Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CSC134 C4
Uploaded by
Aiman NabihahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CSC134 C4
Uploaded by
Aiman NabihahCopyright:
Available Formats
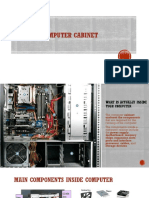
CHAPTER 4 : SYSTEM UNIT COMPONENTS SYSTEM UNIT Case that contains electronic components of computer used to process data.
Motherboard System board, called as system board: main circuit board of system unit. PROCESSOR Also called as CPU : interprets and carries out basic instructions that operate a computer. Processors developed : microprocessor dual-core processor quad-core processor multiprocessor Control units Arithmetic logic unit -components of processor that directs and -performs arithmetic, comparisons, and other coordinates most of operations in computer. operations. Machine cycle System clock -a processor repeats 4 basic operations -control timing of all computer operations -fetch > decode > execute > store -GHz DATA REPRESENTATION -most computers are digital, recognize only two discrete state : on (1) , (0)off. -using binary system MEMORY -Consists of electronic components that stores instructions waiting to be executed by the processor. -basic categories : operating system , application program, data that being processed Bytes and addressable memory Basic storage unit in memory Memory sizes In terms of number of bytes of chips or device has available for storage Types of memory Volatile Nonvolatile Loses contents when computers off. Temporary. Dont lose contents when computer off. RAM Permanent. ROM, flash memory, CMOS RAM -random access memory -basic type : DRAM , SRAM , MRAM Cache -computers improve processing time with cache. Memory cache helps speed the processes of computers because it stores frequently used instructions and data. -type of memory : L1 cache, L2 cache ROM -read-only memory. -cannot modifies. Has firmware(Chip). Flash memory -nonvolatile that can be erased electronically n rewritten. Computer used it to hold startup instructions CMOS -complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) used by some RAM, cache, and other chips to high speeds and consume little power Memory access time -amount of time it takes the processor to read data, instructions, information from memory.
EXPANSION SLOTS AND ADAPTER CARD Expansion slot : socket on motherboard that can hold adapter card/expansion card. Adapter card : circuit board that enhance functions of a component of system unit and/or provide connection to peripherals Peripheral : device that connected to system units and controlled by processor Removable flash memory Include these : memory card, USB flash drives, PC cards/ ExpressCard modules PORT AND CONNECTORS Port : point at which peripheral attaches to or communicates with system unit so peripheral can send data to or receive information from computer Connector : joins cable to a port USB ports -universal series bus port 127 different peripheral FireWire ports -IEEE 1394 port, can connect multiple types of devices that requires faster data Other ports -bluetooth port -SCSI port -eSATA port -IrDA port -MIDI port Port replicators and docking stations Port replicator : external device that provides connections to peripherals through ports built into device. Docking station : external device that attaches to a mobile computer or device, contains power connections to peripherals BUSES -allows various devices both inside and attached to system unit to communicate with each other. -two part : data bus, address bus. -system bus (FSB) : part of motherboard, connect processor to main memory -backside bus (BSB) : connects processor to cache BAYS -opening inside system unit in which can install additional equipment. POWER SUPPLY -component of system unit that convert wall outlet Ac to Dc power KEEPING COMPUTER OR MOBILE DEVICE CLEAN Maintenance requires: - Can of compressed air - Lint-free antistatic wipes and swabs - Screen cleaning solution - Small computer vacuum - Antistatic wristband - Small screwdriver
You might also like
- Components of The System UnitDocument4 pagesComponents of The System UnitAhnNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Troubleshooting ReportDocument8 pagesGroup 2 Troubleshooting ReportClarina Jane DosdosNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument1 pageCentral Processing UnitMarkus AureliusNo ratings yet
- Inside A Computer CabinetDocument14 pagesInside A Computer CabinetJavid HamdardNo ratings yet
- Components of The System UnitDocument33 pagesComponents of The System Unitapi-304500968No ratings yet
- Basic Notes 2Document6 pagesBasic Notes 2jivan jyotNo ratings yet
- Basic Hardware Computer SystemDocument82 pagesBasic Hardware Computer SystemTVET OfficeNo ratings yet
- System Unit: Integrated CircuitDocument3 pagesSystem Unit: Integrated CircuitChuzell LasamNo ratings yet
- A+ Cheat Sheet Best1Document7 pagesA+ Cheat Sheet Best1rem1611100% (2)
- System UnitDocument19 pagesSystem Unitapi-304500968No ratings yet
- Computer Science NotesDocument48 pagesComputer Science NotesaDEOlu AdesinaNo ratings yet
- Typical Configuration of Computer SystemDocument90 pagesTypical Configuration of Computer Systemgani100% (1)
- Week 3Document17 pagesWeek 3Abdullatif KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Basic Hardware II - System UnitDocument51 pagesChapter 3-Basic Hardware II - System UnitNUR AINA FAQIHAH BT AZMIL KTNNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Basic Hardware Components of Computer SystemsDocument26 pagesLESSON 2 Basic Hardware Components of Computer Systemskate cacayNo ratings yet
- Session 2 and 3Document6 pagesSession 2 and 3lucilNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument36 pagesChapter TwoyonasNo ratings yet
- Installing and Configuring Computer SystemsDocument47 pagesInstalling and Configuring Computer SystemsDonna Fe De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Computer System ComponentsDocument11 pagesComputer System ComponentsNoone F. moonNo ratings yet
- PARTS OF A SYSTEM UNITDocument6 pagesPARTS OF A SYSTEM UNITNonoy Enopena100% (2)
- Introducing Hardware - Chapter 1Document7 pagesIntroducing Hardware - Chapter 1Precious StaffordNo ratings yet
- Computer ComponentsDocument32 pagesComputer ComponentsJSPAMoreNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Assignment 1Document3 pagesUnit 5 Assignment 1miller44No ratings yet
- CTC ReviewerDocument4 pagesCTC ReviewerMariell TabanaoNo ratings yet
- ITC Lec 3Document31 pagesITC Lec 3josephNo ratings yet
- Processing System: Processing System, Which Includes The Primary Memory, The Central Processing Unit (CPU), ExpansionDocument10 pagesProcessing System: Processing System, Which Includes The Primary Memory, The Central Processing Unit (CPU), ExpansionAregawi GebreyesusNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware and Software FundamentalsDocument34 pagesComputer Hardware and Software FundamentalsJhayden BlueNo ratings yet
- Basics of Compter SystemsDocument23 pagesBasics of Compter SystemsYogesh KuteNo ratings yet
- 824 Cs 30 HardwareDocument2 pages824 Cs 30 HardwareBamPanggatNo ratings yet
- Motherboard components and functions overviewDocument12 pagesMotherboard components and functions overviewAce BorresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The Components of The System Unit - ReviewDocument2 pagesChapter 4 - The Components of The System Unit - ReviewYūkiHaseNo ratings yet
- The System Unit: Group B By: Fatin Nazwa Adnan Muhammad Faiz TaqiyuddinDocument22 pagesThe System Unit: Group B By: Fatin Nazwa Adnan Muhammad Faiz TaqiyuddinMuhammad Faiz TankNo ratings yet
- System Unit ComponentsDocument53 pagesSystem Unit Componentsk3lvynNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Computer HardwareDocument14 pagesLesson 2 Computer HardwareGel BasabeNo ratings yet
- Lab Outcome: CO 1-Recall The Fundamentals of Computer Hardware. TheoryDocument11 pagesLab Outcome: CO 1-Recall The Fundamentals of Computer Hardware. TheoryasavariNo ratings yet
- Types of Processors and RAM'sDocument26 pagesTypes of Processors and RAM'sSneha NairNo ratings yet
- Acronym of Computer System PDFDocument10 pagesAcronym of Computer System PDFJether Pactol TeroNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMotherboard Components and FunctionsCheryl Dumaguit BelaloNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document7 pagesAssignment 2deepali ghadiaNo ratings yet
- Understanding CPU Components and TerminologyDocument1 pageUnderstanding CPU Components and TerminologyCher LongNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Major Parts and FunctionDocument3 pagesMotherboard Major Parts and FunctionVic Picar0% (1)
- Computer ICTDocument20 pagesComputer ICTmobilelegendshelpcenter2022No ratings yet
- Csc134 Computer & Information Processing Chapter 2: The System UnitDocument29 pagesCsc134 Computer & Information Processing Chapter 2: The System Unitsyuhadah0% (1)
- M-P1-Hardware-Mobile-Devises-Software-Mobile-AppsDocument21 pagesM-P1-Hardware-Mobile-Devises-Software-Mobile-AppsJericho GeranceNo ratings yet
- Read Me After Pre TestDocument4 pagesRead Me After Pre TestNa DzNo ratings yet
- Glossary - ComputersDocument6 pagesGlossary - ComputersensarjusufovicNo ratings yet
- MAass 11Document2 pagesMAass 11FY20H817 Abhijeet BhushariNo ratings yet
- IT Chapter 3Document12 pagesIT Chapter 3Alice HovsepyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. The System UnitDocument6 pagesChapter 4. The System UnitQiu Jun NgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Component of The System UnitDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Component of The System UnitAminiasi SalatovouNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument86 pagesParts of MotherboardKurt BalaniNo ratings yet
- Computer parts and their functionsDocument1 pageComputer parts and their functionsJayareNo ratings yet
- The Motherboard and It'S ComponentsDocument12 pagesThe Motherboard and It'S ComponentsVanessaNo ratings yet
- Computer SystemDocument63 pagesComputer SystemEden Mae Sagadraca TabliagoNo ratings yet
- 02 - Components of The System Unit PDFDocument59 pages02 - Components of The System Unit PDFJohn Michael ÜyNo ratings yet
- Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC)Document9 pagesReduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC)Brian Holub MorvayNo ratings yet
- CS AssgmentDocument8 pagesCS AssgmentbnmNo ratings yet
- Inside the Desktop Computer: A Guide to System Units and ComponentsDocument33 pagesInside the Desktop Computer: A Guide to System Units and ComponentsJohn Mark De JesusNo ratings yet
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12From EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12No ratings yet
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.From EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.No ratings yet
- Jadual Em704 Mac - July 2021 050321Document1 pageJadual Em704 Mac - July 2021 050321Aiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- NanotechnologyDocument54 pagesNanotechnologyAiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- The Power of PCB PDFDocument70 pagesThe Power of PCB PDFAiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- Microelectronics OverviewDocument48 pagesMicroelectronics OverviewAiman Nabihah100% (1)
- CSC134 C9Document2 pagesCSC134 C9Aiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor MaterialDocument55 pagesSemiconductor MaterialAiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- MEMS - The Amazing TechnologyDocument50 pagesMEMS - The Amazing TechnologyAiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Business ModelDocument45 pagesSemiconductor Business ModelAiman Nabihah67% (3)
- Cmos Technology GroupDocument56 pagesCmos Technology GroupAiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- CSC134 C8Document3 pagesCSC134 C8Aiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- CSC134 C5Document3 pagesCSC134 C5Aiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- CSC134 C3Document2 pagesCSC134 C3Aiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- CSC134 C7Document1 pageCSC134 C7Aiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- CSC134 C6Document2 pagesCSC134 C6Aiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- CSC134 C1Document2 pagesCSC134 C1Aiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument13 pagesAnimal TissueAiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument5 pagesPlant TissuesAiman NabihahNo ratings yet
- I. Directions: Give The Two Original Words That Were Combined To Form The Following Blended Words. An Example Given To Help Guide YouDocument1 pageI. Directions: Give The Two Original Words That Were Combined To Form The Following Blended Words. An Example Given To Help Guide YouMarisa LeeNo ratings yet
- Facilities for Persons with Disabilities on Indian RailwaysDocument4 pagesFacilities for Persons with Disabilities on Indian RailwaysThiyagarajan kNo ratings yet
- 5 - 8 Wave Vertical Antenna by DxzoneDocument7 pages5 - 8 Wave Vertical Antenna by DxzoneStephen Dunifer100% (1)
- QSPC Catalog 2011Document20 pagesQSPC Catalog 2011utkal5No ratings yet
- Paul Gilbert.Document10 pagesPaul Gilbert.Anupam GurungNo ratings yet
- Expressing Certainty and Doubt in EnglishDocument62 pagesExpressing Certainty and Doubt in EnglishSekolahDasarNegeriBeriwit-EmpatNo ratings yet
- GS-2498 20230522Document10 pagesGS-2498 20230522風雲造天No ratings yet
- Philippine Folk Dance TraditionsDocument28 pagesPhilippine Folk Dance TraditionsWalang PoreberNo ratings yet
- Poodle Papers Spring 2011Document52 pagesPoodle Papers Spring 2011PCA_websiteNo ratings yet
- ICT 10 q4 ModulesDocument10 pagesICT 10 q4 ModulesJosmineNo ratings yet
- Background Actors - Sag-AftraDocument56 pagesBackground Actors - Sag-Aftratizzler07No ratings yet
- Clases de Ajedrez Dvoretsky85Document5 pagesClases de Ajedrez Dvoretsky85jogonNo ratings yet
- Ultrasone Hfi Pro DJDocument6 pagesUltrasone Hfi Pro DJokibreazy100% (1)
- LCM Exams - Drum Kit Grades Repertoire List - Esamilcm - ItDocument20 pagesLCM Exams - Drum Kit Grades Repertoire List - Esamilcm - ItPiano ForteNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To GravityDocument18 pagesAcceleration Due To Gravityjoshua cerialesNo ratings yet
- Printable Crossword Puzzles For Kids SilenceDocument2 pagesPrintable Crossword Puzzles For Kids Silenceshamin azuraNo ratings yet
- ASPIRE Sport Science Research Publications Sept 2013Document25 pagesASPIRE Sport Science Research Publications Sept 2013pdelcampo1991No ratings yet
- Potential MarketDocument10 pagesPotential MarketSean Carlo LopezNo ratings yet
- Drill PressDocument4 pagesDrill PressSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Adamson Amplification Chart V5.4Document9 pagesAdamson Amplification Chart V5.4rasawiv169No ratings yet
- Pneu Dart 2016 CatalogDocument40 pagesPneu Dart 2016 CatalogWerner Patric WengNo ratings yet
- The Goblin of AdachigaharaDocument2 pagesThe Goblin of AdachigaharaNursela AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Jesus the Greatest SaviorDocument5 pagesJesus the Greatest SaviorMicah StaileyNo ratings yet
- Amazon SWOT Analysis & Financials: Everything You NeedDocument23 pagesAmazon SWOT Analysis & Financials: Everything You NeedD.ANo ratings yet
- B1 Editable Progress Tests KeyDocument4 pagesB1 Editable Progress Tests KeyCherane Christopher0% (1)
- MALAWI - Learn ChichewaDocument4 pagesMALAWI - Learn ChichewamondomondoNo ratings yet
- XDDocument37 pagesXDLuis CarlosNo ratings yet
- APC Schneider Pricing and Product DetailsDocument908 pagesAPC Schneider Pricing and Product Detailscsn_889No ratings yet
- Build A Robot: Prime Lessons Prime LessonsDocument7 pagesBuild A Robot: Prime Lessons Prime LessonsRamaDinakaranNo ratings yet
- Audio recording systems guideDocument2 pagesAudio recording systems guideDarko IlicNo ratings yet