Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 16
Uploaded by
Saidin AhmadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 16
Uploaded by
Saidin AhmadCopyright:
Available Formats
16: MUTATION
Objective Questions 1. Colchicine is a type of mutagen that
A. enhance replication of DNA
B. failure of spindle fiber to form C. spitting of chromosomes into fragments D. change the sequence of base in DNA
2. Figure 1 below shows a type of gene mutation that cause changes from the
normal gene sequence. TACCTTGTCCAT Normal gene sequence TACCTTGGTCCAT mutated gene sequence
Figure 1
What kind of mutation has occur?
A. Base substitution B. Base insertion C. Base deletion D. Base inversion
Biology Unit, Kolej Matrikulasi Melaka
28
3. Which of the following statements about sickle cell anaemia are true?
I.
It is caused by a single base substitution. of haemoglobin.
II. It is caused by a base substitution on the sixth triplet code for polypeptide
III. Nucleotide with thymine is substituted by nucleotide with adenine base. IV. Glycine amino acid is substituted by valine.
A. I, II and III
B. I, II and IV
C. II, III and IV D. I, II, III and IV
4. The diagram below shows two types of chromosomal mutation that cause
changes in the gene sequences. A B C D E F G H I A B E D C F G H II A B E F G H Figure 2
What are the processes that cause chromosomal mutation I and II above to take place? I Inversion Inversion Deletion Translocation II Deletion Duplication Inversion Deletion
A. B. C. D.
5. Robertsonian translocation occurs when I. II. III. short arm of two non homologous chromosomes break at the extreme ends long arms of two non homologous chromosomes fuse at the centromere long arms of a chromosome are lost
Biology Unit, Kolej Matrikulasi Melaka
29
A. B. C. D.
I and II I, II and III I and III II and III
6. Which syndrome is represented by the following variation of aneuploidy? (47, +21) A. B. C. D. Klinefelters syndrome Klinefelters syndrome Downs syndrome Downs syndrome (47, XXY) Turners syndrome Downs syndrome Klinefelters syndrome Turners syndrome (45,X) Downs syndrome Turners syndrome Turners syndrome Klinefelters syndrome
7. Non-disjunction has occurred during meiosis I of spermatogenesis involving X and Y chromosomes. Which of the following are the possible genotypes of the zygote if normal ovum fertilize the sperm? A. B. C. D. XXY and YO XYY and XO XXY and XO XXX and XXY
8. Polyploidy is
A. a condition where somatic an organism have
more than two sets of
chromosomes B. a defect that is not fatal in human C. a condition which usually disadvantageous to plants D. a condition where more than one sperm fertilize an ovum
9. Hybridisation of plant M (2n = 16) with plant N (2n = 20) produces a sterile plant P. Total non-disjunction in plan P produces plant Q. What is the number of chromosomes in plant P and Q? A. B. P 18 36 Q 36 36
Biology Unit, Kolej Matrikulasi Melaka
30
C. D.
36 72
72 72
10. A plant resulting from the combination of chromosome sets from different
species is said to be
A. B. C. D.
Allopolyploid Autohybridoid Polyploid Autopolyploid
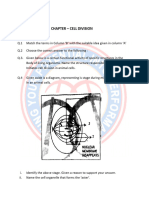
Structured Questions 1. Figure 3 below shows a karyotype of an individual.
Biology Unit, Kolej Matrikulasi Melaka
31
Figure 3
a.
Base on the Figure 3, state if the individual is male or female. Explain your
answer.
___________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ (2 marks)
b.
What is the name of the disease shown by the karyotype? Explain how it occurs.
___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ (3 mark)
c.
Draw a genetic diagram to show how non-disjunction leads to this particular
genetic disorder.
Biology Unit, Kolej Matrikulasi Melaka
32
(3 marks)
d.
State TWO typical characteristic of this genetic disorder.
___________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ (2 marks)
2.
The diagram below shows how modern bread wheat has evolved.
Wild diploid wheat 2n = 14
Triticum monococcum 2n =14
Sterile hybrid A
Fertile Emmer wheat 2n = 28
diploid wheat grass 2n = 14
sterile hybrid B
modern wheat (Triticum aestivum) 2n = 42
a) Explain the meaning of the terms : i. Polyploidy
_______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________
Biology Unit, Kolej Matrikulasi Melaka
33
ii.
Autopolyploidy
_______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________
iii.
Allopolyploidy
_______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________
(3 marks)
b) Give the chromosome number of : i. ii. hybrid A : _____________________ hybrid B : _____________________ (2 marks)
c) Explain fully why hybrids A and B are sterile whereas Triticum aestivum and Emmer are fertile. _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________
(5 marks)
Biology Unit, Kolej Matrikulasi Melaka
34
Essay Questions
1.
(a) Define base substitution. Base substitution can cause missense and nonsense mutation. Define base substitution and differentiate between missense and nonsense mutation. Give one example of disease caused by this type of mutation.
(4 marks)
(b)
Define chromosomal aberration. Describe the FOUR types of chromosomal aberration.
(10 marks)
(c)
Explain the two types of polyploidy. (6 marks)
Biology Unit, Kolej Matrikulasi Melaka
35
Biology Unit, Kolej Matrikulasi Melaka
36
You might also like
- Term 3 Trial Exam STPM 2017Document11 pagesTerm 3 Trial Exam STPM 2017Viola Voon Li WeiNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam - MitosisDocument6 pagesMidterm Exam - MitosisSherefel RosalejosNo ratings yet
- 12th Bio Preboard 1 2023-24Document6 pages12th Bio Preboard 1 2023-24Mubashshir Al NahyanNo ratings yet
- The University of Auckland: Incourse Test 2015 Biological Sciences Biology For Biomedical ScienceDocument31 pagesThe University of Auckland: Incourse Test 2015 Biological Sciences Biology For Biomedical Scienceqwwqwwqwqwwqwwq0% (2)
- Xii - Bio Pre Board QP & MSDocument13 pagesXii - Bio Pre Board QP & MSssatechies62No ratings yet
- Genetics TestDocument9 pagesGenetics TestEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 Q1 Periodical ExaminationDocument4 pagesBiology 1 Q1 Periodical ExaminationJessie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Old 474 ExamsDocument36 pagesOld 474 ExamsEvan FiefNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Sample Mock Paper Term 2 Exam 2021 22Document4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Sample Mock Paper Term 2 Exam 2021 22Abhay PundirNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Quiz QuestionsDocument19 pagesMicrobiology Quiz QuestionsAkram NiaziNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes and Heredity ReviewDocument8 pagesChromosomes and Heredity ReviewarurusipNo ratings yet
- Test 2 Summer 2011 Form ADocument4 pagesTest 2 Summer 2011 Form Aowls_1102No ratings yet
- Chemistry (Organic)Document10 pagesChemistry (Organic)Julia Mibuy Mba OyanaNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam2013Document8 pagesPractice Exam2013Elizabeth LeeNo ratings yet
- S4 Biology Section A and Section B Mid-Year Exam 202021Document20 pagesS4 Biology Section A and Section B Mid-Year Exam 202021(4A19 2122) SIT HEI TINGNo ratings yet
- Wk.2.module 2 .QRT.4 Mitosis & Meiosis, Phenotypic ExpressionDocument34 pagesWk.2.module 2 .QRT.4 Mitosis & Meiosis, Phenotypic ExpressionShanikMendozaNo ratings yet
- HY XI Bio QP Nov 2022Document6 pagesHY XI Bio QP Nov 2022Biswajit BeheraNo ratings yet
- Bio8 1Document3 pagesBio8 1Nomap makNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Active Reading GuideDocument6 pagesChapter 9 Active Reading GuideLâm TặcNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Mid Term ExamDocument6 pagesGen Bio Mid Term ExamWelbert AmarNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Genetics With AnswersDocument6 pagesMCQ in Genetics With AnswersAkram Niazi100% (8)
- Biologi Ting 4 ModulDocument20 pagesBiologi Ting 4 ModulNoine AiniNo ratings yet
- Class Xi Biology Question PaperDocument8 pagesClass Xi Biology Question Paperdeepmalabehera11No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya SangathanDocument7 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathanssatechies62No ratings yet
- K101PracticeExam3 SP19Document8 pagesK101PracticeExam3 SP19Braxton PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Unit C ExamDocument18 pagesUnit C Examapi-199149636No ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggeris Tingkatan 2 (Penilaian Kurikulum 1 / 2009) : SMK Bercham, Ipoh, PerakDocument9 pagesBahasa Inggeris Tingkatan 2 (Penilaian Kurikulum 1 / 2009) : SMK Bercham, Ipoh, PerakMasz MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Bio SPM Intervensi m1Document10 pagesBio SPM Intervensi m1teahockNo ratings yet
- Exam+1+BIOL202+SS2+14 +KEY-2Document8 pagesExam+1+BIOL202+SS2+14 +KEY-2Haley HamillNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument52 pagesScienceVannyNo ratings yet
- MCDB !B Midterm 1 KeyDocument8 pagesMCDB !B Midterm 1 KeyKenji SoaresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Heredity and Variation (Form 4) Section A. 20 Objective QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Heredity and Variation (Form 4) Section A. 20 Objective QuestionsRosni SelamonNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Essay Ques.Document2 pagesExam 3 Essay Ques.adrian nenengNo ratings yet
- STEM Track 2 Gen Bio 1 Unit I Lesson 3Document16 pagesSTEM Track 2 Gen Bio 1 Unit I Lesson 3Suzuki YamamutoNo ratings yet
- General Biology First PerioDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology First PerioJay-Ar MalanaNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2021 Biology TrialsDocument40 pagesJames Ruse 2021 Biology TrialsHewadNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Test in Grade 10 ScienceDocument8 pagesThird Quarter Test in Grade 10 ScienceFroilan AlexNo ratings yet
- Inal Xamination ART: Iology Uman Iology For Ealth Elated Ciences ALLDocument8 pagesInal Xamination ART: Iology Uman Iology For Ealth Elated Ciences ALLabdishakurNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Practice TestDocument19 pagesCell Division Practice TestCorry SepviaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cell Cycle - QuestionsDocument6 pagesLecture 3 Cell Cycle - Questions中华雅思王No ratings yet
- Worksheet Ib HL - Chapter A2.1& 2.2Document12 pagesWorksheet Ib HL - Chapter A2.1& 2.2elizabethNo ratings yet
- F3 Final Exam 11-12Document23 pagesF3 Final Exam 11-12jonas hoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Chapter 2 Test Bank - 14th EditionDocument25 pagesMicrobiology Chapter 2 Test Bank - 14th EditionAnmol33% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology Science Olympiad Div B Invite Fall 2017 ExamDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Science Olympiad Div B Invite Fall 2017 ExamMahbubur BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- Questions OnlehDocument13 pagesQuestions OnlehElcei LazoNo ratings yet
- Board QuestionsDocument79 pagesBoard QuestionsManoj ThakurNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Review - Mitosis & MeiosisDocument12 pagesMultiple Choice Review - Mitosis & MeiosisyoumasankarNo ratings yet
- Final Term XI - 26 MarchDocument6 pagesFinal Term XI - 26 Marchavishank584No ratings yet
- Solving Problems AnimalGeneticsDocument21 pagesSolving Problems AnimalGeneticsrksudheer9768100% (1)
- Biology Question As Level Cambridge PracticeDocument23 pagesBiology Question As Level Cambridge PracticebillaNo ratings yet
- Biol 430 Question Bank MHC and Antigen PresentationDocument8 pagesBiol 430 Question Bank MHC and Antigen PresentationervaishaliNo ratings yet
- Penilaian Kurikulum 2 Tahun 2009Document6 pagesPenilaian Kurikulum 2 Tahun 2009yantraksNo ratings yet
- BI 110 Test 2 2022Document2 pagesBI 110 Test 2 2022b9myjvbgrwNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNo ratings yet
- Exercise On Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesExercise On Cell DivisionNorliyana AliNo ratings yet
- RD ND: ML Bognalbal 1Document4 pagesRD ND: ML Bognalbal 1Dette Dominic BallanoNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper (B) Class12 BiologyDocument4 pagesSample Paper (B) Class12 Biologygulshanprasad510No ratings yet
- Behavior Based Safety ProgramsDocument27 pagesBehavior Based Safety ProgramsEdy Permana Tadjudin100% (2)
- Uuur Uuur: BA BADocument8 pagesUuur Uuur: BA BASaidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument10 pagesChapter 2: Trigonometric FunctionsSaidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER4 QS026 semII 2009 10Document10 pagesCHAPTER4 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER6 QS026 semII 2009 10Document7 pagesCHAPTER6 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- SMK Methodist Kelab SepaktakrawDocument1 pageSMK Methodist Kelab SepaktakrawSaidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER3 QS026 semII 2009 10Document4 pagesCHAPTER3 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER1 QS026 semII 2009 10Document7 pagesCHAPTER1 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cell Division DiagramDocument5 pagesCell Division DiagramSaidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument10 pagesChapter 2: Trigonometric FunctionsSaidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Diagram 2Document5 pagesCell Division Diagram 2Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER1 QS026 semII 2009 10Document7 pagesCHAPTER1 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Diagram 2Document5 pagesCell Division Diagram 2Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER1 QS026 semII 2009 10Document7 pagesCHAPTER1 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER10 QS026 semII 2009 10Document8 pagesCHAPTER10 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER3 QS026 semII 2009 10Document4 pagesCHAPTER3 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER4 QS026 semII 2009 10Document10 pagesCHAPTER4 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument10 pagesChapter 2: Trigonometric FunctionsSaidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER8 QS026 semII 2009 10Document13 pagesCHAPTER8 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER1 QS026 semII 2009 10Document7 pagesCHAPTER1 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER3 QS026 semII 2009 10Document4 pagesCHAPTER3 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER10 QS026 semII 2009 10Document8 pagesCHAPTER10 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER1 QS026 semII 2009 10Document7 pagesCHAPTER1 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER9 QS026 semII 2009 10Document6 pagesCHAPTER9 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin Ahmad0% (1)
- Uuur Uuur: BA BADocument8 pagesUuur Uuur: BA BASaidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER4 QS026 semII 2009 10Document10 pagesCHAPTER4 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER6 QS026 semII 2009 10Document7 pagesCHAPTER6 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER7 QS026 semII 2009 10Document5 pagesCHAPTER7 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER3 QS026 semII 2009 10Document4 pagesCHAPTER3 QS026 semII 2009 10Saidin AhmadNo ratings yet
- STD 8 Bio HRDG 2022Document5 pagesSTD 8 Bio HRDG 2022Jaya SinghNo ratings yet
- DNA Jism Ki Kitab-e-Hidayat PDFDocument21 pagesDNA Jism Ki Kitab-e-Hidayat PDFSyed ShamsuddinNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Crocodilian Nesting Ecology and Behavior: Christopher M. Murray - Brian I. Crother - J. Sean DoodyDocument19 pagesThe Evolution of Crocodilian Nesting Ecology and Behavior: Christopher M. Murray - Brian I. Crother - J. Sean DoodyFlaviana Tamung02No ratings yet
- Starting Mulberry Trees From CuttingsDocument6 pagesStarting Mulberry Trees From CuttingsamacmanNo ratings yet
- Transpiration Diagram-Based QuestionsDocument9 pagesTranspiration Diagram-Based Questionsthe lillyNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Life Science (English) March 2023 Quetion PaperDocument8 pagesGR 10 Life Science (English) March 2023 Quetion PaperitumelengsebolNo ratings yet
- Evidence of Evolution AnswersDocument8 pagesEvidence of Evolution AnswersAnoNo ratings yet
- Adaptations in AnimalsDocument7 pagesAdaptations in AnimalsSean100% (1)
- Genetic Engineering of Microalgae For Enhanced Biorefi - 2020 - BiotechnologyDocument13 pagesGenetic Engineering of Microalgae For Enhanced Biorefi - 2020 - BiotechnologyerosNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes ActivityDocument1 pageChromosomes ActivityNOVA LESLIE AGAPAYNo ratings yet
- Gene Synthesis HandbookDocument18 pagesGene Synthesis HandbookAshfia Desi RahmalinaNo ratings yet
- Fossil FlipbookDocument2 pagesFossil Flipbookapi-405510232No ratings yet
- Biologc3ada La Vida en La Tierra Con Fisiologc3ada 9c2ba Edicic3b3nDocument2 pagesBiologc3ada La Vida en La Tierra Con Fisiologc3ada 9c2ba Edicic3b3nLaura Teresa PinzónNo ratings yet
- The Resistance Test of 10 Rice Plant of Banten Local Variety To The Bacterial Leaf Blight Disease (Xanthomonas Oryzae Pv. Oryzae) Seedling Phase OlehDocument7 pagesThe Resistance Test of 10 Rice Plant of Banten Local Variety To The Bacterial Leaf Blight Disease (Xanthomonas Oryzae Pv. Oryzae) Seedling Phase OlehAmel RahmaNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Biology - C. StoneDocument294 pagesThe Basics of Biology - C. Stonemonicq77100% (1)
- Medical Technology Assessment Program: Parasitology Review NotesDocument8 pagesMedical Technology Assessment Program: Parasitology Review NotesMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- Rna M A Meets Transposable Elements and Chromatin: OmmentaryDocument5 pagesRna M A Meets Transposable Elements and Chromatin: OmmentaryRamona AnaNo ratings yet
- IAL Bio Unit2 Jan 2020Document31 pagesIAL Bio Unit2 Jan 2020Clover HaxorNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and SuperlativesDocument67 pagesComparatives and SuperlativesDIANA CAROLINA CAMACHO AVILANo ratings yet
- PhotoautotrophsDocument2 pagesPhotoautotrophsJane ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Antibiotics: Antimicrobial Agents Antibiotics or AntimicrobialsDocument5 pagesClassification of Antibiotics: Antimicrobial Agents Antibiotics or AntimicrobialsDimple CosNo ratings yet
- Perspectives ZietsmanDocument8 pagesPerspectives ZietsmanDeonNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology: Results & Unit Reference Value Test DescriptionDocument1 pageMolecular Biology: Results & Unit Reference Value Test DescriptionLibu GeorgebabuNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology P43 May2020 QPDocument17 pagesIGCSE Biology P43 May2020 QPPakorn WinayanuwattikunNo ratings yet
- Flora of SurinameDocument147 pagesFlora of SurinameMolineNo ratings yet
- Germs Cause Many Diseases in Humans.: Key ConceptDocument44 pagesGerms Cause Many Diseases in Humans.: Key ConceptmkmanNo ratings yet
- International Gcse Biology Switching Guide V1.1Document13 pagesInternational Gcse Biology Switching Guide V1.1Novanolo Christovori ZebuaNo ratings yet
- A Hungry CrocodileDocument4 pagesA Hungry CrocodileMaulya FaradinaNo ratings yet
- F2 CHP 2 Ecosystem (Chinese)Document12 pagesF2 CHP 2 Ecosystem (Chinese)ChuahSiewHoonNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary Project Lesson PlansDocument10 pagesInterdisciplinary Project Lesson Plansapi-251762082No ratings yet