Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bernoullis Theorem
Uploaded by
Akanksha JagwaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bernoullis Theorem
Uploaded by
Akanksha JagwaniCopyright:
Available Formats
FM 01: BERNOULLIS THEOREM
1. AIM
The aim of the experiment is to verify Bernoullis equation experimentally
2. APPARATUS
The experimental setup consists of a convergent divergent pipe with pressure tapings at various cross sections. The water is supplied to an overhead tank by a centrifugal pump. The flow rates in the pipe can be adjusted with the control valve and bypass valve. The cross - sectional area of the convergent divergent pipe is as follows.
Sr. No 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Cross- Sectional Area A x 10-4 (m2.) 6.1575 4.9088 3.4636 2.4053 1.50 2.4053 3.4636 .4.9088 6.1575 Distance from Reference point S ( m) 0.030 0.059 0.088 0.117 0.146 0.175 0.204 0.233 0.262
3. PROCEDURE FOR COLLECTING EXPERIMENTAL DATA (a) Starting Procedure: 1. Clean the apparatus and make all Tanks free from dust.
2. Close the drain valves provided. 3. Ensure that all On/Off Switches given on the Panel are at OFF position. 4. Now switch on the Main Power Supply. 5. Switch on the Pump. 6. Regulate Flow of water through pipe with the help of given Flow Control Valve. 7. Make sure that there is no water bubbles in the tube for measuring pressure heads. 8. Measure Flow Rate using Measuring Tank and Stop Watch. 9. Calculate the velocity at each section using continuity equation. 10. Repeat the experiment with different flow rates
(b) Shut Down Procedure
1. When experiment is over, Switch off Pump. 2. Switch off Power Supply to Panel. 3. Drain water from all three tanks with the help of given drain valves.
4. RELEVANT THEORY FOR THIS EXPERIMENT:
Bernoullis principle states the relationship between static pressure and velocity for inviscid flow on the basis that the total energy at any section of flow will remain the same provided there is no reduction or addition of energy at any point.
5. TASKS
1. Derive an expression for the theoretical volume flow rate through a venturimeter, for a given area ratio using Bernoulli's equation and continuity equation. 2. Calculate the actual flow rate through the pipe from measuring tank and stop watch data. 3. Calculate the average velocity at each section. 4. Plot the variation of total energy along the length of the pipe. 5. Comment on possible sources of error in the experiment or your derivation that would change your measurements or theoretical estimates. Indicate how these sources would affect the results and make recommendations for improving the experiment.
REFERENCES 1. Class notes, ME 204 Fluid Mechanics, Spring semester , 2009-2010 2. Fox R.W. and McDonald A.T., Fluid Mechanics, John Wiley International, 2005.
You might also like
- Bernoulli's TheoremDocument5 pagesBernoulli's TheoremVrushiket PatilNo ratings yet
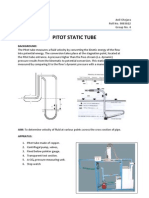
- FM05 Pitot Static Tube PDFDocument2 pagesFM05 Pitot Static Tube PDFAnonymous thaRdEcpD100% (2)
- JJ 308 Experiment 1Document4 pagesJJ 308 Experiment 1Edmond Emmanuel LeeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Report 3Document12 pagesFluid Report 3Arif MuziratNo ratings yet
- 12 Experiment #2: Bernoulli'S Theorem DemonstrationDocument12 pages12 Experiment #2: Bernoulli'S Theorem DemonstrationYasir A. Al-ShataifNo ratings yet
- X4 BernoullisTheoremDemonstration BautistaDerwinDanielDocument16 pagesX4 BernoullisTheoremDemonstration BautistaDerwinDanielNadine Pascual100% (2)
- Lab Report 3Document14 pagesLab Report 3Siti Syuhadah0% (1)
- Lab 4 (Thermofluids Lab)Document32 pagesLab 4 (Thermofluids Lab)Adnan Nanda0% (1)
- Ce422l E5 4eg2Document5 pagesCe422l E5 4eg2Christine Joyce A. CortezNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Bernoulli's TheoremDocument26 pagesExperiment 3 Bernoulli's TheoremSaber Minato Azrul100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Lab-I (Report)Document18 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab-I (Report)Mohammad Usman HabibNo ratings yet
- ME Sessional ThermofluidDocument9 pagesME Sessional Thermofluidnadimduet1No ratings yet
- LAB (Bernoulli's Theorem Demonstration)Document26 pagesLAB (Bernoulli's Theorem Demonstration)Nurul AinNo ratings yet
- FM CompleteDocument19 pagesFM Completenini jasniNo ratings yet
- FM & HM Lab Lab ManualDocument75 pagesFM & HM Lab Lab ManualRajib DasNo ratings yet
- Fluid Lab 2 - Bernoulli ExpDocument19 pagesFluid Lab 2 - Bernoulli ExpCik Tiem Ngagiman89% (65)
- Bernoulli Theorem FM24 Complete Manual PDFDocument36 pagesBernoulli Theorem FM24 Complete Manual PDFKicauan KataNo ratings yet
- Bernoulis TheoremDocument14 pagesBernoulis TheoremKhairulAzwanizamNo ratings yet
- JS03 Fluid Mechanics JJ22Document6 pagesJS03 Fluid Mechanics JJ22HAJAR KHALIDNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document14 pagesLab 4zhems sNo ratings yet
- Problem A1Document8 pagesProblem A1Heidy CruzNo ratings yet
- Orifice Meter ExperimentDocument10 pagesOrifice Meter ExperimentAmoluck BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Asee-Midwest 0008 6430aaDocument13 pagesAsee-Midwest 0008 6430aaAysun GüvenNo ratings yet
- Flowmeter DemonstrationDocument24 pagesFlowmeter DemonstrationNajwa Ghazali100% (16)
- 09 AE2258 Aerodynamics Lab ManualDocument26 pages09 AE2258 Aerodynamics Lab ManualBrandon Spence100% (5)
- Hydraulic Bench and AccessoriesDocument27 pagesHydraulic Bench and AccessoriesWehna SabuLao67% (3)
- Lab 1 Measurement of Airflow Lab Manual-1Document10 pagesLab 1 Measurement of Airflow Lab Manual-1Nadeem Rehman100% (1)
- Session3 PDFDocument28 pagesSession3 PDFgeetanjaliNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli EquationDocument6 pagesBernoulli EquationMohanadAlrofuNo ratings yet
- IndexDocument31 pagesIndexAnonymous l5X3VhTNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2 Bernoullis Energy - 20240223 - 050049 - 0000Document11 pagesLab Report 2 Bernoullis Energy - 20240223 - 050049 - 0000ack awnsNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Venturimeter and OrificemeterDocument6 pagesCalibration of Venturimeter and Orificemeteranil chejara83% (6)
- Flowmeter Demonstration Lab ReportDocument25 pagesFlowmeter Demonstration Lab ReportEZWANNo ratings yet
- Flow Through An OrificeDocument8 pagesFlow Through An OrificeKevin VillaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document6 pagesExperiment 3nurasamaNo ratings yet
- Energy Losses in Bends - : Experiment No. - 09Document7 pagesEnergy Losses in Bends - : Experiment No. - 09John Michael Menoza ZapantaNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Experiment ReportDocument3 pagesBernoulli Experiment ReportAdu Yaw SarkodieNo ratings yet
- Exp 2-Bernoulli Theorem Report-CompletedDocument5 pagesExp 2-Bernoulli Theorem Report-Completedorange_jasm1ne8892100% (2)
- Bernoullis Theorem ProcedureDocument2 pagesBernoullis Theorem ProcedureFatin Izzati HasnanNo ratings yet
- CLR Fluid MechanicsDocument10 pagesCLR Fluid MechanicsJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Sem1 2015 2016-11092015Document26 pagesLab Manual Sem1 2015 2016-11092015Putri SaidatinaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics LabDocument11 pagesFluid Mechanics LabMohid KhanNo ratings yet
- Exp 7 Centrifugal Pump CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesExp 7 Centrifugal Pump CharacteristicsJackSparrow86No ratings yet
- Lab3 HidrauDocument16 pagesLab3 HidrauNurul Abdul JalilNo ratings yet
- Pitot Static TubeDocument4 pagesPitot Static Tubeanil chejara100% (1)
- Lab 2 Bernoulli's EquationDocument12 pagesLab 2 Bernoulli's EquationDário Da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Good ReportDocument14 pagesGood ReportEdison PangNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab 2Document6 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab 2SadiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab ManualDocument53 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab ManualprashanthreddyhNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 3: ObjectivesDocument14 pagesExperiment No: 3: ObjectivesAlimah Azeli100% (1)
- Model FM 03: Bernoulli's Theorem Demonstration ApparatusDocument5 pagesModel FM 03: Bernoulli's Theorem Demonstration ApparatusMayuresh ChavanNo ratings yet
- FM 24 ManualDocument18 pagesFM 24 ManualMohd Nor SollehanNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy: The Bernoulli Equation: Figure 1. A Very Large Venturi MeterDocument8 pagesConservation of Energy: The Bernoulli Equation: Figure 1. A Very Large Venturi Meterdist2235No ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document3 pagesExperiment 3MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Respiration Calorimeters for Studying the Respiratory Exchange and Energy Transformations of ManFrom EverandRespiration Calorimeters for Studying the Respiratory Exchange and Energy Transformations of ManNo ratings yet
- Gases and Vacua: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsFrom EverandGases and Vacua: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckNo ratings yet
- Programming in C PDFDocument177 pagesProgramming in C PDFRameshNo ratings yet
- Ring Programming Language Book - Part 56 of 84Document10 pagesRing Programming Language Book - Part 56 of 84Mahmoud Samir FayedNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering Assignment Question Ii Year/Iii SemesterDocument2 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering Assignment Question Ii Year/Iii SemesterMuthu LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Bounded Rationality - The Adaptive ToolboxDocument371 pagesBounded Rationality - The Adaptive Toolboxorca20280% (5)
- Physics MYP Questions 3Document14 pagesPhysics MYP Questions 3shikhaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2 Module-1 Structural Analysis-IIDocument26 pagesLecture-2 Module-1 Structural Analysis-IIHira WahabNo ratings yet
- Statistics Important QuestionsDocument26 pagesStatistics Important QuestionsAkshit JunejaNo ratings yet
- Elg 3126Document6 pagesElg 3126Serigne Saliou Mbacke SourangNo ratings yet
- Understanding Time Delay Relay FunctionsDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Time Delay Relay FunctionsAndrew BullNo ratings yet
- Graphing Calculator by Mathlab: User ManualDocument119 pagesGraphing Calculator by Mathlab: User ManualddNo ratings yet
- Bored Pile Design in Stiff Clay IDocument21 pagesBored Pile Design in Stiff Clay IVardhanNo ratings yet
- Computing Lab 1 HandoutDocument7 pagesComputing Lab 1 Handoutniwem57100No ratings yet
- Danyal Education: Correct 117.9875 DecimalDocument20 pagesDanyal Education: Correct 117.9875 DecimalbrcraoNo ratings yet
- 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances NotesDocument2 pages10 Motion and Measurement of Distances Notesprem wakodeNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Summer Student Enrichment PacketDocument26 pagesAlgebra 2 Summer Student Enrichment PacketAna ChicasNo ratings yet
- SPM TRIAL STK EXAM 2013 Paper 2 AnswerDocument11 pagesSPM TRIAL STK EXAM 2013 Paper 2 AnswerRofi HussainNo ratings yet
- Sales SkillsDocument31 pagesSales SkillsUmair Gurmani100% (1)
- Aspects of Linear Stability Analysis For Higher-Order Finite-Difference MethodsDocument11 pagesAspects of Linear Stability Analysis For Higher-Order Finite-Difference MethodsKarthikPrakashNo ratings yet
- Performance of Levee Underseepage Controls: A Critical ReviewDocument52 pagesPerformance of Levee Underseepage Controls: A Critical ReviewLuiz AlvesNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming With C: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesComputer Programming With C: Multiple Choice QuestionsAmit sinhaNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument12 pagesMini ProjectParth PethkarNo ratings yet
- Activity 1.1.1 Simple Machine Investigation - Vex: NamesDocument12 pagesActivity 1.1.1 Simple Machine Investigation - Vex: NamesBen Cheng100% (1)
- Study Pack and Formulae of Chapter 4Document15 pagesStudy Pack and Formulae of Chapter 4RatanakNo ratings yet
- ModelingSCBF PDFDocument28 pagesModelingSCBF PDFadnanraisahmedNo ratings yet
- Khubaib Agha - Add Maths Form IIIDocument7 pagesKhubaib Agha - Add Maths Form IIIKhubaib AghaNo ratings yet
- A Hybrid Simulation Approach For Quantitatively Analyzing The Impact ofDocument10 pagesA Hybrid Simulation Approach For Quantitatively Analyzing The Impact ofjose_guerra_73No ratings yet
- Aio PDFDocument256 pagesAio PDFRaja BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Lecture7 PDFDocument16 pagesLecture7 PDFMato KankarašNo ratings yet
- Experimental DesignDocument11 pagesExperimental DesignSarita RathiNo ratings yet
- Electronic - Banking and Customer Satisfaction in Greece - The Case of Piraeus BankDocument15 pagesElectronic - Banking and Customer Satisfaction in Greece - The Case of Piraeus BankImtiaz MasroorNo ratings yet