Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review Notes On The Anatomy of The Lung
Uploaded by
Nabil Abd El-tawabOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Review Notes On The Anatomy of The Lung
Uploaded by
Nabil Abd El-tawabCopyright:
Available Formats
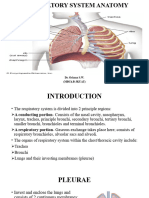
Notes on the Lungs
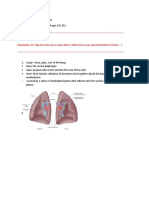
The Lungs
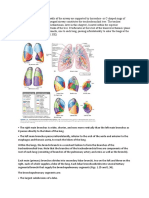
The lungs are elastic and recoil to approx. 1/3 of their size
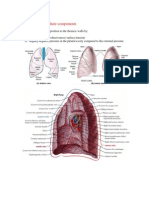
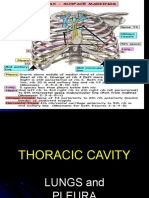
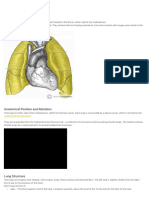
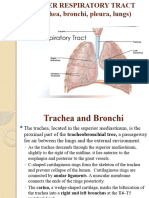
when the thoracic cavity is opened. Sectioning of root of lung before branching of the main bronchus: o Superior-most on left: Pulmonary Artery o Superior-most on right: May be the superior lobar bronchus o Anterior-most: Superior Pulmonary vein o Inferior-most: Inferior Pulmonary Vein o Posterior wall & approx. at middle: Primary bronchus Medial to hilum, root enclosed within area of continuity between visceral and parietal layers: Pleural sleeve/Mesopneumonium Right lung: 3 lobes, larger & heavier that left but shorter & wider because dome of diaphragm is higher (liver) Left Lung: 2 lobes, greatly infringed upon by heart 2/3 of heart is to the left of the mid-line Percussion of lungs helps to establish whether underlying tissues are air filled [resonant sound], fluid filled [dull sound] or solid [flat sound] Trachea & Bronchi Walls of airways are supported by C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage.
Sublaryngeal airway constitutes: Tracheobronchial tree Bifurcation of trachea occurs @ Transverse thoracic plane (SAT4) into main (primary) bronchus (Note: Carina) Right main bronchus: wider, shorter & runs more vertically than left Left main bronchus: passes inferolaterally , inferior to arch of aorta & anterior to esophagus & thoracic aorta Each main bronchus divides into lobar bronchi: (1 per lobe) o 3 on right o 2 on left (Note: Lingular Bronchus) Lobar bronchi divide into segmental bronchi: o Right Upper Lobe: Usually 3 segments o Middle Lobe: Usually 2 segments o Right Lower Lobe: Usually 5 segments o Left Upper Lobe: Usually 5 segments o Left Lower Lobe: Usually 4 segments Bronchopulmonary segments: o Pyrimidal segments of the lung, with apices facing lung root & bases @ pleural surface o Largest subdivision of lobe separated from adjacent segments by connective tissue septa o Named according to segmental bronchi supplying them Beyond segmental bronchi are 20-25 generations, ending in terminal bronchioles
Sequence of Tracheo-broncho-alveolar tree: o Trachea o Main (Primary) Bronchus o Lobar Bronchi o Segmental Bronchi o Large Intrasegmental Bronchi o Small Intrasegmental Bronchi o Bronchiole, consisting of: Lobule, consisting of: Terminal bronchiole Acinus*, consisting of: o Respiratory bronchiole o Alveolar Sacs & Alveoli *Acinus: part of lung supplied by terminal bronchiole Vasculature of the Lungs & Pleurae Each lung: Large pulmonary artery & 2 pulmonary veins Right & Left pulmonary arteries arise from pulmonary trunk at level of sternal angle Arterial branch goes to each lobe and bronchopulmonary segment of the lung, usually on anterior aspect of corresponding bronchus. Pulmonary veins run independantly of arteries and bronchi course between different segments Veins from visceral pleurae drain into pulmonary veins
Bronchial arteries supply blood for nutrition of structures making up root of lungs, supporting tissues of lungs, and visceral pleurae: o 2 left bronchial arteries: usually arise directly from aorta o 1 right bronchial artery: may arise directly/indirectly from aorta either via Intercostal arteries or common trunk with left bronchial arteries Pleurae are supplied by anterior & posterior intercostal arteries Majority of blood drained by pulmonary veins, except most proximal part which is drained by bronchial veins (specifically that part returning from the visceral pleura) o Right bronchial vein drains into azygos vein o Left bronchial vein drains into accessory hemiazygos or superior intercostal vein Nerves of the Lungs & Pleurae Parasympathetic fibres from the Vagus Nerve (CNX): Are motor to the smooth muscle of the bronchial tree Inhibitory to the pulmonary vessels Secretory to the glands of the bronchial tree
Parasympathetic ganglion cells are in the pulmonary plexi and along the branches of the bronchial trees Pulmonary plexi also contain sympathetic fibres from the sympathetic trunks; sympathetic ganglion cells are in the paravertebral sympathetic ganglia of the sympathetic trunks
The sympathetic fibres are: o Inhibitory to the bronchial muscle o Motor to the pulmonary vessels o Inhibitory to the alveolar glands of the bronchial tree T2 secretory epithelial cells of the alveoli Nerves of the parietal pleurae derive from the intercostal and phrenic nerves costal pleura and peripheral part of the diaphragmatic pleura are supplied by the intercostal nerves, mediating touch/pain central part of diaphragmatic pleura and the mediastinal pleura supplied by phrenic nerves
You might also like
- Bronchial Tree: TracheaDocument59 pagesBronchial Tree: TracheaAmanuel mekonnenNo ratings yet
- Lungs 2014Document64 pagesLungs 2014atidNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- THORAX Part 2Document59 pagesTHORAX Part 2idrimuha333No ratings yet
- The Lungs: Dr. J. ShaikDocument20 pagesThe Lungs: Dr. J. ShaikNkosinathi ShongweNo ratings yet
- Anat Case 2Document8 pagesAnat Case 2AnanaaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy RespiratoryDocument68 pagesAnatomy RespiratorydofezdsNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy 4 Thoracic Cavity: Dr. Wesam BaderDocument46 pagesGeneral Anatomy 4 Thoracic Cavity: Dr. Wesam BaderAhmadNo ratings yet
- Vasculature of The Lungs: Learning ObjectivesDocument3 pagesVasculature of The Lungs: Learning ObjectivesUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Anat - Respi Gross CompiledDocument8 pagesAnat - Respi Gross CompiledLeslie Kimberly Lisay100% (1)
- 20-Trachea, Bronchi & BPSDocument37 pages20-Trachea, Bronchi & BPSpm7197362No ratings yet
- Null 4Document47 pagesNull 4Kenyan MillanNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Part 2 Thoracic CavityDocument56 pagesUnit 6 Part 2 Thoracic CavitySiraj ShiferawNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document8 pagesLab 2Ehab AbazaNo ratings yet
- Trachea and LungsDocument25 pagesTrachea and LungsDr.pallavi kumariNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Bronchi .Document22 pagesLungs and Bronchi .Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- The Thorax Part Ii - The Thoracic Cavity: Juan Guido G. Joyo, PTRP Juvi G. Alicabo, PTRP, CCP, CTMBP, CTTTPDocument98 pagesThe Thorax Part Ii - The Thoracic Cavity: Juan Guido G. Joyo, PTRP Juvi G. Alicabo, PTRP, CCP, CTMBP, CTTTPFerjie Angelica DalandaoNo ratings yet
- Overview of Visceral Thorax - PleuraDocument33 pagesOverview of Visceral Thorax - PleuraHrishikesh BirjeNo ratings yet
- Lung AnatomyDocument19 pagesLung AnatomyScott Yee100% (2)
- Trachea, Bronchi, Lungs Bronchopulmonary Segments: Roel Cobarde M.DDocument25 pagesTrachea, Bronchi, Lungs Bronchopulmonary Segments: Roel Cobarde M.DMiriam JonesNo ratings yet
- Case 3 AsthmaDocument203 pagesCase 3 AsthmaMiftahul FauziahNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Pleura Student PC1 2017Document31 pagesLungs and Pleura Student PC1 2017Obongsamuel IdiongNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 13 (Lungs)Document28 pagesAnatomy Lec 13 (Lungs)afzal sulemaniNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument38 pagesRespiratory SystemdjokerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2Document43 pagesAnatomy 2bikedet268No ratings yet
- Checklist 3Document9 pagesChecklist 3FranklinSappNo ratings yet
- Trachea, Bronchial Tree and Bronchopulmonary Segments: by Nitisha GuptaDocument15 pagesTrachea, Bronchial Tree and Bronchopulmonary Segments: by Nitisha GuptaNITISHA GUPTANo ratings yet
- 5.2 Lungs f2f-s1b2-23Document32 pages5.2 Lungs f2f-s1b2-23shlokNo ratings yet
- Pleura and LungsDocument7 pagesPleura and LungsNavisatul MutmainahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Lecture 5, Pleurae & Lungs (Slides)Document21 pagesAnatomy, Lecture 5, Pleurae & Lungs (Slides)Ali Al-Qudsi100% (1)
- Clinical Anatomy of Respiratory System: Dr. Ridwan Harrianto MHSC (Om), SP - OkDocument31 pagesClinical Anatomy of Respiratory System: Dr. Ridwan Harrianto MHSC (Om), SP - OkMahasiswa StrugleNo ratings yet
- Trachea, Lungs, Pleura.Document24 pagesTrachea, Lungs, Pleura.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- PM2 - Anatomy II - The Respiratory SystemDocument35 pagesPM2 - Anatomy II - The Respiratory SystemNsikan GabrielNo ratings yet
- Seminar On: Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument33 pagesSeminar On: Pulmonary TuberculosisPriyaranjan Jose86% (7)
- Lecture ChestDocument467 pagesLecture ChestMai IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Repaso AnatomíaDocument2 pagesRepaso AnatomíasanchezyamnaylameyliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The LungsDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The LungschinecheremnfNo ratings yet
- Lungs and PleuraDocument7 pagesLungs and PleuraArvin ArliandoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Respiratory System - KMUDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Respiratory System - KMUSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Broncho-Pulmonary SegmentsDocument29 pagesBroncho-Pulmonary SegmentsArbin PanjaNo ratings yet
- Pleura & LungsDocument26 pagesPleura & Lungswashma SoomroNo ratings yet
- Dams NotesDocument28 pagesDams NotesmuskanNo ratings yet
- 12 Ana Lungs September 30 CinioDocument5 pages12 Ana Lungs September 30 CiniombdelenaNo ratings yet
- Bronco Pulmonary SegmentDocument24 pagesBronco Pulmonary SegmentAnkit PancholiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Notes 3Document3 pagesAnatomy Notes 3Nia IarajuliNo ratings yet
- Pleura: LungsDocument7 pagesPleura: LungsbarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary CirculationDocument4 pagesPulmonary CirculationDr Md Abedur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesRespiratory SystemMusadiq Khan DurraniNo ratings yet
- The LungsDocument6 pagesThe LungsnandaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi BronkusDocument3 pagesAnatomi BronkusstrywygarNo ratings yet
- Thorax LungsDocument128 pagesThorax LungsVernon MasakayanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of LungsDocument22 pagesAnatomy of Lungsnadya0% (1)
- RTS1-K13-Anatomy of LungsDocument22 pagesRTS1-K13-Anatomy of LungsYohanna SinuhajiNo ratings yet
- L5 Surface Anatomy & DiaphragmDocument45 pagesL5 Surface Anatomy & DiaphragmatefmoussaNo ratings yet
- Lungs-WPS OfficeDocument23 pagesLungs-WPS Officezenith parmarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument56 pagesRespiratory SystemSalma NawazNo ratings yet
- Human Tractus RespiratoriusDocument5 pagesHuman Tractus RespiratoriusDading Satrio SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Lower Resp TractDocument32 pagesLower Resp TractTakshikaNo ratings yet
- Neck PainDocument185 pagesNeck PainGalang Kusuma100% (1)
- Lit ReviewDocument12 pagesLit ReviewNabil Abd El-tawabNo ratings yet
- Aloe Barbadensis GelDocument21 pagesAloe Barbadensis GelNabil Abd El-tawabNo ratings yet
- Aloe Vera - A Wound Healer: CH Uma Reddy, Komar Suresh Reddy, Jaddu Jyothirmai ReddyDocument2 pagesAloe Vera - A Wound Healer: CH Uma Reddy, Komar Suresh Reddy, Jaddu Jyothirmai ReddyNabil Abd El-tawabNo ratings yet
- Community Based Rehabilitation Part IDocument46 pagesCommunity Based Rehabilitation Part INabil Abd El-tawabNo ratings yet
- Aloe VeraDocument4 pagesAloe Veratony6111100% (1)
- Neuro Rehab Course Dec 2012Document3 pagesNeuro Rehab Course Dec 2012Nabil Abd El-tawabNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument45 pagesLymphatic SystemNabil Abd El-tawabNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound UsDocument30 pagesUltrasound UsNabil Abd El-tawabNo ratings yet
- Focused Neurological AssessmentDocument23 pagesFocused Neurological AssessmentNabil Abd El-tawab100% (1)
- Ultrasound UsDocument30 pagesUltrasound UsNabil Abd El-tawabNo ratings yet
- Sun Fit and Well Advantage 10 (500K) - RidersDocument16 pagesSun Fit and Well Advantage 10 (500K) - RidersGSAFINNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Cardiovascular System: Group 7Document33 pagesDrugs Affecting The Cardiovascular System: Group 7Jann ericka JaoNo ratings yet
- 2023 Free 120Document65 pages2023 Free 120Edmund BlackadderNo ratings yet
- Assignment:: Course Title Course Code:Bph-115Document14 pagesAssignment:: Course Title Course Code:Bph-115toushif ahmedNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة العاشرة مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولى طب اسنانDocument9 pagesالمحاضرة العاشرة مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولى طب اسنانAbdullah TheNo ratings yet
- Joseph A. Ladapo, M.D., Ph.D. Curriculum Vitae Business InformationDocument33 pagesJoseph A. Ladapo, M.D., Ph.D. Curriculum Vitae Business InformationWCTV Digital TeamNo ratings yet
- RewtrewyewtewDocument9 pagesRewtrewyewtewNom NomNo ratings yet
- Gastro-Quiz-GERDDocument3 pagesGastro-Quiz-GERDIja Lourice RosalNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Clopidogrel)Document7 pagesDRUG STUDY (Clopidogrel)Fatima MohammedNo ratings yet
- Paclitaxel Trastuzumab Breast Cancer ProtocolDocument9 pagesPaclitaxel Trastuzumab Breast Cancer ProtocolsmokkerNo ratings yet
- Who Pen 2020Document85 pagesWho Pen 2020Faye PalmaresNo ratings yet
- Code Sisrute 5Document41 pagesCode Sisrute 5Bayu BimarthaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Artery DiseaseDocument8 pagesPeripheral Artery DiseaseDrNadia ZubairNo ratings yet
- Platelet Count Direct Method Activity (MANALO)Document3 pagesPlatelet Count Direct Method Activity (MANALO)Rose ValerieNo ratings yet
- RESPI QuestionDocument14 pagesRESPI QuestionPrince Charles AbalosNo ratings yet
- GRADE HandbookDocument75 pagesGRADE HandbookEzequiel ZacañinoNo ratings yet
- Emergency Medicine CritiquesDocument9 pagesEmergency Medicine CritiqueskayalNo ratings yet
- Gpe in cvs-1Document172 pagesGpe in cvs-1DrSrinivas JayanthurNo ratings yet
- Case Study #1 (NCM116RC)Document4 pagesCase Study #1 (NCM116RC)Dexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Casi Clinici Medicine and Critical CareDocument85 pagesCasi Clinici Medicine and Critical CarePaolo OnidaNo ratings yet
- Preparing A Patient For Cardiac Catheterization.4Document1 pagePreparing A Patient For Cardiac Catheterization.4Quality PmnhNo ratings yet
- Compiled Skills LabDocument14 pagesCompiled Skills LabJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- PNP RequirementsDocument22 pagesPNP RequirementsJEREMY WILLIAM COZENS-HARDYNo ratings yet
- Allergy and Immunology: Immunodeficiency 10 Warning Signs of ImmunodeficiencyDocument24 pagesAllergy and Immunology: Immunodeficiency 10 Warning Signs of Immunodeficiencyacque100% (2)
- Managerial Business Analytics Mgt782 (Finished)Document22 pagesManagerial Business Analytics Mgt782 (Finished)Eryn LisaNo ratings yet
- Uveitis EnglishDocument28 pagesUveitis EnglishGermanyNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of CopperDocument3 pagesHealth Benefits of CopperHasari UmekaNo ratings yet
- ACLS DrugsDocument4 pagesACLS DrugsEduard Espeso Chiong-Gandul Jr.No ratings yet
- Drugs RespiratoryDocument15 pagesDrugs RespiratoryLuiciaNo ratings yet
- Rat Dissection Without MusclesDocument45 pagesRat Dissection Without MusclesAshly GonNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (26)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingFrom EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1138)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)