Professional Documents
Culture Documents
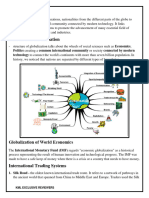
Economies of All of The World's Countries, National Economies
Uploaded by
stillnotbeaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Economies of All of The World's Countries, National Economies
Uploaded by
stillnotbeaCopyright:
Available Formats
Bea Diaz Period 2 WHAP A.
Conceptual Identification Chapter 17- The West and the World 1) Diffusion (pg 383 ) the spread of social institutions (and myths and skills) from one society to another Context: Previous periods had seen important steps toward greater diffusion of goods and ideas. Significance: This diffusion of ideas and interactions with other societies became an important feature of the basic economic structure. Themes: social- societies interacted with each other; cultural- spread of ideas/ beliefs 2) world economy(pg 383, 390) The world economy, or global economy, generally refers to the economy, which is based on economies of all of the world's countries, national economies. Context: Furthermore, international trade became so significant that it forged different relationships between key societies, based on the kind of goods and amount of control contributed to the surging world economy. Significance: Relationships were based on the contributions brought forth from their world economies. Themes: social-relationships between societies; economic- international tradeeconomy 3) core nations; dependent areas (pg 391)- A core nation is a nation that dominates trade, controls the most advanced technologies, and have high levels of productivity within diversified economies Context: The dominant core nations in the new world system supplemented their growing economic prowess by self-serving political policies. Significance: Nations that enjoyed profit from world economy controlled international banking and commercial services such as shippingthey also exported manufactured goods for raw materials. Themes: social- a nation; economic- dominates tradehigh production rates; TED- had the most advanced economies 4) coercive labor systems (pg 392)- A civil relationship in which one person has absolute power over the life, fortune, and liberty of another Context: Coercive labor systems spread. Significance: These labor systems were formed because dependent economies relied on cheap production of unprocessed goods. Themes: social- oppressive relationship; economic- resulted because of dependent economies 5) colonialism; colonization (pg 387)- The act of colonizing, or the state of being colonized; the formation of a colony or colonies. Context: Englands serious work began in the 17th century, with the colonization of the east coast of North America. Significance: Colonization from the North European expeditions led to their expansion. Themes: social- regrouping of peopleestablishing a society
You might also like
- Capitalism, Alone: The Future of the System That Rules the WorldFrom EverandCapitalism, Alone: The Future of the System That Rules the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (7)
- TCW Midterms Notes and LEDocument17 pagesTCW Midterms Notes and LEAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World 5 PDF FreeDocument3 pagesContemporary World 5 PDF FreeAlmira SocorNo ratings yet
- Contemporary WorldDocument12 pagesContemporary WorldTherese PagayNo ratings yet
- Notes in Contemporary WorldDocument6 pagesNotes in Contemporary WorldHazelNo ratings yet
- Prep For Final KDQTDocument22 pagesPrep For Final KDQTHà ThanhNo ratings yet
- GEC 3AA ReviewerDocument11 pagesGEC 3AA ReviewerairaelaydayandayanNo ratings yet
- "Socialism": Dictionary MeaningsDocument3 pages"Socialism": Dictionary MeaningsSyed Salman AhmedNo ratings yet
- TCW Midterm ReviewerDocument3 pagesTCW Midterm ReviewerCarmella AfableNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Module Contemporary WorldDocument2 pagesWeek 3 Module Contemporary Worldkassel PlacienteNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World ReviewerDocument8 pagesContemporary World ReviewerSunshine KhuletzNo ratings yet
- Prelim Lesson 1 B. History of GlobalizationDocument18 pagesPrelim Lesson 1 B. History of GlobalizationJANETH SATRAINNo ratings yet
- Economic GlobalizationDocument23 pagesEconomic GlobalizationChristian LaguidaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 What Is GlobalizationDocument6 pagesChapter 1 What Is GlobalizationAnonymous rpDEhiLuNo ratings yet
- Globalization TheoriesDocument4 pagesGlobalization TheoriesHafidh SongweNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World: Chapter 1: What Is Globalization?Document15 pagesContemporary World: Chapter 1: What Is Globalization?maeyonnaise92No ratings yet
- Contemporary World ReviewerDocument5 pagesContemporary World ReviewerAshiro Dump100% (1)
- Contem ReviewerDocument9 pagesContem ReviewerKenNo ratings yet
- GE104 - MODULE 1.1 - GlobalizationDocument47 pagesGE104 - MODULE 1.1 - GlobalizationKimberly Joyce Olivia Navarro100% (1)
- Lecture 09Document10 pagesLecture 09fortextbooks plsNo ratings yet
- Contempo ReviewerDocument9 pagesContempo ReviewerIanna ManieboNo ratings yet
- VND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Wordprocessingml Documentrendition1Document18 pagesVND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Wordprocessingml Documentrendition1sachied1023No ratings yet
- Contemporary World ReviewerDocument5 pagesContemporary World RevieweralyNo ratings yet
- THE CONTEMPORARY WORLD Prelim ReviewerDocument6 pagesTHE CONTEMPORARY WORLD Prelim ReviewerJohn Mark MadrazoNo ratings yet
- GE 3 - Reviewer THE CONTEMPORARY WORLDDocument7 pagesGE 3 - Reviewer THE CONTEMPORARY WORLDKissey EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World Prelim ReviewerDocument15 pagesContemporary World Prelim ReviewerLJ RamirezNo ratings yet
- Contemp RevDocument9 pagesContemp RevNubskie 314No ratings yet
- Globalization Arthur Macewan Jim DatorDocument12 pagesGlobalization Arthur Macewan Jim DatorMae JessaNo ratings yet
- Theories of GlobalizationDocument4 pagesTheories of GlobalizationAries Queencel Bernante Bocar100% (1)
- Comtemporary World LectureDocument10 pagesComtemporary World LectureJed Nicole AngonNo ratings yet
- Globalisation Vs RegionalisationDocument6 pagesGlobalisation Vs RegionalisationSubhash SoniNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary WorldDocument6 pagesThe Contemporary WorldREINA GERONA AUREONo ratings yet
- GE WORLD NotesDocument6 pagesGE WORLD NotesGian Carla RicoNo ratings yet
- Third WorldDocument5 pagesThird Worldpascalokonye19No ratings yet
- International Political EconomyDocument39 pagesInternational Political EconomyTooba ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Araquel PortfolioDocument6 pagesAraquel PortfolioHaven Vence AraquelNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 Economic GlobalizationDocument8 pagesTOPIC 2 Economic GlobalizationAngel CamatNo ratings yet
- "The Contemporary World": Lesson 1: Concept of GlobalizationDocument6 pages"The Contemporary World": Lesson 1: Concept of GlobalizationKimmyNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary World Prelim ReviewerDocument6 pagesThe Contemporary World Prelim Revieweraprilrobles08No ratings yet
- Global Political EconomyDocument58 pagesGlobal Political EconomyRhenmar Morales Galvez50% (2)
- PLT College, Inc.: College of Arts and Sciences and EducationDocument3 pagesPLT College, Inc.: College of Arts and Sciences and EducationZanesville Lymont L. SubidoNo ratings yet
- Contemporary WorldDocument12 pagesContemporary WorldLouie D.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 4Document165 pagesChapter 1 4Lex BactolNo ratings yet
- Contempo 1-10 - 082715Document5 pagesContempo 1-10 - 082715Keren hope BarriosNo ratings yet
- Apuntes IpeDocument120 pagesApuntes IpeLuis Fernández ChacónNo ratings yet
- Lecture IPEDocument44 pagesLecture IPEsana mehmoodNo ratings yet
- The Global EconomyDocument33 pagesThe Global EconomyCharls Patrick BaqueroNo ratings yet
- What Does "Globalization" Mean?Document46 pagesWhat Does "Globalization" Mean?Aduniya MulugetaNo ratings yet
- International Political EconomyDocument45 pagesInternational Political Economysaad ali0% (1)
- Demystifying The Complex World of International Political EconomyDocument6 pagesDemystifying The Complex World of International Political EconomyMelit Jane YuNo ratings yet
- OutlineDocument6 pagesOutlinesantosdanroseNo ratings yet
- TCW Economic Globalization (4 Files Merged)Document77 pagesTCW Economic Globalization (4 Files Merged)Jan Rey GregorioNo ratings yet
- Globalization and The North-South DivideDocument4 pagesGlobalization and The North-South DivideGreen ArcNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World: Mr. Sam Barbo, JRDocument50 pagesContemporary World: Mr. Sam Barbo, JRLikith Kumar LikithNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument12 pagesGlobalizationsaloni_gothiNo ratings yet
- AdeelQureshi - 1701 - 18669 - 2 - L11 Philosophy of EconomicsDocument26 pagesAdeelQureshi - 1701 - 18669 - 2 - L11 Philosophy of EconomicsAmmad AktharNo ratings yet
- GLOBALISATIONDocument34 pagesGLOBALISATIONBea SantosNo ratings yet
- Module 1-3Document4 pagesModule 1-3Sicad, Jhenny DNo ratings yet
- Summary Chapters 1 and 2Document6 pagesSummary Chapters 1 and 2Mark Alvin De LeonNo ratings yet
- Svetovka Prezentace (Vseborec - Cz-Ac8uj)Document68 pagesSvetovka Prezentace (Vseborec - Cz-Ac8uj)Kateřina KundratováNo ratings yet
- Ch. 17 Reading Notes: Bea Diaz Period 2 WhapDocument3 pagesCh. 17 Reading Notes: Bea Diaz Period 2 WhapstillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- Ch.19 Reading Notes: Bea Diaz Period 1.20.13Document3 pagesCh.19 Reading Notes: Bea Diaz Period 1.20.13stillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- CH 16 C, D, eDocument2 pagesCH 16 C, D, estillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- CH 15 CDocument1 pageCH 15 CstillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- CH 16 IDsDocument2 pagesCH 16 IDsstillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- Ch.16 Reading Notes: Bea Diaz Period 2 Whap 1.14.13Document3 pagesCh.16 Reading Notes: Bea Diaz Period 2 Whap 1.14.13stillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- Ch.14 Reading Notes: Chapter Title: Chronology (Time Period & Major Events)Document3 pagesCh.14 Reading Notes: Chapter Title: Chronology (Time Period & Major Events)stillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 21 Reading Notes: Bea Diaz Period 2 WHAP 1.23.13Document4 pagesCh. 21 Reading Notes: Bea Diaz Period 2 WHAP 1.23.13stillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- CH 14 C & DDocument2 pagesCH 14 C & Dstillnotbea100% (1)
- CH 11 NotesDocument3 pagesCH 11 NotesstillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- CH 21 CdefDocument2 pagesCH 21 Cdefstillnotbea100% (1)
- Chapter 13-The Spread of Chinese Civilization: Japan, Korea, and VietnamDocument1 pageChapter 13-The Spread of Chinese Civilization: Japan, Korea, and VietnamstillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- CH 13 IDsDocument1 pageCH 13 IDsstillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- CH 13 NotesDocument2 pagesCH 13 NotesstillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- Chap 12 IDSDocument2 pagesChap 12 IDSstillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Reunification and Renaissance in Chinese Civilization: in The Era of The Tang and Song Dynasties C. Focus QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 12 - Reunification and Renaissance in Chinese Civilization: in The Era of The Tang and Song Dynasties C. Focus QuestionsstillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- CH 11 C and DDocument1 pageCH 11 C and DstillnotbeaNo ratings yet
- Sampling Technique For Qualitative ResearchDocument5 pagesSampling Technique For Qualitative ResearchArun PrasadNo ratings yet
- Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility On The Financial Performance of BanksDocument8 pagesImpact of Corporate Social Responsibility On The Financial Performance of BanksHaider SarwarNo ratings yet
- Elvis: Hound Dog' and in The Ghetto'Document6 pagesElvis: Hound Dog' and in The Ghetto'demelza_42No ratings yet
- To Kill A Mockinbird: A Brillian BildungsromanDocument5 pagesTo Kill A Mockinbird: A Brillian BildungsromanSarah Hannah100% (2)
- Exploitation of Women in The Music IndustryDocument8 pagesExploitation of Women in The Music IndustryLeslie BrownNo ratings yet
- Statistics PWDs PHDocument5 pagesStatistics PWDs PHStephen TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Health CareDocument9 pagesDiversity in Health Careapi-403183907100% (1)
- Harm and Offense in Mill's Conception of LibertyDocument36 pagesHarm and Offense in Mill's Conception of LibertyNeil G100% (1)
- Vaastu Affects Your WellbeingDocument1 pageVaastu Affects Your Wellbeingmonicca869581No ratings yet
- JUTA's StatementDocument1 pageJUTA's StatementThe WireNo ratings yet
- Fifa Code of EthicsDocument58 pagesFifa Code of EthicsAri Surya MiharjaNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesQuestionnaireG Sindhu RavindranNo ratings yet
- CorruptionDocument2 pagesCorruptionawaisNo ratings yet
- Written By, Dr. Rick Brinkman Dr. Rick Kirschner: Sameer Kumar RaiDocument17 pagesWritten By, Dr. Rick Brinkman Dr. Rick Kirschner: Sameer Kumar RaiPerrin HaarpNo ratings yet
- Safai Karamchari Andolan and Ors Vs Union of India and Ors On 27 March, 2014Document14 pagesSafai Karamchari Andolan and Ors Vs Union of India and Ors On 27 March, 2014Velmurugan ElumalaiNo ratings yet
- Indigenous Ally Toolkit enDocument8 pagesIndigenous Ally Toolkit enJoe TongNo ratings yet
- Brief of Vice Admiral Mario Ivan Carratú MDocument1 pageBrief of Vice Admiral Mario Ivan Carratú MSoyLibertadNo ratings yet
- Race, Equity and Inclusion in San Diego Febraury 10, 2017Document23 pagesRace, Equity and Inclusion in San Diego Febraury 10, 2017Ralph DimarucutNo ratings yet
- Ethics Testbank Chapter 1Document36 pagesEthics Testbank Chapter 1boardwalk1234100% (5)
- Strength of Our MothersDocument205 pagesStrength of Our MothersKim FoaleNo ratings yet
- Jock Young - Social Exclusion PDFDocument5 pagesJock Young - Social Exclusion PDFAdrian SilvaNo ratings yet
- The Paranoid Style in American PoliticsDocument3 pagesThe Paranoid Style in American PoliticsRaquel ManaigNo ratings yet
- Code of EthicsDocument8 pagesCode of EthicsviorelNo ratings yet
- Peer Mediation TrainingDocument94 pagesPeer Mediation Trainingapi-314325235No ratings yet
- PGCC Soc1010Document20 pagesPGCC Soc1010seunfutaNo ratings yet
- Glass. London: Routledge, 2006.: ND RDDocument9 pagesGlass. London: Routledge, 2006.: ND RDRyana AndryanaNo ratings yet
- Brigada ScriptDocument3 pagesBrigada ScriptEhdz B Visperas-TarangcoNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument4 pagesRRLcezcil72No ratings yet
- Essay 2 Psyc 4p71Document14 pagesEssay 2 Psyc 4p71api-534375900No ratings yet
- 01.03 Citizens in ActionDocument2 pages01.03 Citizens in Actionhgeriuh100% (1)
- The Hotel on Place Vendôme: Life, Death, and Betrayal at the Hotel Ritz in ParisFrom EverandThe Hotel on Place Vendôme: Life, Death, and Betrayal at the Hotel Ritz in ParisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (49)
- Bind, Torture, Kill: The Inside Story of BTK, the Serial Killer Next DoorFrom EverandBind, Torture, Kill: The Inside Story of BTK, the Serial Killer Next DoorRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (77)
- Hunting Eichmann: How a Band of Survivors and a Young Spy Agency Chased Down the World's Most Notorious NaziFrom EverandHunting Eichmann: How a Band of Survivors and a Young Spy Agency Chased Down the World's Most Notorious NaziRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (157)
- The Lost Peace: Leadership in a Time of Horror and Hope, 1945–1953From EverandThe Lost Peace: Leadership in a Time of Horror and Hope, 1945–1953No ratings yet
- Dunkirk: The History Behind the Major Motion PictureFrom EverandDunkirk: The History Behind the Major Motion PictureRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- The Rape of Nanking: The History and Legacy of the Notorious Massacre during the Second Sino-Japanese WarFrom EverandThe Rape of Nanking: The History and Legacy of the Notorious Massacre during the Second Sino-Japanese WarRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (63)
- The Quiet Man: The Indispensable Presidency of George H.W. BushFrom EverandThe Quiet Man: The Indispensable Presidency of George H.W. BushRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Rebel in the Ranks: Martin Luther, the Reformation, and the Conflicts That Continue to Shape Our WorldFrom EverandRebel in the Ranks: Martin Luther, the Reformation, and the Conflicts That Continue to Shape Our WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Never Surrender: Winston Churchill and Britain's Decision to Fight Nazi Germany in the Fateful Summer of 1940From EverandNever Surrender: Winston Churchill and Britain's Decision to Fight Nazi Germany in the Fateful Summer of 1940Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (45)
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyFrom EverandDigital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- The Great Fire: One American's Mission to Rescue Victims of the 20th Century's First GenocideFrom EverandThe Great Fire: One American's Mission to Rescue Victims of the 20th Century's First GenocideNo ratings yet
- Hubris: The Tragedy of War in the Twentieth CenturyFrom EverandHubris: The Tragedy of War in the Twentieth CenturyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (23)
- We Crossed a Bridge and It Trembled: Voices from SyriaFrom EverandWe Crossed a Bridge and It Trembled: Voices from SyriaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- Making Gay History: The Half-Century Fight for Lesbian and Gay Equal RightsFrom EverandMaking Gay History: The Half-Century Fight for Lesbian and Gay Equal RightsNo ratings yet
- Reagan at Reykjavik: Forty-Eight Hours That Ended the Cold WarFrom EverandReagan at Reykjavik: Forty-Eight Hours That Ended the Cold WarRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Future of Capitalism: Facing the New AnxietiesFrom EverandThe Future of Capitalism: Facing the New AnxietiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Project MK-Ultra: The History of the CIA’s Controversial Human Experimentation ProgramFrom EverandProject MK-Ultra: The History of the CIA’s Controversial Human Experimentation ProgramRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Desperate Sons: Samuel Adams, Patrick Henry, John Hancock, and the Secret Bands of Radicals Who Led the Colonies to WarFrom EverandDesperate Sons: Samuel Adams, Patrick Henry, John Hancock, and the Secret Bands of Radicals Who Led the Colonies to WarRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- They All Love Jack: Busting the RipperFrom EverandThey All Love Jack: Busting the RipperRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (30)
- Witness to Hope: The Biography of Pope John Paul IIFrom EverandWitness to Hope: The Biography of Pope John Paul IIRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- Knowing What We Know: The Transmission of Knowledge: From Ancient Wisdom to Modern MagicFrom EverandKnowing What We Know: The Transmission of Knowledge: From Ancient Wisdom to Modern MagicRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- Daughters of the Flower Fragrant Garden: Two Sisters Separated by China’s Civil WarFrom EverandDaughters of the Flower Fragrant Garden: Two Sisters Separated by China’s Civil WarRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (14)
- The OSS and CIA: The History of America’s Intelligence Community during World War II and the Establishment of the Central Intelligence AgencyFrom EverandThe OSS and CIA: The History of America’s Intelligence Community during World War II and the Establishment of the Central Intelligence AgencyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- The Ship of Dreams: The Sinking of the Titanic and the End of the Edwardian EraFrom EverandThe Ship of Dreams: The Sinking of the Titanic and the End of the Edwardian EraRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (38)
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailFrom EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (237)
- 1963: The Year of the Revolution: How Youth Changed the World with Music, Fashion, and ArtFrom Everand1963: The Year of the Revolution: How Youth Changed the World with Music, Fashion, and ArtRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Pursuit of Happiness: How Classical Writers on Virtue Inspired the Lives of the Founders and Defined AmericaFrom EverandThe Pursuit of Happiness: How Classical Writers on Virtue Inspired the Lives of the Founders and Defined AmericaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)