Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 2 2marks
Uploaded by
Kannan TindivanamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 2 2marks
Uploaded by
Kannan TindivanamCopyright:
Available Formats
ARUNAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE,
TIRUVANNAMALAI - 606603
Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering
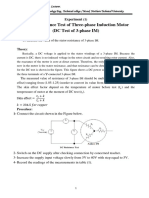
GE2151 BASIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
PART A (2 MARKS)
UNIT: 2 ELECTRICAL MECHANICS
PART A (2 MARKS) 1. In what respect does a 1-phase Induction motor differ from a 3-phase Induction motor? Construction wise a plain 1-phase Induction motor is more or less similar to a 3-phase squirrelcage Induction motor except that its stator is provided with only 1-phase winding. 2. What are the inherent characteristics of plain 1-phase Induction motor? A plain 1-phase Induction motor is not used in practice due to the following inherent characteristics A plain 1-phase Induction motor does not have any starting torque However, if the rotor is initially given a starting torque, by some means, the motor can pick up its speed in a direction at which the initial torque is given and deliver the required output. 3. Name the two diffe rent theories with which principle of 1-phase induction motors are explained. The two different theories are Double revolving field theory Cross field theory 4. State double revolving field theory. Double revolving theory, formulated by Ferrari, states that a single pulsating synchronous speed proportional to the frequency of the pulsating field 5. Name any four types of 1-phase induction motors. Based on the method of starting arrangement provided, the 1-phase Induction motors are classified as follows Split-phase motor Capacitor start motor Capacitor start and run motor Shaded pole motor
C.Kannan.ME., Asst.Prof/EEE/Arunai Engineering College, Tiruvannamalai
1
Repulsion start Induction run motor 6. Why are centrifugal s witches provided on many 1 -phase Induction motors? Centrifugal switches are provided on many 1-phase Induction motors to disconnect the starting / auxiliary winding from the supply when the motor reaches about 70% of its synchronous speed. 7. How is the direction of a capacitor start Induction motor be reversed? The direction of rotation can be reversed by interchanging the terminals of either t he main winding or the starting winding. 8. State the principle of 3 phase IM? While starting, rotor conductors are stationary and they cut the revolving magnetic field and so an EMF is induced in them by electromagnetic induction. This induced EMF produces a current if the circuit is closed. This current opposes the cause by Lenzs law and hence the rotor starts revolving in the same direction as that of the magnetic field. 9. Induction motor can run at synchronous speed ? True or false? Explain . No, if the speed of induction motor is Ns then the relative speed between the rotating flux and the rotor will be zero and so no torque is produced. 10. An induction motor is generally analogous to ? It is analogous to a winding rotating transformer with its secondary circuit closed. 11. Can the starting torque of of a slip ring induction motor being increased? Yes. It can be increased by adding resistances to the rotor. 12. What would happen if a 3 phase induction motor is switched on with one phase Disconnected? The motor is likely to burn . 13. What happens if the air gap flux density in an induction motor increases? The increase in air gap flux increases iron loss and hence efficiency decreases. 14. State the advantages of skewing? It reduces humming and hence quite running of motor is achieved. It reduces magnetic locking of the stator and rotor. 15. State the condition at which the starting torque developed in a slip-ring induction motor is maximum. When R2=X2
C.Kannan.ME., Asst.Prof/EEE/Arunai Engineering College, Tiruvannamalai
2
16 What are the effects of increasing rotor resistance on starting current and starting torque? The additional external resistance reduces the rotor current and hence the current drawn from the supply. It improves the starting torque developed by improving the power factor in high proportion to the decrease in rotor current. 17. What is slip of an induction motor? The slip speed expressed as the ratio of synchronous speed is defined as slip. Percentage slip S=Ns-N/Ns*100 18. How the magnitude of rotor e mf is related to the slip in an I M? Rotor circuit emf per phase E2r=SE2 19. How the frequency of rotor emf is related to the slip in an I M? Frequency of rotor emf/current fr=Sfs 20. What is the normal value of slip of an I M ope rating at full load? 3 - 5% 21. Why is not possible for the rotor speed of an I M to be equal to the speed of its rotating magnetic field? The machine will not be able to develop any mechanical torque to run as a motor. 22. State the condition at which the torque developed in a 3 phase induction motor is maximum. When R2=SX2 23. What are the advantages of slip-ring I M over cage I M? Rotor circuit is accessible for external connection. By adding external resistance to the rotor circuit the starting current is reduced with the added advantage of improving starting torque. Additional speed control methods can be employed with the accessibility in the rotor circuit.
C.Kannan.ME., Asst.Prof/EEE/Arunai Engineering College, Tiruvannamalai
3
24. What are the losses occurring in an I M and on what factors do they depend? Magnetic losses Wi Electrical losses Wcu Mechanical losses Wm For I M operating in normal condition (with constant voltage and frequency) magnetic and mechanical losses remain constant whereas electrical losses vary in square proportion to the current. 25. What care should be taken at the time of construction to reduce eddy curre nt losses in I M? Make the resistance of the core body as large as possible. This is achieved by laminating the stator core, stacked and revetted at right angles to the path of eddy current. The laminations are insulated from each other by thin coat of varnish. 26. Why is there a not appreciable magnetic loss in the rotor core of Induction motors? Although the rotor core is also subjected to magnetic flux reversals and since the frequency of flux reversals in the rotor, fr = Sfs, is very small, the iron loss incurred in the rotor core is negligibly small. 27. How does the shaft torque differ from the torque developed in 3 -phase Induction motor? The mechanical power developed Pd causes the rotor to rotate at a speed Nr due to the torque Td developed in the rotor. Therefore, equation for Pr can be written as Pd __ 1rTd / 60 The remaining power, after the mechanical losses Wm are met with, available in the shaft as mechanical power output Po Po = Pd Wm The mechanical power output Po, which is less than Pd is available in the shaft running at a speed of Nr and with a shaft torque T. Therefore the shaft torque (T) is slightly less than the torque developed Td, Pd_ __ 1rT / 60 Wm = Pd Po_ _>_ 1r(Td T)] / 60 28. Name the tests to be conducted for pre determining the performance of 3-phase induction machine. (a) No load test (b) Blocked rotor test
C.Kannan.ME., Asst.Prof/EEE/Arunai Engineering College, Tiruvannamalai
4
29. What is the informations obtained from no-load test in a 3-phase I M? No load input current per phase, Io No load power factor and hence no load phase angle Iron and mechanical losses together Elements of equivalent circuit shunt branch 30. What are the informations obtained from blocked rotor test in a 3-phase I M? Blocked rotor input current per phase at normal voltage Blocked rotor power factor and hence phase angle Total resistance and leakage reactance per phase of the motor as referred to the stator 31. What is circle diagram of an I M? When an I M operates on constant voltage and constant frequency source, the loci of stator current phasor is found to fall on a circle. This circle diagram is used to predict the performance of the machine at different loading conditions as well as mode of operation. ADDITIONAL UNIV QUESTION 2 MARKS 1. What is the basic principle of a dc generator? 2. What are the basic parts of a dc generator? 3. What is the purpose of yoke in a dc machine? 4. Mention the 2 types of armature winding in a dc machine. 5. What is the function of commutator in a dc generator? 6. Write down the EMF equation of a dc generator. 7. What are the different types of dc generators? 8. Draw the circuit diagram of any two types of DC generators. 9. What is the material used for armature core, field winding, commutator and brushes? 10. List out the different types of DC motor. 11. Why is a shunt motor called constant speed drive? 12. Define the term speed regulation of a DC motor. 13. Write down the torque equation of a DC motor. 14. Give the significance of back emf in a dc motor. 15. Define transformation ratio. 16. Define voltage regulation of a transformer.
C.Kannan.ME., Asst.Prof/EEE/Arunai Engineering College, Tiruvannamalai
5
17. What are the types of transformers based on construction? 18. What are the different types of single phase induction motor? 19. What are the applications and characteristics of capacitor-start capacitor run motor? 20. What are the classifications of single phase induction motor based on the method of starting? PART B 1. Explain the principle of operation of a DC generator and derive the emf equation. Discuss in detail about the construction of DC generator with the neat sketch. (16) 2. Derive the equation for induced emf of a DC machine. (16) 3. Give the significance of back emf in a DC motor. (16) 4. Derive the torque equation of DC motor. (16) 5. Describe the construction details of transformer and also explain the principle of operation.(16) 6. Explain the principle of operation of single phase 2-winding transformer. (16) 7. Derive the emf equation of a transformer. (16) 8. Explain the principle of operation of single phase induction motor. (16) 9. Explain double field revolving theory. (16) 10. What are the classifications of single phase induction motor based on the method of starting?(16) 11. A transformer with 40 turns on the high voltage winding is used to step down the voltage from 240V to 120V. Find the number of turns in the low voltage winding. (16) 12.A 4 pole, wave wound generator having 40 slots and 10 conductors placed per slot. The flux per pole is 0.02 wb. Calculate the generated emf when the generator is drive at 1200 rpm. (16) 13.A 25kw, 250V, dc shunt generator has armature and field resistances of 0.06ohm and 100ohm respectively. Determine the total armature power developed when working (1) as a generator delivering 25 kw output and (2) as a motor taking 25kw. (16)
C.Kannan.ME., Asst.Prof/EEE/Arunai Engineering College, Tiruvannamalai
6
You might also like
- Electrical Machines-II Units-III & IV Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesElectrical Machines-II Units-III & IV Questions and AnswersJoseph Harindranath100% (2)
- UNIT-III Three Phase & Single Phase Induction MotorsDocument8 pagesUNIT-III Three Phase & Single Phase Induction MotorsRahulRamamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines II AnswerDocument24 pagesElectrical Machines II AnswerGurulathan SoosairajNo ratings yet
- PX7203-Special Electrical Machines PDFDocument11 pagesPX7203-Special Electrical Machines PDFvaishnavisriNo ratings yet
- EE6504 Electrical Machines-II (2 Mark Q & A) PDFDocument16 pagesEE6504 Electrical Machines-II (2 Mark Q & A) PDFUnknownNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2HardikSinghNegiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: DEPARTMENT OF EEE/Electrical Machines-II/III YEARDocument22 pagesQuestion Bank: DEPARTMENT OF EEE/Electrical Machines-II/III YEARPartha Roy100% (1)
- Electrical Machines-II QBDocument6 pagesElectrical Machines-II QBsathishnatarajNo ratings yet
- 3 PH Induction Motor IntroductionDocument37 pages3 PH Induction Motor IntroductionNaga Raju AngajalaNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument20 pagesInduction MotorC V VIJAY KUMASRNo ratings yet
- What Is Meant by A Load On A Generator? A Load On A Motor?Document9 pagesWhat Is Meant by A Load On A Generator? A Load On A Motor?I am Just TrollingNo ratings yet
- Ee LawDocument11 pagesEe LawI am Just TrollingNo ratings yet
- II yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IIDocument5 pagesII yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IIanunilaNo ratings yet
- CSPDocument8 pagesCSPmeghraj01100% (1)
- Question BankDocument17 pagesQuestion BankJeslin CharlesNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument43 pagesInduction MotorJanine Jade SetiasNo ratings yet
- EE8401 Electrical Machines - II Important Part A, Part B & Part C QuestionsDocument7 pagesEE8401 Electrical Machines - II Important Part A, Part B & Part C QuestionssivaNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument1 pageInduction MotorHarpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Inductioin Motor Test AhmedDocument9 pagesThree Phase Inductioin Motor Test Ahmedmearggebremedhin2013No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Induction Motors (Part1)Document18 pagesChapter 6 - Induction Motors (Part1)SanjanaLakshmiNo ratings yet
- PX7203 SpecialElectricalMachinesDocument11 pagesPX7203 SpecialElectricalMachines1balamanianNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Working Principle Types PDFDocument6 pagesInduction Motor Working Principle Types PDFdumpyNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Working Principle, Types, &Document6 pagesInduction Motor: Working Principle, Types, &0409piyushNo ratings yet
- Assignment-6 DC MotorDocument3 pagesAssignment-6 DC MotornikunjNo ratings yet
- AC Machines Lab. Experiment No.1: University Electronics Engineering College Systems and Control DepDocument5 pagesAC Machines Lab. Experiment No.1: University Electronics Engineering College Systems and Control DepQusai JamalNo ratings yet
- Question Bank of PecDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank of PecSudip SaketNo ratings yet
- EES (Lec20)Document16 pagesEES (Lec20)Muhammad SagheerNo ratings yet
- Repulsion MotorDocument10 pagesRepulsion MotorAhmed Abd El MoatiNo ratings yet
- 1-EM Section 1 Motor OperationDocument38 pages1-EM Section 1 Motor Operationmhafidz49No ratings yet
- Motor Current Analysis and Its Applications in Induction Motor Fault DiagnosisDocument21 pagesMotor Current Analysis and Its Applications in Induction Motor Fault DiagnosisEbrahim JozariNo ratings yet
- DC Shunt Motor.Document7 pagesDC Shunt Motor.Ghost ReaconNo ratings yet
- Starting Methods of 1-Phase & 3-Phase IMs - 100255KDocument14 pagesStarting Methods of 1-Phase & 3-Phase IMs - 100255KChamath Kirinde100% (2)
- Electrical Engg & InstrumentationDocument8 pagesElectrical Engg & InstrumentationEugin RajNo ratings yet
- EEE Part-II (Electrical Machines II)Document202 pagesEEE Part-II (Electrical Machines II)siva shankar100% (2)
- 2-Em2 em - OptDocument17 pages2-Em2 em - OptVenkatasamy VijayarajNo ratings yet
- Eem507 Electrical Technology: Unit - 1 D.C.MotorDocument7 pagesEem507 Electrical Technology: Unit - 1 D.C.MotorShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document33 pagesUnit 4SidhuSidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 and 5 QuastionDocument10 pagesChapter 4 and 5 Quastionbekabeki829No ratings yet
- Be3251 Beee QBDocument3 pagesBe3251 Beee QBMr MovieNo ratings yet
- DC Machines Conceptual Qtns and SolutionsDocument7 pagesDC Machines Conceptual Qtns and SolutionsBaluku DavidNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-III Semester: EEE 223 - Electrical Machines & DrivesDocument29 pagesQuestion Bank-III Semester: EEE 223 - Electrical Machines & DrivesKalaiselvan PunniyamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Engineering Analysis and Design (EEN 206)Document6 pagesLab Report: Engineering Analysis and Design (EEN 206)saksham mahajanNo ratings yet
- Braking Schemes of TractionDocument7 pagesBraking Schemes of TractionSuraj BhushanNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Question Bank Ee 6504 Electrical Machines Ii Unit I Synchronous Generator Part ADocument8 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Question Bank Ee 6504 Electrical Machines Ii Unit I Synchronous Generator Part ASarvasaisrinathNo ratings yet
- Parameter Estimation of Three Phase Induction Motor An Innovative Approach ThesisDocument58 pagesParameter Estimation of Three Phase Induction Motor An Innovative Approach ThesisIrfan Ashraf0% (1)
- Capacitor Start/Run Induction Motor: ExperimentDocument9 pagesCapacitor Start/Run Induction Motor: ExperimentMarcos Roberto ReinertNo ratings yet
- 19EE402 AC MachinesDocument4 pages19EE402 AC Machinespramana_gmritNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Induction Motor Tests: Technical ReportDocument10 pagesThree-Phase Induction Motor Tests: Technical ReportPrashant PuriNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Basics - of - 3phase - Induction - Motor - Part - 1Document4 pages1.1 Basics - of - 3phase - Induction - Motor - Part - 1Edison EstrellaNo ratings yet
- EEE Lab Viva QDocument5 pagesEEE Lab Viva Qkamalilakshmanan3No ratings yet
- Repulsion Motor SSCJE QUICK NOTE1Document5 pagesRepulsion Motor SSCJE QUICK NOTE1bmanisankarNo ratings yet
- Viva Questions On AlternatorsDocument6 pagesViva Questions On AlternatorsKashif Hussain RazwiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document128 pagesUnit 4kkarthiksNo ratings yet
- EE1301 Electrical Machines II PDFDocument7 pagesEE1301 Electrical Machines II PDFsivaeinfoNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument16 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorPushan Kumar DattaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: Arunai Engineering College TiruvannamalaiDocument56 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits: Arunai Engineering College TiruvannamalaiKannan TindivanamNo ratings yet
- Engineering College, Thiruvannamalai, TamilnaduDocument1 pageEngineering College, Thiruvannamalai, TamilnaduKannan TindivanamNo ratings yet
- MainDocument1 pageMainvasanthanbNo ratings yet
- SCT ModelDocument4 pagesSCT ModelKannan TindivanamNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 2marksDocument6 pagesUnit 1 2marksKannan TindivanamNo ratings yet
- Company NameDocument2 pagesCompany NameKannan TindivanamNo ratings yet
- Kyn LJN Tat 12534 19-12-2011 Mohammad Rashid (Altamash Bhai Ticcket)Document2 pagesKyn LJN Tat 12534 19-12-2011 Mohammad Rashid (Altamash Bhai Ticcket)zaheerbcNo ratings yet
- EDC 2 MarksDocument38 pagesEDC 2 MarksKannan TindivanamNo ratings yet
- Transforming SDocument17 pagesTransforming SEscalona, Michael Joshua S.No ratings yet
- Gandham Ravi Kumar Electrical EngineerDocument3 pagesGandham Ravi Kumar Electrical EngineerOwais MalikNo ratings yet
- Ch7 G4010-R1Document140 pagesCh7 G4010-R1MoshNo ratings yet
- Differential Relay: Power System ProtectionDocument12 pagesDifferential Relay: Power System ProtectionAbdallah DaldoomNo ratings yet
- GB 50053-2013Document26 pagesGB 50053-2013IRELECNo ratings yet
- 2-Stability and Reliability Improvement in Solar Wind Hybrid Power System With Battery Energy Storage StationDocument9 pages2-Stability and Reliability Improvement in Solar Wind Hybrid Power System With Battery Energy Storage StationEngrImranKhanNo ratings yet
- Sizing Cable MotorDocument65 pagesSizing Cable MotorDoly DamanikNo ratings yet
- ATyS MAnualDocument44 pagesATyS MAnualJose Vladimir100% (1)
- T3000 Thermal Power SupplyDocument44 pagesT3000 Thermal Power Supplyronal552No ratings yet
- Repulsion MotorDocument8 pagesRepulsion MotorPravin HandeNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ibrahim El-Amin - Power System ProtectionDocument53 pagesDr. Ibrahim El-Amin - Power System ProtectionElizabeth Villegas HuapayaNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice For The Electricity (Wiring) Regulations: 2015 EditionDocument356 pagesCode of Practice For The Electricity (Wiring) Regulations: 2015 EditionjackwpsoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4: Self-Excited Compound-Wound DC GeneratorDocument11 pagesAssignment 4: Self-Excited Compound-Wound DC GeneratorRenz MykoNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Multifunctional PMR PDFDocument14 pagesData Sheet Multifunctional PMR PDFTaufik RahmanNo ratings yet
- Tmda Inverter Catalog Update 20220610Document24 pagesTmda Inverter Catalog Update 20220610monozone789No ratings yet
- Vela Motors Vl2-Series Catalogue Electric MotorsDocument3 pagesVela Motors Vl2-Series Catalogue Electric Motorsangel flores añezNo ratings yet
- Etap Solutions Overview PDFDocument29 pagesEtap Solutions Overview PDFAndreyDhoNo ratings yet
- University of Mumbai Examination Dec 2020: Superposition TheoremDocument4 pagesUniversity of Mumbai Examination Dec 2020: Superposition TheoremSaud ShaikhNo ratings yet
- New Electricity Tariff RatesDocument2 pagesNew Electricity Tariff RatesAda DeranaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Flatpack2 Rectifier 48-3000Document2 pagesDatasheet Flatpack2 Rectifier 48-3000Arif RahmantoNo ratings yet
- UT139A.ut139B.ut139C Manual enDocument14 pagesUT139A.ut139B.ut139C Manual enalberto1954No ratings yet
- Windpower TechnologyDocument496 pagesWindpower TechnologyRelu Chiru100% (2)
- Transformer Model ATY72Z01S1: GeneralDocument2 pagesTransformer Model ATY72Z01S1: GeneralprokjongNo ratings yet
- AZ 2005-02-14 State Programme On Fuel and Energy Sector EngDocument15 pagesAZ 2005-02-14 State Programme On Fuel and Energy Sector Engadams abdallaNo ratings yet
- How To Design Multi-kW DC - DC Converters For Electric Vehicles (EVs) - Power Factor and Harmonic CurrentsDocument1 pageHow To Design Multi-kW DC - DC Converters For Electric Vehicles (EVs) - Power Factor and Harmonic CurrentsThien DinhNo ratings yet
- NETA Article - Low Voltage Breaker TestingDocument5 pagesNETA Article - Low Voltage Breaker TestinglimresNo ratings yet
- Ac 2106 SPDocument5 pagesAc 2106 SPAbdelkader Bendjedid100% (1)
- Lincoln-Electric Welding Inverter PC65-PC105Document33 pagesLincoln-Electric Welding Inverter PC65-PC105andtib100% (1)
- GE Multilin - 1craig Wester, John LevineDocument90 pagesGE Multilin - 1craig Wester, John LevineEduardo Salgado CarBajal100% (1)