Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elevated Blood Pressure
Uploaded by
Sean MercadoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elevated Blood Pressure
Uploaded by
Sean MercadoCopyright:
Available Formats
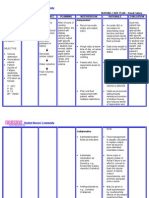
Nursing Diagnosis Risk for decreased cardiac output related to increased vascular vasoconstriction Assessment: Subjective Data: I do not
really feel well, right now. My blood pressure is always high and I feel light headed when I suddenly move. as claimed by patient. Objective Data: -Pale in color -Skin cool and moist to touch -Jugular vein can be easily seen and bounding upon palpation -Verbalized light headedness on sudden change of position -Easy fatigability and occasional dyspnic occurrences upon exertion -Blood pressure ranging
Patient Outcomes Outcome Identification:
Nursing Interventions
Rationale Nursing Care Plan for Hypertension 1. Bounding carotid, jugular, radial, femoral pulses may be observed/ palpated. Pulses in the leg may be diminished, implicating effects of vasoconstriction and venous congestion. 2. S3 and S4 heart sounds may indicate atrial and venous hypertrophy and impaired functioning. 3. Presence of adventitious breath sounds may indicate pulmonary congestion secondary to developing heart failure. 4. Presence of pallor; cool and moist skin and delayed capillary refill may be due to peripheral vasoconstriction or
Evaluation Please refer to the Patient Outcomes tab
The patient will Independent: participate in activities that 1. Monitor blood reduce cardiac pressure workload by periodically. 04/18/12. Measure both arms The patient will three times; 3-5 maintain blood mins apart while pressure within patient is at rest for acceptable range initial evaluation. by 04/19/12. 2. Note presence of, The patient will quality of central demonstrate stable and peripheral cardiac rhythm pulses. and rate within 3. Auscultate heart patients normal tones and breath range by 04/19/12. sounds 4. Observe skin color, moisture, temperature and capillary refill time. 5. Note independent or general edema 6. Provide a calm environment; minimizing noise; limiting visitors and length of stay. 7. Maintain activity restrictions (bed rest) and assist patient with selfcare activities.
from 140/90 to 150/100 mmHg, BP as of 6:00 A.M. 04/17/12 is 150/90 mmHg -Pulse rate of 110 beats per minute as of 6:00 A.M. 04/17/12 -Capillary refill of 2-3 seconds
8. Provide comfort measures, i.e. elevation of head 9. Encourage relaxation techniques like guided imagery and distractions 10. Monitor response to medications to control blood pressure Depedent 11. Administer medications like diuretics, alpha and beta antagonists, calcium channel blockers, and vasodilators. Collaborative 12. Instruct and implement to patient dietary restrictions in sodium, fat and cholesterol
5.
6. 7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
decreased cardiac output. It may indicate heart failure, vascular or renal impairment. Promotes relaxation. It reduces physical stress and stimuli that affect the blood pressure. Decreases discomfort and may reduce sympathetic stimulation It helps reduce stressful stimuli, thereby decreases blood pressure. Response to drug is dependent on both the individual and the synergistic effect of the drug. It is also important to check for any untoward signs and symptoms of the medications. These medications should be medically prescribed by the physician and dose and timing of medications should
be followed. Checking BP prior to giving of medications is always a must to prevent hypotension. 12. This restrictions help manage fluid retention and decrease myocardial workload.
You might also like
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map On CVA Bleed Left Thalamo-Ganglionic Bleed Patient Name: Mr. DGDDocument1 pageConcept Map On CVA Bleed Left Thalamo-Ganglionic Bleed Patient Name: Mr. DGDBert Brian Bolido100% (1)
- Nursing care plan for cardiomyopathyDocument7 pagesNursing care plan for cardiomyopathyKym RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Hiatal Hernia Case StudyDocument7 pagesHiatal Hernia Case StudybabiNo ratings yet
- Aguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Hypochloremia & HyperchloremiaDocument9 pagesAguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Hypochloremia & HyperchloremiaSophia Kaye AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF THE OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATIONDocument5 pagesASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF THE OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATIONRussel SantosNo ratings yet
- Aminogen Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAminogen Drug Studymilesmin100% (1)
- Managing Upper GI Bleeding in a Male PatientDocument19 pagesManaging Upper GI Bleeding in a Male PatientMary Ann Garcia100% (1)
- Case Study Ugib Lower MBDocument65 pagesCase Study Ugib Lower MBQuolette Constante100% (1)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPranee diane0% (1)
- Fdar 3Document2 pagesFdar 3Loungayvan BatuyogNo ratings yet
- 13 Areas of Assessment Surgical WardDocument4 pages13 Areas of Assessment Surgical WardEsvinch EsvinchNo ratings yet
- Final Course in The WardDocument4 pagesFinal Course in The WardMichael Boado100% (1)
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPMarius Clifford BilledoNo ratings yet
- NCP - Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument12 pagesNCP - Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisAya BolinasNo ratings yet
- Case Study 3 - HCVDDocument12 pagesCase Study 3 - HCVDJilkiah Mae Alfoja CampomanesNo ratings yet
- University of Northern PhilippinesDocument1 pageUniversity of Northern PhilippinesCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionClaidelyn De Leyola100% (1)
- Gi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesGi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeEvangeline Villa de Gracia100% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Document3 pagesPATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Giselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Case StudyDocument5 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Case StudyClaudine Lacaden0% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis for Pleural EffusionDocument10 pagesNursing Diagnosis for Pleural EffusionEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing GunshotDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing GunshotMikko Enoc100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiggy SikatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument4 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Impaired Gas ExchangeShen Paril0% (1)
- Diarrhea NCP 1Document1 pageDiarrhea NCP 1Rhence Efner Saylon50% (2)
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- Gouty Arthritissss PathophyDocument2 pagesGouty Arthritissss Pathophybilliam123No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureLeng Royo BrionesNo ratings yet
- Age With Moderate Dehydration New 1Document74 pagesAge With Moderate Dehydration New 1Jhade Relleta100% (1)
- Excess Fluid Volume - Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan - NurseslabsDocument8 pagesExcess Fluid Volume - Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan - NurseslabsEricsonMitraNo ratings yet
- Animal Farm Essay PDFDocument5 pagesAnimal Farm Essay PDFAndrei CristeaNo ratings yet
- CAP and Hypertension: Predisposing and Precipitating FactorsDocument5 pagesCAP and Hypertension: Predisposing and Precipitating FactorsLeonaPunzalanNo ratings yet
- NCP-fluid Volume DeficitDocument4 pagesNCP-fluid Volume DeficitChrissa Mae Aranilla MayoNo ratings yet
- CHOLElithiasisDocument93 pagesCHOLElithiasisfranciscomaricris13No ratings yet
- Leukemias: Care SettingDocument11 pagesLeukemias: Care SettingTinNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology Sickle Cell AnemiaTine GuibaoNo ratings yet
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Anthony Alexander University of The West Indies at MonaDocument40 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Anthony Alexander University of The West Indies at MonaAy Alex0% (1)
- Anemia Unspecified FinalDocument47 pagesAnemia Unspecified FinalMaria Paula BungayNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument40 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDavid Seroney100% (1)
- Assisted with ambulation as toleratedDocument4 pagesAssisted with ambulation as toleratedGalileo AragonaNo ratings yet
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
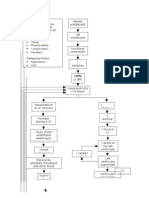
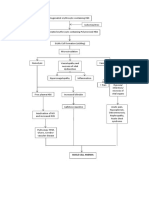
- Pathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease (HCVDDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease (HCVDNicolne Lorraine100% (1)
- Emj Cases : Questions For Case 1Document8 pagesEmj Cases : Questions For Case 1Azmyza Azmy100% (1)
- Ugib Case StudyDocument36 pagesUgib Case StudyRJ MarquezNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Risk Assessment and ManagementDocument3 pagesNutrition Risk Assessment and ManagementSitty Aizah MangotaraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaJake Caballo100% (1)
- Case StudyDocument49 pagesCase StudyLennie Marie B Pelaez100% (1)
- Revised NCP (Baiae)Document9 pagesRevised NCP (Baiae)Jennifer BactatNo ratings yet
- Risk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPPaula AbadNo ratings yet
- NCP For OsteomyleitisDocument5 pagesNCP For OsteomyleitisAyaBasilioNo ratings yet
- NCP Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid Volume DeficitNecheal BaayNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Case Study: Toddler Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument5 pagesPneumonia Case Study: Toddler Diagnosis and TreatmentcrisolandNo ratings yet
- Ecologic Model NRMFDocument4 pagesEcologic Model NRMFgreyzelNo ratings yet
- NCP - Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP - Fluid Volume DeficitPatrice LimNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis92% (13)
- Assessment: Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument3 pagesAssessment: Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDelaine Mae MierNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Case PresDocument6 pagesCase PresCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Edwards Hloomstrong: 123 Park Avenue, Big Rapids, MI 68965Document4 pagesEdwards Hloomstrong: 123 Park Avenue, Big Rapids, MI 68965Sean MercadoNo ratings yet
- 58 Traditional EleganceDocument3 pages58 Traditional EleganceSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- General ObjectivesDocument1 pageGeneral ObjectivesSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument14 pagesBasic Life SupportSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- Descriptin Dian HansonDocument1 pageDescriptin Dian HansonSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- CSDocument11 pagesCSSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementsDocument36 pagesAcknowledgementsRonan PapassoniNo ratings yet
- Descriptin Dian HansonDocument1 pageDescriptin Dian HansonSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementsDocument36 pagesAcknowledgementsRonan PapassoniNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis Case For PrintingDocument12 pagesCirrhosis Case For PrintingSean Mercado100% (1)
- Nursing Ethics and JurisprudenceDocument18 pagesNursing Ethics and JurisprudenceNiña Lyn Paican PonlaNo ratings yet
- Word Danger Sign of PregyDocument5 pagesWord Danger Sign of PregySean MercadoNo ratings yet
- CVD Case StudyDocument12 pagesCVD Case StudySean MercadoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- Scabies PeduculosisDocument35 pagesScabies PeduculosisSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hypertensionmariejo89% (82)
- Nursing Made Easy ICU VisitationDocument1 pageNursing Made Easy ICU VisitationSean Mercado100% (1)
- NCP HP FinalDocument2 pagesNCP HP FinalSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document14 pagesLecture 1Sean MercadoNo ratings yet
- Medical Common AbbreviationDocument8 pagesMedical Common AbbreviationSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- 1987 ConstiDocument2 pages1987 ConstiSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- New Wordpad DocumentDocument1 pageNew Wordpad DocumentSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- LAMINECTOMYDocument1 pageLAMINECTOMYSean MercadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Renal FailureMark Jason Rabadan100% (1)
- Display PDFDocument6 pagesDisplay PDFoneoceannetwork3No ratings yet
- Staffing Process and Job AnalysisDocument8 pagesStaffing Process and Job AnalysisRuben Rosendal De Asis100% (1)
- Shouldice Hospital Ltd.Document5 pagesShouldice Hospital Ltd.Martín Gómez CortésNo ratings yet
- Pfr140 User ManualDocument4 pagesPfr140 User ManualOanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Kathy Davis - Dancing Tango - Passionate Encounters in A Globalizing World-New York University Press (2015)Document236 pagesKathy Davis - Dancing Tango - Passionate Encounters in A Globalizing World-New York University Press (2015)Csongor KicsiNo ratings yet
- Vector 4114NS Sis TDSDocument2 pagesVector 4114NS Sis TDSCaio OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Physics Derived Units and Unit Prefixes Derived UnitDocument15 pagesPhysics Derived Units and Unit Prefixes Derived UnitJohnRenzoMolinarNo ratings yet
- Shopping Mall: Computer Application - IiiDocument15 pagesShopping Mall: Computer Application - IiiShadowdare VirkNo ratings yet
- There Is There Are Exercise 1Document3 pagesThere Is There Are Exercise 1Chindy AriestaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Problem?: Method + Answer SolutionDocument17 pagesWhat Is A Problem?: Method + Answer SolutionShailaMae VillegasNo ratings yet
- Indian Journal of Natural Products and Resources Vol 1 No 4 Phytochemical pharmacological profile Cassia tora overviewDocument8 pagesIndian Journal of Natural Products and Resources Vol 1 No 4 Phytochemical pharmacological profile Cassia tora overviewPRINCIPAL BHILWARANo ratings yet
- (123doc) - Chapter-24Document6 pages(123doc) - Chapter-24Pháp NguyễnNo ratings yet
- eHMI tool download and install guideDocument19 pageseHMI tool download and install guideNam Vũ0% (1)
- Reading Comprehension Exercise, May 3rdDocument3 pagesReading Comprehension Exercise, May 3rdPalupi Salwa BerliantiNo ratings yet
- Excel Solver Optimization ReportDocument9 pagesExcel Solver Optimization ReportMy Duyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- CS709 HandoutsDocument117 pagesCS709 HandoutsalexNo ratings yet
- 4 Influencing Factors of Learners Career Choice Parents Choice Vs Personal DescisionDocument24 pages4 Influencing Factors of Learners Career Choice Parents Choice Vs Personal Descisionmatteo mamaloNo ratings yet
- Alignment of Railway Track Nptel PDFDocument18 pagesAlignment of Railway Track Nptel PDFAshutosh MauryaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Transmission Media: Dr. Mohammad AdlyDocument14 pagesComputer Networks Transmission Media: Dr. Mohammad AdlyRichthofen Flies Bf109No ratings yet
- CENG 5503 Intro to Steel & Timber StructuresDocument37 pagesCENG 5503 Intro to Steel & Timber StructuresBern Moses DuachNo ratings yet
- Exercise-01: JEE-PhysicsDocument52 pagesExercise-01: JEE-Physicsjk rNo ratings yet
- AVR Instruction Set Addressing ModesDocument4 pagesAVR Instruction Set Addressing ModesSundari Devi BodasinghNo ratings yet
- Grading System The Inconvenient Use of The Computing Grades in PortalDocument5 pagesGrading System The Inconvenient Use of The Computing Grades in PortalJm WhoooNo ratings yet
- CDI-AOS-CX 10.4 Switching Portfolio Launch - Lab V4.01Document152 pagesCDI-AOS-CX 10.4 Switching Portfolio Launch - Lab V4.01Gilles DellaccioNo ratings yet
- Special Power of Attorney: Benedict Joseph M. CruzDocument1 pageSpecial Power of Attorney: Benedict Joseph M. CruzJson GalvezNo ratings yet
- Extrajudicial Settlement of Estate Rule 74, Section 1 ChecklistDocument8 pagesExtrajudicial Settlement of Estate Rule 74, Section 1 ChecklistMsyang Ann Corbo DiazNo ratings yet
- Mutual Fund PDFDocument22 pagesMutual Fund PDFRajNo ratings yet
- Arta Kelmendi's resume highlighting education and work experienceDocument2 pagesArta Kelmendi's resume highlighting education and work experienceArta KelmendiNo ratings yet
- Unr Ece R046Document74 pagesUnr Ece R046rianteri1125No ratings yet
- Condition Based Monitoring System Using IoTDocument5 pagesCondition Based Monitoring System Using IoTKaranMuvvalaRaoNo ratings yet