Professional Documents
Culture Documents
34 Alcohols & Ethers - Problems For Practice - Level 1
Uploaded by
Abuturab MohammadiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
34 Alcohols & Ethers - Problems For Practice - Level 1
Uploaded by
Abuturab MohammadiCopyright:
Available Formats
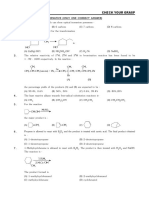
EXERCISE-I(A)
Q.1 Which of the following reaction is called as BouveaultBlanc reduction (A) Reduction of acyl halide with H2PdBaSO4 (B) Reduction of ester with Na/C2H5OH (C) Reduction of anhydride with LiAlH4 (D) Reduction of carbonyl compounds with Na/HgHCl Glycol on treatment with PI3 mainly gives (A) Ethylene (B) Ethylene iodide
Q.2
(C) Ethyl iodide
(D) Ethane
Q.3
Acrolein is formed when glycerol is heated with (A) Acidified KMnO4 (B) Br2 water (C) KHSO4 Glycerol on treatment with oxalic acid at 110C forms (A) Allyl alcohol (B) Formic acid (C) CO2 and CO
(D) HNO3 (D) Glyceric acid
Q.4
Q.5
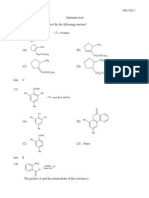
If the starting material is 1methyl1,2epoxy cyclopentane, of absolute configuration, decide which one compound correctly represent the product of its reaction with sodium methoxide in methanol.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Q.6
When phenol is treated with PCl5, the yield of chlorobenzene is generally poor because of the formation of (A) Benzoyl chloride (B) pchorophenol (C) ochlorophenol (D) Triphenyl phosphate In the following reaction, final product is
H ClCH 2 CH C H 2 NaOC 2 5 \ / O
Q.7
14
14
14
(A) ClCH 2CH C H 2OC 2 H 5 | OH (C) C H 2 CHCH 2 OC 2 H 5 \ / O
14
(B) ClCH 2CH C H 2ONa | OC 2 H 5 (D) CH 2 CH C H 2OC 2 H 5 \ / O
14
Q.8
Consider the reaction of HI with the following: I II (D) none
Which forms di-iodide on reaction with HI (excess)? (A) I and II both (B) II only (C) I only Q.9
Ethanol on reaction with acetic anhydride gives (A) Acetic ester (B) Formic ester (C) Ethanoic acid (D) Acetic ester and Ethanoic acid both Ethanol cannot be dried by anhydrous CaCl2 due to formation of the following solvated product (A) CaCl22C2H5OH (B) 2CaCl23C2H5OH (C) CaCl23C2H5OH (D) CaCl2C2H5OH Rate of hydration of
Q.10 Q.11
, will be in order: (A) I < II < III Q.12 Q.13 Q.14 Q.15 Q.16
(B) I < III < II
(C) II < I < III
(D) III < II < I
The reaction of CH3OC2H5 with HI gives (A) CH3I (B) C2H5OH
(C) CH3I + C2H5OH (D) C2H5I + CH3OH
The number of methoxy groups in a compound can be determined by treating it with (A) HI and AgNO3 (B) Sodium carbonate (C) Sodium hydroxide (D) Acetic acid Most acidic alcohol out of following compounds is (A) (CH3)3COH (B) CH3CH2OH (C) CH3OH Action of HNO2 on CH3NH2 gives following as major product (A) CH3OH (B) CH3OCH3 (C) CH3ON=O (D) PhOH (D) CH3NO2
A compound X with molecular formula C3H8O can be oxidised to a compound Y with the molecular formula C3H6O2, X is most likely to be (A) Primary alcohol (B) Secondary alcohol (C) Aldehyde (D) Ketone Diethyl ether and air gives ether hydroperoxide. The mechanism of the reaction is (A) Nucleophilic substitution (B) Free radical addition (C) Free radical substitution (D) None of the above Ether on carbonylation gives (A) Alkanoic acid (B) Alkanone
Q.17
Q.18
(C) Alkyl alkanoate
(D) Alkanal
Q.19
I R O R ' RI + R'OH true about this mechanism | H
(A) SN1 in gas phase (C) both of the above Q.20 Phenol with Hinsbergs reagent gives (A) Sulphone (B) Sulphanilic acid
(B) SN2 in aqueous phase (D) none (C) Sulphonic ester (D) Sulphonal
Q.21
Select the odd structure out (A) CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3 (C) CH3CH(OH)CH3
4 Glycerol 4 A B A and B are: (A) Acrolein, allyl alcohol (C) Allyl alcohol, acrolein
(B) CH3CH(OH)CH2CH2CH3 (D) CH3CH2CH(OH)C2H5
Q.22
KHSO
LiAlH
(B) Glyceryl sulphate, acrylic acid (D) Only acrolein (B is not formed)
Q.23
An ether is heated with phosphorous penta sulphide to give (A) Alkanthiol (B) Dialkyl sulphide (C) Hydrogen sulphide (D) Thioester
O i ) NaOH Phenol ( A 2 B Al2 C 3 H+ / H O
Q.24
( ii ) CO 2 / 140C
CH3COOH ,
In this reaction, the end product C is: (A) salicylaldehyde (B) salicylic acid Q.25
(C) phenyl acetate
(D) aspirin
In the Liebermanns nitroso reaction changes in the colour of phenol occurs as: (A) Brown or red-greenish red-deep blue (B) red-deep blue-green (C) red-green-white (D) white-red-green
Q.26
A. A is
H 3O
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Q.27 A and B are: (A)
cold A CrO3 B alkaline KMnO
4
AcOH
(B)
(C)
(D) no formation of A and B
Q.28
B 4
NaBH
2 CH = CH CHO A
H / Pt
A and B are: (A) (B) (C) (D) CH2CH2CHO, CH2CH2CH2OH, CH = CHCH2OH CH = CH CH2OH
CH= CHCH2OH in both cases CH2CH2CH2OH in both cases
Q.29
3 B
CH OH
2 A
H O18 H+
CH 3ONa
A and B are CH 3 | (A) CH 3 C CH 2 | | OH OH 18
CH 3 | , CH 3 C CH 2 | | OH OCH 3
CH 3 CH 3 | | (B) CH 3 C CH 2 , CH 3 C CH 2 | | | | OH18OH OH OCH 3
CH 3 CH 3 | | (D) CH 3 C CH 2 , CH C CH 3 2 | | | | 18 OCH 3 OH 18OH OH
CH 3 CH 3 | | (C) CH 3 C CH 2 , CH 3 C CH 2 | | | | 18 OH OH OH OH 18
18
Q.30
Oxalic acid + A hence A conc. H 2SO 4 B, B is: (C) CH 2 O CH 2 | | OH OH
(A)
(B)
(D) None
Q.31
Select schemes A, B, C out of I acid catalysed hydration (A) I in all cases (B) I, II, III Q.32 Dehydration of the alcohols
II
HBO (C) II, III, I
III
oxymercuration-demercuration (D) III, I, II
will be in order (A) IV > III > II > I
(B) I > II > III > IV
H O+
(C) IV > II > III > I
(D) II > IV > I > III
Q.33
CH3MgBr + E is (A)
HCHO HBr Mg / ether 3 HI A B C D E H O+
3
(B)
(C)
(D)
Q.34
H ? Product is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Q.35 (A) (C)
Alc. Major product is KOH (B) (D)
Q.36
RMgX ? Product Obtained is:
H 2O
R | (A) R 'C CH 2OH | R''
R' R R | | | (B) RCH 2 C OH (C) R ' CH 2 C OH (D) R ' ' CH 2 C OH | | | R' ' R' R''
Q.37
I / NaOH
+ A, A is H
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Q.38
3 (A)
CH OH CH3O
3 (B) A & B are:
H 2SO 4
CH OH
(A)
&
(B)
&
(C)
&
(D)
&
Q.39
3 ? Major Product is:
AlCl
(A)
(B) H3COC
OH
(C)
(D)
Q.40
? Product is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D) no reaction
Q.41
3 [X] here X is:
( i ) CHCl + KOH
(ii ) CH 2I 2 + NaOH
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Q.42
(CH 3 ) 2 C C(CH 3 ) 2 | | OH OH (A) OH at C2 is more basic than that of at C5 (B) OH at C2 is more acidic than at C5. (C) both have same basicity (D) both have same acidic strength . In this diol
2 (CH3)2C = C(CH3)2 A OH B
Q.43
H 2O
(A)
(B) (CH 3 ) 2 C C(CH 3 ) 2 | | OH Cl (D) None
(C)
Q.44 A is
2 A
NaNO HCl
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Q.45
CH 2 = CHCHCH 2CH 2OH | OH (A) CH 2 = CHCCH 2 CH 2OH || O
A. A is
(B)
(C)
(D)
Q.46
HCO 3H H3O Acetophenone A B + C Indicator (D) +
Pthalic Anhydride H
C & D are
(A) CH3OH &
(B) PhOH &
(C) PhOH &
(D) CH3OH &
MnO CH 2 CHCHCH 2CHO CHO =2 CHCCH 2O || || CH 2 = CHCCH 2COH OH O || O
Q.47
m-Aminophenol on treatment with NaOH and CO2 gives which of the following as major product?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Question No 48 to 50 (3 questions)
Q.48
Compound 'B' is? (A) (B) (C) (D)
Q.49
Organic compound A does not undergo de carboxylation reaction because? (A) Intermediate does not follow Saytzeff'n rule (B) Intermediate does not follow Hofmann's rule (C) Intermediate does not follow Bredict's rule (D) Intermediate does not follow MarkwoniKoffs rule Total No. of stereoisomers of B are? (A) 2 (B) 4 (C) 3 (D) 6
Q.50
EXERCISE-I(B)
Q.1 Compound which gives alcohol on reduction is/are (A) Me C Cl || O Q.2 (B) (C) (D)
Phenol and ethanol are distinguished by the reaction with (A) Red litmus (B) NaHCO3 (C) FeCl3
H
(D) NaOH
Q.3
dil. H 2SO 4 2 2O In the reaction sequence, CaC2 H A B C, true about the product C is +2 Hg Ni
(A) give yellow ppt. with NaOI (B) its final oxidation product is carbonyl compound (C) its final oxidation product is CO2 and H2O (D) its final oxidation product is CH3COOH Q.4 Which can be cleaved by HIO4? O O || || (A) CH CH CCH CCH 3 2 2 3 OH O O | O Me C CH 2 CH NH |2| | |||\ /| | (B) CH 3CHCCH CH Me O O Me2 3 C OC O O || || (D) CH 3CCH 2 CHCH 2CCH 3 | OH
(C)
Q.5
HBO, oxymercuration-demercuration and acid catalysed hydration will not give same product in (A) (B) (C) (D)
Q.6
Diethyl ether reacts with PCl5 to form (A) Ethyl chloride (C) Ethenol
(B) Phosphorous oxy trichloride (D) Ethene
Q.7
Select the correct synthesis products (A)
2 2 3 NaOH
BH THF
H O , OH
(B)
2 4 NaOH
Hg ( OAc) H 2O
NaBH
(C) (D) Q.8
mCPBA
CH 2Cl2
The molecules of ether dehydrates in the presence of (A) Al2O3 (B) H3PO4 (C) H2S2O7 Anhydride of alcohol is (A) Ether (C) Alkyl hydrogen sulphere (B) Aldehyde (D) Alkene
(D) liq. NH3
Q.9
Q.10
Lucas test is used to make distinction between 1, 2 and 3 alcohols ROH + HCl anhydrous ZnCl 2
conc.
RCl
White turbidity
+ H2O
This shows that (A) ROH behaves as a base (B) greater the value of pKa (alcohol), greater the reactivity with conc. HCl and thus sooner the formation of white turbidity. (C) alcohol which reacts fastest with Na metal, will give turbidity at fastest rate (D) alcohol which gives red colour during Victor Mayor test, will give turbidity at slower rate then those giving blue or white colour during Victor Mayor test. Q.11 If ethanol dissolves in water, then which of the following would be done (A) Absorption of heat (B) Emission of heat (C) Increase in volume (D) Contraction in volume Which method is useful for the synthesis of ether? (A) (B) C2H5ONa + (CH3)2SO4 (C) CH3ONa + CH3CH2OSO2 (D) (CH3)3CBr + CH3CH2ONa Q.13 Which of the following can react with TsCl (A) Glycerol (C) Oil of wintergreen (B) Oximinoacetone (D) dimethyl amine aq. NaOH
Q.12
Q.14
Which is/are correct statements? (A)
(B)
(C) This is only affected in reduction to 2 alcohol
NaBH
CH3OH
(D)
Q.15
3-methyl-3-hexanol can be prepared by (A) CH3MgI and 3-hexanone, followed by hydrolysis (B) C2H5MgI and 2-pentanone, followed by hydrolysis (C) C3H7MgI and 2-butananone, followed by hydrolysis (D) C4H9MgI and propanone, followed by hydrolysis In which cases product formed are not according to reaction? (A) (B) + HNO3 H 2SO 4 + HNO3 H 2SO 4
Q.16
(C) CH2 = CHCHO + LiAlH4 CH3 CH2CH2OH (D) Q.17 + CH3ONa
Dehydration of alcohols take place more rapidly with POCl3 than with H2SO4. Select the correct statement(s) about the following dehydration reaction.
3
POCl
pyridine
(A) It does not involve carbocation. (B) It involves ROPOCl2 with OPOCl2 as a better leaving group. (C) It involves E2 mechanism as pyridine base abstracts proton from the adjacent carbon as the same time at which OPOCl2 is leaving. (D) It is E1 reaction without formation of carbocation.
Q.18
Which of the following will get oxidised by Br2 / KOH into carboxylic acid? (A) CH3CH2OH (B)
CH CH 3 | OH
(C) Q.19
CH2OH
(D)
In Kolbe-Schmidt reaction, o-hydroxy benzoic acid is predominantly formed. This is because (A) salicylate anion is a stronger base than phenoxide ion (B) salicylate anion is a weaker base than phenoxide ion (C) p-hydroxy benzoate ion is a stronger base than phenoxide ion (D) p-hydroxy benzoate ion is a stronger base than salicylate ion Methanol can be distinguished from ethanol by (A) Heating with I2 and alkali (B) Treating with schiffs reagent (C) Treating with CrO3 solution in dil. H2SO4 (D) Treating with Lucas reagent Products form by following reactions are
Q.20
Q.21
CHCl +KOH
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Q.22
For the reactions shown below, identify the correct statement(s) with regard to the products formed: (i) MeOH, P H
+
(ii)
NaOMe Q / MeOH
(A) P and Q are identical (B) P is recemic and Q is optically active (C) P and Q are positional isomers (D) both are optically active Q.23
Tilden NaNO2 NH C2N5NH2 (i) 3 (ii) (iii). The product (iii) can be reagent
HCl
(A) Alcohol
(B) Ether
(C) Alkyl chloride
(D) Alkyl nitrite
Q.24
Products form during dehydration of following alcohols are
(A) Q.25
(B)
(C)
(D)
Consider the following compound A (below)
Select the correct statement(s) (A) It is more acidic than CH3OH (C) It reacts very fast with Lucas reagent Q.26 Match the following: Reaction (A)
2 4
O || (B) It is more acidic than CH 3COH (D) It is a diacid base Mechanism
Conc.H SO
(P)
change in number of carbon in cycle
(B)
HIO
(Q)
Pinacol rearrangement
(C)
H
heat H O heat
(R)
Oxidative bond cleavage
(D) Q.27
(S)
Ketone as product
Match the column: Column I (A) Identification of 1, 2& 3 Alcohols (B) Identification of 1, 2& 3 Nitro alkanes (C) Formation of alcohol by anti Markovnikov's addition of H2O (D) Formation of alcohol by Markovnikov's addition
(P) (Q) (R) (S) (T)
Column II Oxymercuration demercuration Cu/300 heat Victor Mayer's test Hydroboration oxidation Lucas test
Q.28
Match the column: Column I (A) Oxidation of 1alcohol in aldehyde (B) CrO3 . .HCl
(P) (Q)
Column II KMnO4/ Collin's reagent
(C) (D) Q.29
CrO3 .2 Oxidation of alkene into acid
(R) (S)
Jone's reagent P.C.C
Match the products of following: Column I (A) (B)
HI
Column II (P) (Q) I CH2OH
Violet color is obtain by the reaction of neutral FeCl3 with
(C)
Reaction of benzaldehyde with LiAlH4 / H2O gives
(R)
OH
(D)
+ KI ?
Q.30
CH 3 CH CH = CH 2 | CH 3
which is true about alcohol and R? Alcohol (A)
(S) CH2 I CH 3 agent R CH CH 3 CH Re OH | | CH 3 CH CH 2CH 3 C OH 3 Alcohol | CH 3
Reagent B2H6 , H2O2 / NaOH
CH 3 CH CH 2 CH 2OH | CH 3
(B)
PdCl2, H2O, O2 / LAH
(C)
OH | CH 3 C CH 2CH 3 | CH 3
Hg(OAc)2, H2O / NaBH4
(D)
dil. H2SO4
You might also like
- Rhode Island Brewery HistoryDocument517 pagesRhode Island Brewery HistoryThe 18th Century Material Culture Resource CenterNo ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Correct Choice) : HC CH 1.1eq Nanh Nanh Nanh X XDocument14 pagesSection-I (Single Correct Choice) : HC CH 1.1eq Nanh Nanh Nanh X XPriyansh YadavNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivatives PDFDocument32 pagesHalogen Derivatives PDFRaju Singh100% (1)
- Alcohol & EtherDocument217 pagesAlcohol & EtherAmitNo ratings yet
- (Xii) Alcohol, Phenol, EtherDocument10 pages(Xii) Alcohol, Phenol, EtherAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class Test-1-Aldehydes & Ketones - PreparationDocument5 pagesClass Test-1-Aldehydes & Ketones - PreparationSarthak VermaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Alcohols & EtherDocument18 pagesAlcohols & EtherRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Isobutylene PresentationDocument50 pagesIsobutylene PresentationMissQiah0% (1)
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument16 pagesAromatic CompoundsadityaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument29 pagesAldehydes and KetonesJiya singhNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and Ketone (DPP)Document12 pagesAldehyde and Ketone (DPP)Shreeyansh Bhardwaj0% (1)
- 3 - Aldehydes and Ketones (Assignment) Booklet-2Document15 pages3 - Aldehydes and Ketones (Assignment) Booklet-2kraken monsterNo ratings yet
- Alcohol & Ether B Lord of The RingsDocument13 pagesAlcohol & Ether B Lord of The RingsadityaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols & EthersDocument36 pagesAlcohols & EthersKaveesh KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Iit Questions On Carbonyl Compounds & Carboxylic Acid and Its DerivativeDocument12 pagesIit Questions On Carbonyl Compounds & Carboxylic Acid and Its DerivativeRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Alcohol EtherDocument36 pagesAlcohol EtherAnand MurugananthamNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument39 pagesHydrocarbonSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Oxygen Containing Organic Compounds IIDocument10 pagesJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Oxygen Containing Organic Compounds IIvarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes & KetonesDocument23 pagesAldehydes & KetonesManthan JhaNo ratings yet
- HC Docx1Document13 pagesHC Docx1ayushsekhariNo ratings yet
- Halogen Containing CompoundsDocument67 pagesHalogen Containing Compoundsonline_mktg100% (6)
- Carbonyl Compounds SheetDocument133 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Sheetadityavaish739No ratings yet
- Aromatic Compounds (13th)Document24 pagesAromatic Compounds (13th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- CadDocument8 pagesCadRamesh Babu GarlapatiNo ratings yet
- 12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS QDocument20 pages12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS Q123No ratings yet
- BT Alcolhols Phenls and Ethers - ExerciseDocument20 pagesBT Alcolhols Phenls and Ethers - ExerciseSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Corbonyl CompOUND AND Corboxilic AcidDocument12 pagesCorbonyl CompOUND AND Corboxilic AcidApex InstituteNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds 12thDocument24 pagesCarbonyl Compounds 12thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 12 Carboxyloc AcidDocument3 pages12 Carboxyloc Acidimu4u_786No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry-JeeDocument33 pagesOrganic Chemistry-JeeRamesh Babu GarlapatiNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon 4Document35 pagesHydrocarbon 4AjayNo ratings yet
- NSEC Solved Paper 2010Document7 pagesNSEC Solved Paper 2010whatismyusername1947No ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Acid Derivatives Carbonyl PDFDocument124 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Acid Derivatives Carbonyl PDFrvignesh2809No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument7 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acidskavitha2511977No ratings yet
- Exercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HODocument29 pagesExercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HOHet PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- P Block Elements QBDocument12 pagesP Block Elements QBRajeev KaushikNo ratings yet
- Exercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HODocument7 pagesExercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HOChesta MalhotraNo ratings yet
- National Standard Examination in Chemistry 2014: QP Code C 203Document15 pagesNational Standard Examination in Chemistry 2014: QP Code C 203Karan TejwaniNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundDocument197 pagesCarbonyl CompoundAmitNo ratings yet
- Halogen DerivativesOrganic Chem Class XIIDocument32 pagesHalogen DerivativesOrganic Chem Class XIIDwaipayan Pradhan100% (2)
- Jee 2014 Booklet5 HWT HalidesDocument12 pagesJee 2014 Booklet5 HWT Halidesvarunkohliin100% (2)
- WORK BOOK - Exercise in ChemistryDocument28 pagesWORK BOOK - Exercise in ChemistryTikeshwar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Jee MainDocument15 pagesChemistry Jee MainAt TanwiNo ratings yet
- (Xii) Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument11 pages(Xii) Haloalkanes and HaloarenessitaramroyalNo ratings yet
- Quiz Organic 1Document6 pagesQuiz Organic 1ronakgupta332005No ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 882Document107 pagesNotes Chapter 882notime ReactionNo ratings yet
- Goc & Eas Test-IiDocument7 pagesGoc & Eas Test-IiAniket GuptaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons A 1Document4 pagesHydrocarbons A 1REJA MUKIB KHANNo ratings yet
- Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes ObjectiveDocument7 pagesAlkanes Alkenes Alkynes ObjectiveVishal_93No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon TestDocument7 pagesHydrocarbon TestRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- CC 13Document6 pagesCC 13Deepak SethyNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 MCQDocument7 pagesUnit 11 MCQJay VermaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol & Ether: A O CH C HDocument6 pagesAlcohol, Phenol & Ether: A O CH C HJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Hydrocar SHEET3Document4 pagesHydrocar SHEET3Aayush SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Answers To ROH Tutorial PDFDocument12 pagesAnswers To ROH Tutorial PDFCorvo Haosen Al-Han0% (1)
- Resonance Chemistry DPP 6 (Advanced)Document11 pagesResonance Chemistry DPP 6 (Advanced)Anurag1210701067% (6)
- JMS-5 Paper - 2Document7 pagesJMS-5 Paper - 2janmanchiNo ratings yet
- Chirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesFrom EverandChirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesF. Richard KeeneNo ratings yet
- Riscv Spec v2.1 PDFDocument131 pagesRiscv Spec v2.1 PDFAshwini PatilNo ratings yet
- Vliw Architecture StudyDocument9 pagesVliw Architecture StudyAbuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CUDA CDocument67 pagesIntroduction To CUDA CAbuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- VLSI ALU VerilogDocument19 pagesVLSI ALU VerilogAbuturab Mohammadi100% (1)
- Basic Analog For TIDocument2 pagesBasic Analog For TIAbuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Mathworks Placement ProcessDocument1 pageMathworks Placement ProcessAbuturab Mohammadi100% (2)
- Sensys Ch5 MacDocument37 pagesSensys Ch5 MacAbuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Optics Iit MaterialDocument27 pagesOptics Iit MaterialAbuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- 22 Answers To Organic Class Sheet 1, 2 & 3Document20 pages22 Answers To Organic Class Sheet 1, 2 & 3Abuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Oc and SC Tests On A Single-Phase Transformer: Experiment No. 1Document5 pagesOc and SC Tests On A Single-Phase Transformer: Experiment No. 1Abuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1Abuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab Manual - 2014-15 - Cycle I-11!08!2014Document52 pagesElectrical Machines Lab Manual - 2014-15 - Cycle I-11!08!2014Abuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- 16 Yearly CalendarDocument6 pages16 Yearly CalendarAbuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Date To DayDocument2 pagesDate To DayAbuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- 07 Spiral MatrixDocument3 pages07 Spiral MatrixAbuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Gabriel's Phthalimide SysthesisDocument7 pagesGabriel's Phthalimide SysthesisAbuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- 1 Organic Class Sheet 1 - NomenclatureDocument12 pages1 Organic Class Sheet 1 - NomenclatureAbuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- 2 Organic Class Sheet 2 - IsomerismDocument13 pages2 Organic Class Sheet 2 - IsomerismAbuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- 3 Organic Class Sheet 3 - GOCDocument14 pages3 Organic Class Sheet 3 - GOCAbuturab MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Paper Ethanol Corrosion Cavalcanti1987Document3 pagesPaper Ethanol Corrosion Cavalcanti1987Eduardo CavalcantiNo ratings yet
- Building Mental Models: Teaching Carbon and Its Components To Class XDocument13 pagesBuilding Mental Models: Teaching Carbon and Its Components To Class Xloly62006No ratings yet
- Experiment 1-6 ReviewerDocument2 pagesExperiment 1-6 ReviewerpsychcookieNo ratings yet
- A02 115Document29 pagesA02 115jaime0% (1)
- C B S E Chemistry - SrSec - 2022-23Document8 pagesC B S E Chemistry - SrSec - 2022-23divyaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Heat and AlcoholDocument6 pagesEffect of Heat and AlcoholRoxanne Jane Birondo100% (1)
- Cee Model Examinaton: Model Questions For Common Medical Entrance MBBS/BDS/BSC Nursing/Baslp 2078 Online (Set-Iii)Document70 pagesCee Model Examinaton: Model Questions For Common Medical Entrance MBBS/BDS/BSC Nursing/Baslp 2078 Online (Set-Iii)Ashik jhaNo ratings yet
- Hominids Adapted To Metabolize Ethanol Long Before Human Directed Fermentation 2014Document12 pagesHominids Adapted To Metabolize Ethanol Long Before Human Directed Fermentation 2014Gaby ArguedasNo ratings yet
- Kerala State BeveragesDocument73 pagesKerala State BeveragesRuben Morales50% (20)
- Sisi Footwear Catalogue Vol 1 2020 r2 1.compressedDocument24 pagesSisi Footwear Catalogue Vol 1 2020 r2 1.compressedJaney-Dell NelNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year CHEMISTRY CH Wise 2021 by 786 AcademyDocument14 pages2nd Year CHEMISTRY CH Wise 2021 by 786 AcademyAbdul Majeed Maitla100% (2)
- Lecture Notes 13 - Esters88Document4 pagesLecture Notes 13 - Esters88Surendra RamkissoonNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument82 pagesAldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Ch12org MetalicoDocument21 pagesCh12org MetaliconicoleNo ratings yet
- Densities and Viscosities of Fatty Acid Ethyl EstersDocument10 pagesDensities and Viscosities of Fatty Acid Ethyl EstersNéia CostaNo ratings yet
- PhenolDocument16 pagesPhenolAmanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and Phenols - MC MurrayDocument54 pagesAlcohols and Phenols - MC MurrayIqra BaigNo ratings yet
- 03 111139e Kolliphor+ELDocument5 pages03 111139e Kolliphor+ELGialuu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde-Ketone - 1Document31 pagesAldehyde-Ketone - 1Hendra Apnizar KuswalaNo ratings yet
- Saponification of Ester ReportDocument11 pagesSaponification of Ester Reportapi-397833575100% (3)
- Organic As Test P-2Document9 pagesOrganic As Test P-2zafarchem_iqbalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Tests PDFDocument2 pagesChemical Tests PDFSyafiqah ArinaNo ratings yet
- Final Touch (RCC Do / Die Questions)Document24 pagesFinal Touch (RCC Do / Die Questions)harita shinde100% (1)
- Hazy Jane: New England IpaDocument1 pageHazy Jane: New England Ipaesteban pedrazNo ratings yet
- Exp7 Synthesis of 2-Methyl-2 - Butene ChazaDocument5 pagesExp7 Synthesis of 2-Methyl-2 - Butene ChazaAnthony TannousNo ratings yet
- 2019-04 Cosphatec Suggestions EN PDFDocument6 pages2019-04 Cosphatec Suggestions EN PDFZimzelena Kozmetika100% (1)
- Powerpoint Intro Bar Service 2Document14 pagesPowerpoint Intro Bar Service 2Taufik GinanjarNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and Phenol (II Part)Document10 pagesAlcohol and Phenol (II Part)Somil NegiNo ratings yet