Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transducer: Applications
Uploaded by
SachithHiroshanaWijethungaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transducer: Applications
Uploaded by
SachithHiroshanaWijethungaCopyright:
Available Formats
Transducer
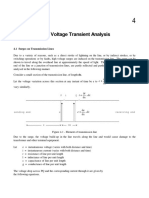
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump to: navigation, search This article is about transducers in mechanical and electrical engineering. For other forms of transduction, see Transduction. For transducers in theoretical computer science and automata theory, see Finite state machine. A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy to another. Energy types include (but are not limited to) electrical, mechanical, electromagnetic (including light), chemical, acoustic or thermal energy. While the term transducer commonly implies the use of a sensor/detector, any device which converts energy can be considered a transducer. Transducers are widely used in measuring instruments. A sensor is used to detect a parameter in one form and report it in another form of energy (usually an electrical and/or digital signal). For example, a pressure sensor might detect pressure (a mechanical form of energy) and convert it to electricity for display at a remote gauge. An actuator accepts energy and produces movement (action). The energy supplied to an actuator might be electrical or mechanical (pneumatic, hydraulic, etc.). An electric motor and a loudspeaker are both actuators, converting electrical energy into motion for different purposes. Combination transducers have both functions; they both detect and create action. For example, a typical ultrasonic transducer switches back and forth many times a second between acting as an actuator to produce ultrasonic waves, and acting as a sensor to detect ultrasonic waves. Rotating a DC electric motor's rotor will produce electricity and voice-coil speakers can also act as microphones.
[edit] Applications
Transducers are used in electronic communications systems to convert signals of various physical forms to electronic signals, and vice versa.
Electromagnetic: o Antenna converts propagating electromagnetic waves to and from conducted electrical signals
o o o
Magnetic cartridge converts relative physical motion to and from electrical signals Tape head, Disk read-and-write head - converts magnetic fields on a magnetic medium to and from electrical signals Hall effect sensor converts a magnetic field level into an electrical signal
Electrochemical: o pH probes o Electro-galvanic fuel cell o Hydrogen sensor Electromechanical (electromechanical output devices are generically called actuators): o Electroactive polymers o Galvanometer o Microelectromechanical systems o Rotary motor, linear motor o Vibration powered generator o Potentiometer when used for measuring position o Linear variable differential transformer or Rotary variable differential transformer o Load cell converts force to mV/V electrical signal using strain gauge o Accelerometer o Strain gauge o String potentiometer o Air flow sensor o Tactile sensor Electroacoustic: o Loudspeaker, earphone converts electrical signals into sound (amplified signal magnetic field motion air pressure) o Microphone converts sound into an electrical signal (air pressure motion of conductor/coil magnetic field electrical signal) o Pickup (music technology) converts motion of metal strings into an electrical signal (magnetism electrical signal) o Tactile transducer converts electrical signal into vibration ( electrical signal vibration) o Piezoelectric crystal converts deformations of solid-state crystals (vibrations) to and from electrical signals o Geophone converts a ground movement (displacement) into voltage (vibrations motion of conductor/coil magnetic field signal) o Gramophone pickup (air pressure motion magnetic field electrical signal) o Hydrophone converts changes in water pressure into an electrical signal o Sonar transponder (water pressure motion of conductor/coil magnetic field electrical signal) o Ultrasonic transceiver, transmitting ultrasound (transduced from electricity) as well as receiving it after sound reflection from target objects, availing for imaging of those objects.
Electro-optical (Photoelectric): o Fluorescent lamp converts electrical power into incoherent light o Incandescent lamp converts electrical power into incoherent light o Light-Emitting Diode converts electrical power into incoherent light o Laser Diode converts electrical power into coherent light o Photodiode, photoresistor, phototransistor, photomultiplier converts changing light levels into electrical signals o Photodetector or photoresistor or light dependent resistor (LDR) converts changes in light levels into changes in electrical resistance o Cathode ray tube (CRT) converts electrical signals into visual signals Electrostatic: o Electrometer Thermoelectric: o Resistance temperature detector (RTD) - converts temperature into an electrical resistance signal o Thermocouple - converts relative temperatures of metallic junctions to electrical voltage o Peltier cooler o Thermistor (includes PTC resistor and NTC resistor) Radioacoustic: o GeigerMller tube converts incident ionizing radiation to an electrical impulse signal o Receiver (radio) o transmitter-propagates electromagnetic transmissions to sound
[edit] See also
Tactile sensor Horn analyzer
[edit] External links
Introduction to Closed Loop Hall Effect Current Transducers Federal Standard 1037C, August 7, 1996: transducer Transducer
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Transducer&oldid=524503738" View page ratings Rate this page What's this? Trustworthy
Objective Complete Well-written I am highly knowledgeable about this topic (optional) I have a relevant college/university degree It is part of my profession It is a deep personal passion The source of my knowledge is not listed here I would like to help improve Wikipedia, send me an e-mail (optional) We will send you a confirmation e-mail. We will not share your e-mail address with outside parties as per our feedback privacy statement. Submit ratings Saved successfully Your ratings have not been submitted yet Your ratings have expired Please reevaluate this page and submit new ratings. An error has occurred. Please try again later. Thanks! Your ratings have been saved. Do you want to create an account? An account will help you track your edits, get involved in discussions, and be a part of the community. Create an accountorLog in Maybe later Thanks! Your ratings have been saved. Did you know that you can edit this page? Edit this page Maybe later Categories:
Transducers
Personal tools
Create account Log in
Namespaces
Article Talk
Variants
Views Actions Search
Special:Search
Read Edit View history
Navigation
Main page Contents Featured content Current events Random article Donate to Wikipedia
Interaction Toolbox
Help About Wikipedia Community portal Recent changes Contact Wikipedia
What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Rate this page
Print/export
Create a book Download as PDF Printable version
Languages
Catal Dansk Deutsch Espaol Franais Gaeilge Italiano Bahasa Melayu Nederlands Norsk (nynorsk) Polski Portugus Romn / srpski Basa Sunda Trke This page was last modified on 23 November 2012 at 14:22. Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. See Terms of Use for details. Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization. Contact us Privacy policy About Wikipedia Disclaimers Mobile view
You might also like
- Transducer: Controller (Control Theory)Document5 pagesTransducer: Controller (Control Theory)Farrukh JamilNo ratings yet
- Quick Review Outline - Masschusetts Testing for Educator Licensure (MTEL) Tech and Eng ExamFrom EverandQuick Review Outline - Masschusetts Testing for Educator Licensure (MTEL) Tech and Eng ExamNo ratings yet
- TransducerDocument3 pagesTransducerPambuditu LooseNo ratings yet
- TransducersDocument24 pagesTransducersChandra Sekher Reddy BhimiReddyNo ratings yet
- Transducer: TypesDocument39 pagesTransducer: Typestujuh belasNo ratings yet
- Transducer: Mechanical and Electrical TransducersDocument4 pagesTransducer: Mechanical and Electrical TransducersKhaled RabeaNo ratings yet
- Transducer, Sensor & ActuatorDocument8 pagesTransducer, Sensor & ActuatorkumareshbabaNo ratings yet
- Report On TransducersDocument36 pagesReport On Transducerspunith666No ratings yet
- TransducersDocument17 pagesTransducers9897856218No ratings yet
- Transducer RheaDocument3 pagesTransducer Rhea12u88elNo ratings yet
- TransducersDocument2 pagesTransducersMark Stephen GreavesNo ratings yet
- TransducerDocument11 pagesTransducerQazi Faiz Ullah Qazi Zaki UllahNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 TransducerDocument19 pagesChapter-3 Transducerethiomoney15No ratings yet
- Instrumentation PDFDocument19 pagesInstrumentation PDFM Venkata SaiNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical SystemsDocument1 pageElectromechanical SystemsKenneth DomingoNo ratings yet
- Module1 Basics of Energy TransformationDocument10 pagesModule1 Basics of Energy TransformationSanjana SNo ratings yet
- Info From WikepediaDocument137 pagesInfo From WikepediaBkhitesh KariaNo ratings yet
- TransducersDocument43 pagesTransducersArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Bio Instrumentation: ECG, EEG, EMG, Cardiovascular Measurements & Venous PressureDocument11 pagesBio Instrumentation: ECG, EEG, EMG, Cardiovascular Measurements & Venous PressureSaeed Ali ShahaniNo ratings yet
- @ at @ at Photograph ©: Rapid ElectronicsDocument3 pages@ at @ at Photograph ©: Rapid ElectronicsSameer KodilkarNo ratings yet
- Sensor: Thermal SensorsDocument6 pagesSensor: Thermal SensorsSaiprabhakar DevineniNo ratings yet
- Transducer: Made byDocument15 pagesTransducer: Made byHayder AliNo ratings yet
- Electrical Transducers: MIEE2110N/MIOG 2120 Electrical TechnologyDocument8 pagesElectrical Transducers: MIEE2110N/MIOG 2120 Electrical TechnologysaravananvietwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document46 pagesChapter 2kidanemariam tesera100% (1)
- Bright Hub EngineeringDocument102 pagesBright Hub EngineeringMadhusudanan AshokNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University: Term Paper ON Transducers and Its ApplicationsDocument8 pagesLovely Professional University: Term Paper ON Transducers and Its ApplicationsRudra FouzdarNo ratings yet
- TRANSDUCERDocument49 pagesTRANSDUCERgotiwo7723No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Sensors and TransducersDocument42 pagesUnit 2 Sensors and Transducersbhuyanuttam7No ratings yet
- Lecture Two InstDocument16 pagesLecture Two InstKenani SaningaNo ratings yet
- Transducer PracticalDocument6 pagesTransducer PracticalBhumit TrivediNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Transducers and Their ApplicationsDocument15 pagesDifferent Types of Transducers and Their Applicationshayumbe08No ratings yet
- Instrumentation TransducersDocument9 pagesInstrumentation TransducersbekaluNo ratings yet
- Electrotherapy 1Document14 pagesElectrotherapy 1Ajay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document23 pagesChap 4Liransu DastaNo ratings yet
- Research Electronics 4 19 9 19Document7 pagesResearch Electronics 4 19 9 19HarshilNo ratings yet
- Mech Transducer ReportDocument18 pagesMech Transducer ReportHome DecorsNo ratings yet
- Transducers: Historical BackgroundDocument40 pagesTransducers: Historical BackgroundTheCycleboYNo ratings yet
- Unit II Notes I&CDocument65 pagesUnit II Notes I&CShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Title Page: Various Electrical TransducersDocument13 pagesTitle Page: Various Electrical TransducersKushal AvaiyaNo ratings yet
- LEDsDocument14 pagesLEDsShon LaeNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Lecture 2Document18 pagesInstrumentation Lecture 2adisebastian100% (1)
- Eee 308Document52 pagesEee 308Samuel SamsonNo ratings yet
- Minor Project On FM - Reciver Dept of Electrical $ Electronics SESSION-2011-12Document20 pagesMinor Project On FM - Reciver Dept of Electrical $ Electronics SESSION-2011-12guptaankita41843No ratings yet
- Basic PhysicsDocument54 pagesBasic PhysicsKarttikeya Mangalam NemaniNo ratings yet
- Eee 205Document29 pagesEee 205Md. AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document15 pagesModule 6syamalaNo ratings yet
- Measurement and InstrumentDocument42 pagesMeasurement and InstrumentShubham BansalNo ratings yet
- Level Transducer IME Project ReportDocument6 pagesLevel Transducer IME Project ReportSanskar BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transducers Hand Written Class NotesDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Transducers Hand Written Class NotesBhushan SoniNo ratings yet
- Group1 1Document16 pagesGroup1 1Butch ArmonesNo ratings yet
- Tranducers 2Document10 pagesTranducers 2Preston JerryNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IV Part-3 Sensors and TransducersDocument26 pagesUNIT-IV Part-3 Sensors and TransducersmahiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Practices Laboratory (12F1Z9) : Lab ManualDocument51 pagesEngineering Practices Laboratory (12F1Z9) : Lab ManualJoao Carlos DrumondNo ratings yet
- GGGGDocument6 pagesGGGGmostafa elsayedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transducers: Primary Knowledge Participant GuideDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Transducers: Primary Knowledge Participant GuidePrashu PrashanthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Transducers & Measuring InstrumentsDocument85 pagesChapter 3 - Transducers & Measuring InstrumentsYab TadNo ratings yet
- TransdureDocument14 pagesTransdureRana Vivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics NotesDocument5 pagesBasic Electronics NotesRolando Carlos FloresNo ratings yet
- Study On Different Types of TransducersDocument12 pagesStudy On Different Types of TransducersS shek DhavudNo ratings yet
- SLS 573Document156 pagesSLS 573qsbhagya95% (37)
- Ex 02-Corona CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesEx 02-Corona CharacteristicsSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- Green BuildingDocument46 pagesGreen BuildingSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- SLS 573Document156 pagesSLS 573qsbhagya95% (37)
- ACDocument570 pagesACSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2011Document203 pagesAnnual Report 2011SachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- HBon PIBDocument69 pagesHBon PIBSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- OU8769-MEX3235-L 3-FinalDocument4 pagesOU8769-MEX3235-L 3-FinalSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- Gummen PoolDocument29 pagesGummen PoolvanithapremkumarNo ratings yet
- BJT - Ebers Moll EquationDocument12 pagesBJT - Ebers Moll EquationMichele CinottiNo ratings yet
- Tti3236 2013Document8 pagesTti3236 2013SachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- D J WimalasurendraDocument28 pagesD J WimalasurendraSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- ECE 334 Chapter 5 Biopolar Small Signal TransistorsDocument9 pagesECE 334 Chapter 5 Biopolar Small Signal TransistorsSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- BJT Ebers Moll ModelDocument5 pagesBJT Ebers Moll ModelShiraz HusainNo ratings yet
- Student Guide Book - Faculty of Engineering TechnologyDocument84 pagesStudent Guide Book - Faculty of Engineering TechnologyShera0% (1)
- EthicsDocument16 pagesEthicsKrishnakaparNo ratings yet
- HV Chap1Document21 pagesHV Chap1sdsamarakkody0% (1)
- Lattice DiagramDocument19 pagesLattice DiagramDDragos GeorgeNo ratings yet
- HV Chap2Document12 pagesHV Chap2SachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- 09 FindingfDocument5 pages09 FindingfSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart SymbolsDocument1 pageFlow Chart SymbolsAinun Najwa AzizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document50 pagesChapter 04Md. Ashraf Hossain SarkerNo ratings yet
- ManagementDocument19 pagesManagementSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- Flowcharts GuideDocument4 pagesFlowcharts GuideSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor Interfacingprogramming Microcontroller - PHPDocument7 pagesStepper Motor Interfacingprogramming Microcontroller - PHPSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- (M-101) Unit I: Engineering AthematicsDocument89 pages(M-101) Unit I: Engineering AthematicsSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- ExamplelfFlowChart PDFDocument5 pagesExamplelfFlowChart PDFSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- Ch03 Flowchart and Pseudo Code ExamplesDocument4 pagesCh03 Flowchart and Pseudo Code ExamplesLee Kah Hou67% (3)
- TransducersDocument52 pagesTransducersBasavaraja K M KotyalNo ratings yet
- Therm Is Tor Temp Transducer To ADC ApplicationDocument5 pagesTherm Is Tor Temp Transducer To ADC Applicationsumitsahu009No ratings yet
- Brochure Seamless Tubes For Hycy 20210525Document28 pagesBrochure Seamless Tubes For Hycy 20210525Carlos BenitezNo ratings yet
- Combilift C3500 C10000 Forklift Trucks Operator's & Service Manual PDFDocument72 pagesCombilift C3500 C10000 Forklift Trucks Operator's & Service Manual PDFVüsal 1100% (2)
- Final PPT Optical ComputersDocument24 pagesFinal PPT Optical Computersvidwathgowda75% (8)
- M32195F4TFPDocument1,044 pagesM32195F4TFPnorbertoNo ratings yet
- 12 Ip Sample Model Paper Oct2021Document8 pages12 Ip Sample Model Paper Oct2021niyamathNo ratings yet
- Stanford Research Institute InternationalDocument3 pagesStanford Research Institute InternationalstanscimagNo ratings yet
- Speed and Delay Study On National HighwayDocument20 pagesSpeed and Delay Study On National HighwayAshutosh Arun100% (1)
- PX01X XXX XXX Axxx enDocument12 pagesPX01X XXX XXX Axxx enPatrick BrilhanteNo ratings yet
- GTC 400EX Trifold2013Document6 pagesGTC 400EX Trifold2013RobertNo ratings yet
- Graduate Profile SEECS BICSEDocument46 pagesGraduate Profile SEECS BICSEHajiasifAliNo ratings yet
- JIO Mini-ProjectDocument26 pagesJIO Mini-ProjectAliNo ratings yet
- MvnoDocument23 pagesMvnoThanh-Nhan VONo ratings yet
- Scott GroverDocument3 pagesScott GroverJoe StephensNo ratings yet
- SRS FormatDocument3 pagesSRS FormatMayank Saraswat50% (4)
- Gigaset N870 IP PRO - Multicell System - en - INTDocument122 pagesGigaset N870 IP PRO - Multicell System - en - INTfredon quentinNo ratings yet
- Puff PlantDocument9 pagesPuff Planttauseef52No ratings yet
- CS SP Prraaccttiiccaall F Fiille e Se Essssiio On n2 20 02 233 - 2 24 4 Clla AS SS S 112 2Document30 pagesCS SP Prraaccttiiccaall F Fiille e Se Essssiio On n2 20 02 233 - 2 24 4 Clla AS SS S 112 2piyushkumar155900No ratings yet
- ConfigAdmin AG v2016EEDocument156 pagesConfigAdmin AG v2016EEpatologicoNo ratings yet
- Joby Charging GEACS FinalDocument2 pagesJoby Charging GEACS Finalhjkim0907No ratings yet
- SI3000 Pono Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesSI3000 Pono Datasheet PDFJose JoseNo ratings yet
- Yokogawa UT351Document94 pagesYokogawa UT351Brayan Sthip LLauceNo ratings yet
- Rangkaian RangkaianDocument30 pagesRangkaian RangkaianAhmad JuheriNo ratings yet
- Degree Programme Table: Advanced Chemical Engineering (MSC) - 1 Year (Full-Time)Document3 pagesDegree Programme Table: Advanced Chemical Engineering (MSC) - 1 Year (Full-Time)Petra SitanggangNo ratings yet
- Pilar, Sorsogon Power PointDocument2 pagesPilar, Sorsogon Power PointOscar MirandaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For ICT-RTMDocument45 pagesGuidelines For ICT-RTMDesi MundaNo ratings yet
- SFERE Energy Meter3706581013667435464Document2 pagesSFERE Energy Meter3706581013667435464Cho Cho MyintNo ratings yet
- Operation ManagementDocument11 pagesOperation ManagementRajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Spirion Thales - Integration Guide FINAL 20220517Document20 pagesSpirion Thales - Integration Guide FINAL 20220517tekena.alaminaNo ratings yet
- American Series ManualDocument26 pagesAmerican Series ManualIsael HernandezNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Gap Analysis AssignmentDocument3 pagesWeek 5 Gap Analysis AssignmentcatherineholthausNo ratings yet
- Nature-Based Learning for Young Children: Anytime, Anywhere, on Any BudgetFrom EverandNature-Based Learning for Young Children: Anytime, Anywhere, on Any BudgetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8From EverandLower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Interactive Science Notebook: The Human Body WorkbookFrom EverandInteractive Science Notebook: The Human Body WorkbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- How to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionFrom EverandHow to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- AI and the Future of Education: Teaching in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandAI and the Future of Education: Teaching in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- How Do Cell Phones Work? Technology Book for Kids | Children's How Things Work BooksFrom EverandHow Do Cell Phones Work? Technology Book for Kids | Children's How Things Work BooksNo ratings yet
- Interactive Notebook: Life Science, Grades 5 - 8From EverandInteractive Notebook: Life Science, Grades 5 - 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Nature Preschools and Forest Kindergartens: The Handbook for Outdoor LearningFrom EverandNature Preschools and Forest Kindergartens: The Handbook for Outdoor LearningRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- STEM Labs for Physical Science, Grades 6 - 8From EverandSTEM Labs for Physical Science, Grades 6 - 8Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- How to Think Like a Lawyer--and Why: A Common-Sense Guide to Everyday DilemmasFrom EverandHow to Think Like a Lawyer--and Why: A Common-Sense Guide to Everyday DilemmasRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- RASPBERRY PI FOR BEGINNERS: TIPS AND TRICKS TO LEARN RASPBERRY PI PROGRAMMINGFrom EverandRASPBERRY PI FOR BEGINNERS: TIPS AND TRICKS TO LEARN RASPBERRY PI PROGRAMMINGNo ratings yet
- The Big Book of Nature Activities: A Year-Round Guide to Outdoor LearningFrom EverandThe Big Book of Nature Activities: A Year-Round Guide to Outdoor LearningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)