Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bab 2 PDF
Uploaded by
Izudin HasanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bab 2 PDF
Uploaded by
Izudin HasanCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 2 NUTRITION
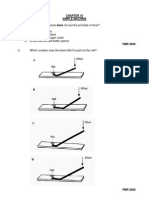
Which food pyramid is the best guide to plan a balanced diet?
PMR 2008
The calorific value of rice is 15 kJ/g. Calculate the calorific value in 100g of rice. A B C D 15 kJ 30 kJ 1500 kJ 3000 kJ PMR 2007
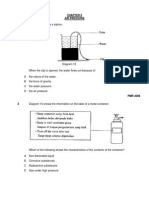
The diagram shows organs in a human digestive system.
Which of the following are the functions of J, K, L and M? J A B C D To digest starch To digest starch To digest protein To digest protein K To perform peristalsis To digest protein To perform peristalsis To digest starch L To digest protein To digest fat To digest fat To perform peristalsis M To digest fat To perform peristalsis To digest starch To digest fat PMR 2006
The diagram shows a boy who is suffering from kwashiorkor disease.
Which of the following is the cause of the disease? A B C D Drinking too much water Lack of protein in the diet Lack of calcium in the diet Too much carbohydrate in the diet PMR 2005
Which of the following pairs of food classes and examples is not correct? Food class A B C D Protein Carbohydrate Roughage Fat Example Chicken meat Noodles Papaya Potato PMR 2004
Figure 1.1 shows the human digestive system.( PMR 2004)
Figure 1.1 (a) (i) Label one of the following structures in Figure 1.1. Pancreas Liver Oesophagus Mouth (1mark) (ii) State one function of the structure in (a) (i). _________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) (b) A student carried out a food test on sample X. Table 1.2 shows the results of the test. Food test Sample X is crushed and added with Millon's reagent Sample X tested on filter paper Observation Red precipitate was formed ___________________ Grease spot was formed ___________________ TABLE 1.2 (i) Complete Table 1.2 by naming the food classes that are present in sample X. (1 mark) (ii) Explain what happens to the food sample X while it is inside structure Q. ___________________________________________________________________ (2 marks) (iii) State what happens to the final product in (b) (ii). __________________________________________________________________ Food class
__________________________________________________________________ (1 mark)
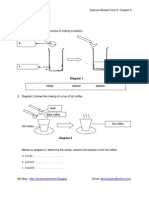
Figure 2.1 shows an experiment to study the action of saliva on starch. The result of the experiment after 30 minutes is shown in Table 2.2. (PMR 2005)
Figure 2.1
Test tube X Y
Presence of starch No Yes
Table 2.2 Based on Figure 2.1 and Table 2.2, answer the following questions. (a) (i) Why must test tubes X and Y be kept in the water bath at 37oC?
_________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) (ii) State the reason why there is no starch in test tube X. ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ (2 marks) (iii) In which part of the alimentary canal does the same enzyme action occur as in the test tube X? ________________________________________________________________ (1 mark)
(b) Figure 2.2 shows pictures of several foods.
Figure 2.2 Based on the pictures, complete the table below by writing the different food classes and their food samples. Food classes (i) Carbohydrate Bread Food sample
(ii) ______________________________
______________________________
(iii)_______________________________
______________________________
(iv)_______________________________
______________________________
(v)_______________________________
______________________________
(vi)_______________________________
______________________________
(5 marks)
NUTRITION ANSWER: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. C C A B D
Nutrition PMR 2004 1(a) (i) Label one of the following structures:Pancreas, liver, oesophagus or mouth (ii) State one function of the labelled structure. Pancreas : Secretes enzyme / examples of enzyme Secretes hormones / examples of hormone Liver : Produces bile / remove toxins from blood / changes excess amino acids to urea / changes glucose into glycogen Oesophagus : Moves the food from the mouth to the stomach Mouth : Churns food Starch is broken down by amylase into maltose.
(b)
(i) 1. Protein 2. Fats (ii) Proteins is broken down into amino acids. Fats is broken down into glycerol and fatty acids (iii) The digested food is absorbed into the blood capillaries.
PMR 2005 2(a) (i) The enzyme in saliva works best at body temperature 37oC. (ii) The enzyme amylase in saliva has changed the starch to sugar. (iii) Mouth (b) Food classes (ii) Protein (iii) Vitamins /fibre (iv) Fats (v) Fibre / vitamin (vi) Water / mineral / fats / proteins Food sample Fish Tomatoes Margarine Vegetables / fruit Fresh milk
You might also like
- f4 Soalan Ict Bulanan 2 TH 2010Document6 pagesf4 Soalan Ict Bulanan 2 TH 2010Izudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Force PDFDocument30 pagesForce PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- f2 Revision Chapter 10 PDFDocument6 pagesf2 Revision Chapter 10 PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NutritionDocument13 pagesChapter 2 NutritionMusfafirdaus MusaNo ratings yet
- Exercise BiodiversityDocument17 pagesExercise BiodiversityAl Amin Azman100% (9)
- Bab 3 PDFDocument7 pagesBab 3 PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Bab 7 PDFDocument6 pagesBab 7 PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Bab 8 PDFDocument3 pagesBab 8 PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document24 pagesChapter 5Ros Mawar MelatiNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 7 F2 PDFDocument29 pagesExercise Chapter 7 F2 PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Bab 9 PDFDocument5 pagesBab 9 PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Chater 6 - EXERCISE AIR PRESSURE WITHOUT SCHEME PDFDocument14 pagesChater 6 - EXERCISE AIR PRESSURE WITHOUT SCHEME PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Force PDFDocument30 pagesForce PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Module (Notes) Science Form 2Document48 pagesModule (Notes) Science Form 2Nur Hafizah Alwi40% (5)
- Bab 4 PDFDocument10 pagesBab 4 PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Bab 10 PDFDocument12 pagesBab 10 PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Exercise Digestive System PDFDocument22 pagesExercise Digestive System PDFIzudin Hasan86% (7)
- Exercisesc.f2.c5. Chapter 5 SambunganDocument22 pagesExercisesc.f2.c5. Chapter 5 SambunganMohd Helmy RosliNo ratings yet
- Bab 9 PDFDocument5 pagesBab 9 PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 PDFDocument4 pagesBab 1 PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 PDFDocument6 pagesBab 6 PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- Bab 5 PDFDocument17 pagesBab 5 PDFIzudin HasanNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Safety Data Sheet: Jotun Peroxide 1Document12 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Jotun Peroxide 1EngTamerNo ratings yet
- GATE 2000 Que PaperDocument10 pagesGATE 2000 Que PaperSHRIKANTNo ratings yet
- A1 Halogenoalkanes WS1Document15 pagesA1 Halogenoalkanes WS1chantellelimNo ratings yet
- Water Tightness EquipmentDocument9 pagesWater Tightness EquipmentZivadin LukicNo ratings yet
- 04 - 01 - Curriculum Design of POC-III - IV Sem-1Document4 pages04 - 01 - Curriculum Design of POC-III - IV Sem-1TamuNo ratings yet
- Development and CharacterizationDocument17 pagesDevelopment and Characterizationahmad dewantoroNo ratings yet
- (Biochem A) 1.1 Carbohydrate Chemistry (Asis)Document8 pages(Biochem A) 1.1 Carbohydrate Chemistry (Asis)Faye AquinoNo ratings yet
- Volume 6, Issue 1 (2019) Tropical Plant ResearchDocument167 pagesVolume 6, Issue 1 (2019) Tropical Plant ResearchTropPlResNo ratings yet
- AQA A Level Chemistry Student Book 1Document378 pagesAQA A Level Chemistry Student Book 1Mahdiya71% (7)
- Multiple Choice Questions From Chapters 7-12 Chapter 7: Multiple ChoiceDocument15 pagesMultiple Choice Questions From Chapters 7-12 Chapter 7: Multiple ChoiceRavindra AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 5 Chemical ResistanceDocument8 pages5 Chemical ResistanceMohamed NouzerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 4 NotesLEE JIAN HAO MoeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8.2 PhotosynthesisDocument16 pagesLesson 8.2 Photosynthesisamr.rag550No ratings yet
- Department of Chemical Engineering, University of The Philippines, Diliman, Quezon CityDocument2 pagesDepartment of Chemical Engineering, University of The Philippines, Diliman, Quezon CityElaine Nicole CanebaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIIDocument5 pagesChapter IIIFaiz NobhanNo ratings yet
- FP 10 WalfordDocument15 pagesFP 10 WalfordAbraham.CastilloNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument89 pagesDocumentRajeev Sharma100% (1)
- Effects of Different Levels of Humic Acid, Amino Acid and Fulvic Acid On The Growth and Yield of Basil PlantsDocument3 pagesEffects of Different Levels of Humic Acid, Amino Acid and Fulvic Acid On The Growth and Yield of Basil Plantsyasir majeedNo ratings yet
- BRGT 3092Document4 pagesBRGT 3092sunifeb128075No ratings yet
- PharmaceuticalDocument19 pagesPharmaceuticalfaissalNo ratings yet
- MCQs of Biology Book of Class IXDocument25 pagesMCQs of Biology Book of Class IXShazil HameedNo ratings yet
- Effect of Degree, Type, and Position of UnsaturationDocument7 pagesEffect of Degree, Type, and Position of UnsaturationBernardo DavisNo ratings yet
- 02 Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances, Vol 02Document571 pages02 Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances, Vol 02nur syaraNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Health Benefits MilletsDocument9 pagesNutritional Health Benefits MilletsbhargavmitraNo ratings yet
- DNA Analysis Student Exploration SheetDocument7 pagesDNA Analysis Student Exploration SheetTamira SmithNo ratings yet
- Production of Biodegradable Detergent From Castor Oil: ProductionofbiodegradabledetergentfromcastoroilDocument5 pagesProduction of Biodegradable Detergent From Castor Oil: ProductionofbiodegradabledetergentfromcastoroiledreamerNo ratings yet
- Human Genomic Dna Extraction and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification of Alu PV92Document10 pagesHuman Genomic Dna Extraction and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification of Alu PV92Saya SufiaNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Seniority Rules PDFDocument10 pagesIUPAC Seniority Rules PDFAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Astm-D-1078 Rango de DestilacionDocument9 pagesAstm-D-1078 Rango de DestilacionepilfigueroaNo ratings yet
- Amoeba Sisters Video Recap:BiomoleculesDocument2 pagesAmoeba Sisters Video Recap:BiomoleculesKimo GamerYTNo ratings yet