Professional Documents
Culture Documents
X 104 Formulas of Electrotechnic and Electronic
Uploaded by
ABELWALIDCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
X 104 Formulas of Electrotechnic and Electronic
Uploaded by
ABELWALIDCopyright:
Available Formats
Formulas of electrotechnic and electronic
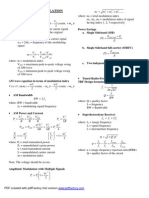
Cross-section for single wire round 2 or D2 0,7854 q = D 4 Cross-section for bunched wire 2 q = d n or d2 0,7854 n 4 Diameter for single wires cross-section D = q 4 or q 1,2732 Ohms Law The current intensity (I) is proportional to voltage (U) and inversely proportional to resistance (R) I = U R = U U = I R R l I = current intensity (Amps - A) R = electrical resistance ( ) U = electrical voltage (V) Conductance 1 1 G = 1 1S = or 1 S = R 1 1M S (Siemens) = reziprocal value of a resistance is used as conductance 1 Siemens = 1/Ohm G = electrical conductance Capacitance Single core against earth r 103 (nF/km or pF/m) CB = 18 ln Di d Unshielded symmetrical twisted pair r 103 CB = 2a (nF/km or pF/m) 36 ln d Coaxial pair r 103 CB = Di (nF/km or pF/m) 18 ln d Shielded symmetrical twistet pair r 103 (nF/km or pF/m) CB = 2a (Da2 a2) 36 ln d (Da2 a2) Di = outer diameter over single core (mm) Da = outer diameter of multicores (mm) d = conductor diamete (mm) a = distance between two conductors mid to mid of both conductors Inductance of parallel cores at low frequencies L = 0,4 (In Da + 0,25) mH/km r at high frequencies L = 0,4 (In Da + 0) mH/km r Inductance of coaxial cable at high frequencies L = 0,2 (In Da + 0) mH/km r Da = distance between two conductors mid to mid of both conductors r = radius of a conductor r = dielectric constant Impedance (Z) for coaxial cable Z = 60 In D ( ) r d D = diameter over insulation d = conductor diameter for communication cable Z= at low frequencies R ( ) tan C = 1, = 45
Diameter for bunched wires D = 1,34 n d
q = cross-section(mm2) D = conductor diameter (mm) d = single wire diameter (mm) n = number of wires Conductor Resistance l l R = oder q q 2l p R Schleife = 2l oder q q R = Electrical direct-current resistant (Ohm) = Resistance of a complete circuit R Schleife q = cross-section (mm2 or q mm) (Kappa) = Conductivity (Rho) = Specic resistance ( = 1 ) I = Conductor length (m) Materials Conductivity
m mm2
Spec. resistance
mm2 m
Copper Aluminium Silver Iron Constantan
58,00 33,00 62,00 7,70 2,00
0,01724 0,0303 0,1613 0,1299 0,50
Serial connection Resistance: R = R1 + R2 + R3 + ... + Rn 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + ... + 1 Capacitance: C C1 C2 C3 Cn Inductance: L = L1 + L2 + L3 + ... + Ln Parallel connection Resistance: R = 1 + 1 + 1 + ... 1 Rn R1 R2 R3 Capacitance: C = C1 + C2 + C3 + ... Cn L = 1 + 1 + 1 + ... 1 Ln L 1 L 2 L3 Equivalent resistance of 2 parallel connected resistance R = R1 R2 R1 + R 2 Mutual capacity (C) r 103 C= coaxial cable 18 ln Da (nF/km) Inductance:
d
parallel core shielded twisted pair r 103 CB = (Da2 a2) 2a 36 ln d 2 2
(Da a )
C=
r 103 36 ln Da (nF/km)
d
(nF/km)
Da = Ds = d = a = =
Outer diameter over insulation diameter over shield diameter of conductor distance - mid to mid of both conductors dielectric constant
L ( ) at high frequencies Z= C R = Resistance ( /km) L = Inductance (mH/km) C = Capacitance (nF/km) = 2 f Wave length =v f = wave length V = propagation velocity (velocity of light: 300 000 km/s) f = frequency units of attenuation - Neper (N), decibel (dB) and Bel (B) 1 Np = 8,686 dB 1 1 dB = 0,1151 Np = 10 Bel 1 Bel = 10 dB = 1,1513 Np
X 104
You might also like
- Transmission LinesDocument77 pagesTransmission LinesMaraMendozaNo ratings yet
- EE251 Note 2 - Sequence Impedance of Transmission LinesDocument96 pagesEE251 Note 2 - Sequence Impedance of Transmission LinesRogzJrBernzNo ratings yet
- Iphone 6s Manual User GuideDocument196 pagesIphone 6s Manual User GuideSamuel ShepherdNo ratings yet
- FE Exam Review2011Document53 pagesFE Exam Review2011Juan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Power Systems K-NotesDocument36 pagesPower Systems K-NotesAkashGaurav100% (1)
- Allen Bradley Low Voltage Switchgear and ControlgearDocument176 pagesAllen Bradley Low Voltage Switchgear and Controlgearbsunanda01No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- McCubbin, H. I., & Patterson, J. M. (1983) - The Family Stress Process. Marriage & Family Review, 6 (1-2), 7-37Document33 pagesMcCubbin, H. I., & Patterson, J. M. (1983) - The Family Stress Process. Marriage & Family Review, 6 (1-2), 7-37Gimena MottaNo ratings yet
- Consultants Guide Fire Alarm Systems PDFDocument115 pagesConsultants Guide Fire Alarm Systems PDFABELWALIDNo ratings yet
- EG 0 Power System Earthing Guide For WebsiteDocument120 pagesEG 0 Power System Earthing Guide For WebsiteKiki Tata100% (9)
- ABB Technical Guide To IEC61439 - QT11Document84 pagesABB Technical Guide To IEC61439 - QT11hahahih100% (3)
- ABB Technical Guide To IEC61439 - QT11Document84 pagesABB Technical Guide To IEC61439 - QT11hahahih100% (3)
- Navajo Hearing ProgramDocument3 pagesNavajo Hearing Programjamesmith100000% (1)
- Basler Transformer Protection Application Guide PDFDocument33 pagesBasler Transformer Protection Application Guide PDFAbrakain69No ratings yet
- S6MT 1Q w1 3 MELC1 SLM MIXTURES FinalCopy09082020Document26 pagesS6MT 1Q w1 3 MELC1 SLM MIXTURES FinalCopy09082020Rona Dindang100% (1)
- Transmission LinesDocument114 pagesTransmission LinesRad Sison LagoNo ratings yet
- ADA Design Guide 2010Document7 pagesADA Design Guide 2010Jack BarkerNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines: Electronic Systems and TechnologiesDocument73 pagesTransmission Lines: Electronic Systems and TechnologiesKier SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Sequence Impedance of Transmission LinesDocument48 pagesLecture 2 Sequence Impedance of Transmission LinesCatrina FedericoNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesFrom EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Piaggio MP3 300 Ibrido LT MY 2010 (En)Document412 pagesPiaggio MP3 300 Ibrido LT MY 2010 (En)Manualles100% (3)
- Module 3.1Document52 pagesModule 3.1JASPER PAYAPAYANo ratings yet
- Project Report On Air FilterDocument5 pagesProject Report On Air FilterEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- Metering Best Practices 2015Document106 pagesMetering Best Practices 2015sandystays100% (1)
- Lightening Protection - AssignmentDocument11 pagesLightening Protection - AssignmentNalaka SiyanthaNo ratings yet
- MV network design guide for substations and devicesDocument37 pagesMV network design guide for substations and devicesAbdourazak Abou100% (1)
- COMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsDocument24 pagesCOMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsAllan Paul Lorenzo Abando76% (17)
- Linear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandLinear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Computation of TR Line Parameters & ModellingDocument18 pagesComputation of TR Line Parameters & ModellingVibin NivasNo ratings yet
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksFrom EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Medium Voltage Technical Guide: Basics For MV Cubicle DesignDocument84 pagesMedium Voltage Technical Guide: Basics For MV Cubicle DesignVasu Devan100% (3)
- Transmission Line ParameterDocument75 pagesTransmission Line Parameteraregawi weleabezgi100% (1)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Target ListDocument9 pagesTarget ListChaitali DegavkarNo ratings yet
- Capital Cost Mining PDFDocument263 pagesCapital Cost Mining PDFsue1001No ratings yet
- Unit6 Resonance Circuit (VTU)Document23 pagesUnit6 Resonance Circuit (VTU)fanah_13100% (1)
- Ch5 Power System - Transmission Line ParametersDocument60 pagesCh5 Power System - Transmission Line Parametershafiz azman100% (3)
- Electrical Interview Questions & Answers - Hydro Power PlantDocument2 pagesElectrical Interview Questions & Answers - Hydro Power PlantLaxman Naidu NNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Power System Slide07Document89 pagesCh4 Power System Slide07hafiz azman100% (2)
- Adult Congenital Heart Disease Board ReviewDocument76 pagesAdult Congenital Heart Disease Board ReviewOQAB13No ratings yet
- Transmission Line ParametersDocument63 pagesTransmission Line Parametersmustafaayman6No ratings yet
- Electrical Fire Prevension GuideDocument34 pagesElectrical Fire Prevension GuideDhanushka RathnasooriyaNo ratings yet
- Fire Engineering PDFDocument642 pagesFire Engineering PDFABELWALIDNo ratings yet
- Task 3 - Electromagnetic Waves in Guided Media Individual WorkDocument21 pagesTask 3 - Electromagnetic Waves in Guided Media Individual WorkAndres Murcia33% (3)
- LV SWBDQualityInspectionGuideDocument72 pagesLV SWBDQualityInspectionGuiderajap2737No ratings yet
- BasicDocument10 pagesBasicAkram ElhdeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document26 pagesLecture 2Ano Ni MousNo ratings yet
- Power SystemsDocument19 pagesPower SystemsjredfrondaeeNo ratings yet
- BasicDocument2 pagesBasicsouvik5000No ratings yet
- Formula for Inductance of a CoilDocument26 pagesFormula for Inductance of a CoilByond TheuniversNo ratings yet
- Electrical Components From EMC Perspective: 2.1 ConductorsDocument27 pagesElectrical Components From EMC Perspective: 2.1 ConductorsMiguel AngelNo ratings yet
- Power SystemsDocument19 pagesPower SystemsMary Rose OleaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledJohn Matthew Taule OboNo ratings yet
- Module1 TransmissionLinesDocument7 pagesModule1 TransmissionLinesFrancis LebadesusNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetMax MartinNo ratings yet
- Parameters in The Transmission LineDocument30 pagesParameters in The Transmission LineRaju ShanNo ratings yet
- JJDocument17 pagesJJVibin NivasNo ratings yet
- Class Presentation On CH 6 Interconnect: ECE 525 Digital Integrated Circuit Design-1 Presenter Zahed Reza KhurasaniDocument27 pagesClass Presentation On CH 6 Interconnect: ECE 525 Digital Integrated Circuit Design-1 Presenter Zahed Reza KhurasaniGuru VelmathiNo ratings yet
- EnergyProject Capacity of Transmission LinesDocument2 pagesEnergyProject Capacity of Transmission LinesPKN1990No ratings yet
- Transmission Lines and NetworksDocument18 pagesTransmission Lines and NetworkszgxfsbjbnNo ratings yet
- EE525 Power Analysis and Design Lecture 1Document74 pagesEE525 Power Analysis and Design Lecture 1Fremon RamosNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity DoneDocument36 pagesCurrent Electricity DonewhyreadNo ratings yet
- f - But the line reactance ωL increasesDocument20 pagesf - But the line reactance ωL increasesseelan9No ratings yet
- Part BDocument9 pagesPart Bsramalingam288953No ratings yet
- Notes 4 - Series Line Parameters R XL PDFDocument47 pagesNotes 4 - Series Line Parameters R XL PDFCristele Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lec.4 (Prameters of OHTL Pt.1)Document9 pagesLec.4 (Prameters of OHTL Pt.1)AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Hand Book Formulas Communication TeliDocument3 pagesHand Book Formulas Communication TeliJet'sNo ratings yet
- BLOCK II: Reasons of EMI: Division For Electricity and Lightning Research Uppsala UniversityDocument34 pagesBLOCK II: Reasons of EMI: Division For Electricity and Lightning Research Uppsala UniversityArnulfo SuarezNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of TLDocument18 pagesFundamentals of TLYazid AbouchihabeddineNo ratings yet
- Electrical Characteristics of Underground CablesDocument55 pagesElectrical Characteristics of Underground CablesAhmed SeddikNo ratings yet
- Underground Cable 2Document39 pagesUnderground Cable 2Ranajoy BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Physics Experiment 01 (Ohm's Law) - 2Document2 pagesPhysics Experiment 01 (Ohm's Law) - 2yubraj sethNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDocument0 pagesElectrical Engineering FormulasPULKITJOSHI100% (1)
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDocument4 pagesElectrical Engineering FormulasVinod MuruganNo ratings yet
- 24 WiresDocument38 pages24 WiresGokul KuthatiNo ratings yet
- Basics of Microwave MeasurementsDocument18 pagesBasics of Microwave MeasurementsPrashanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Midterm1 2afgkmnbv FormulasDocument1 pageMidterm1 2afgkmnbv FormulasManny LemosNo ratings yet
- Microwave Networks: DR L.Anjaneyulu NIT, WarangalDocument79 pagesMicrowave Networks: DR L.Anjaneyulu NIT, Warangalnaveenchennuri_iasNo ratings yet
- C 3Document47 pagesC 3Saurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- ABB Cabling SystemsDocument36 pagesABB Cabling SystemsABELWALIDNo ratings yet
- ABB Cabling SystemsDocument36 pagesABB Cabling SystemsABELWALIDNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Electrical Measurements in Low Voltage SwitchboardsDocument72 pagesPractical Guide To Electrical Measurements in Low Voltage SwitchboardssibilavaneNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Electrical Measurements in Low Voltage SwitchboardsDocument72 pagesPractical Guide To Electrical Measurements in Low Voltage SwitchboardssibilavaneNo ratings yet
- 2016 Electrical Standards Products Guide PDFDocument93 pages2016 Electrical Standards Products Guide PDFABELWALIDNo ratings yet
- Designing A Metering System For Buildings PDFDocument60 pagesDesigning A Metering System For Buildings PDFABELWALIDNo ratings yet
- Copie de Tarif - ABB - KAUFEL - 2019 - 02 - v3Document207 pagesCopie de Tarif - ABB - KAUFEL - 2019 - 02 - v3ABELWALIDNo ratings yet
- Pub 119 Earthing PracticeDocument108 pagesPub 119 Earthing Practicecosmin75No ratings yet
- A Practical Guide To Earth Resistance TestingDocument41 pagesA Practical Guide To Earth Resistance Testingcabrito_lightNo ratings yet
- cc2715 Lighting Solutions 2015 11technical and Index Emergency Lighting Design Guide PDFDocument9 pagescc2715 Lighting Solutions 2015 11technical and Index Emergency Lighting Design Guide PDFABELWALIDNo ratings yet
- cc2715 Lighting Solutions 2015 11technical and Index Lighting Design Guide PDFDocument2 pagescc2715 Lighting Solutions 2015 11technical and Index Lighting Design Guide PDFABELWALIDNo ratings yet
- 054604g0 Op Ackermann Katalog PDFDocument128 pages054604g0 Op Ackermann Katalog PDFABELWALIDNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Current List PDFDocument9 pagesGuidelines Current List PDFABELWALIDNo ratings yet
- Hospital Product Application GuideDocument49 pagesHospital Product Application GuidepavloneNo ratings yet
- Motor ClasstyDocument128 pagesMotor Classtywatep_08No ratings yet
- cc2715 Lighting Solutions 2015 11technical and Index Emergency Lighting Design Guide PDFDocument9 pagescc2715 Lighting Solutions 2015 11technical and Index Emergency Lighting Design Guide PDFABELWALIDNo ratings yet
- cc2715 Lighting Solutions 2015 11technical and Index Lighting Design Guide PDFDocument2 pagescc2715 Lighting Solutions 2015 11technical and Index Lighting Design Guide PDFABELWALIDNo ratings yet
- Jamec Air FittingsDocument18 pagesJamec Air Fittingsgoeez1No ratings yet
- Oxihalide AcisDocument8 pagesOxihalide AcisDina Ikrama PutriNo ratings yet
- Mola SubseaDocument10 pagesMola Subseashahbaz akramNo ratings yet
- Cswip Visual Welding Inspector 3.0 BrochureDocument1 pageCswip Visual Welding Inspector 3.0 BrochureNasfauzan100% (2)
- Group 17-Solid State NMR - Questions-AnswersDocument5 pagesGroup 17-Solid State NMR - Questions-AnswersOmkar AkulwarNo ratings yet
- 2005-05-12Document18 pages2005-05-12The University Daily KansanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Philippine Disaster Risk Reduction and Management SystemDocument11 pagesLesson 8 - Philippine Disaster Risk Reduction and Management SystemMary Joy CuetoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 Quarter 1 - Module 10: Through The SlateDocument10 pagesPractical Research 1 Quarter 1 - Module 10: Through The SlateMark Allen Labasan100% (1)
- Rise School of Accountancy Test 08Document5 pagesRise School of Accountancy Test 08iamneonkingNo ratings yet
- Product GuideDocument13 pagesProduct Guidekhalid mostafaNo ratings yet
- Baileys in 2009: Case Study Reference No 509-050-1Document17 pagesBaileys in 2009: Case Study Reference No 509-050-1Ernesto KulasinNo ratings yet
- PhilLife claims process ECQDocument18 pagesPhilLife claims process ECQNoel EboniaNo ratings yet
- Ulcus Decubitus PDFDocument9 pagesUlcus Decubitus PDFIrvan FathurohmanNo ratings yet
- 21 - Effective Pages: Beechcraft CorporationDocument166 pages21 - Effective Pages: Beechcraft CorporationCristian PugaNo ratings yet
- 2022 TESAS PublicationDocument103 pages2022 TESAS PublicationNathan LakaNo ratings yet
- SEXUALABUSEDocument12 pagesSEXUALABUSERyoman EchozenNo ratings yet
- Catálogo SEDIVERDocument32 pagesCatálogo SEDIVEREnver Rojas DiazNo ratings yet
- Adolescent and Sexual HealthDocument36 pagesAdolescent and Sexual Healthqwerty123No ratings yet
- Jaimin PatelDocument3 pagesJaimin PatelSanjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Kootenay Lake Pennywise October 17, 2017Document40 pagesKootenay Lake Pennywise October 17, 2017Pennywise PublishingNo ratings yet