Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Checklist
Uploaded by
Jaymark LambinoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Checklist
Uploaded by
Jaymark LambinoCopyright:
Available Formats
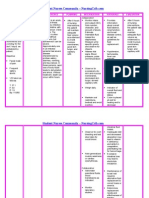
Nursing Diagnosis Risk for latex allergy response
Risk for Impaired Liver Function
Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity
Risk for Unstable Blood Glucose
Bowel Incontinence
Constipation
Diarrhea
Functional Urinary Incontinence
Impaired Urinary Elimination
Overflow urinary incontinence
Perceived Constipation
Readiness for enhanced urinary elimination
Reflex Urinary Incontinence
Risk for Constipation
Risk for urge urinary incontinence
Defining Characteristics Risk Factors: > History of reactions to latex > Allergies to bananas, avocados, tropical fruits, kiwi, chestnuts, poinsettia plants > history of allergies or asthma > Professions with daily exposure to latex > Multiple surgical procedures, especially from infancy Risk Factors: > Viral Infection ( Hepatitis A, B, C, Epstein - Barr) > HIV co-infection > Hepatotoxic medications (Acetaminophen, Statins) > Substance Abuse (Alcohol, coccaine) Risk Factors: External: > Chemical Substance; radiation > Hypothermia; Hyperthermia > Physical immobilization > Excretions; Secretions; humidity; moisture > Mechanical Factors (Shearing forces, pressure, restraint) > Extremes of Age Internal: > Medications > Imbalanced nutrition state (obesity, emaciation) > impaired metablic state (flud status) > skeletal prominence > changes in skin turgor (presence of edema) > impaired circulation. Sensation > changes in pigmentation > developmental factors > psychogemetic factors
YES
NO
> immunologic factors Risk Factors: > lack of acceptance of diagnosis > deficient knowledge of diabetes management > lack of diabetes management/ adherance to diabetes management > dietary intake; weight gain/ weight loss; rapid growth periods; pregnancy Physical health status/ activity level Stress; mental health status Developmental level
Subjective: - recognizes rectal fullness, but reports inability to expel formed stool. - Urgency, inability to delay defecation Self-report of inability to feel rectal fullness
Objectives: - Constant dribbling of soft stool Fecal staining of clothing/ bedding Fecal odor Red perianal skin Inability to recognize/ inattention to urge to defecate Hyperactive bowel sounds At least three loose liquid stools per day
Subjective:
- Change in bowel pattern; unable to pass stool; decreased frequency, decreased volume of stool - Increased abdominal pressure; feeling of rectal fullness/ pressure
- Abdominal pain; pain with defecation; nausea; vomiting; headache; indigestion; generalized fatigue Objective: Hard, formed stool Straining with defecation Hypoactive, hyperactive bowel sounds; borborygmi
- Distended abdomen; abdominal tenderness with/without palpable muscle resistance; palpable rectal Percussed abdominal dullness
Subjective: Abdominal pain Urgency, cramping Objective: Hyperactive bowel sounds At least three loose liquid stools per day Reports involuntary leakage of small volumes of urine Nocturia Objective: Bladder distention High post-void residual volume
- Observed involuntary leakage of small amounts of urine Subjective: Senses need to void (voiding in large amounts)
Objective:
- Loss of urine before reaching toilet; amount of time required to reach toilet exceeds length of time between sensing urge and uncontrolled voiding Subjective Frequency, urgency Hesitancy Dysuria Nocturia (enuresis) Objective: Incontinence Retention Subjective: Reports involuntary leakage of small volumes of urine
Nocturia Objective: Bladder distention High post-void residual volume
- Observed involuntary leakage of small amounts of urine
Subjective: Expectation of a daily bowel movement Expected passage of stool at the same time every day Overuse of laxatives/ enemas/ suppositories
Subjective: Expresses willingness to enhance urinary elimination Positions self for emptying of bladder Objective: Urine is straw colored/ odorless
- Amount of output/ specific gravity is within normal limits Fluid intake is adequate for daily needs
Subjective: No sensation of bladder fullness/ urge to void/ voiding
- Sensation of urgency without voluntary inhibition of bladder contraction - Sensations associated with full bladder(sweating, restlessness, abdominal discomfort) Objective: Predictable pattern of voiding Inability to voluntary inhibit/initiate voiding
- Complete emptying (brain) lesion above sacral micturition center Risk Factors: FUNCTIONAL:
- Irregular defecation habits; inadequate toileting (timeliness, positioning for defecation, privacy)
- Insufficient physical activity; abdominal muscle weakness Recent environmental changes Habitual denial/ ignoring urge to defecate PSYCHOLOGICAL: Emotional stress, depression, mental confusion PHYSIOLOGICAL
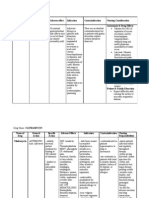
- Change in usual foods/ eating patterns; insufficient fiber/fluid intake, dehydration; poor eating habits - Inadequate dentition or oral hygiene - Decreased motility of gastrointestinal tract - PHARMACOLOGICAL - Phenothiazides, NSAIDS, sedatives, aluminumcontaining antacids, laxative overuse, bismuth salts, iron salts, anticholinergics, anti-depressants, calcium carbonate, diuretics, sympathomimetics, opiates - MECHANICAL - Hemorrhoids;pregnancy;obesity - Rectal abcess/ulcer; rectal anal stricture/fissures; rectal prolapse; rectocele - Prostate enlargement; post-surgical obstruction - Neurological impairment; hirschsprungs disease; tumor - Electrolyte imbalance - Risk factors: - Effects of medications/caffeine/ alcohol - Detrusor hyperreflexia(fr. Cystitis, urethritis, tumors, renal calculi, CNS disorders above pontine micturition center) - Impaired bladder contractility; involuntary sphincter relaxation - Ineffective toileting habits - Small bladder capacity
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Colon Cleansing Kit Users GuideDocument74 pagesColon Cleansing Kit Users GuideYoungBody0% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Basic Nursing Fundamentals EliminationDocument35 pagesBasic Nursing Fundamentals Eliminationlisa100% (1)
- History Taking FormDocument14 pagesHistory Taking FormFebbie ArcalesNo ratings yet
- Separate Hard Lumps, Like Nuts: Constipated Stool - Types 1 or 2 Diarrheal Stool - Types 6 or 7Document2 pagesSeparate Hard Lumps, Like Nuts: Constipated Stool - Types 1 or 2 Diarrheal Stool - Types 6 or 7nicky_lauw5885No ratings yet
- HEMORRHOID (Case Study)Document45 pagesHEMORRHOID (Case Study)enny92% (24)
- NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeRedwing_Dc_854758% (12)
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument16 pagesNursing DiagnosisSi Bunga JonquilleNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - CholeraDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Choleraderic87% (30)
- NCP For Acute Gastroenteritis (Pediatric)Document6 pagesNCP For Acute Gastroenteritis (Pediatric)abcel76% (21)
- NCP For Acute Gastroenteritis (Pediatric)Document6 pagesNCP For Acute Gastroenteritis (Pediatric)abcel76% (21)
- Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone SodiumJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ProfileDocument14 pagesCardiac ProfileJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ProfileDocument14 pagesCardiac ProfileJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone SodiumJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone SodiumJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone SodiumJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone SodiumJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- An A PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAn A PhysiologyJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Criteria For WebsiteDocument3 pagesCriteria For WebsiteJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone SodiumJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone SodiumJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone SodiumJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone SodiumJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone SodiumJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- An A PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAn A PhysiologyJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ProfileDocument14 pagesCardiac ProfileJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeDocument6 pagesDrug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Book1 NandaDocument10 pagesBook1 NandaJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- 6206 13778 1 PBDocument11 pages6206 13778 1 PBJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Transfusion ReactionsDocument11 pagesTransfusion ReactionsJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Module - MotionDocument51 pagesModule - MotionJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- GenericDocument8 pagesGenericJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Pott's DseDocument4 pagesPott's DseJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant Drug Effects and Depression SeverityDocument15 pagesAntidepressant Drug Effects and Depression SeverityJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Toileting Definition - Google SearchDocument1 pageToileting Definition - Google SearchJucie MariaNo ratings yet
- Small and Large Intestines-0Document23 pagesSmall and Large Intestines-0Siraj ShiferawNo ratings yet
- SRUS Clinical FeaturesDocument8 pagesSRUS Clinical FeaturesRam C. HumagainNo ratings yet
- Gordons Interview Form (MCN)Document5 pagesGordons Interview Form (MCN)teuuuuNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument29 pagesHuman Digestive SystemRagini Dubey100% (1)
- SR23510123232Document8 pagesSR23510123232Mobasshir AlamNo ratings yet
- 251 - TMBO MekongDocument14 pages251 - TMBO MekongWahyu IndraNo ratings yet
- Bladder & Bowel Elimination PDFDocument37 pagesBladder & Bowel Elimination PDFSwarna JayarathnaNo ratings yet
- Skills Lab FCP 201922Document57 pagesSkills Lab FCP 201922Corillo, Fionnula JeanNo ratings yet
- Bowel EliminationDocument34 pagesBowel EliminationAnastasia LubertaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanWhela SabueroNo ratings yet
- ConstipationDocument6 pagesConstipationاحمد محمدNo ratings yet
- Copia de Copia de SEGUIMIENTO A NUMERO DE MIPRES-1Document105 pagesCopia de Copia de SEGUIMIENTO A NUMERO DE MIPRES-1Bleydis S'pNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 GastrointestinalDocument9 pagesChapter 11 GastrointestinalChyNo ratings yet
- Colic in Horse: A Presentation OnDocument32 pagesColic in Horse: A Presentation OnMuhammad Saif KhanNo ratings yet
- Bowel Elimination:: DiarrheaDocument44 pagesBowel Elimination:: DiarrheaBashracel Marie M. SALMORINNo ratings yet
- Konstipasi 1Document7 pagesKonstipasi 1NagistinaNo ratings yet
- Quality of Life in Pregnant Women With and Without ConstipationDocument8 pagesQuality of Life in Pregnant Women With and Without ConstipationMichimichi 78No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ForDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan ForVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Constipation in School-Aged Children at Public Schools in Rio de Janeiro, BrazilDocument7 pagesConstipation in School-Aged Children at Public Schools in Rio de Janeiro, BrazilZakia AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Nama: Rina Agustina Nim: 22018028 Unit 7 Promoting Hygiene 3 (Assissting With Elimination)Document3 pagesNama: Rina Agustina Nim: 22018028 Unit 7 Promoting Hygiene 3 (Assissting With Elimination)rinaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management OF Git Problems Gastric and Duodenal DisordersDocument109 pagesNursing Management OF Git Problems Gastric and Duodenal DisorderstantanbaragoNo ratings yet
- Bleed From Anal Means - Google SearchDocument1 pageBleed From Anal Means - Google SearchKaran deep SinghNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of DigestionDocument18 pagesThe Chemistry of DigestionHarsh PatelNo ratings yet