Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Segui NCP
Uploaded by
Richelle TalaguitOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Segui NCP
Uploaded by
Richelle TalaguitCopyright:
Available Formats
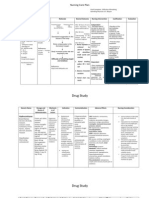
NURSING CARE PLAN:
Assessment Subjective: nahihirapan akong huminga...) as verbalized by the client . Objective: RR= 23 breaths/ min PR= 95 beats/min T= 37.5 degree Celsius Easy fatigability Productive cough Chills at night Loss of appetite as claimed Chest X- ray and sputum examination revealed positive for pulmonary tuberculosis
Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective Airway Clearance related to presence of bronchial infection and secretion
Inference
Outcome
Nursing Interventions
Rationale
Cough is the most common symptom of pulmonary tuberculosis. It may produce yellowish or greenish colored sputum especially during the day. Eventually, the sputum may be streaked with blood. Furthermore, a person with PTB may experience fatigue and loss of energy. It may affect his or her ability to expectorate secretions, too. Aside from that, difficulty of breathing signifies that there may be an accumulation of secretion in the bronchial cavity of the lungs.
After 8 hours of nursing care, client will be able to readily expectorate secretions and will have absence or decrease in episodes of dyspnea.
-Maintain infection control through the use of mask and performance of hand washing before and after contact with client.
-PTB is transmitted via droplet inhalation so proper precaution should be performed to avoid transmission to other clients. - Elevating the head of the bed and turning client every two hours help in decreasing the -Place client in high pressure placed on the fowlers position and diaphragm. encourage reposition every two hours. - Allergen may trigger more accumulation of secretion due to respiratory response. - These exercises hasten the - Maintain room or expulsion of sputum and aids in environment free from any maintaining airway patency. sorts of allergen. - Fluids help loosen secretion in - Teach and encourage deep the lungs. breathing and coughing exercises. -Warm fluids help in loosening the secretions while cold liquids -Emphasize to increase triggers cough more often. fluid intake depending on individual tolerability or as - Through the aid of gravity and indicated. percussion secretions are readily expelled. - Instruct to take warm liquids instead of cold ones. - It provides baseline data for
future comparison in the evaluation of disease condition. -Provide postural drainage and percussion. - PTB can be transmitted through droplet inhalation and 6 months compliance to -Monitor breathing patterns medication is needed in order to and breath sounds. be treated with it. -Educate client and family about disease condition and the need for compliance with the therapeutic regimen.
DRUG STUDY GENERI C NAME: Ketorolac BRAND NAME: Toradol DOSAG E: 30mg/am p1 amp IM CLASSIFICATI ON: Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents, nonopioid analagesics MECHANISM OF ACTION: - Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, producing peripherally mediated analgesia - Also has antipyretic and antiinflammatory properties. - Therapeutic effect:Decreased pain INDICATION: Short term managemen t of pain (not to exceed 5 days total for all routes combined) CONTRAINDICATI ONS - Hypersensitivity - Cross-sensitivity with other NSAIDs may existPre- or perioperative use - Known alcohol intoleranceUse cautiously in: 1) History of GI bleeding 2) Renal impair-ment (dosage reduction may be required) 3) Cardiovascular disease SIDE EFFECTS/ ADVERSE EFFECTS: - CNS: 1) drowsiness 2) abnormal thinking 3) dizziness 4) euphoria 5) headache- RESP: 1) asthma 2) dyspnea - CV: 1) edema 2) pallor 3) vasodilation - GI: 1) GI Bleeding 2) abnormal taste 3) diarrhea 4) dry mouth 5) dyspepsia 6) GI pain 7) nausea - GU: 1) oliguria 2) renal toxicity 3) urinary frequency - DERM: 1) pruritis 2) purpura 3) sweating 4) urticaria - HEMAT: NURSING IMPLICATIONS/RE SPONSIBILITIES: - Patients who have asthma, aspirininduced allergy, and nasal polyps are at increased risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions. Assess for rhinitis, asthma, and urticaria. - Assess pain (note type, location, and intensity) prior to and 1-2 hr following administration. - Ketorolac therapy should always be given initially by the IM or IV route. Oral therapy should be used only as a continuation of parenteral therapy. - Caution patient to avoid concurrent use of alcohol, aspirin, NSAIDs, acetaminophen, or other OTC medications without consulting health care professional.
1) prolonged bleeding time - LOCAL: 1) injection site pain - NEURO: 1) paresthesia - MISC: 1) allergic reaction, anaphylaxis
- Advise patient to consult if rash, itching, visual disturbances, tinnitus, weight gain, edema, black stools, persistent headche, or influenza-like syndromes (chills,fever,muscles aches, pain) occur. - Effectiveness of therapy can be demonstrated by decrease in severity of pain. Patients who do not respond to one NSAIDs may respond to another.
You might also like
- Tuberculosis Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesTuberculosis Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceCyrus De Asis86% (36)
- Drug Study Amlodipine & HydrocortisoneDocument4 pagesDrug Study Amlodipine & HydrocortisoneJohn Kristoffer JisonNo ratings yet
- Aspiration PneumoniaDocument27 pagesAspiration PneumoniaReya Awali SuasoNo ratings yet
- Management Guidelines of Common PoisioningDocument52 pagesManagement Guidelines of Common PoisioningshravaniNo ratings yet
- Name of The Drug Date Ordered Classification Dose Frequency Route Mechanism of Action Specific Indication Side Effects Nursing ImplicationDocument9 pagesName of The Drug Date Ordered Classification Dose Frequency Route Mechanism of Action Specific Indication Side Effects Nursing ImplicationFrances Oscar GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Woman With PneumoniaDocument9 pagesWoman With PneumoniaNohaira SADANGNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of BurnDocument40 pagesNursing Management of BurnSalinKaur0% (1)
- Toxicology (Lecture 2) ManagementDocument46 pagesToxicology (Lecture 2) ManagementyousernameNo ratings yet
- Drug Study QiDocument7 pagesDrug Study QiJeremiah Mauricio100% (1)
- Pneumonia: Case PresentationDocument12 pagesPneumonia: Case PresentationgelaneNo ratings yet
- Almaarefa College Adult Nursing Care Practice II Weekly Report Name of Student: Najwa Thawab - Day/DateDocument2 pagesAlmaarefa College Adult Nursing Care Practice II Weekly Report Name of Student: Najwa Thawab - Day/DateNajwa1991No ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument47 pagesCOPDMegha VadanereNo ratings yet
- Brand NameDocument8 pagesBrand NameChristine Joy CamachoNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia GhuDocument29 pagesPneumonia Ghun0ire.h3ck3rNo ratings yet
- NANDA DefinitionDocument5 pagesNANDA DefinitionAngel_Liboon_388No ratings yet
- Sedation in Critically IllDocument32 pagesSedation in Critically IllSamantha Deshapriya100% (1)
- Hypoglycaemia - Acute Management - AbcdeDocument8 pagesHypoglycaemia - Acute Management - Abcderjohn 7No ratings yet
- Nclex Disease: 4. Oral ContraceptivesDocument7 pagesNclex Disease: 4. Oral ContraceptivesMeijia SongNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Day 1Document17 pagesNCLEX Day 1jasonNo ratings yet
- Organophosphate Poisoning GuidelineDocument5 pagesOrganophosphate Poisoning Guidelinelamoleverde9297No ratings yet
- Intensive Care Unit Case ReportDocument27 pagesIntensive Care Unit Case ReportKadek ArianiNo ratings yet
- Guillain Barre Syndrome (G5)Document9 pagesGuillain Barre Syndrome (G5)elspaey sakrNo ratings yet
- COPD Acute Management ABCDEDocument11 pagesCOPD Acute Management ABCDESSNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument82 pagesASTHMAImmanuel100% (1)
- Anaphylaxis Acute Management ABCDEDocument8 pagesAnaphylaxis Acute Management ABCDESSNo ratings yet
- Supportive Care in Clinical ToxicologyDocument13 pagesSupportive Care in Clinical ToxicologyKausal VermaNo ratings yet
- Guillian-Barre Syndrome: Renalyn Galache Gladys Gegare BSN-3BDocument18 pagesGuillian-Barre Syndrome: Renalyn Galache Gladys Gegare BSN-3BGLadys GegareNo ratings yet
- Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesSubjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objectivechaoz09No ratings yet
- Asthma For PTDocument52 pagesAsthma For PTAnn SibyNo ratings yet
- Finals CA 1 - ReviewerDocument4 pagesFinals CA 1 - ReviewerkcharmaigneNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical ATI Proctored Exam 2019 With Rationale Detailed AnswerDocument62 pagesMedical Surgical ATI Proctored Exam 2019 With Rationale Detailed Answerkinyuaboris990No ratings yet
- Ketoprofen Supposutoria Induce Anaphylactic ShockDocument25 pagesKetoprofen Supposutoria Induce Anaphylactic ShockZulfahmi ZulfaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxDocument8 pagesCase Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- Lung Expansion RevisionDocument89 pagesLung Expansion RevisionPatrick RoqueNo ratings yet
- Liberation From Mechanical VentilationDocument21 pagesLiberation From Mechanical VentilationRins Chacko50% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Impaired Gas ExchangeZycon Rodney Ae'zecquel Gachallan50% (2)
- Medical Surgical Nursing Bridging Program Academic Year 1434-1435 / 2013-2014Document8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Bridging Program Academic Year 1434-1435 / 2013-2014Hamss AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nle Tips 3Document11 pagesNle Tips 3glenard-roble-1251No ratings yet
- Salbutamol Drug Study Generic Name: Brand NameDocument4 pagesSalbutamol Drug Study Generic Name: Brand NameLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- NCPsDocument13 pagesNCPsRocel DevillesNo ratings yet
- CADDocument2 pagesCADJessica Koch100% (1)
- Ms Flash CardsDocument15 pagesMs Flash CardsMia MalazoNo ratings yet
- Cast Study 1Document4 pagesCast Study 1Thelda Mae Arteche SablanNo ratings yet
- Syncope: - Selvarathi KDocument27 pagesSyncope: - Selvarathi KSelvarathi KandhaswamyNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Inhaled Droplet NucleiDocument4 pagesTuberculosis: Inhaled Droplet Nucleirhiesa75No ratings yet
- Amanda AquiliniDocument2 pagesAmanda AquilinineoclintNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesNursing Care PlanMerfat Abubakar100% (1)
- Emergency Treatment OF Anaphylactic ReactionsDocument40 pagesEmergency Treatment OF Anaphylactic Reactions'ranu HerjunaNo ratings yet
- NCP and DrugsDocument13 pagesNCP and DrugsApRil ANn ChUa BingcangNo ratings yet
- NCP and DStudyDocument8 pagesNCP and DStudyJessica Rosan Hewald ManapatNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug StudyDocument11 pagesNCP and Drug StudyTonio PagaoNo ratings yet
- Apnea 2019Document10 pagesApnea 2019aiswarya sreekumarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Management Protocol and Infection Control GuidelinesDocument16 pagesClinical Management Protocol and Infection Control Guidelinesalfaz lakhaniNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation Problem Notes and Nursing InterventionsDocument7 pagesOxygenation Problem Notes and Nursing InterventionsAnna TaylorNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- 100 Item Quiz 401Document21 pages100 Item Quiz 401Sheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Case Study: (Sepsis Secondary To Diabetes Ulcer Mangioma)Document6 pagesCase Study: (Sepsis Secondary To Diabetes Ulcer Mangioma)Richelle TalaguitNo ratings yet
- Segui NCPDocument4 pagesSegui NCPRichelle TalaguitNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan RuthDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan RuthRichelle TalaguitNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan RuthDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan RuthRichelle TalaguitNo ratings yet
- Documentation in Psychiatric Nursing PracticeDocument25 pagesDocumentation in Psychiatric Nursing PracticeRichelle TalaguitNo ratings yet
- Emotionally Focused Therapy (Eft) and Emotionally Focused Family Therapy (Efft) : A Challenge/opportunity For Systemic and Post-Systemic TherapistsDocument5 pagesEmotionally Focused Therapy (Eft) and Emotionally Focused Family Therapy (Efft) : A Challenge/opportunity For Systemic and Post-Systemic TherapistsEFTcouplesNo ratings yet
- Mcguire 1991Document8 pagesMcguire 1991Angela RamirezNo ratings yet
- Introduction Definition: Types of PacemakersDocument8 pagesIntroduction Definition: Types of PacemakersPrasann RoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1 Components of Sewage Collection SystemDocument19 pagesLecture - 1 Components of Sewage Collection SystemDanial Abid100% (1)
- AHA ACLS Megacode ScenariosDocument6 pagesAHA ACLS Megacode ScenariosVitor Hugo G Correia86% (7)
- Emotional IntelligenceDocument19 pagesEmotional IntelligenceShweta ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ASCCP Management Guidelines - August 2014 PDFDocument24 pagesASCCP Management Guidelines - August 2014 PDFAnita BlazevskaNo ratings yet
- (Therapy in Practice Series) Rosemary Gravell, Jenny France (Auth.) - Speech and Communication Problems in Psychiatry (1991, Springer US) PDFDocument364 pages(Therapy in Practice Series) Rosemary Gravell, Jenny France (Auth.) - Speech and Communication Problems in Psychiatry (1991, Springer US) PDFmelike50% (2)
- Massage Therapy PDFDocument1 pageMassage Therapy PDFVirgilio BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Admission Nursing AssessmentDocument20 pagesAdmission Nursing AssessmentKhaskheli NusratNo ratings yet
- 15 PsychiatricDocument35 pages15 PsychiatricSami Ullah Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Bioethics OutlineDocument30 pagesBioethics OutlineJason KeithNo ratings yet
- Handbook: For Clinical Management of DengueDocument124 pagesHandbook: For Clinical Management of DengueraattaiNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Dust SuppressantDocument3 pagesMSDS - Dust SuppressantJc RamírezNo ratings yet
- Anti Aging and LongevityDocument37 pagesAnti Aging and LongevityrehanfasihNo ratings yet
- Tropocells 4 Pages PDF Format January 2011Document4 pagesTropocells 4 Pages PDF Format January 2011robertoblumandradeNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Screening and Antimicrobial Assay of Various SeedsDocument9 pagesPhytochemical Screening and Antimicrobial Assay of Various SeedsWendy FXNo ratings yet
- VOLUX 尖沙咀 chung parr hall 鍾伯豪醫生 PDFDocument8 pagesVOLUX 尖沙咀 chung parr hall 鍾伯豪醫生 PDFAnonymous YT4f4ejNtH100% (1)
- Peter Pan SyndromeDocument4 pagesPeter Pan SyndromeDaltry Gárate100% (2)
- Punjab Drugs Rules 2007Document33 pagesPunjab Drugs Rules 2007RphNaeemMalik75% (12)
- Lecture 2Document4 pagesLecture 2Peter KiptumNo ratings yet
- ANAESTHESIA FOR GASTROINTESTINAL CANCER SURGERIES AutosavedDocument40 pagesANAESTHESIA FOR GASTROINTESTINAL CANCER SURGERIES AutosavedKavyasree KatamNo ratings yet
- ASEAN Guideline On Stability of Drug ProductDocument8 pagesASEAN Guideline On Stability of Drug ProductSanjiv MenonNo ratings yet
- Myles Textbook For Midwives, 15th Edition: Journal of Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocument3 pagesMyles Textbook For Midwives, 15th Edition: Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecologyintan wahyuNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Chapter 13Document84 pagesAbnormal Psychology Chapter 13Summer LeeNo ratings yet
- HAAD Exam QsDocument2 pagesHAAD Exam Qsdrkhalilezekiel93% (15)
- Final Exam LecturesDocument329 pagesFinal Exam LecturesBrettSkillettNo ratings yet
- Hamilton D ScoringDocument1 pageHamilton D ScoringJoezerk Jhon BielNo ratings yet
- K6 - Tetanus PEDIATRICDocument23 pagesK6 - Tetanus PEDIATRICbanuperiahNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument15 pagesResearch ProposalEarl NavarroNo ratings yet