Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circulatory System
Uploaded by
Anonymous iOaluenhOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circulatory System
Uploaded by
Anonymous iOaluenhCopyright:
Available Formats
C A S A
THE NUTRITIONAL FUNCTION
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
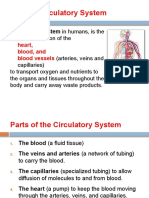
The Circulatory System is responsible for transporting materials throughout the entire body. It transports nutrients,
water, and oxygen to your billions of body cells and carries away wastes such as carbon dioxide that body cells produce. The heart, blood, and blood vessels work together to service the cells of the body.
RED BLOOD CELLS
The function of red blood cells is to carry oxygen to all the cells of the body.
They have no nucleus, meaning that there is more room for haemoglobin.
They are small and flexible, in order to pass through small blood vessels.
They are shaped as small biconcave discs, providing maximun surface area
to volume ratio for absorbing oxygen.
They contain a substance called haemoglobin. In the lungs this substance
combines with oxigen to form oxyhaemoglobin. In the tissues it gives up
the oxygen to form haemoglobin again.
O2 + haemoglobin
oxyhaemoglobin
WHITE BLOOD CELLS
The main function of white blood cells is defence against disease.
They have a large nucleus.
They are larger than red blood cells and their shape varies.
They have a flexible shape, in order to engulf microorganisms.
There are two main types of white blood cells that can multiply if needed.
Macrophage: this type of white blood cell kills microbes by ingesting them.
Lymphocytes: this type of white blood cell sends out antibodies which kill microbes.
PLATELETS
Platelets are fragments of cells. Their function is to clot the blood
so you do not bleed to death if you cut yourself.
PLASMA
Plasma is a yellow fluid. It consists mainly of water with many substances dissolved in it. These substances include soluble food, salts, carbon dioxide, urea,
hormones, antibodies and plasma proteins. Its function is to transport these
substances around the body.
29
C A S A
THE NUTRITIONAL FUNCTION
ACTIVITIES
1)Which fluid transports food to cells?
A)
bile
B)
blood
C)
saliva
D)
urine
2)Wich cell has a variable shape?
A)
all of them
B)
platelet
C)
red blood cell
D)
White blood cell
3)Which structure is only a cell fragment?
A)
plasma
B)
platelet
C)
red blood cell
D)
white blood cell
4)What colour is plasma?
A)
blue
B)
green
C)
red
D)
yellow
5)The diagram shows some of the components of blood.
A
B
C
A) Name the labelled structures
A............................
B............................
C.............................
B) What are the jobs of these structures?.
A..............................................................................................................................................................
B..............................................................................................................................................................
C..............................................................................................................................................................
C) Which part of the blood is not shown in the diagram?........................................................................
6)
A) Which cellular structure is missing from a red blood cell and how does this help in carrying oxygen?
.................................................................................................................................................................
B) Explain how red blood cells are adapted to carry out their function.
7)
...................................................................................................................................................................
A) What is the main component of plasma?
...................................................................................................................................................................
B) List four other components of plasma.
8)
...................................................................................................................................................................
A) Name two types of white blood cell.
...................................................................................................................................................................
B) How are the white blood cells different from the red blood cells?.
...................................................................................................................................................................
30
C A S A
THE NUTRITIONAL FUNCTION
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
BLOOD VESSELS
VEINS: Veins carry mainly deoxygenated blood, blood that has given up its oxygen to
the body tissues. They carry the blood back to the heart from the body at low pressure. They have valves to prevent the blood flowing backwards. Veins have a large
lumen, or hole, in the middle.
ARTERIES: Arteries carry mainly oxygenated blood. They carry blood away from the
heart, towards the body, at high pressure. They have very thick, muscular, elastic
walls to withstand the high pressure. The high pressure in the arteries causes a pulse that can be felt in
the wrist and neck.
CAPILLARIES: Capillaries are only one cell thick and have very thin, permeable walls, to allow oxygen and
nutrients to diffuse out of them. When something is permeable, it has tiny holes in it that allow small
substances to flow through. These capillaries are the site of exchange between the blood and the cells of
the body.
Fluid leaks out of the capillaries and bathes the surrounding cells. This is called tissue fluid. The tissue
fluid delivers the food and oxygen to the cells and receives waste products, which are reabsorbed back
into the capillaries.
THE HEART
The heart consists of a special type of muscle called cardiac muscle. It contracts continuously without getting tired. The heart is a
double pump. The left side pumps oxygenated blood out of the
aorta at high pressure to other arteries, to deliver substances
around the body. The right side of the heart carries deoxygenated blood and pumps it to the lungs to be oxygenated.
The left side of the heart has much thicker walls, as it has to
pump blood at high pressure all the way around the body. The
top two chambers of the heart are called atria (the singular of
which is atrium). They receive blood from the body and the
lungs. The bottom two chambers of the heart are called ventricles. They pump the blood out of the heart.
QUICK TEST (ORAL)
1-Which side of the heart contains deoxygenated blood?.
2-Name two blood vessels that enter the heart:
3-Name two blood vessels that leave the heart.
4-What are aortic and pulmonary valves for?.
5-Why do arteries have elastic, muscular walls?.
6-Which blood vessel contains valves?.
7-Which blood vessels are the site of exchange of substances between the blood and the body?.
31
C A S A
THE NUTRITIONAL FUNCTION
ACTIVITIES
1)What type of muscle is the heart made of?
A)
cardiac
B)
coronary
C)
circulatory
D)
capillary
2)
A) The capillaries in the body go to all organs. Suggest an organ they might go to.
.................................................................................................................................................................
B) What type of blood is in the vein coming from the lungs?.
.................................................................................................................................................................
C) What substance is passed out of the blood in the capillaries in the body?.
.................................................................................................................................................................
3)Each statement refers to a blood vessel. Put a tick in the correct box to show which blood vessel the statement
refers to.
Statement
Artery
Vein
Capillary
Takes blood away from the heart
Carries mainly oxygenated blood
Blood is under high pressure
Where an exchange of substances takes place
Carries blood to the heart
Contains valves
Has walls one cell thick
Carries deoxygenated blood
Has thick muscular walls
4)
A) What type of blood vessel is the aorta?.
.................................................................................................................................................................
B) The blood returns from the lungs. Describe the route it takes through the heart on its way to the body
cells.
.................................................................................................................................................................
C) What type of blood returns to the heart from the body?
.................................................................................................................................................................
Visit this web page, listen the audio and answer: What is anemia?
http://kidshealth.org/teen/diseases_conditions/blood/anemia.html
32
You might also like
- Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesCirculatory SystemWisdom DzombeNo ratings yet
- 07 Human Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFDocument27 pages07 Human Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFJohn DeHans100% (2)
- CIRCULATION SYSTEMDocument136 pagesCIRCULATION SYSTEMamir kingNo ratings yet
- Transport System in HumanDocument7 pagesTransport System in HumanMSMohanaNo ratings yet
- Bio Sum CH 3Document5 pagesBio Sum CH 3Thijmen van de VrieNo ratings yet
- Complete - SLASh - Science9 - Week 1 and 2Document5 pagesComplete - SLASh - Science9 - Week 1 and 2Creative ImpressionsNo ratings yet
- Asm 8300Document2 pagesAsm 8300Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Composed With Epsilon Notes in AndroidDocument8 pagesCirculatory System: Composed With Epsilon Notes in AndroidTanaka muzuwaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument50 pagesThe Circulatory SystemIshan Jacob PiadocheNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument50 pagesThe Circulatory Systemfan dingNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument50 pagesThe Circulatory SystemGay For anime girlzNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemSaadNo ratings yet
- Transport in HumansDocument10 pagesTransport in Humanseugene_970418755No ratings yet
- KS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2Document15 pagesKS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2f72ktyd78nNo ratings yet
- Types of CirculationDocument7 pagesTypes of Circulationhow are you?No ratings yet
- Science 9 ReviewerDocument22 pagesScience 9 ReviewerRio OrpianoNo ratings yet
- Transportation in AnimalsDocument6 pagesTransportation in AnimalskrovrainkNo ratings yet
- Animal TransportDocument20 pagesAnimal TransportFeranmi AkinboboyeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesCirculatory SystemrhaiceenNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemGennelle GabrielNo ratings yet
- Biology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemDocument58 pagesBiology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemmemmotilalNo ratings yet
- 2.14 - Circulatory SystemDocument3 pages2.14 - Circulatory SystemAbba LexiNo ratings yet
- Transport Systems in HumansDocument4 pagesTransport Systems in HumansLenon TemboNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument33 pagesCirculatory SystemMarco DadoNo ratings yet
- Science - 020121 - TRANSPORTATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALSDocument9 pagesScience - 020121 - TRANSPORTATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALSDeepak KansalNo ratings yet
- The Heart Pumps Blood CirculationDocument9 pagesThe Heart Pumps Blood CirculationShokefun OlawaleNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals o Level2018Document12 pagesTransport in Animals o Level2018MuneebNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemYusuf AzeezNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesBlood Circulatory SystemstephanietoppoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Transport and Blood CirculationDocument10 pagesCirculatory System: Transport and Blood Circulationadriann strakerNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System (Cardiovascular System) Pumps Blood From TheDocument6 pagesThe Circulatory System (Cardiovascular System) Pumps Blood From ThevanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument37 pagesCirculatory SystemKathleen DuenasNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Lecture - NotesDocument23 pagesCardiovascular System Lecture - NotesParker KapembwaNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Notes Chapter 1Document39 pagesBiology Form 5 Notes Chapter 1Mayghen SelvanayagamNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Facts & Function: Top 10 Amazing Facts About Your HeartDocument6 pagesCirculatory System: Facts & Function: Top 10 Amazing Facts About Your HeartVance CeballosNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesCirculatory SystemYzza Veah Esquivel100% (2)
- Functions of The Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesFunctions of The Circulatory SystemJulliane OrtizNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory SystemgusneriNo ratings yet
- Biology - Circulatory System Notes 1Document13 pagesBiology - Circulatory System Notes 1archit.kulkarni7756No ratings yet
- Lesson 3.1Document2 pagesLesson 3.1Evangelia GkNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Sir Jayr TaroyDocument30 pagesCirculatory System: Sir Jayr TaroyDelfin Jr UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Biology-The HeartDocument7 pagesBiology-The Heart2k7wmbhxqfNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System ExplainedDocument31 pagesThe Circulatory System ExplainedKalev MaricqNo ratings yet
- Three Circulatory Systems Working TogetherDocument4 pagesThree Circulatory Systems Working TogetherSteven OwenNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: VocabularyDocument4 pagesRespiratory System: VocabularyFely NatadNo ratings yet
- Lec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesLec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and Transport: Prepared By: PN - Tan Seoah Chee SMK Desa Skudai 2010Document61 pagesBlood Circulation and Transport: Prepared By: PN - Tan Seoah Chee SMK Desa Skudai 2010lccjane8504100% (1)
- Chloe Reviewer SCience - Full BurstDocument3 pagesChloe Reviewer SCience - Full BurstKim Carlo AglinaoNo ratings yet
- Presidium Indirapuram Students Handout-3 Grade X (Biology) Chapter: Life Processes Topic: TransportationDocument8 pagesPresidium Indirapuram Students Handout-3 Grade X (Biology) Chapter: Life Processes Topic: TransportationSaniya nebNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory SystemAliAshalNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Components and FunctionsDocument9 pagesCirculatory System Components and FunctionsHimanshu JindalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 42 Reading GuideDocument5 pagesChapter 42 Reading GuideCaleb SchantzNo ratings yet
- CirculatoryDocument9 pagesCirculatoryJason Vinluan Carinan100% (1)
- Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCirculatory SystemTan XiangNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemChelsea EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory SystemGO BIGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Making Inferences (3) : 제 7회차: BloodDocument7 pagesChapter 3: Making Inferences (3) : 제 7회차: Bloodgreen1458No ratings yet
- Transport in Animals (1)Document12 pagesTransport in Animals (1)Jedidiah DickNo ratings yet
- Comenius Meeting ProgrammeDocument2 pagesComenius Meeting ProgrammeAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- The Water Cycle PDFDocument1 pageThe Water Cycle PDFAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument3 pagesAir PollutionAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Planets From The Inner Solar SystemDocument1 pagePlanets From The Inner Solar SystemAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Digestivo 1Document4 pagesDigestivo 1Anonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Nervous SystemAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument4 pagesThe EyeAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Programme Seville PDFDocument1 pageProgramme Seville PDFAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument3 pagesAir PollutionAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Drug Problems PDFDocument2 pagesDrug Problems PDFAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- 3-6 Biology 3Document4 pages3-6 Biology 3Anonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Bill Nye SongDocument2 pagesBill Nye SongAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument3 pagesExcretory SystemAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- A Balanced Diet and Nutrition: The Nutritional FunctionDocument4 pagesA Balanced Diet and Nutrition: The Nutritional FunctionAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Digestivo 1Document4 pagesDigestivo 1Anonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Bill Nye SongDocument2 pagesBill Nye SongAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument1 pageGenetic EngineeringAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Inherited DiseasesDocument4 pagesInherited DiseasesAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Writind Activity Dna StructureDocument1 pageWritind Activity Dna StructureAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living ThingsDocument2 pagesClassification of Living ThingsAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- What Is Cancer ArticleDocument3 pagesWhat Is Cancer ArticleAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Listening ExerciseDocument1 pageMeiosis Listening ExerciseAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Micro OrganismsDocument3 pagesMicro OrganismsAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument4 pagesGenetic EngineeringAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Medical Surgical NursingDocument86 pagesIntroduction of Medical Surgical NursingSeema YadavNo ratings yet
- Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (MSAFP)Document2 pagesMaternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (MSAFP)Shaells JoshiNo ratings yet
- Health - Questions - Pdf-Igcse Biology WorksheetDocument22 pagesHealth - Questions - Pdf-Igcse Biology WorksheetPrincess KimNo ratings yet
- Nose Examination:: INSPECTION - ExternalDocument1 pageNose Examination:: INSPECTION - ExternalMark ColganNo ratings yet
- Drug MenuDocument17 pagesDrug MenukathlynmangasiNo ratings yet
- Circular Covid-19 Measures: INCO International Fz. Co. ح م ش ﺔﯾﻟودﻟا وﻛﻧاDocument2 pagesCircular Covid-19 Measures: INCO International Fz. Co. ح م ش ﺔﯾﻟودﻟا وﻛﻧاErin JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Panvax H1N1 PI Vaccine Packaging InsertDocument7 pagesPanvax H1N1 PI Vaccine Packaging Insertrakky4No ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument19 pagesHypertensionmr_coolz282344No ratings yet
- NGT Insertion Guide: 40 Steps for Safe PlacementDocument11 pagesNGT Insertion Guide: 40 Steps for Safe PlacementJan Federick BantayNo ratings yet
- 1 MSN UNIT 1introductionDocument57 pages1 MSN UNIT 1introductionVikash PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- What Is Cancer? What Causes Cancer?: Discovered An Important Clue As To Why Cancer Cells SpreadDocument8 pagesWhat Is Cancer? What Causes Cancer?: Discovered An Important Clue As To Why Cancer Cells SpreadAlfred Melvin SolivaNo ratings yet
- Role of ICT in HealthcareDocument19 pagesRole of ICT in HealthcareRama VenugopalNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGY HOMEWORK SET B-AnswersDocument7 pagesMICROBIOLOGY HOMEWORK SET B-AnswerschristinejoanNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Zodiacal Degrees PDFDocument6 pagesAnatomical Zodiacal Degrees PDFMaria Marissa100% (2)
- Dr. Kuntal Das - ResumeDocument5 pagesDr. Kuntal Das - ResumeKuntal DasNo ratings yet
- Lipaglyn Product MonographDocument64 pagesLipaglyn Product Monographanurag3069No ratings yet
- Coping Mechanisms in A NutshellDocument33 pagesCoping Mechanisms in A NutshellAngeloVenturaKadusaleNo ratings yet
- PRC Informed Consent Form for Licensure Exams during COVIDDocument3 pagesPRC Informed Consent Form for Licensure Exams during COVIDVincent GtnNo ratings yet
- PEDIA Review TransesDocument12 pagesPEDIA Review TransesJennie KimNo ratings yet
- Ataxia 10Document19 pagesAtaxia 10Cristina GhizdavetNo ratings yet
- Avian Flu: Emerging IllnessesDocument11 pagesAvian Flu: Emerging IllnessesPrincess Aliah M. MaruhomNo ratings yet
- Pyrantel Dosage Guide With PrecautionsDocument1 pagePyrantel Dosage Guide With PrecautionsMey KhNo ratings yet
- Inadequate Oral Intake (NI-2.1Document2 pagesInadequate Oral Intake (NI-2.1Hasna KhairunnisaGIZINo ratings yet
- Rome III Diagnostic Criteria FGIDsDocument14 pagesRome III Diagnostic Criteria FGIDsPutu Reza Sandhya PratamaNo ratings yet
- DSM-5 Changes to Psychotic and Mood Disorder CriteriaDocument9 pagesDSM-5 Changes to Psychotic and Mood Disorder CriteriaMonika LangngagNo ratings yet
- Employer's Work Accident ReportDocument1 pageEmployer's Work Accident ReportAlex Elle0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for a Patient with Tuberculosis (TBDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for a Patient with Tuberculosis (TBVen Belista86% (14)
- Complementary and supplementary feeding essentialsDocument23 pagesComplementary and supplementary feeding essentialsArchana100% (1)
- April 28 FibrinolysisDocument7 pagesApril 28 FibrinolysisCzarina Mae IlaganNo ratings yet
- Declaracion Conformidad IFMR-45-GeneFinder-COVID-19-Plus-RealAmp-KitDocument2 pagesDeclaracion Conformidad IFMR-45-GeneFinder-COVID-19-Plus-RealAmp-KitalexanderNo ratings yet