Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metronidazole drug information summary
Uploaded by
Kaloy AnneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Metronidazole drug information summary
Uploaded by
Kaloy AnneCopyright:
Available Formats
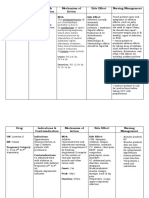
Drug
Indication
Action Disrupts DNA and protein synthesis in susceptible organisms Bactericidal, or amebicidal action
Contraindication Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to metronidazole; pregnancy (do not use for trichomoniasis in first trimester). Use cautiously with CNS diseases, hepatic disease, candidiasis (moniliasis), blood dyscrasias, lactation.
Generic name: metronidazole
Amebicidal in the Brand Name: Apomanagement of Metronidazole (CAN), amoebic Flagyl, Flagyl 375, Flagyl ER, dysentery Flagyl IV, Flagyl IV RTU, MetroCream (CAN), MetroGel, Metro I.V., NeoTric (CAN), NidaGel (CAN), Noritate, Novonidazol (CAN), PMS-Metronidazole (CAN), Protostat, Trikacide (CAN CLASSIFICATION: Antiinfectives, Anti-protozoals
Adverse reaction/ side effects Headache, dizziness, ataxia, vertigo, incoordination, insomnia, seizures, peripheral neuropathy, fatigue Unpleasant metallic taste, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, GI upset, cramps Dysuria, incontinence, darkening of the urine Thrombophlebitis (IV); redness, burning, dryness, and skin irritation (topical) Severe, disulfiram-like interaction with alcohol, candidiasis (superinfection)
Nursing responsibilities Administer with food or milk to minimize GI irritation. Tablets may be crushed for patients with difficulty swallowing. Instruct patient to take medication exactly as directed evenly spaced times between dose, even if feeling better. Do not skip doses or double up on missed doses. If a dose is missed, take as soon as remembered if not almost time for next dose. May cause dizziness or lightheadedness. Caution patient or other activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known. Inform patient that medication may cause an unpleasant metallic taste. Inform patient that medication may cause urine to turn dark. Advise patient to consult health care professional if no improvement in a few days or if signs and symptoms of superinfection (black furry overgrowth on tongue; loose or foul-smelling stools develop)
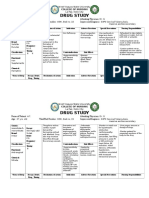
Drug GENERIC NAME: ampicillin BRAND NAME: Omnipen, Polycillin, Principen CLASSIFICATIONS Therapeutic: Anti-infectives Pharmacologic: Aminopenicillins/ beta lactamase inhibitors PREPARATIONS: Capsul es: 250 and 500 mg. Powder oral suspension: 125 and 250 mg/5mL. Powder for injection: 250 mg, 500 mg, 1g, and 2 g.
Indication Ampicillin is used for treating infections of the middle ear, sinuses, stomach and intestines, bladder, and kidney caused by susceptible bacteria. It also is used for treating uncomplicated gonorrhea, meningitis, endoc arditis and other serious infections.
Action Physiologic Mechanism Bactericidal action. Active against: Streptococci, Penumococci, Enterococci, Haemophilus influenzae, Use should be reserved for infections caused by beta-lactamaseproducing strains. Pharmacologic Mechanism Binds to bacteria cell wall, resulting in cell death, spectrum is broader than that of penicillin. Addition of sulbactam increases resistance to betalactamase, enzymes produced by bacteria that may inactivate ampicillin.
Adverse reaction/ side effects The use Common side effects of of Ampicillin ampicillin include iscontraindicated nausea, vomiting, loss of inindividuals with appetite, ahistory diarrhea, abdominal pain, of hypersensitivityr rash, itching, headache, eactionsto any of confusion and dizziness. thepenicillins. Patients with a history of allergic reactions to other penicillins should not receive ampicillin. Persons who are allergic to the cephalosporin class of antibiotics, which are related to the penicillins, for example, cefaclor (Ceclor), cephalexin (Keflex), and cefprozil (Cefzil), may or may not be allergic to penicillins. Serious but rare reactions include seizures, severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), and low platelet or red blood cell count
Contraindication
Nursing responsibilities Assess patient for infection (vital signs, wound appearance, sputum, urine, stool, and WBCs) at beginning and throughout therapy. Obtain a history before initiating therapy to determine previous use of and reactions to penicillins or cephalosporins. Persons with a negative history of penicillin sensitivity may still have an allergic response. Obtain specimens for culture and sensitivity before therapy. First dose may be given before receiving results. Observe patients for signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis (rash, pruritus, laryngeal edema, wheezing). Discontinue the drug and notify the physician immediately if these occur. Keep epinephrine, an antihistamine, and resuscitation equipment close by in the event of an anaphylactic reaction. Caution patient to notify physician if fever and diarrhea occur, especially if stool contains blood, pus, or mucus. Advise patient not to treat diarrhea without consulting health care professional. May occur up to several weeks after discontinuation of medication. Instruct patient to notify physician if symptoms do not improve
Drug Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) Classification: antipyretics, nonopioid analgesics Dosage: PO/Rectal 0.5-1 g 4-6 hrly when needed. Max: 4 g/day. IV >50 kg: 1 g 46 hrly (Max: 4 g/day); <50 kg: 15 mg/kg 4-6 hrly (Max: 60 mg/kg/day)
Indication Mild to moderate pain a nd fever.
Action Inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins that mayserve asmediators of pain andfever, primarily in the CNS.
Contraindication Hypersensitivity; intolerance to tartrazine (yellow dye #5), alcohol, table sugar, saccharin.
Adverse reaction/ side effects Hema: hemolyticanemia, neutropenia, leukopenia, pancytopenia. Hepa: jaundice Metabolic: hypoG GI: HEPATICFAILURE,HEPATOT OXICITY(overdose) GU: renalfailure(highdoses/chr onic use). Derm: rash,urticaria
Nursing responsibilities BEFORE: ~ Advise parents or caregivers to checkconcentrations of liquidpreparations. Errorshave resulted in seriousliver damage. ~ Assess fever; notepresence of associatedsigns (diaphoresis,tachycardia, andmalaise). DURING: ~ Adults should not takeacetaminophen longer than 10 days andchildren not longer than5 days unless directedby health careprofessional. ~ Advise mother or caregiver to take medicationexactly as directed andnot to take more thanthe recommendedamount. AFTER: ~ Advise patient to consulthealth care professionalif discomfort or fever isnot relieved by routinedoses of this drug or if fever is greater than39.5C (103F) or lastslonger than 3 days.
Drug Zinc Brand Names: Eye-SedSolution 0.25%, Orazinc Verazinc, Zinc 15, Zinc220, Zinca-Pak Classification: Vitamins and Minerals Dosage: Syr Acute diarrhea with reduced osmolarity ORS Childn 6 mth 5 mL, <6 mth 2.5 mL. Nutritional supplementAdult 2.5-5 mL. Childn 9-13 yr 2.55 mL, 4-8 yr2.5 mL, 1-3 yr 1.25 mL. Drops Acute diarrhea with reduced osmolarity ORS Childn 6 mth 2 mL, <6 mth 1 mL. Nutritional supplement Childn 1-3 yr 0.5 mL, 6-11 mth 0.5 mL.
Indication Supplement to correct Zn deficiency e.g. malabsorption syndromes & in conditions w/ increased body losses.
Adverse reaction/ side effects E-Zinc contains zinc. Zinc helps Nausea, stomach upset, hypersensitive to iodine the body's natural defense Use cautiously: Lactating heartburn may occur. If against damaging free radicals any of and Pregnant Women (antioxidant effect) and helps these effects persist or boost immune function. Free worsen, notify your radicals are highly reactive and doctor or pharmacist unstable chemicals generated promptly. Tell your doctor during normal body activities that immediately if any of require oxygen (eg, respiration, these unlikely but digestion, blood circulation, serious side effects immune system response, etc) and after exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, cigarette smoke and various pollutants. One major effect of zinc is on the ability of cells to properly replicate the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which is required for cells to multiply. Hence, zinc is needed for normal growth.
Action
Contraindication
Nursing responsibilities 1. Check levels of trace elements in patients who have received TPN for 2 months or longer. Give supplement, if ordered. Report low levels of thee elements. 2. Normal level is 88 to 112 mcg/dl zinc. 3. Solutions of trace elements are compounded by pharmacist for addition to TPN solutions according to various formulas. 4. Explain need for zinc administration to patient and family. 5. Tell patient to report signs of hypersensitivity promptly. 6. Inform patient and family that trace elements are normally received from dietary intake that, when patient begins eating well, supplements wont be needed.
You might also like
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFINAL Drug StudycasedraftNo ratings yet
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Document4 pagesChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayDocument4 pagesMetronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayCrisyl LipawenNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument11 pagesCefuroximeAlmira Ballesteros CestonaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AzithromycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study Azithromycinkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PediaDocument5 pagesDrug Study Pediajulesubayubay5428No ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTramadol Drug StudyTipey Segismundo0% (1)
- CeftriaxoneDocument1 pageCeftriaxoneJayson Almario Aranas100% (2)
- AmikinDocument2 pagesAmikinLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone IM Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCeftriaxone IM Drug StudyCastillo MikaellaNo ratings yet
- Mupirocin DSDocument2 pagesMupirocin DSArnzz AgbulosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDrug Study (Acetaminophen)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study BISACODYLDocument1 pageDrug Study BISACODYLAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- CetirizineDocument1 pageCetirizineGabby Robles PajeNo ratings yet
- StreptomycinDocument1 pageStreptomycinDemilyn Fat100% (2)
- AMINOPHYLLINEDocument2 pagesAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- Azithromycin Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesAzithromycin Nursing ConsiderationsKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- What Is Tonsillitis?: City of Malolos, BulacanDocument7 pagesWhat Is Tonsillitis?: City of Malolos, BulacanElijah AmbeguiaNo ratings yet
- CefoperazoneDocument3 pagesCefoperazoneBaim FarmaNo ratings yet
- Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Document1 pageCyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- AmbroxolDocument1 pageAmbroxolPrecious CarmelaNo ratings yet
- Resource Unit OliveDocument14 pagesResource Unit OliveCaryl AlivioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study IsoniazidDocument1 pageDrug Study IsoniazidEphraim MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Quinine anti-malarial drugDocument3 pagesQuinine anti-malarial drugDoubleHeartedNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Effects and UsesDocument11 pagesDrug Study Effects and UsesVincent QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Methyldopa nursing management for hypertensionDocument4 pagesMethyldopa nursing management for hypertensionRico Mae ValenciaNo ratings yet
- TB DrugsDocument14 pagesTB DrugsLexy CadigalNo ratings yet
- BNP (C)Document2 pagesBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJan DeeNo ratings yet
- MSU-IIT Student Drug Study on TygacilDocument2 pagesMSU-IIT Student Drug Study on TygacilVanessa Egao100% (1)
- Duavent Drug Study - CunadoDocument3 pagesDuavent Drug Study - CunadoLexa Moreene Cu�adoNo ratings yet
- Indications:: Brand Name: Classificati OnDocument1 pageIndications:: Brand Name: Classificati OnTel SisonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - VancomycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - VancomycinKhatlen BagaresNo ratings yet
- Oxacillin Nursing ConsiderationsDocument1 pageOxacillin Nursing Considerationsnerissa_villanueva3523No ratings yet
- Carboprost TromethamineDocument2 pagesCarboprost TromethamineDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- Iron supplements and antianginal drug studyDocument4 pagesIron supplements and antianginal drug studyLene ThereseNo ratings yet
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDocument2 pagesDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient MonitoringDocument2 pagesDrug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient Monitoringpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument5 pagesKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNo ratings yet
- Fluconazole drug classification, indications, side effects and nursing responsibilitiesDocument1 pageFluconazole drug classification, indications, side effects and nursing responsibilitiescen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoel MadjosNo ratings yet
- PiroxicamDocument2 pagesPiroxicamVirginia Aira Lara MarquezNo ratings yet
- Vii. Drug Study Drug Mechanism of ActionDocument7 pagesVii. Drug Study Drug Mechanism of ActionRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of ChloramphenicolDocument3 pagesDrug Study of Chloramphenicolcasimir1128No ratings yet
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDocument1 pageDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- XtendaDocument2 pagesXtendaAlexis CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Amoxicillin Mechanism and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Amoxicillin Mechanism and Nursing ResponsibilitiesKrzia TehNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TBDocument5 pagesDrug Study TBSanvar Mal SoniNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime drug study titleDocument2 pagesCefuroxime drug study titleDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Burn - Concept MapDocument1 pageBurn - Concept MapAaron RafaelNo ratings yet
- TB Drug StudyDocument15 pagesTB Drug StudyKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument3 pagesDrug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumPrincess Queenie OlarteNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin Nursing GuideDocument2 pagesCephalexin Nursing GuideKatyana Cesar100% (1)
- Acetaminophen Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAcetaminophen Drug StudyCath Bril100% (1)
- Drug Study 408Document13 pagesDrug Study 408Jheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Silver Sulfadiazine Cream Prevents Burn InfectionsDrug NameDosageTherapeuticActionIndicationContraindicationAdverse EffectNursing ConsiderationDocument11 pagesSilver Sulfadiazine Cream Prevents Burn InfectionsDrug NameDosageTherapeuticActionIndicationContraindicationAdverse EffectNursing ConsiderationKristine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Snakebite Drug StudyDocument7 pagesSnakebite Drug StudyDevon RevillaNo ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesAmoxicillindheng05No ratings yet
- Catholics Can Support The RH Bill in Good ConscienceDocument13 pagesCatholics Can Support The RH Bill in Good ConscienceKaloy AnneNo ratings yet
- BattleshipDocument3 pagesBattleshipAnne VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- ColonosDocument2 pagesColonosKaloy AnneNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument22 pagesStrokeKaloy AnneNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDocument1 pageAmniotic Fluid EmbolismAnne VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDocument1 pageAmniotic Fluid EmbolismAnne VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Insulin and Metformin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesInsulin and Metformin Drug StudyKaloy AnneNo ratings yet
- BT PprocedureDocument3 pagesBT PprocedureAnne VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- BT PprocedureDocument3 pagesBT PprocedureAnne VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Bone FracturesDocument2 pagesBone FracturesKaloy AnneNo ratings yet
- Stains For Microbiology SpecimensDocument5 pagesStains For Microbiology SpecimensambadepravinNo ratings yet
- 11th & 12th Science Do You Know e.mDocument12 pages11th & 12th Science Do You Know e.mS SARAVANANNo ratings yet
- Bsmmu DDV Curriculum 2012 New EdDocument18 pagesBsmmu DDV Curriculum 2012 New Edshahed100% (1)
- Desordenes Comunes de AmazonasDocument6 pagesDesordenes Comunes de AmazonasJessica RuizNo ratings yet
- Chap 011Document17 pagesChap 011alexa chalhoubNo ratings yet
- CRISPR Regulators of Cancer Cell PhagocytosisDocument32 pagesCRISPR Regulators of Cancer Cell Phagocytosiskatie weiNo ratings yet
- Virus HVB Host TestingDocument8 pagesVirus HVB Host Testingmariano villavicencioNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument7 pagesResearchVictor Lorenz LimosneroNo ratings yet
- Botany Mock Test 1 PDFDocument16 pagesBotany Mock Test 1 PDFSubir DasNo ratings yet
- API Staph Id System HandoutDocument5 pagesAPI Staph Id System HandoutWJ Ng0% (1)
- Review of ImmunomodulatorsDocument126 pagesReview of ImmunomodulatorsManice Bastinen100% (1)
- Dna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 1Document4 pagesDna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 1afkogsfea100% (2)
- AslotDocument4 pagesAslotDrAlaa ZidanNo ratings yet
- Paris by MoonlightDocument3 pagesParis by Moonlightchocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Fungal InfectionsDocument70 pagesPathogenesis of Fungal Infectionsማላያላም ማላያላም100% (15)
- Ensayo StreptococoDocument3 pagesEnsayo StreptococoEfraín Carrera FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology-ScDocument23 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology-ScSelena MoonNo ratings yet
- 0221 Thermo Purification Efficiency Ebook 8Document8 pages0221 Thermo Purification Efficiency Ebook 8liondredNo ratings yet
- 100 MCQ Questions On DiseaseDocument31 pages100 MCQ Questions On DiseaseDineshPrakashNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Divisionchar montejeroNo ratings yet
- Learn About Genes, DNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesLearn About Genes, DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesisbrenden chapmanNo ratings yet
- PenisDocument23 pagesPenisWira DharmaNo ratings yet
- DPS Revision Offline Test - 1: Based On DPS 1 To DPS 30Document16 pagesDPS Revision Offline Test - 1: Based On DPS 1 To DPS 30Savitri HegdeNo ratings yet
- Dementia A Neurodegenerative DisorderDocument16 pagesDementia A Neurodegenerative DisorderRishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Microbiolspec - Arba 0009 2017Document26 pagesMicrobiolspec - Arba 0009 2017Rossio Noelia Jurado NaciónNo ratings yet
- Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis: Moderator-Dr. Seema Meena Presenter - Dr. Sulabh SahuDocument58 pagesVernal Keratoconjunctivitis: Moderator-Dr. Seema Meena Presenter - Dr. Sulabh SahuSulabh SahuNo ratings yet
- On Agents of MutationDocument22 pagesOn Agents of Mutationmine_ne361No ratings yet
- Influvac Insert 2017Document2 pagesInfluvac Insert 2017Anonymous hiGVMZA0B100% (1)
- ScribtDocument7 pagesScribtSeenu Nadarajan NNo ratings yet
- Flushing DifferentialDocument16 pagesFlushing DifferentialMinaKrstićNo ratings yet