminal InfrastructureDocument5 pagesBus Terminal InfrastructureDENNIS IBUINo ratings yet
- Sustainable Parking Management: Practices, Policies, and MetricsFrom EverandSustainable Parking Management: Practices, Policies, and MetricsNo ratings yet
- Speech by Giovanni Capannelli at Parliamentary Hearings On Drinking Water SupplyDocument5 pagesSpeech by Giovanni Capannelli at Parliamentary Hearings On Drinking Water SupplyAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- GMS 2017-2018 Calendar of Events - As of 8feb 2017Document4 pagesGMS 2017-2018 Calendar of Events - As of 8feb 2017Asian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- GMS 2018 Calendar of EventsDocument2 pagesGMS 2018 Calendar of EventsAsian Development Bank Conferences100% (1)
- ECF-8 - Session 6 LogisticsDocument23 pagesECF-8 - Session 6 LogisticsAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- ECF-8 - Session 2 Lao Bao - Densavanh SSI-SWIDocument60 pagesECF-8 - Session 2 Lao Bao - Densavanh SSI-SWIAsian Development Bank Conferences100% (1)
- RPTCC-20 Summary ProceedingsDocument221 pagesRPTCC-20 Summary ProceedingsAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- 37th Working Group On Tourism - Meeting Report 20176Document225 pages37th Working Group On Tourism - Meeting Report 20176Asian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- ECF-8 - Session 7a. Gov ForumDocument7 pagesECF-8 - Session 7a. Gov ForumAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- 20th Subregional Transport Forum - Summary of ProceedingsDocument379 pages20th Subregional Transport Forum - Summary of ProceedingsAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- UTF-5 AgendaDocument3 pagesUTF-5 AgendaAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- ECF-8 Session 7b E-CommerceDocument21 pagesECF-8 Session 7b E-CommerceAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- ECF-8 - Session 5 ANZDocument23 pagesECF-8 - Session 5 ANZAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Pushkar Manandhar 8 April 2016Document5 pagesPushkar Manandhar 8 April 2016Asian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan Solar ParksDocument7 pagesRajasthan Solar ParksAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- ECF-8 - Session 4 UCDFDocument25 pagesECF-8 - Session 4 UCDFAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- GMS 2016 Calendar of EventsDocument3 pagesGMS 2016 Calendar of EventsAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- ECF-8 - Session 1 GMS Corridor ConfigurationDocument26 pagesECF-8 - Session 1 GMS Corridor ConfigurationAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Private Sector Partnership For Inclusive Solar Park Development in RajasthanDocument25 pagesPrivate Sector Partnership For Inclusive Solar Park Development in RajasthanAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- 100% Solar in South Asia Implications For Technological and Social TransformationDocument5 pages100% Solar in South Asia Implications For Technological and Social TransformationAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Subregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 5 - Paul Hattle Minigrid Systems For Remote Disadvantaged Communities in BangladeshDocument2 pagesSubregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 5 - Paul Hattle Minigrid Systems For Remote Disadvantaged Communities in BangladeshAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Subregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 5 Rudra Khanal Minigrid System For Remote Disadvantaged Communities in NepalDocument6 pagesSubregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 5 Rudra Khanal Minigrid System For Remote Disadvantaged Communities in NepalAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Subregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 6 Farzana Rahman Sustainable Business Models For Rural Electrification in BangladeshDocument12 pagesSubregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 6 Farzana Rahman Sustainable Business Models For Rural Electrification in BangladeshAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Subregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 5 Vivek Porwal Feeder SeparationDocument3 pagesSubregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 5 Vivek Porwal Feeder SeparationAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Session4 Brajesh Panth Employment Generation in Emerging Clean Energy IndustriesDocument15 pagesSession4 Brajesh Panth Employment Generation in Emerging Clean Energy IndustriesAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Subregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter Session 5 Greg Adamson Background Paper (Ssitapc12 - Submission - 82 (1) )Document5 pagesSubregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter Session 5 Greg Adamson Background Paper (Ssitapc12 - Submission - 82 (1) )Asian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- GMS 2016 Calendar of EventsDocument3 pagesGMS 2016 Calendar of EventsAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Parthasarathi Sensarma Innovative and Disruptive Technologies and ProcessesDocument2 pagesSession 5 Parthasarathi Sensarma Innovative and Disruptive Technologies and ProcessesAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan Solar ParksDocument7 pagesRajasthan Solar ParksAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- GMS 2018 Calendar of EventsDocument2 pagesGMS 2018 Calendar of EventsAsian Development Bank Conferences100% (1)
- Private Sector Partnership For Inclusive Solar Park Development in RajasthanDocument25 pagesPrivate Sector Partnership For Inclusive Solar Park Development in RajasthanAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Tata Securities BranchesDocument6 pagesTata Securities BranchesrakeyyshNo ratings yet
- Niela Marie H. - GEC105 - SLM7 - MPHosmilloDocument4 pagesNiela Marie H. - GEC105 - SLM7 - MPHosmilloNiela Marie HosmilloNo ratings yet
- Qualities of Officiating OfficialsDocument3 pagesQualities of Officiating OfficialsMark Anthony Estoque Dusal75% (4)
- Buku Drawing - REV - 02Document40 pagesBuku Drawing - REV - 02agung kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Selected Candidates For The Post of Stenotypist (BS-14), Open Merit QuotaDocument6 pagesSelected Candidates For The Post of Stenotypist (BS-14), Open Merit Quotaامین ثانیNo ratings yet
- VisitBit - Free Bitcoin! Instant Payments!Document14 pagesVisitBit - Free Bitcoin! Instant Payments!Saf Bes100% (3)
- Managing The Law The Legal Aspects of Doing Business 3rd Edition Mcinnes Test BankDocument19 pagesManaging The Law The Legal Aspects of Doing Business 3rd Edition Mcinnes Test Banksoutacheayen9ljj100% (22)
- Dissertation 1984 OrwellDocument6 pagesDissertation 1984 OrwellCanSomeoneWriteMyPaperForMeMadison100% (1)
- SFL - Voucher - MOHAMMED IBRAHIM SARWAR SHAIKHDocument1 pageSFL - Voucher - MOHAMMED IBRAHIM SARWAR SHAIKHArbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- UGC Project FormatDocument19 pagesUGC Project FormatAmit GautamNo ratings yet
- Ra 4136Document12 pagesRa 4136Rizaida DiestoNo ratings yet
- Demographic and Clinical Pattern of Uveitis in Tertiary Eye Care Institute of Central IndiaDocument7 pagesDemographic and Clinical Pattern of Uveitis in Tertiary Eye Care Institute of Central Indiajassi nishadNo ratings yet
- What's New?: Changes To The English Style Guide and Country CompendiumDocument40 pagesWhat's New?: Changes To The English Style Guide and Country CompendiumŠahida Džihanović-AljićNo ratings yet
- CH08 Location StrategyDocument45 pagesCH08 Location StrategyfatinS100% (5)
- MGT 101Document13 pagesMGT 101MuzzamilNo ratings yet
- Admin Project1 RecuitmentDocument18 pagesAdmin Project1 Recuitmentksr131No ratings yet
- Electrical Energy Audit and SafetyDocument13 pagesElectrical Energy Audit and SafetyRam Kapur100% (1)
- Ebook Imperva SecureSphere DAP Getting StartedDocument26 pagesEbook Imperva SecureSphere DAP Getting Startedjairo_lindeman100% (1)
- Varifuel2 300-190 30.45.300-190D: Technical Reference Material Created by DateDocument1 pageVarifuel2 300-190 30.45.300-190D: Technical Reference Material Created by DateRIGOBERTO LOZANO MOLINANo ratings yet
- Intern Ship Final Report Henok MindaDocument43 pagesIntern Ship Final Report Henok Mindalemma tseggaNo ratings yet
- The Wizards' Cabal: Metagaming Organization ReferenceDocument3 pagesThe Wizards' Cabal: Metagaming Organization ReferenceDawn Herring ReedNo ratings yet
- Impact of corporate governance on firm performanceDocument4 pagesImpact of corporate governance on firm performancesamiaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A Ransomware Operation 1663902494Document12 pagesAnatomy of A Ransomware Operation 1663902494Sai SubuNo ratings yet
- Bid for Solar Power Plant under Institute for Plasma ResearchDocument10 pagesBid for Solar Power Plant under Institute for Plasma ResearchDhanraj RaviNo ratings yet
- International Conference GREDIT 2016Document1 pageInternational Conference GREDIT 2016Οδυσσεας ΚοψιδαςNo ratings yet
- Judgment at Nuremberg - Robert ShnayersonDocument6 pagesJudgment at Nuremberg - Robert ShnayersonroalegianiNo ratings yet
- Economical Writing McCloskey Summaries 11-20Document4 pagesEconomical Writing McCloskey Summaries 11-20Elias Garcia100% (1)
- Narcotic Drugs (Control Enforcement and Sanctions) Law, 1990Document32 pagesNarcotic Drugs (Control Enforcement and Sanctions) Law, 1990Kofi Mc SharpNo ratings yet
- STP Analysis of ICICI BANK vs SBI for Savings AccountsDocument28 pagesSTP Analysis of ICICI BANK vs SBI for Savings AccountsUmang Jain0% (1)