Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(A4) XIAOMEI - Guangzhou BRT and New BRT in China - Ed
Uploaded by
Asian Development Bank ConferencesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(A4) XIAOMEI - Guangzhou BRT and New BRT in China - Ed
Uploaded by
Asian Development Bank ConferencesCopyright:
Available Formats
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Duan Xiaomei Karl Fjellstrom, ITDP ITDP-China, www.itdp-china.org, www.itdp.org Manila, 8 Nov 2012 ADB Transport Forum 2012
Guangzhou BRT and New BRT Ini7a7ves in China
Structure
Guangzhou BRT
Planning & design Infrastructure & operations Impacts
New BRT initiatives in China
Lanzhou BRT Yichang BRT others
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Beijing BRT: In all corridors the large majority of bus demand is outside the BRT, making an overall time saving benefit for bus passengers unlikely. Corr. 2&3 demand ~2,000 pphpd in BRT
BRT in Hangzhou. Bus and mixed traffic congestion, including for most buses, outside the BRT
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Structure
Guangzhou BRT
Planning & design Infrastructure & operations Impacts
New BRT initiatives in China
Lanzhou BRT Yichang BRT others
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Asian BRT systems speed and demand comparison. Note that these figures refer to actual maximum passenger demand, not theoretical maximum capacity. All figures are from ITDP field surveys.
Guangzhou BRT Corridor: 23 km with 26 stations
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
BRT system with 31 routes
Before BRT, in the BRT corridor. Bus stop congestion bad for all modes
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
A typical scene at Gangding bus stop before the BRT implementation.
A typical scene at Gangding bus stop before the BRT implementation.
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Tianhe Gongyuan before the BRT
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Bus stop
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Gangding BRT station 3 stopping areas or sub-stops
Selected BRT Station layouts
1-module configurations offset, at grade
1-module configurations offset, footbridge
2-module configurations facing, at grade crossing)
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
10
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Shangshe BRT station in the morning peak. Highest demand stations include escalators
Tiyu Zhongxin BRT station, connecting to a north-south linear park and pedestrian network
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
11
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
New high density development lines the BRT corridor. Shipaiqiao station includes a metro connection and a connection into the adjoining shopping mall
3 substops, Gangding station.
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
12
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
3 substops, Tangxia station. Tangxia station has around 8,500 passenger boardings in a single hour during the morning peak. Station access is via a bridge with escalators, and a pedestrian crossing with refuge islands
Tangxia BRT station and urban village
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
13
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Substops per BRT station planning to determine station sizes in 2007
Next-bus arrival information at each BRT station substop
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
14
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Substop information inside Tiyu Zhongxin BRT station
BRT-watching on a Saturday night in Tangxia
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
15
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Intersection design. Chebei BRT station was changed from 4-phase to 2-phase
Chebei intersection change from 4-phase (before BRT) to 2-phase (with BRT)
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
16
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Dongpu BRT station. At-grade station access at both ends, combined with u-turn
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
17
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Guangzhou BRT management structure
KGC (transit planning agency)
Mayor / City Government
Communications Commission
TSCAC (bus stop & terminal managt agency)
YCT (smart card company)
BRT operators (3 groups, 7 companies)
BRT management company
Bike sharing company
BRT Control Center
No. 3 Bus Company (station fare collection cash & card pay)
Clearing account
Station cleaning and maintenance company
1. Provides bus-km data which, after adjustment for complaints and compliance with stipulated operational frequencies, is the basis for proportional payment of revenues to operators 2. Pays into clearing account based on smart card usage data from stations and on buses 3. Fare box revenue (cash payment outside the BRT corridor) is paid into the clearing account by the individual operators. Boxes opened in presence of all operators and BRT management co.
BRT control centre
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
18
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
BRT operators are paid per bus-km, with the BRT regulator controlling bus frequency
Guangzhou BRT is the 1st in China with more than one bus operating company. 7 companies in 3 groups
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
19
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Direct-service operations
Trunk & feeder operations
Trunk & feeder vs direct-service operations. The Guangzhou BRT does not require any transfer terminals, hubs, or interchanges
Quito transfer terminal
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
20
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
In Guangzhous direct-service BRT system, BRT buses can run outside the corridor. The graphic above shows the 31 BRT routes, with the main concentration along the 23km BRT corridor, but a total of 273km of roads covered
BRT bus operating off-corridor
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
21
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
22
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Origins, with destination at Gangding BRT station, AM peak. The direct-service operational mode allows most of these trips to be met without requiring passengers to transfer between buses
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
23
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
AM o/d
Integration of BRT station bridge & building, with double-tier bike parking under the bridge.
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
24
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
! !
BRT-metro connection at Shipaiqiao station
BRT-metro connection at Shipaiqiao
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
25
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
BRT-metro-mall connection at Shipaiqiao
Current bike parking guided bike parking facili7es we provided along the BRT corridor
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
26
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Around 40 loca1on have installed double 1er bike racks
Guangzhou BRT - bike sharing metro integration
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
27
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Public bikes at Huajing Xincheng BRT station. The bike lane is paved with asphalt and separated by a line of trees
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
28
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
The BRT and bike sharing system is encouraging the development of new bike facilities
Bike sharing: 5,000 bikes at 113 stations. Contact: shanshan@itdp-china.org
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
29
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
At-grade access to Chebei BRT station
At-grade access at both ends of Dongpu BRT station
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
30
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
At-grade access to Dongpu BRT station
Gangding BRT station, after the BRT implementation
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
31
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
The Guangzhou BRT and integrated bike sharing system won the 2011 Sustainable Transport Award. It has been covered in the New York Times, featured in major reports and publications, exhibited by the Smithsonian in the lobby of the United Nations building in New York (in October-November 2011) and featured in a Smithsonian channel documentary and other media, featured on the front cover of the influential Urban Transport of China journal, and seen hundreds of visiting delegations from China and around the world.
Exhibition by Smithsonian in United Nations Headquarters Lobby in New York, October-November 2011
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
32
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Tianhe Gongyuan before the BRT
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
33
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Tianhe Gongyuan after the BRT implementation (Shangshe BRT station)
Tianfu Lu intersection before and after BRT
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
34
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Good or very good Neutral Bad or very bad
Satisfaction Normal Dissatisfaction
66% 44% 40% 48% 39% 29% 16% 13% 21% 6% 28% 50%
65%
33%
2%
2007 2007
2008
2008
2009 Date
2009 Aug-10
2010 Dec-10
BRT BRT Before BRT After BRT
70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Before BRT -10% Bus With BRT Before BRT With BRT
Agree/Strongly Agree Neutral Disagree/Strongly Disagree
Before BRT Bike
With BRT
Pedestrian
Before BRT : December 2009 With BRT: August 2010
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
35
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Before BRT: December,2009
80% 60% 40% 20% 0% 80% 60% 40%
24% up
After BRT: August,2010
80% 60% 40% 20% 0%
Car Drivers
Bus Passengers
33%
up
Agree/Strongly Agree
Neutral
Disagree/Strongly
Disagree
80%
Agree/Strongly Agree
Neutral
Disagree/Strongly Disagree
Pedestrians
Cyclists
60%
40%
20% 0%
20%
Agree/Strongly Agree
Neutral
Disagree/Strongly Disagree
0%
Agree/Strongly Agree
Neutral
Disagree/Strongly Disagree
Bus Speed in Peak hour before and after BRT
22 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Before BRT (average speed in 2009) Bus speed (km/h) 15
km/hour
After BRT (average speed from Oct,2010-Jan, 2011) 21
Saving 6.6mins for each passenger
Saving 88381 passenger- hours each day
Saving 32 million passenger-hours each year
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
36
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Bus Passengers Self Reported Trip Costs (in RMB)
6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0
Cost for trip
Before BRT(Dec.2009) 4.9
After BRT(Aug.2010) 2.6
(non-BRT)
vehicle
volumes
along
the
BRT
corridor,
before
and
after
BRT
8000
Passenger
car
units
per
hour
7000
6000
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
0
2009.11
2010.03
2010.09
2011.01
2551
2816
3967
3348
3229
4125
4233
4257
2692
6337
5627
6713
200+% Increase 31% Increase 32% Increase
200+% Increase
2912 5904 5403 7267
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
37
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Vehicle speeds per hour, before and after BRT. Car speeds have significantly increased along the BRT corridor, along with volumes
Proposal for greening of Gangding BRT station
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
38
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Adding new roof for footbridges
4 substops, Shida Jida station (has most bus routes and highest bus volumes)
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
39
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Recently covered bridge & escalators at Shidajida; installation proceeding at other stations
Structure
Guangzhou BRT
Planning & design Infrastructure & operations Impacts
New BRT initiatives in China
Lanzhou BRT Yichang BRT others
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
40
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Lanzhou
Western
China. Capital of Gansu
Province Population around 4 million ADB loan funded BRT project Under construction, will open next month
Lanzhou current bus ows
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
41
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
BRT Network Plan
Phase 1
12.5Km, 19 sta7ons
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
42
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
BRT Boarding and alighting and cross section demand
19000//
BRT demand and transfers
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
43
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Lanzhou unique station design
Xi Zhan !
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
44
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
lanzhou
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
45
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
BRT under construction in Lanzhou
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
46
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
47
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Segrated bike lanes along lanzhou BRT
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
48
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
49
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Yichang
Central
China, site of Three Gorges Dam, second largest city in Hubei Province, after Wuhan Population around 4 million ADB loan funded BRT is currently in planning and design Will start construction late next year
23Km 38 stations 40-50m red line width for most of the corridor; half as wide in northern section
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
50
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
2011. Daily public transport demand around half million per day
58 routes and more than 700 buses in city
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
51
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
52
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
53
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
54
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Boarding & Aligh7ng at stops per hour-AM peak
Total OD for BRT
Origins O inside O inside
Destinations trips/hour D inside D outside 12409 9807 6557 27702 56475
percentage 22% 17% 12% 49% 100%
O outside D inside O outside D outside ! !
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
55
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
BRT routes in the north corridor BRT
Demand north corridor
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
56
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
NMT Integration and intersection improvements in city center
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
57
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
58
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Bike sharing stations integrated with BRT & covering city center
Lessons learned (1)
Guangzhou BRT, Lanzhou BRT, Yichang BRT: metrolevel capacity delivered by buses. This provides new mass transit options for rapidly growing cities. Many critical aspects to BRT project success:
stations (placement relative to
corridor selection, data collection & analysis, operational design, institutions & regulation, communications and outreach control centre & ITS
intersections, configuration, length, width, spacing, and architecture), fare collection, vehicles, traffic engineering & management, intersection design & signal phases, modal integration (metro, bicycle, pedestrians), ancillary measures such as parking & urban design.
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
59
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Lessons learned (2)
The first BRT corridor should serve high demand, congested locations, including the city centre. The infrastructure has to be correctly planned and designed together with an operational plan that meets passenger demand BRT stations should be designed to meet passenger demand levels and accommodate growth
There are many advantages to having multiple BRT operators Intermodal integration is often neglected during BRT planning, to the detriment of the BRT systems involved A successful BRT corridor should be a beautiful urban corridor
More information and photos www.chinabrt.org www.publicbike.net www.itdp-china.org www.transportphoto.net
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
60
ITDP-China; UNDP delegation, 9-10 July 2012
Guangzhou BRT Planning and Design
61
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- 20th Subregional Transport Forum - Summary of ProceedingsDocument379 pages20th Subregional Transport Forum - Summary of ProceedingsAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- ECF-8 - Session 2 Lao Bao - Densavanh SSI-SWIDocument60 pagesECF-8 - Session 2 Lao Bao - Densavanh SSI-SWIAsian Development Bank Conferences100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 100% Solar in South Asia Implications For Technological and Social TransformationDocument5 pages100% Solar in South Asia Implications For Technological and Social TransformationAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Rajasthan Solar ParksDocument7 pagesRajasthan Solar ParksAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- GMS 2018 Calendar of EventsDocument2 pagesGMS 2018 Calendar of EventsAsian Development Bank Conferences100% (1)
- Pushkar Manandhar 8 April 2016Document5 pagesPushkar Manandhar 8 April 2016Asian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Private Sector Partnership For Inclusive Solar Park Development in RajasthanDocument25 pagesPrivate Sector Partnership For Inclusive Solar Park Development in RajasthanAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Subregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 3 Adnan Tareen Demand Side Management UzbekistanDocument4 pagesSubregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 3 Adnan Tareen Demand Side Management UzbekistanAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Subregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 5 Vivek Porwal Feeder SeparationDocument3 pagesSubregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 5 Vivek Porwal Feeder SeparationAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Subregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 3 Harsha Wickramasinghe-DSM Sri LankaDocument11 pagesSubregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 3 Harsha Wickramasinghe-DSM Sri LankaAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
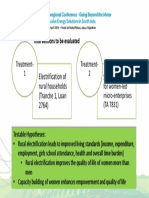
- Subregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 3 Ranen Banerjee - Interventions To Be EvaluatedDocument1 pageSubregional Conference Going Beyond The Meter: Inclusive Energy Solutions in South Asia Session 3 Ranen Banerjee - Interventions To Be EvaluatedAsian Development Bank ConferencesNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Painting WorksDocument2 pagesMethod Statement For Painting Worksmustafa100% (3)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Salmonella - Methods and Protocols.-springer-Verlag New York (2020)Document215 pagesSalmonella - Methods and Protocols.-springer-Verlag New York (2020)Yudith ParamitadeviNo ratings yet
- Pocket Book AGDocument67 pagesPocket Book AGsudiraharjaNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Reservoir Rock PropertiesDocument148 pagesReservoir Rock Propertiesiscribdusername100% (7)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- NSTM.512v0.FANS.S9086 RS STM 010 CH 512R21Sep99Document60 pagesNSTM.512v0.FANS.S9086 RS STM 010 CH 512R21Sep99jwfqcw74mfNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Nature 00869Document3 pagesNature 00869鍾宗霖No ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Dragons and Winged SerpentsDocument5 pagesDragons and Winged SerpentsYuna Raven100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- MIKE21BW Step by Step GuideDocument124 pagesMIKE21BW Step by Step Guideflpbravo100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Msds - Lemon Detergent Acco BrandsDocument10 pagesMsds - Lemon Detergent Acco Brandsfitri widyaNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Fill in The Table by Determining The Functions of The Following ItemsDocument6 pagesFill in The Table by Determining The Functions of The Following ItemsJessabel CandidatoNo ratings yet
- 9 Daftar Pustaka VaricelaDocument2 pages9 Daftar Pustaka VaricelaAfrina FaziraNo ratings yet
- Study Antimicrobial Activity of Lemon (Citrus Lemon L.) Peel ExtractDocument5 pagesStudy Antimicrobial Activity of Lemon (Citrus Lemon L.) Peel ExtractLoredana Veronica ZalischiNo ratings yet
- Grand Vitara 2005Document35 pagesGrand Vitara 2005PattyaaNo ratings yet
- 1 Soundcraft Notepad User GuideDocument40 pages1 Soundcraft Notepad User GuideNives KurjakNo ratings yet
- 159 SnackDocument97 pages159 SnackGuy PlaterNo ratings yet
- MC 1Document109 pagesMC 1ricogamingNo ratings yet
- Block-1 BLIS-03 Unit-2 PDFDocument15 pagesBlock-1 BLIS-03 Unit-2 PDFravinderreddynNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment 3 Test For CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesLaboratory Experiment 3 Test For CarbohydratesRenee Dwi Permata MessakaraengNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- 12.1 ANSYS CompositePrepPostDocument2 pages12.1 ANSYS CompositePrepPostLakmal ArandaraNo ratings yet
- Macedonian KavalDocument1 pageMacedonian Kavalmikiszekely1362No ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet 3D TRASAR® 3DT128: Section: 1. Product and Company IdentificationDocument10 pagesSafety Data Sheet 3D TRASAR® 3DT128: Section: 1. Product and Company IdentificationEscobar ValderramaNo ratings yet
- Construction Companies in AlbaniaDocument17 pagesConstruction Companies in AlbaniaPacific HRNo ratings yet
- Itinerary - State 2010Document3 pagesItinerary - State 2010purest123No ratings yet
- Despiesse de Las Guallas D6H SERIE 3ZF06342Document4 pagesDespiesse de Las Guallas D6H SERIE 3ZF06342David manjarresNo ratings yet
- Notes StressDocument4 pagesNotes StressRohitKalraNo ratings yet
- Squares and Square Roots Chapter Class ViiiDocument24 pagesSquares and Square Roots Chapter Class ViiiManas Hooda100% (1)
- DPWH ReviewerDocument597 pagesDPWH Reviewercharles sedigoNo ratings yet
- The Sparkle EffectDocument22 pagesThe Sparkle EffectVida Betances-ReyesNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Practice of Veterinary Anesthesia - Small Animals, Birds, Fish, and ReptilesDocument382 pagesThe Practice of Veterinary Anesthesia - Small Animals, Birds, Fish, and ReptilesMárcio MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Pottery Making May06 Poi0506dDocument52 pagesPottery Making May06 Poi0506dMadeleineNo ratings yet