Professional Documents
Culture Documents
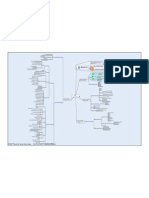
MindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap
Uploaded by
cpawan_69Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap
Uploaded by
cpawan_69Copyright:
Available Formats
Motivation and Study Techniques to help you learn, remember, and pass your technical exams!
Cisco CISSP CEH More coming soon...
Visit us IKE Phase One
Router(cong)#crypto isakmp enable Enable ISAKMP
www.mindcert.com
Step 1
Provides security services at the IP layer A framework of services Adds security to the upper layers in the OSI model
By Implementing a new set of headers One SA is required per direction
ISAKMP is enabled by default Dene the ISAKMP policy 3DES DES 128-bit 1932-bit 256-bit MD5 SHA Have to set a pre-shared key Router(cong)#crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 1.1.1.1 Would set the key cisco123 for the peer 1.1.1.1 RSA-Encr RSA-Sig 1 2 5 60-86400 Seconds DH Group Pre-Share Authentication Hash Parameters that are used during ISAKMP negotiation AES Encryption
Denition
Utilizes Security Associations (SA)
A router to router IPsec VPN will use two SA's
One in each direction
Authentication Header
AH ESP
Both change the datagram
Encapsulating Security Payload AH IP Protocol 51
Origin authentication
Does a one-way hash of the packet
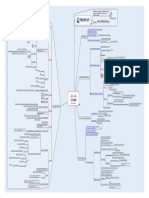
Step 2
Provides DOES NOT OFFER DATA CONFIDENTIALITY Encryption
Authentication Header
SA Lifetime 56-bit DES Supports Encryption SHA RSA-Sig 768-bit Hash Defaults Transport Mode Tunnel Mode
Adds a new header Authenticates the whole new datagram Authenticates the whole existing datagram
Not compliant with NAT
As NAT changes the IP Header The will break AH authentication
Authentication 1 DH Group
Two Frame Formats
ESP IP Protocol 50 Provides
One Day
Condentiality Integrity
Encryption
86400 Seconds
SA Lifetime
Router(cong)#crypto isakmp identity {address | hostname}
Congure the ISAKMP Identity method IP Address Hostname IP Address Options Default
Origin Authentication Original datagram is placed in the encrypted ESP payload Tunnel Mode Supports Uses encrypted ESP headers Cannot detect tampering whilst delivered Although payload is fully secure
Step 3
Encapsulating Security Payload
IKE Phase Two
Router(cong)#crypto ipsec transform-set myset esp-des esp-md5-hmac This would create a transform set called myset using ESP and DES for Encryption using ESP and MD5 for Authentication You are then in crypto transform conguration mode Router(cfg-crypto-trans)#mode {transport | tunnel} Sets the mode to either Transport or Tunnel Default is Tunnel Dene Crypto ACL Crypto ACL is the Access Control List that species the traffic to be sent over the VPN Would encrypt traffic with IPsec from host 1.1.1.1 to host 2.2.2.2 Router(cong)#access-list 199 permit ip host 1.1.1.1 host 2.2.2.2 Further conguration Dene IPsec Transform Sets
Keeps the existing IP header and encrypts the original payload Transport Mode Only authenticates the ESP header and payload cannot detect tampering whilst delivered Although payload is fully secure
Cisco IPsec Conguration
Step 4
Transport Mode
Is Compliant with NAT Protects the payload of the original IP datagram Used for end to end sessions Cannot be used When NAT is required
Two Protection Modes
Tunnel Mode
Protects entire datagram Places whole datagram in a new datagram Works with NAT
Step 5
In IPsec, Key Exchange is provided by the Internet Key Exchange IKE provides scalability for exchanging keys between IPsec IKE is synonymous with ISAKMP
IKE
Router(cong)#crypto map mymap 10 ipsec-isakmp The Crypto Map will use ISAKMP Description of the Crypto Map description dialer match Dene Crypto Maps Crypto Map conguration commands Congures a Crypto Map with a sequence number of 10
No security is currently in place Master secret is exchanged to authenticate the peers IKE Phase One sets the secure channel for the data encryption key exchange which is done in IKE Phase Two
Dialer related commands Match crypto ACL Commands for reverse route injection Identies the IPsec peer Identies which transform set to use
IKe Phase One negotiates IKE SAs Hash Authentication
IKE SA parameters are agreed at Phase One IKE Phase One Aggressive Mode
reverse-route peer
Eliminates several Phase One steps Faster but less secure Three way packet exchange
transform-set pfs set
Use PFS or not Lifetime Set SA parameters
Step 6
Key Exchange
IKE has two phases
Typically used in Remote Access VPNs Two Modes Main Mode Cisco devices use main mode Slower but more secure Six way packet exchange Can respond to peers that use aggressive mode
security-association Crypto maps pull together various parts used to set up the IPsec SAs All entries are pre-congured Entries are congured dynamically as the result of IPsec negotiation Crypto Maps are applied to the interface where the traffic leaves and enters a router You must apply the crypto map both the the physical and logical interface when using GRE tunnels Apply the Crypto Map Static Types Dynamic IKE Phase Two
Uses Diffie-Hellman (DH) to create the secure channel IKE negotiates the IPsec SAs and generates the required key material for IPsec Transform set and all other IPsec parameters are agreed at Phase Two One Mode Quick Mode PFS Perfect Forward Secrecy If enabled, occurs at IKE Phase Two Carries out a new DH exchange with each Quick Mode Reinitiates to refresh the SA
You might also like
- MindCert CISSP Cryptography MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Cryptography MindMapjayarajanNo ratings yet
- CCNA CheatSheet PDFDocument19 pagesCCNA CheatSheet PDFpranali50% (2)
- Cissp Information PDFDocument4 pagesCissp Information PDFZaheer BkNo ratings yet
- MindCert CISSP Application Development MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Application Development MindMapjayarajanNo ratings yet
- A Docker Tutorial For BeginnersDocument54 pagesA Docker Tutorial For BeginnersEduardoSouza100% (1)
- Lumion 8 3D Rendering Workshop: Imarta - SketsaDocument12 pagesLumion 8 3D Rendering Workshop: Imarta - Sketsaklemens denzel100% (1)
- ASA Firewall LabDocument5 pagesASA Firewall LabLindsey Benter100% (3)
- MindCert CISSP Access Control MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Access Control MindMapjayarajan100% (1)
- SOC Analyst Cyber Security Intrusion Training From ScratchDocument3 pagesSOC Analyst Cyber Security Intrusion Training From ScratchHitesh RahangdaleNo ratings yet
- MindCert CISSP Physical Security MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Physical Security MindMapbesmart2000100% (1)
- OSCP Offensive Security Certified Professional Practice Tests With Answers To Pass the OSCP Ethical Hacking Certification ExamFrom EverandOSCP Offensive Security Certified Professional Practice Tests With Answers To Pass the OSCP Ethical Hacking Certification ExamNo ratings yet
- Cisco Netflow ConfigurationDocument19 pagesCisco Netflow Configurationfabio almeidaNo ratings yet
- Cisco ISE OverviewDocument2 pagesCisco ISE OverviewRaghad JamilNo ratings yet
- StealthwatchSolutionOverview TechTalk SecurityDocument107 pagesStealthwatchSolutionOverview TechTalk SecurityHasitha SiriwardhanaNo ratings yet
- CISSP Mem AidDocument4 pagesCISSP Mem Aidsandra072353100% (2)
- CISSP CryptographyDocument1 pageCISSP CryptographyonlysubasNo ratings yet
- Cbtnuggets SY0-501 v2017-11-09 by Keith 521q PDFDocument232 pagesCbtnuggets SY0-501 v2017-11-09 by Keith 521q PDFZeeshan RanaNo ratings yet
- A+,Net+ Mcsa, Cap, Ccna, Scrum Master: Abraham MoncarDocument4 pagesA+,Net+ Mcsa, Cap, Ccna, Scrum Master: Abraham MoncarNick RecruitNo ratings yet
- Cisco ASADocument6 pagesCisco ASAsrk_ukNo ratings yet
- Network +security L3 - Computa CenterDocument9 pagesNetwork +security L3 - Computa CenterAsifNo ratings yet
- Security+ Lab AnswersDocument160 pagesSecurity+ Lab Answersdeepholm0% (1)
- Cisco TAC Entry Training - 9 - Network Address Translation (NAT)Document40 pagesCisco TAC Entry Training - 9 - Network Address Translation (NAT)FerasHamdanNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint FireWall 1Document176 pagesCheckpoint FireWall 1Fabricio Silva0% (1)
- Zivame Project Submission PPTDocument9 pagesZivame Project Submission PPTKAMESH MASIWALNo ratings yet
- CCNA Sec 02Document36 pagesCCNA Sec 02Aissa ChaabiNo ratings yet
- CCIE Wireless v3 Preparation TipsDocument7 pagesCCIE Wireless v3 Preparation TipsDibyani NayakNo ratings yet
- CISSPDocument66 pagesCISSPicvNo ratings yet
- Cisco Press - Deploying Cisco VOIPDocument519 pagesCisco Press - Deploying Cisco VOIPAl BingawyNo ratings yet
- Simulating A Network Lab in GNS3Document25 pagesSimulating A Network Lab in GNS3Buddika WijesooriyaNo ratings yet
- CCNA Security Interview QuestionsDocument14 pagesCCNA Security Interview QuestionsKrishnaBandhaviramam'sNo ratings yet
- Network Security Unit 1,2,3,4,5Document435 pagesNetwork Security Unit 1,2,3,4,5DlxbjsvNo ratings yet
- CSS Mastery, 3rd Edition PDFDocument428 pagesCSS Mastery, 3rd Edition PDFNestorNo ratings yet
- CUCM Traces Analysis - CUCM ArchitectureDocument10 pagesCUCM Traces Analysis - CUCM ArchitecturesenthilNo ratings yet
- Certified Cloud Security Professional WorkbookDocument341 pagesCertified Cloud Security Professional Workbookha maNo ratings yet
- 300-135 TSHOOT Study GuideDocument272 pages300-135 TSHOOT Study GuideLuke RobertsonNo ratings yet
- Configuring Site To Site IPSec VPN Tunnel Between Cisco RoutersDocument6 pagesConfiguring Site To Site IPSec VPN Tunnel Between Cisco Routerskymk21No ratings yet
- Cisco IronPortDocument59 pagesCisco IronPortMuralyNo ratings yet
- MindCert Wireshark MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert Wireshark MindMapacehussainNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8: IPSecDocument61 pagesLesson 8: IPSecMahmmoud MahdiNo ratings yet
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express: Terminology SCCP Phone ConfigurationDocument3 pagesCisco Unified Communications Manager Express: Terminology SCCP Phone ConfigurationHugo Cesar Flores OrtizNo ratings yet
- Ccda SlidesDocument650 pagesCcda SlidesElias Leonardo RockoNo ratings yet
- Domain 4 Communication and Network SecurityDocument9 pagesDomain 4 Communication and Network Securitysrivatsan_eceNo ratings yet
- FW Monitor Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesFW Monitor Cheat SheetnetzsheriffNo ratings yet
- CISSP Telecommunications and Network SecurityDocument1 pageCISSP Telecommunications and Network SecurityonlysubasNo ratings yet
- Cryptography, Network Security, and CyberlawDocument234 pagesCryptography, Network Security, and Cyberlaw1am17ec014 ashnal ahmedNo ratings yet
- Windows Security Event IDsDocument215 pagesWindows Security Event IDssuperresolution0% (1)
- BRKCRS 2891 PDFDocument140 pagesBRKCRS 2891 PDFNitinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FirePOWER & FireSIGHT Policies PDFDocument20 pagesIntroduction To FirePOWER & FireSIGHT Policies PDFBharathNo ratings yet
- CiscoDocument73 pagesCiscoMohamed WahiebNo ratings yet
- Palo Alto Interview Questions - (Cyber Security)Document40 pagesPalo Alto Interview Questions - (Cyber Security)Mahmud AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Tecccie 8002Document294 pagesTecccie 8002Yordan PetkovNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint FirewallDocument10 pagesCheckpoint FirewallNay LinNo ratings yet
- MindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap PDFDocument1 pageMindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap PDFzinzinNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise: SubnettingDocument27 pagesLab Exercise: SubnettingMahmmoud MahdiNo ratings yet
- CCSA R75 Presentation-8 ModulesDocument58 pagesCCSA R75 Presentation-8 ModulesMichael ResnickNo ratings yet
- TSHOOT 15min GuideDocument13 pagesTSHOOT 15min GuidejuliosistemasNo ratings yet
- Private VLANsDocument4 pagesPrivate VLANsAlexShearNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer ASA VPN LabDocument3 pagesPacket Tracer ASA VPN LabElverGalarga0% (1)
- Ensilo/Fortiedr: Course DescriptionDocument2 pagesEnsilo/Fortiedr: Course DescriptionhoadiNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Training Career Pathways - Final v1.0 Rev 10062020Document2 pagesCybersecurity Training Career Pathways - Final v1.0 Rev 10062020HafizPradanaGemilangNo ratings yet
- Network Segmentation Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandNetwork Segmentation Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- PMP Session1Document33 pagesPMP Session1cpawan_69No ratings yet
- PMP Session3Document88 pagesPMP Session3cpawan_69No ratings yet
- PMP Risk ManagementDocument51 pagesPMP Risk Managementcpawan_69No ratings yet
- Dump Sheet For PMzilla Raj PavaniDocument3 pagesDump Sheet For PMzilla Raj Pavanicpawan_69No ratings yet
- Basic CUCM Connectivity DiagramDocument1 pageBasic CUCM Connectivity Diagramcpawan_69No ratings yet
- Creating Next Generation Cloud Computing Operation Support Services by Social OSS Contribution With Telecom NGN ExperienceDocument6 pagesCreating Next Generation Cloud Computing Operation Support Services by Social OSS Contribution With Telecom NGN Experiencecpawan_69No ratings yet
- SipDocument43 pagesSipSridatta PranavNo ratings yet
- Cisco Mobile 8.0 For Iphone CUCM ConfigurationDocument2 pagesCisco Mobile 8.0 For Iphone CUCM Configurationcpawan_69No ratings yet
- Configuring SIP Route Patterns in CUCM - Posted - 1!14!09Document11 pagesConfiguring SIP Route Patterns in CUCM - Posted - 1!14!09marmozsdxNo ratings yet
- DPM 2009Document572 pagesDPM 2009Santosh Mishra100% (1)
- Algorithms Checklist PDFDocument29 pagesAlgorithms Checklist PDFcpawan_699508No ratings yet
- UMTS Forum Towards Global Mobile Broadband LTE White PaperDocument12 pagesUMTS Forum Towards Global Mobile Broadband LTE White PaperAmit ChakradeoNo ratings yet
- Flash Professional 8 TutorialDocument42 pagesFlash Professional 8 Tutorialmy_ke202100% (11)
- A 05 MTPDocument10 pagesA 05 MTPcpawan_69No ratings yet
- 3-Day MBA in Telecoms SingaporeDocument4 pages3-Day MBA in Telecoms Singaporeazrito2No ratings yet
- LTE TechnologyDocument28 pagesLTE Technologyradiotech1No ratings yet
- 3glte Mobile Backhaul Network MPLSTP Based Solution 3499Document14 pages3glte Mobile Backhaul Network MPLSTP Based Solution 3499cpawan_69No ratings yet
- DPM 2009Document572 pagesDPM 2009Santosh Mishra100% (1)
- SWOT Analysis Project ReportDocument3 pagesSWOT Analysis Project ReportPratish ShindeNo ratings yet
- Clickstream Analysis Using HadoopDocument16 pagesClickstream Analysis Using HadoopAbhishekNo ratings yet
- House Hearing, 112TH Congress - China's Censorship of The Internet and Social Media: The Human Toll and Trade ImpactDocument77 pagesHouse Hearing, 112TH Congress - China's Censorship of The Internet and Social Media: The Human Toll and Trade ImpactScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- AdhdfcrtbkjuuvuDocument588 pagesAdhdfcrtbkjuuvudocwavyNo ratings yet
- NC-WR744G: AC1200 Wireless Dual Band RouterDocument3 pagesNC-WR744G: AC1200 Wireless Dual Band RouterJuan Luis Meroño CanovasNo ratings yet
- XML Services Developer's Guide 7.1Document80 pagesXML Services Developer's Guide 7.1dragan-djordjevic-7134No ratings yet
- Word Files Email InfoDocument1 pageWord Files Email Infoapi-3700469No ratings yet
- Iot Fundamentals: Iot Security Final (Eoc) Assessment AnswersDocument8 pagesIot Fundamentals: Iot Security Final (Eoc) Assessment AnswersFatjonNo ratings yet
- Dell Networking S5000 Spec SheetDocument4 pagesDell Networking S5000 Spec Sheetfun kumarNo ratings yet
- Port Facilities - Spain: Page 1 of 6 Printed: 26/03/2009Document6 pagesPort Facilities - Spain: Page 1 of 6 Printed: 26/03/2009EvrenNo ratings yet
- Exam 49-50Document28 pagesExam 49-50audrey mae faeldoniaNo ratings yet
- Apple Computer, Inc.: Maintaining The Music Business While Introducing Iphone and Apple TVDocument8 pagesApple Computer, Inc.: Maintaining The Music Business While Introducing Iphone and Apple TVAkarshNo ratings yet
- Blue JackingDocument8 pagesBlue JackingJagadesh Kumar50% (2)
- Smarthome Catalog Vol. 131Document68 pagesSmarthome Catalog Vol. 131IBJSC.comNo ratings yet
- Veeam Backup Free Vs FullDocument3 pagesVeeam Backup Free Vs Fullbgiangre8372No ratings yet
- EAS2 Hardware DescriptionDocument24 pagesEAS2 Hardware DescriptionThunder-Link.comNo ratings yet
- Support ProfessionalDocument2 pagesSupport ProfessionalscriNo ratings yet
- Recruitment: External Recruitment-Outside Sources Are ConsideredDocument10 pagesRecruitment: External Recruitment-Outside Sources Are ConsideredPillos Jr., ElimarNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 CCNDocument4 pagesLab 3 CCNAreeba NoorNo ratings yet
- Wireline Niche Guide V 1.2Document9 pagesWireline Niche Guide V 1.2Mark MarquezNo ratings yet
- Key CloudDocument5 pagesKey CloudLiNuNo ratings yet
- Through The Barricades Chords by Spandau Ballet Tabs at Ultimate Guitar ArchiveDocument2 pagesThrough The Barricades Chords by Spandau Ballet Tabs at Ultimate Guitar Archivefrancodlh0% (1)
- The Office Torrent DubladoDocument3 pagesThe Office Torrent DubladoAna PaulaNo ratings yet
- 3com SuperStack 4 Switch 5500G-EI - Configuration GuideDocument432 pages3com SuperStack 4 Switch 5500G-EI - Configuration GuideAndresito de PereiraNo ratings yet
- WE Manual Complete MoizDocument238 pagesWE Manual Complete MoizMoiz HussainNo ratings yet
- 12 Weeks JAIIB Study Plan For JAIIB Exam (May 2021) - IIBF: Recent BlogsDocument4 pages12 Weeks JAIIB Study Plan For JAIIB Exam (May 2021) - IIBF: Recent BlogsMy Online PrepNo ratings yet