Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group 5 Manzanam Insurance
Uploaded by
anant_jain88114Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group 5 Manzanam Insurance
Uploaded by
anant_jain88114Copyright:
Available Formats
Manzana Insurance Case Analysis Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore October 7, 2010 In Submitted to: Professor Haritha Saranga
on Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for Operations Management Course By: Jayaprasad V (1011243) Jagadeesh Y (1011242) Nirmal Preethi G (1011257) Pava n Jayanti (1011261) Sameer Thombare (1011276) Vijay K (1011292)
Contents Problem Definition: ............................................................ ........................................................... 3 Factors Affecting the Performance: ............................................................... ................................ 3 Process Flow & Capacity Analysis:............ ................................................................................ ...... 4 Turn Around Time: ..................................................... ................................................................ 4 Capacity Util ization: ....................................................................... ............................................ 4 Recommendations:................. ................................................................................ ....................... 5 APPENDIX ............................................. ................................................................................ ......... 6 Exhibit 1- Work flow process ....................................... ............................................................... 6 Exhibit 2 Operat ing Activities ................................................................. ................................. 6 Exhibit 3- Turnaround Time.................. ................................................................................ ...... 7 Exhibit 4 : Capacity Utilization of Underwriting teams ................ ................................................ 7 Exhibit 5: Capacity utilisati on ............................................................................. ........................ 9 Exhibit 6: Expected profit from Renewal policies..... ................................................................. 10
Problem Definition: The case talks about the inefficiencies in operations at Fruitvale branch of Man zana Insurance Company. Major concerns are: 1) High and increasing Turn-Around T ime (TAT) - Total time required to completely process the insurance request comp ared to its competitor, Golden Gate. Golden Gate has recently announced TAT of o ne day, which can add serious competition-resulting in increasing renewal loss r ate (47%) and late renewals (44%). 2) Declining profitability- the branch report ed a loss of $174,000 and $121,000 during the first quarters of 1991. 3) Backlog of policies. 4) Improper work load balancing among employees resulting in tight er schedules and idle times. Factors Affecting the Performance: As stated in the problem statement, the inefficiencies of the organization resul ts in an increased TAT. We shall now look at the factors increasing TAT. 1. Prio ritizing: Though the company s policy was to use FIFO system at each stage of the un derwriting process, RUNs and RAPs are given more priority over RAINs and RERUNs. This is because of the new policies are the most profitable ones and also the g eneral perception that customers will anyway renew their policies. Also the comp any s compensation policy is to pay incentive payment for new policies written. In c ase of RUNs, agents receive 25% commission where as in case of RERUNs, they rece ive only 7%. Hence, for both the agents and employees emphasis is on following f or new requests. This results in increased backlog of RERUNs and sending notice to agents in last day. 2. Underutilization: The capacity utilization calculation shown in exhibit 2 is below 80% for rating and policy writers. The reason for t he same can be increased waiting time and uneven pattern of loads given by utili zation team. The capacity calculations of the underwriting teams in Exhibit 4 sh ow that there is a level of uneven load distribution among the teams. The team 1 has a high level of utilization at around 97%, while teams 2 & 3 have utilizati ons of around 78% and 70% respectively. So there will be situations where one te am is completely loaded while the other teams may not have that much of work to do. Hence we can say that the strategy being followed by the company in allocati ng different territories for different teams might not be the correct strategy f or the company in its present condition to follow.
3. Loss of Renewals: According to the data given, over the last quarters, the co mpany has some 44% of renewals processed late and 47% of renewals lost. When com pany gives very short notice for RERUNs to agents, they tend to recommend other insurance agencies to clients. The inability of the company to provide timely pr ocessing of RERUNs is causing the loss of a large volume of valuable customer ba se, thus reducing its revenue and hence the profitability. 4. Very low conversio n of RAPs to RUNs: Though the conversion rate of RAP to RUN is only 15%, it had been given a high preference, next only to RUN and also they take up a significa nt time for processing. But, then considering the conversion percentage, this pr iority doesn t sound valid. Process Flow & Capacity Analysis: Now that we have seen where Fruitvale branch is going wrong, let us analyse how much impact it has on their operations. Turn Around Time: Turn-Around Time (TAT) is the total time required for complete processing of one policy. According to the case, TAT is calculated and found to be 8.2 days. Howe ver, there is couple of flaws in the method used to calculate TAT: 1. The mean t ime for processing should be considered for the calculations instead of the 95% SCT (Standard Completion Time). Mean process time provided already accounts for time required for non-productive work. 2. Once the process reach a steady state, the TAT will not be addition of through put time of all 4 processes as the proc esses will run parallel, reducing the overall TAT. Moreover, it will also depend on the individual loads of UT teams 1,2 & 3. Hence, considering above flaw, the revised TAT is 4.7 days which is still higher than Golden Gate. Exhibit 3 shows the new calculated TAT considering the mean time for each process. Also by Litt le s law Throughput time= Work in progress/Throughput rate= 82/40 = 2(Approx). Our c alculated time is very high compared to this, maybe due to above stated reasons. Capacity Utilization: The request for insurance is processed through 4 steps. As the time required for each step for each kind of request is different, we need to calculate capacity utilization for each step individually and compare the capacity utilization of e ach step to arrive at the bottleneck.
To calculate capacity utilization, we need to calculate the total processing tim e utilized by each of the function. From the process description, we know that t he RAP does not require going through Policy Writing Process. Only, those RAPs w hich are converted into RUNs will need Policy writing. Hence, only RUN, RERUN, R AIN and converted RUN. The capacity utilization analysis (Exhibit 5) shows that the underwriting is the bottleneck process as the UT Team 1 is fully utilized. T he underwriting team is also affected by the regionalization. The Exhibit 4 show s that the team 1 was overburdened where as the team 2 and team 3 were seating i dle for quiet a sometime. Hence, the overall operations at the Fruitvale branch of Manzana Insurance are not properly designed and need restructuring. We shall see the recommendations required to be improve the situation at Fruitvale. Recommendations: 1. The RERUNs should be given equal priority. They should be processed as they c ome. In effect, FCFS (First Come First Served) should be implemented for all req uests. 2. TAT (Turnaround time) can be improved by balancing the workload of the three underwriting teams by pooling the teams together and diving the work as w hen they come. This will reduce the waiting time and will ensure proper load to rating and policy writing. 3. The commission structure of agents needs changes. Since the renewals are quite profitable for the company, the commission for rene wals can be revised upwards. Model showing additional profits to company by incr easing commission is given in exhibit 5. 4. The compensation structure for the e mployees needs to be reviewed. Salary must include variable pay for reduction in processing time and performing in par with other market leaders in efficiency. 5. The processing time given in case is based on late 1980s data. However with t he usage of computers and the routine work performed, the processing time can be reduced further. 6. By observing the nature of the rating and policy writing jo bs, the underutilization of distribution clerks, we found that it will be econom ic to train employees to handle the whole range of jobs so that in case of overl oading of the staff with RAP requests, policy writers can help distribution cler ks and raters.
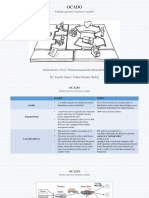
APPENDIX Exhibit 1- Work flow process Exhibit 2 Operating Activities Review and Distribution Arrival Rate Average time per Request (min.) Total time Required (hrs) Personnel available Capacity available (hrs @ 7.5 hrs/day) Capaci ty Utilization 40 40 26.67 4 30.00 88.9% Underwriting 40 30 20.00 3 22.50 88.9% Rating 40 70 46.67 8 60.00 77.78% Policy Writing 40 55 27.50 5 37.50 73.33%
Exhibit 3- Turnaround Time Workers/ Teams Total Throughput time(Days) Operating Steps Number of requests Mean Time Distribution Total time taken Numbe r of requests Mean Time Underwriting Total time taken Number of requests Mean Ti me Rating Total time taken Number of requests Policy Writing Mean Time Total tim e taken RUNs RAPs 1 68.5 68.5 4 43.6 174. 4 5 75.5 377. 5 5 71 355 3 50 150 10 38 380 12 64.7 776. 4 0 NA NA RAINs 1 43.5 43.5 7 22.6 158.2 8 65.5 524 9 54 486 RERUNs 11 28 308 47 18.7 878.9 54 75.5 4077 56 50.1 2805.6 4 0.32 3 1.18 8 1.60 5 1.62 Total TAT days 4.72 Exhibit 4 : Capacity Utilization of Underwriting teams Underwriting Team 1 RUNs Territory 1 Mean time Total time 162 43.6 7063.2 RAPs 7 61 38 28918 RAINs 196 22.6 4429.6 RERUNs 636 18.7 11893.2 52304 29.80 14.63 Tota l 1755 Average Processing Time per request Total Requests per day
Average Time utilized per day Capacity Utilization (total of 450 mins-7.5*60) Un derwriting Team 2 RUNs Territory 1 Mean Time Total time 100 43.6 4360 RAPs 513 3 8 19494 RAINs 125 22.6 2825 RERUNs 840 18.7 15708 435.87 96.86% Total 1578 42387 26.86 13.15 353.23 78.49% Average Processing Time per request Total Requests per day Average Time utilized per day Capacity Utilization (total of 450 mins-7.5*60) Underwriting Team 3 RUNs Territory 1 Mean Time Total time 88 43.6 3836.8 RAPs 52 4 38 19912 RAINs 130 22.6 2938 RERUNs 605 18.7 11313.5 38000.3 28.21 11.23 316.6 7 70.37% Total 1347 Average Processing Time per request Total Requests per day Average Time utilized per day Capacity Utilization (total of 450 mins-7.5*60)
Exhibit 5: Capacity utilisation Percentage of RAPs in policies = 1798/4680 = 38.42% Percentage of RAPs not conve rted to RUNs = 1524/1798 = 84.76% Percentage of policies not processed by Policy Writers = 0.3842*0.8476 = 32.56% Demand for the first three stages = 22 +17 =39 policies/day Demand for the last stage = 0.6744*39 = 26.3 policies/day Capacity Utilization of a stage = Demand for the stage / Capacity Process Flow Analysis: Stage DC Average Processing Time 41 29.80 UT 26.86 28.21 R PW 70.4 54.8 Capacit y 43.90 15.10 16.75 15.95 51.14 41.06 Capacity Utilization (%) 88.83 96.98 78.49 70.37 76.27 63.97 DC: Distribution Clerk UT: Underwriting Team R: Raters PW: policy Writers
Exhibit 6: Expected profit from Renewal policies 1990 1st qtr Renewal loss Renewal premium lost Commission Expenses at 15% Expect ed Profit 400 2252 169 2083 2nd qtr 414 2331 175 2156 3rd qtr 436 2455 184 2271 4th qtr 467 2629 197 2432 1st qtr 429 2415 181 2234 1991 2nd qtr 497 2798 210 25 88 * Expected profit and commission expense calculated considering 50% additional c onversion of renewal premium lost
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- CSR Report 5 - Shaina ShriambDocument3 pagesCSR Report 5 - Shaina Shriambanant_jain88114No ratings yet
- Dabur CSRDocument22 pagesDabur CSRanant_jain88114No ratings yet
- Practice Questions 2012-13Document2 pagesPractice Questions 2012-13anant_jain88114No ratings yet
- Practice Questions 2012-13Document2 pagesPractice Questions 2012-13anant_jain88114No ratings yet
- Culture UAEDocument12 pagesCulture UAEanant_jain88114No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- DoD Risk MGT Guide v7 Interim Dec2014Document100 pagesDoD Risk MGT Guide v7 Interim Dec2014Bre TroNo ratings yet
- List SponsorDocument11 pagesList SponsoregieprajaNo ratings yet
- TOURIST VISA CHECKLIST (Sweden)Document1 pageTOURIST VISA CHECKLIST (Sweden)bhushan kumar100% (1)
- Kinvey How To Make An Android App PDFDocument29 pagesKinvey How To Make An Android App PDFEr Ritika RitiNo ratings yet
- Bidder's Checklist of Requirements For Its Bid, Technical ProposalsDocument2 pagesBidder's Checklist of Requirements For Its Bid, Technical ProposalsJoseph Santos GacayanNo ratings yet
- SalesInvoiceImport 02 MARET 2023Document6 pagesSalesInvoiceImport 02 MARET 2023Fakta IdNo ratings yet
- Invoice - Amazon PDFDocument2 pagesInvoice - Amazon PDFRohan DesaiNo ratings yet
- Rewards of EntrepreneurshipDocument18 pagesRewards of EntrepreneurshipHemanidhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- British Airways PLC (BA) Is TheDocument47 pagesBritish Airways PLC (BA) Is ThePrasath KrishnarajaNo ratings yet
- CSR of GoogleDocument28 pagesCSR of GooglePooja Sahani100% (1)
- How To Start A Gold Refining Business - EHowDocument6 pagesHow To Start A Gold Refining Business - EHowJack Rose100% (1)
- Ra List Report Updatedupto17dec2021Document227 pagesRa List Report Updatedupto17dec2021Geetha KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice/ReceiptDocument1 pageTax Invoice/ReceiptRikhil NairNo ratings yet
- BASIC ECONOMICS CompilationDocument65 pagesBASIC ECONOMICS CompilationJabby SultanNo ratings yet
- Wa0010.Document7 pagesWa0010.nitish.thukralNo ratings yet
- LSB Building, Rizal St. Legazpi CityDocument5 pagesLSB Building, Rizal St. Legazpi Cityhey heyNo ratings yet
- Mergers & AqcusitionDocument34 pagesMergers & AqcusitionDeepaNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument18 pagesBusiness Plandua maqsoodNo ratings yet
- History of Foreign Exchange RatesDocument2 pagesHistory of Foreign Exchange RatesDustin PlaasNo ratings yet
- Pampanga PB ValisesDocument20 pagesPampanga PB Valisesallyssa monica duNo ratings yet
- MGT 111 - Module 1Document2 pagesMGT 111 - Module 1Super Man of SteelNo ratings yet
- A Tale of Two Electronic Components DistributorsDocument2 pagesA Tale of Two Electronic Components DistributorsAqsa100% (1)
- Logistics Distribution TescoDocument10 pagesLogistics Distribution TescoSanchit GuptaNo ratings yet
- New Audit Report Format Including CARO 2016Document8 pagesNew Audit Report Format Including CARO 2016CA Shivang SoniNo ratings yet
- Curriculum - Application (Solution) Consultant SAP SCM - SAP ERP - Order Fulfillment (Sales Order Management)Document3 pagesCurriculum - Application (Solution) Consultant SAP SCM - SAP ERP - Order Fulfillment (Sales Order Management)fiestamixNo ratings yet
- Case 1: Komatsu NotesDocument4 pagesCase 1: Komatsu NotesCindy WangNo ratings yet
- A Five Step Guide To Budget DevelopmentDocument15 pagesA Five Step Guide To Budget DevelopmentGhassanNo ratings yet
- Magazine Still Holds True With Its Mission Statement-Dedicated To The Growth of TheDocument5 pagesMagazine Still Holds True With Its Mission Statement-Dedicated To The Growth of TheRush YuviencoNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Embedded DerivativesDocument22 pagesAccounting For Embedded Derivativeslwilliams144No ratings yet
- Cta Eb CV 01054 D 2015jan13 AssDocument18 pagesCta Eb CV 01054 D 2015jan13 AssMarcy BaklushNo ratings yet