Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ylp F4
Uploaded by
Ismaliza IshakOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ylp F4
Uploaded by
Ismaliza IshakCopyright:
Available Formats
Scheme of work Science Form 4 2012
Week 1 4/1/12 6/1/12 2 9/1/12 -13/1/12 3-7 16/1/12 13/2/12
Theme Introducing science
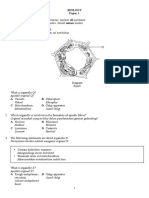
Learning area Scientific investigation Body coordination
Learning objective Learning outcome FORM FOUR ORIENTATION WEEK Analysing method of scientific Explain the steps in investigation scientific investigation Understanding body coordination Describe what body coordination is Identify the body systems that control and regulate coordination Identify the component parts of the human nervous system State the function of each component part of the nervous system Identify the parts of a neurone Identify the different types of neurone Explain the reflex action and a reflex arc Explain what proprioceptors are Identify the main parts and functions of the brain Explain what voluntary and involuntary actions are Describe what a hormone and an endocrine glands are Compare and contrast nervous coordination with
Learning activity Discussion on the steps in scientific investigation Carry out a scientific investigation (SPS activities 1.1 and 1.2) Examine models of body coordination (SPS activity 2.1) Discuss the importance of body coordination in daily activities (SPS activity 2.1) Observes charts of the human nervous system (SPS activity 2.2) Observe transparencies of the central nervous system (SPS activity 2.2) Observe the transparency on the structure of a neuron (SPS activity 2.3) Observe charts on the different types of neurones (SPS activity 2.3) Carry out activity to study the knee-jerk as a reflex action (SPS activities 2.4 and 2.5) Carry out activity to study the proprioceptors (SPS activity 2.6) Observe the model of human brain (SPS activity 2.7) Carry out activity to differentiate the voluntary and involuntary actions (SPS activity 2.8) Observe the chart on human endocrine glands (SPS activity 2.9) Carry out activities to differentiate the nervous coordination and hormonal
Maintenance and continuity of life
Understanding he human nervous system
Analysing nervous coordination Understanding the role of proprioceptors in maintaning balance and coordination Understanding the human brain and its complexity
Understanding hormonal coordination in the body Analysing coordination between the nervous system and the endocrine 1
Scheme of work Science Form 4 2012
Week
Theme
Learning area
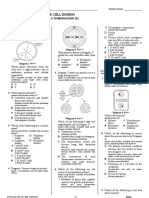
system Learning objective Evaluating the effects of drug abuse on body coordination and health Analysing the effects of excessive consumption of alcohol on body coordination and health Realising the importance of sound and healthy mind Understanding cell division
hormonal coordination Learning outcome Explain what drug abuse is Describe the effects of excessive consumption of alcohol on body coordination and health Identify factors that affect the mind Describe the relationship between gene, DNA and chromosome Describe the process of mitosis Describe the process of meiosis Compare the processes of mitosis and meiosis Explain what dominant genes and recessive genes are Illustrate the mechanism of inheritance of traits using schematic diagram Predict the genotype and phenotype ratios of a monohybrid cross Explain the determination of sex of offspring Explain the formation of identical and non-identical twins Compare identical with non-identical twins
coordination (SPS activity 2.10) Learning activity Gather information on example of drug and its effects (SPS activity 2.11) Gather information on example of alcohol and its effects (SPS activity 2.12) Discussion on the sound and healthy mind (SPS activity 2.13) Discussion on the relationship between gene, DNA and chromosome (SPS activity 3.1) Discussion on the process of mitosis (SPS activity 3.2) Discussion on the process of meiosis (SPS activity 3.3) Discussion on the comparison between the process of mitosis and meiosis (SPS activities 3.4 and 3.5) Identify dominant traits and recessive traits in human (SPS activity 3.6) Carry out activity to illustrate the mechanism of inheritance of traits using schematic diagram (SPS activity 3.7) Carry out activity to predict the genotype and phenotype ratios of a monohybrid cross Carry out activity to determine of sex of offspring (SPS activities 3.8 and 3.9) Discussion on the formation of identical and non-identical twins (SPS activity 3.10) Discussion on the comparison of identical and non-identical twins (SPS activity 3.10)
8-10 20/2/12 9/3/12
Maintenance and continuity of life
Heredity and variation
Understanding the principles and mechanism of inheritance
Understanding gender determination of a child and the occurrence of twins in human beings
Scheme of work Science Form 4 2012
Week
Theme
Learning area
Learning objective Understanding mutation Evaluating the effects of genetic research on human life Analysing variation among living things
Learning outcome State the types of mutation Explain selective breeding in plants and livestock Classify variation into continuous and discontinuous variation Identify factors that cause variation
Learning activity Discussion on the types of mutation (SPS activities 3.11 and 3.12) Discussion on selective breeding in plants and livestock (SPS activities 3.13 and 3.14) Carry out activity to identify and classify variation among students in a class (SPS activities 3.15, 3.16 and 3.17) Discussion on the factors that cause variation and their importance (SPS activity 3.18)
11 15 19/3/12 20/4/12
Matter in nature
6/3/12 - 9/3/12 UJIAN PENGESANAN 10/3/12 18/3/12 CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL Matter and substance Analysing changes in the states of Explain the interconversion of matter the three states of matter based on the kinetic theory of matter Understanding the structure of an Identify the subatomic atom particles Applying the idea of proton number Relate the number of protons, and nucleon number in atoms of neutrons and electrons in an elements atom to its proton number and nucleon number State what isotopes are Understanding the classification of Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table elements in the periodic table Understanding the properties of Describe what atoms, substances based on the particles molecules and ions are present in them Identify the particles in substances as atoms, molecules and ions Compare and contrast substances that are made of atoms, molecules and ions
Carry out an activity to observe changes in the states of matter (SPS activities 4.1 and 4.2) Discussion on the subatomic particles (SPS activity 4.3) Carry out activity to relate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom to its proton number and nucleon number (SPS activities 4.4 and 4.5) Discussion on isotopes (SPS activity 4.6) Discussion on the arrangement of elements in the periodic table (SPS activity 4.7) Discussion on the atoms, molecules and ions (SPS activity 4.8) Carry out activity to identify the particles in substances as atoms, molecules and ions (SPS activity 4.8) Carry out activity to compare the particles in substances made of atoms, molecules and ions (SPS activities 4.9, 4.10 and 4.11)
Scheme of work Science Form 4 2012
Week
Theme
Learning area
Learning objective Understanding the properties and uses of metals and non-metals Analysing methods of purifying substances
Learning outcome Classify metals and nonmetals Compare and contrast metals and non-metals State the characteristics of pure substances State the characteristics of pure substances and the different methods of purification of substances
Learning activity Carry out activity to classify metals and nonmetals (SPS activity 4.12) Carry out activity to compare metals and nonmetals (SPS activities 4.13 and 4.14) Carry out activity to study the effect of impurities on the boiling point of a pure liquid (SPS activity 4.16) Carry out activity to purify substance via distillation (SPS activity 4.17) Carry out activity to purify substance via crystallization (SPS activity 4.18) Discussion on the application of distillation and crystallisation on everyday life Carry out activity to compare and contrast physical changes and chemical changes (SPS activities 5.1 and 5.2) Carry out activity to compare and contrast physical changes and chemical changes (SPS activity 5.3) Carry out activity to study exothermic and endothermic reactions (SPS activity 5.4) Carry out activity to study the reactivity of metals with water (SPS activity 5.5) Carry out activity to study the reactivity of metals with acids (SPS activity 5.6) Carry out activity to study the reactivity of metals with oxygen (SPS activity 5.7) Discussion on the construction of the reactivity series of metals based on reactivity of metals with oxygen (SPS activity 5.7) Carry out activity to identify the position of carbon in the reactivity series of metals (SPS
16 - 17 27/4/124/5/12
Energy in life
Energy and chemical changes
Understanding physical and chemical changes
Analysing heat change in chemical reaction Synthesising the reactivity series of metals
Compare and contrast physical and chemical changes Compare and contrast physical changes and chemical changes State what exothermic and endothermic reactions are Describe the reactivity of metals with water Describe the reactivity of metals with acids Describe the reactivity of metals with oxygen Construct the reactivity series of metals based on reactivity of metals with oxygen Identify the position of carbon in the reactivity series of
Scheme of work Science Form 4 2012
metals Applying the concept of the reactivity series of metals Relate the position of metals in the reactivity series to the method of extraction of metals from their ores State what electrolysis is and state what anode, cathode, anion, cation and electrolyte are in an electrolytic cell Describe the electrolysis of an electrolyte using carbon electrode Describe the electroplating of metals Explain other uses of electrolysis Describe how a simple cell works List the various types of cells and their uses Give examples of chemical reactions that require light and explain the effect of light on photosensitive chemicals
activity 5.8) Carry out activity to relate the position of metals in the reactivity series to the method of extraction of metals from their ores (SPS activities 5.9 and 5.10) Discuss the extraction of metals using electrolysis Carry out an activity to study the electrolysis of lead(II) bromide using carbon electrode (SPS activity 5.11) Carry out an activity to electroplate an iron nail with copper (SPS activity 5.12) Explain on other uses of electrolysis Carry out an activity to built a simple voltaic cell with fruits (SPS activity 5.13) Discussion on the various types of cells and their uses (SPS activity 5.14) Experiment to study the effect of light on chemical reactions (SPS activity 5.15)
Understanding electrolysis
Understanding the production of electrical energy from chemical reactions Understanding the chemical reactions that occur in the presence of light
WEEK 18 -20 7/5/12 24/5/11 PEPERIKSAAN PERTENGAHAN TAHUN
26/5/12 10/6/12 CUTI PERTENGAHAN TAHUN
Scheme of work Science Form 4 2012
Week 21- 22 11/6/12 22/6/12
Theme Energy in life
Learning area Nuclear energy
Learning objective Understanding radioactive substances
Learning outcome Classify radioactive radiation and compare the penetration power of radioactive rays Name the three types of radioactive radiations Explain the uses of radioactive substances Describe the production of nuclear energy through nuclear fission and nuclear fusion Explain the effects of nuclear energy production Describe the correct way of handling radioactive substances and radioactive waste State the characteristics of images formed by a plane mirror State the characteristics of images formed by a convex lens Compare and contrast images of distant objects formed by convex lenses and concave lenses Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image by light rays passing through a convex lens and concave lens Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image by light rays passing through a
Learning activity Discussion on the process of radioactive decay (SPS activity 6.1) Discussion on the three types of radioactive radiations (SPS activity 6.2) Discussion on the uses of radioactive substances (SPS activity 6.3) Discussion on the production of nuclear energy (SPS activity 6.4) Discussion on the effects of nuclear energy production (SPS activity 6.5) Discussion on the effects of radioactive substances on living things (SPS activity 6.6)
Understanding the production of nuclear energy and its uses
Aware of the need for proper handling of radioactive substances
23 - 30 25/6/12 17/8/12
Energy in life
Light, colour and sight
Synthesising the formation of image by plane mirrors and lenses
Carry out activity to observe the image formed by a plane mirror (SPS activity 7.1) Carry out activity to observe the image formed by a convex and a concave lens (SPS activity 7.2) Carry out activity to compare and contrast images of distant objects formed by convex lenses and concave lenses Carry out activity to label the parts of the convex lens and concave lens (SPS activity 7.3) Carry out activity to draw a labeled ray diagram to show the formation of image by light rays passing through a convex and a
Scheme of work Science Form 4 2012
convex and a concave lens Week Theme Learning area Learning objective Learning outcome Carry out an activity to determine the focal length of a convex lens Identify the parts of optical instruments involved in image formation Draw ray diagrams for light rays passing through an optical instrument Compare and contrast the mechanisms in focusing and controlling the amount of light that enters human eyes and a camera Explain through examples how dispersion of light occurs Explain through examples how dispersion of light occurs State what light scattering is Give examples of phenomena related to light scattering Explain how addition of primary colours produces secondary colours. Explain the subtraction of colours by coloured filters.
concave lens (SPS activities 7.4 and 7.5) Learning activity Plan and carry out an activity to determine the focal length of a convex lens (SPS activity 7.6) Discussion on the parts of optical instruments involved in image formation (SPS activity 7.7) Carry out activity to construct a pinhole camera (SPS activity 7.8) Carry out activity to compare and contrast the mechanisms in focusing and controlling the amount of light that enters human eyes and a camera (SPS activity 7.9) Carry out activity to investigate light dispersion using a prism (SPS activity 7.10) Carry out activity to investigate the rainbow formation and draw a labelled diagram to show dispersion of light (SPS activity 7.11) Carry out activity to investigate light scattering and its effects (SPS activity 7.12) Discussion on the examples of phenomena related to light scattering (SPS activity 7.13) Carry out activity to investigate the addition of primary colours to form secondary colours (SPS activities 7.14 and 7.15) Carry out activity to investigate the effects of primary and secondary coloured filters on white and coloured light (SPS activities 7.16 and 7.17) Carry out activity to observe and study the colour of objects under white and coloured lights (SPS activities 7.18 and 7.19)
Synthesising the formation of image by optical instruments
Analysing light dispersion
Analysing light scattering Analysing light dispersion Analysing the addition and subtraction of coloured lights
Applying the principle of subtraction of coloured light to explain the appearance of 7
Explain subtraction of coloured lights by coloured objects
Scheme of work Science Form 4 2012
coloured objects Week Theme Learning area Learning objective Analysing the effect of mixing pigments
State the function of rod and cone cells in the eye
Discussion on the function of rod and cone cells in the eye (SPS activity 7.20) Learning activity Discussion on what a pigment is and the comparison of the mixing of pigments with the addition of coloured lights (SPS activity 7.21) Discussion on the importance of colours to living things (SPS activities 7.22 and 7.23) Discussion on the examples of alloys and its content and functions (SPS activity 8.1) Discussion on the relation the changes in the properties of metals when they are converted to alloys to the arrangement of particles in the alloys (SPS activities 8.2 and 8.3) Discussion on the relation of the properties of alloys to their uses in daily life (SPS Activity 8.4) Discussion on how ammonia is produced in industries (SPS Activity 8.5) Discussion on how ammonia is used to produce ammonium salt fertilisers and urea (SPS activity 8.6) Discussion on the effects of industrial waste disposal to survival of living things (SPS activity 8.7) Discussion on the methods of controlling industrial waste disposal to avoid pollution (SPS activity 8.8)
31-32 27/8/12 7/9/12
Technological and industrial development in society
Disediakan Oleh: 8
Learning outcome State what pigment is and compare the mixing of pigments with the addition of coloured lights Evaluating the importance of Justify the importance of colour colours in daily life to living things 18/8/12 26/8/12 CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL II DAN HARI RAYA PUASA Chemicals in industry Understanding the properties of Give examples of alloys and alloys and their uses in industries its content and functions Relate the changes in the properties of metals when they are converted to alloys to the arrangement of particles in the alloys Relate the properties of alloys to their uses in daily life and state what superconductor alloys are Analysing the production and uses Describe how ammonia is of ammonia in industry produced in industries Describe how ammonia is used to produce ammonium salt fertilisers and urea Analysing the effects of industrial Relate the effects of industrial waste disposal on the environment waste disposal to survival of living things State with examples the methods of controlling industrial waste disposal to avoid pollution 33-36 10/9/12 5/10/11 ULANGKAJI TERANCANG 10/11/12 1/1/13 CUTI AKHIR TAHUN Disemak Oleh:
Disahkan Oleh:
Scheme of work Science Form 4 2012
(Pn Ismaliza bt. Ishak) Guru Sains Tingkatan 4
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 3 (BL)Document8 pagesIT Bio F4 Topical Test 3 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 7 (BL)Document14 pagesIT Bio F4 Topical Test 7 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 5 (BL)Document5 pagesIT Bio F4 Topical Test 5 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Document8 pagesIT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 8 (BL)Document9 pagesIT Bio F4 Topical Test 8 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Bio 2011 JawapanDocument4 pagesBio 2011 JawapanIsmaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 5 (BL)Document5 pagesIT Bio F4 Topical Test 5 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Saturday, 2 April 2016: 5 Kepentingan Air Kepada Benda HidupDocument12 pagesSaturday, 2 April 2016: 5 Kepentingan Air Kepada Benda HidupIsmaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Document8 pagesIT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Bio Past Year 2012Document7 pagesBio Past Year 2012Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Bio 2012 JawapanDocument4 pagesBio 2012 JawapanIsmaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Bio Past Year 2012Document17 pagesBio Past Year 2012Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Biology Paper 1: This Question Paper Consists of 50 Questions. Answer All QuestionsDocument23 pagesBiology Paper 1: This Question Paper Consists of 50 Questions. Answer All QuestionsIsmaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Bio 2011 JawapanDocument1 pageBio 2011 JawapanIsmaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Bab 3 f5 Dan Bab 2 f4Document43 pagesBab 3 f5 Dan Bab 2 f4Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Bab 5 f5Document13 pagesBab 5 f5Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Bab 8 f4Document30 pagesBab 8 f4Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
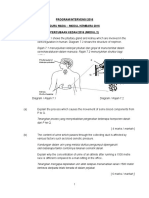
- Program Intervensi 2016 Guru Muda - Modul Kembara 2016 Percubaan Kedah 2016 (Modul 2)Document7 pagesProgram Intervensi 2016 Guru Muda - Modul Kembara 2016 Percubaan Kedah 2016 (Modul 2)Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Modul Biologi 2016 t4 Soalan PDFDocument87 pagesModul Biologi 2016 t4 Soalan PDFIsmaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Bio P2 Skema PP SPM 2016Document11 pagesBio P2 Skema PP SPM 2016Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Modul Biologi 2016 t5 Skema PDFDocument43 pagesModul Biologi 2016 t5 Skema PDFIsmaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- SBP Trial Biologi 10 Kertas 2 PDFDocument17 pagesSBP Trial Biologi 10 Kertas 2 PDFIsmaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Soalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4 PDFDocument22 pagesSoalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4 PDFIsmaliza Ishak0% (1)
- Numerous Calcified Nodes Containing W. Bancrofti MafiDocument5 pagesNumerous Calcified Nodes Containing W. Bancrofti MafiIsmaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Modul Biologi 2016 t4 SkemaDocument65 pagesModul Biologi 2016 t4 SkemaIsmaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Science Aurora 2005Document38 pagesScience Aurora 2005rafaebhattiNo ratings yet
- STM 005 - Sas MergedDocument140 pagesSTM 005 - Sas MergedmidzyonceuNo ratings yet
- SWOT Sheet For NEETDocument42 pagesSWOT Sheet For NEETArbind KumarNo ratings yet
- How To Teach Intermolecular ForcesDocument6 pagesHow To Teach Intermolecular ForcesMSHYDERABAD4334No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Organic WizardDocument17 pagesOrganic Wizardapi-182809945No ratings yet
- Modul 4-Basic ChemDocument10 pagesModul 4-Basic ChemSaravanan ManiamNo ratings yet
- 11 MYE Syllabus AY 2023-24Document2 pages11 MYE Syllabus AY 2023-24maazeen.1524.ebs.onlineNo ratings yet
- General Organic and Biological Chemistry 2Nd Edition Frost Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesGeneral Organic and Biological Chemistry 2Nd Edition Frost Test Bank Full Chapter PDFBradMartiniczn100% (10)
- Topic 1 MCQDocument20 pagesTopic 1 MCQrania samirNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco - Manual Do Ar Comprimido - Capítulo 1Document27 pagesAtlas Copco - Manual Do Ar Comprimido - Capítulo 1André CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- C3 Calculations Formulas EquationsDocument44 pagesC3 Calculations Formulas EquationsFelix SalongaNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Organic Chemistry Test Bank Smith 5 ED.Document347 pagesOrganic Chemistry Test Bank Smith 5 ED.Katie Wilson80% (5)
- Polyhedron: Katharina Kubic Ek, Sreevidya Thekku Veedu, Darina Storozhuk, Reza Kia, Simone TechertDocument11 pagesPolyhedron: Katharina Kubic Ek, Sreevidya Thekku Veedu, Darina Storozhuk, Reza Kia, Simone TechertJoakin BahamondesNo ratings yet
- C3L6 Student Exam 2021Document9 pagesC3L6 Student Exam 2021Đức ThànhNo ratings yet
- Chem SketchDocument17 pagesChem SketchUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- AS/A2 - Chemistry: 2021-23 CurriculumDocument80 pagesAS/A2 - Chemistry: 2021-23 CurriculumenderothNo ratings yet
- Bonding LabDocument2 pagesBonding LabSiddharth Rajendran0% (1)
- Midterm Physical ScienceDocument3 pagesMidterm Physical ScienceMary Charmine Grace Olete-Baniago100% (1)
- WWW - Chemguide.co - Uk Analysis Masspec Fragment - HTMLDocument9 pagesWWW - Chemguide.co - Uk Analysis Masspec Fragment - HTMLorgche_mawadNo ratings yet
- COMPLEXATIONDocument22 pagesCOMPLEXATIONAgilandeswari Devarajan100% (1)
- Bonga University Instrumental Analysis II: (Chem.2052)Document56 pagesBonga University Instrumental Analysis II: (Chem.2052)ashenafiNo ratings yet
- Bonding and StructuresDocument10 pagesBonding and StructuresFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry I Quarter 1 ModulesDocument153 pagesGeneral Chemistry I Quarter 1 ModulesAlthea Lei Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Reflection 3 Chem LecDocument3 pagesReflection 3 Chem LecPaul Winston RegaladoNo ratings yet
- 0620 m18 QP 32Document16 pages0620 m18 QP 32HaziraAzlyNo ratings yet
- Textbook Ebook Chemistry Chemical Reactivity 10Th Edition John C Kotz All Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesTextbook Ebook Chemistry Chemical Reactivity 10Th Edition John C Kotz All Chapter PDFdebra.lee709100% (5)
- Wolkenstein1960-The Electron Theory of Catalysis On SemiconductorsDocument76 pagesWolkenstein1960-The Electron Theory of Catalysis On SemiconductorsYair CruzNo ratings yet
- Branches of ChemistryDocument3 pagesBranches of ChemistryAnna Marie SantosNo ratings yet
- Burgot G., Burgot J.-L. - General Analytical Chemistry - SeparationDocument60 pagesBurgot G., Burgot J.-L. - General Analytical Chemistry - SeparationAytekin GaribliNo ratings yet
- Chem QueastionsDocument137 pagesChem QueastionsdjftNo ratings yet