Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Interview Questions Linux
Uploaded by
log4jpOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Interview Questions Linux
Uploaded by
log4jpCopyright:
Available Formats
Interview Questions : Unix/Linux : Part-1
1: What is a shell? Shell is a interface between user and the kernel. Even though there can be only one kernel ; a system can have many shell running simultaneously . Whenever a user enters a command through keyboard the shell communicates with the kernel to execute it and then display the output to the user. 2: What are the different types of commonly used shells on a typical linux system? csh,ksh,bash,Bourne . The most commonly used and advanced shell used today is Bash .
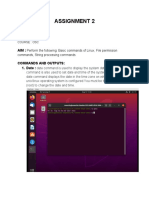
3:What is the equivalent of a file shortcut that we have on window on a Linux system? Shortcuts are created using links on Linux. There are two types of links that can be used namely soft link and hard link 4:What is the difference between soft and hard links? Soft links are link to the file name and can reside on different filesytem as well; however hard links are link to the inode of the file and has to be on the same filesytem as that of the file. Deleting the orginal file makes the soft link inactive (broken link) but does not affect the hard link (Hard link will still access a copy of the file) 5: How will you pass and access arguments to a script in Linux? Arguments can be passed as: scriptName Arg1 Arg2.Argn and can be accessed inside the script as $1 , $2 .. $n 6: What is the significance of $#? $# shows the count of the arguments passed to the script. 7: What is the difference between $* and $@? $@ treats each quoted arguments as separate arguments but $* will consider the entire set of positional parameters as a single string. 8: Use sed command to replace the content of the file (emulate tac command) Eg: if cat file1 ABCD EFGH Then O/p should be EFGH ABCD sed '1! G; h;$!d' file1 Here G command appends to the pattern space, h command copies pattern buffer to hold buffer and d command deletes the current pattern space. 9: Given a file, replace all occurrence of word ABC with DEF from 5th line till end in only those lines that contains word MNO
sed n 5,$p file1|sed /MNO/s/ABC/DEF/ 10: Given a file , write a command sequence to find the count of each word. tr s (backslash)040 <file1|tr s (backslash)011|tr (backslash)040 (backslash)011 (backslash)012 |uniq c where (backslash)040 is octal equivalent of space (backslash)011 is octal equivalent of tab character and (backslash)012 is octal equivalent of newline character. 11: How will you find the 99th line of a file using only tail and head command? tail +99 file1|head -1 12: Print the 10th line without using tail and head command. sed n 10p file1 13:In my bash shell I want my prompt to be of format $Present working directory:hostname> and load a file containing a list of user defined functions as soon as I login , how will you automate this? In bash shell we can create .profile file which automatically gets invoked as soon as I login and write the following syntax into it. export PS1=$ `pwd`:`hostname`> .File1 Here File1 is the file containing the user defined functions and . invokes this file in current shell. 14: Explain about s permission bit in a file? s bit is called set user id (SUID) bit. s bit on a file causes the process to have the privileges of the owner of the file during the instance of the program. Eg: Executing passwd command to change current password causes the user to writes its new password to shadow file even though it has root as its owner. 15: I want to create a directory such that anyone in the group can create a file and access any persons file in it but none should be able to delete a file other than the one created by himself. We can create the directory giving read and execute access to everyone in the group and setting its sticky bit t on as follows: mkdir direc1 chmod g+wx direc1 chmod +t direc1 16: How can you find out how long the system has been running? Command uptime 17: How can any user find out all information about a specific user like his default shell, real life name, default directory,when and how long he has been using the sytem? finger loginName where loginName is the login name of the user whose information is expected. 18: What is the difference between $$ and $!? $$ gives the process id of the currently executing process whereas $! shows the process id of the process that recently went into background.
19: What are zombie processes? These are the processes which have died but whose exit status is still not picked by the parent process. These processes even if not functional still have its process id entry in the process table. 20: How will you copy file from one machine to other? We can use utilities like ftp ,scp or rsync to copy file from one machine to other. Eg: Using ftp: ftp hostname >put file1 >bye Above copies file file1 from local system to destination system whose hostname is specified. 21: I want to monitor a continuously updating log file, what command can be used to most efficiently achieve this? We can use tail f filename . This will cause only the default last 10 lines to be displayed on std o/p which continuously shows the updating part of the file. 22: I want to connect to a remote server and execute some commands, how can I achieve this? We can use telnet to do this: telnet hostname l user >Enter password >Write the command to execute >quit 23: I have 2 files and I want to print the records which are common to both. We can use comm command as follows: comm -12 file1 file2 12 will suppress the content which are unique to 1st and 2nd file respectively. 24: Write a script to print the first 10 elemenst of Fibonacci series. #!/bin/sh a=1 b=1 echo $a echo $b for I in 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 do c=a b=$a b=$(($a+$c)) echo $b done 25: How will you connect to a database server from linux? We can use isql utility that comes with open client driver as follows: isql S serverName U username P password
Interview Questions : Linux/Unix : Part-2
1: What are the 3 standard streams in Linux? Output stream , represented as 0 , Input stream, represented as 1 and Error stream represented as 2. 2: I want to read all input to the command from file1 direct all output to file2 and error to file 3, how can I achieve this? command <file1 0>file2 2>file3
3: What will happen to my current process when I execute a command using exec? exec overlays the newly forked process on the current process ; so when I execute the command using exec a new process corresponding to the command will be created and the current process will die. Eg: Executing exec com1 on command prompt will execute com1 and return to login prompt since my logged in shell is superimposed with the new process of the command . 4: How will you emulate wc l using awk? awk END {print NR} fileName 5: Given a file find the count of lines containing word ABC. grep c ABC file1 6: What is the difference between grep and egrep? egrep is Extended grep that supports added grep features like + (1 or more occurrence of previous character),?(0 or 1 occurrence of previous character) and | (alternate matching) 7: How will you print the login names of all users on a system? /etc/shadow file has all the users listed. awk F : {print $1} /etc/shadow|uniq -u 8: How to set an array in Linux? Syntax in ksh: Set A arrayname= (element1 element2 .. element) In bash A=(element1 element2 element3 . elementn) 9: Write down the syntax of for loop Syntax: for iterator in (elements) do execute commands done 10:How will you find the total disk space used by a specific user? du -s /home/user1 .where user1 is the user for whom the total disk space needs to be found.
11: Write the syntax for if conditionals in linux? Syntax If condition is successful then execute commands else execute commands fi 12:What is the significance of $? ? $? gives the exit status of the last command that was executed. 13: How do we delete all blank lines in a file? sed ^ [(backslash)011(backslash)040]*$/d file1 where (backslash)011 is octal equivalent of space and (backslash)040 is octal equivalent of tab 14: How will I insert a line ABCDEF at every 100th line of a file? sed 100i\ABCDEF file1 15: Write a command sequence to find all the files modified in less than 2 days and print the record count of each. find . mtime -2 exec wc l {} \; 16: How can I set the default rwx permission to all users on every file which is created in the current shell? We can use: umask 777 This will set default rwx permission for every file which is created to every user. 17: How can we find the process name from its process id? We can use ps p ProcessId 18: What are the four fundamental components of every file system on linux? bootblock, super block, inode block and datablock 19: What is a boot block? This block contains a small program called Master Boot record(MBR) which loads the kernel during system boot up. 20: What is a super block? Super block contains all the information about the file system like size of file system, block size used by it,number of free data blocks and list of free inodes and data blocks. 21: What is an inode block?
This block contains the inode for every file of the file system along with all the file attributes except its name. 22: How can I send a mail with a compressed file as an attachment? zip file1.zip file1|mailx s subject Recepients email id Email content EOF 23: How do we create command aliases in shell? alias Aliasname=Command whose alias is to be created 24: What are c and b permission fields of a file? c and b permission fields are generally associated with a device file. It specifies whether a file is a character special file or a block special file. 25: What is the use of a shebang line? Shebang line at top of each script determines the location of the engine which is to be used in order to execute the script.
1) What is UNIX? It is a portable operating system that is designed for both efficient multi-tasking and mult-user functions. Its portability allows it to run on different hardware platforms. It was written is C and lets user do processing and control under a shell. 2) What are filters? The term Filter is often used to refer to any program that can take input from standard input, perform some operation on that input, and write the results to standard output. A Filter is also any program that can be used between two other programs in a pipeline.
3) What is a typical syntax being followed when issuing commands in shell? Typical command syntax under the UNIX shell follows the format: Command [-argument] [-argument] [--argument] [file] 4) Is there a way to erase all files in the current directory, including all its sub-directories, using only one command? Yes, that is possible. Use rm r * for this purpose. The rm command is for deleting files. The r option will erase directories and subdirectories, including files within. The asterisk represents all entries. 5) What is the chief difference between the v and x option s to set? The v option echoes each command before arguments and variables have been substituted for; the x option echoes the commands after substitution has taken place. 6) What is Kernel?
Kernel is the UNIX operating system. It is the master program that controls the computers resources, allotting them to different users and to different tasks. However, the kernel doesnt deal directly with a user. Instead, it starts up a separate, interactive program, called a shell, for each user when he/she logs on. 7) What is Shell? A shell acts as an interface between the user and the system. As a command interpreter, the shell takes commands and sets them up for execution. 8 ) What are the key features of the Korn Shell? - history mechanism with built-in editor that simulates emacs or vi - built-in integer arithmetic - string manipulation capabilities - command aliasing - arrays - job control 9) What are some common shells and what are their indicators? sh Bourne shell csh C SHell bash Bourne Again Shell tcsh enhanced C Shell zsh Z SHell ksh Korn SHell 10) Differentiate multiuser from multitask. Multiuser means that more than one person can use the computer at the same time. Multitask means that even a single user can have the computer work on more than one task or program at the same time. 11) What is command substitution? Command substitution is one of the steps being performed every time commands are processed by the shell. Commands that are enclosed in backquotes are executed by the shell. This will then replace the standard output of the command and displayed on the command line. 12) What is a directory? Every file is assigned to a directory. A directory is a specialized form of file that maintains a list of all files in it. 13) What is inode? An inode is an entry created on a section of the disk set aside for a file system. The inode contains nearly all there is to know about a file, which includes the location on the disk where the file starts, the size of the file, when the file was last used, when the file was last changed, what the various read, write and execute permissions are, who owns the file, and other information.
14) You have a file called tonky in the directory honky. Later you add new material to tonky. What changes take place in the directory, inode, and file? The directory entry is unchanged, since the name and inode number remain unchanged. In the inode file, the file size, time of last access, and time of last modification are updated. In the file itself, the new material is added. 15) Describe file systems in UNIX Understanding file systems in UNIX has to do with knowing how files and inodes are stored on a system. What happens is that a disk or portion of a disk is set aside to store files and the inode entries. The entire functional unit is referred to as a file system. 16) Differentiate relative path from absolute path. Relative path refers to the path relative to the current path. Absolute path, on the other hand, refers to the exact path as referenced from the root directory. 17) Explain the importance of directories in a UNIX system Files in a directory can actually be a directory itself; it would be called a subdirectory of the original. This capability makes it possible to develop a tree-like structure of directories and files, which is crucial in maintaining an organizational scheme. 18) Briefly describe the Shells responsibilities - program execution - variable and file name substitution - I/O redirection - pipeline hookup - environment control - interpreted programming language 19) What are shell variables? Shell variables are a combination of a name ( identifier), and an assigned value, which exist within the shell. These variables may have default values, or whose values can be manually set using the appropriate assignment command. Examples of shell variable are PATH, TERM and HOME. 20) What are the differences among a system call, a library function, and a UNIX command? A system call is part of the programming for the kernel. A library function is a program that is not part of the kernel but which is available to users of the system. UNIX commands, however, are stand-alone programs; they may incorporate both system calls and library functions in their programming. 21) What is Bash Shell? It is a free shell designed to work on the UNIX system. Being the default shell for most UNIX-based systems, it combines features that are available both in the C and Korn Shell. 22) Enumerate some of the most commonly used network commands in UNIX - telnet used for remote login - ping an echo request for testing connectivity
- su user switching command - ftp file transfer protocol used for copying files - finger information gathering command 23) Differentiate cmp command from diff command. The cmp command is used mainly to compare two files byte by byte, after which the first encountered mismatch is shown. On the other hand, the diff command is used to indicate the changes that is to be made in order to make the two files identical to each other. 24) What is the use of -l when listing a directory? -l, which is normally used in listing command like ls, is used to show files in a long format, one file per line. Long format refers to additional information that is associated with the file, such as ownership, permissions, data and filesize.
Interview Questions : Linux/Unix : Part - 4
1) What is piping? Piping, represented by the pipe character |, is used to combine two or more commands together. The output of the first command serves as input the next command, and so on. 2) What is a superuser? A superuser is a special type user who has open access to all files and commands on a system. Note that the superusers login is usually root, and is protected by a so-called root password.
3) How do you determine and set the path in UNIX? Each time you enter a command, a variable named PATH or path will define in which directory the shell will search for that command. In cases wherein an error message was returned, the reason maybe that the command was not in your path, or that the command itself does not exist. You can also manually set the path using the set path = [directory path] command. 4) Is it possible to see information about a process while it is being executed? Every process is uniquely identified by a process identifier. It is possible to view details and status regarding a process by using the ps command. 5) What is the standard convention being followed when naming files in UNIX? One important rule when naming files is that characters that have special meaning are not allowed, such as * / & and %. A directory, being a special type of file, follows the same naming convention as that of files. Letters and numbers are used, along with characters like underscore and dot characters. 6) Why is it that it is not advisable to use root as the default login? The root account is very important, and with abusive usage, can easily lead to system damage. Thats because safeguards that normally apply to user accounts are not applicable to the root account.
7) What is the use of the tee command? The tee command does two things: one is to get data from the standard input and send it to standard output; the second is that it redirects a copy of that input data into a file that was specified. 8) Differentiate cat command from more command. When using the cat command to display file contents, large data that does not fit on the screen would scroll off without pausing, therefore making it difficult to view. On the other hand, using the more command is more appropriate in such cases because it will display file contents one screen page at a time. 9) What is parsing? Parsing is the process of breaking up of a command line into words. This is made possible by using delimiters and spaces. In the event that tabs or multiple spaces are part of the command, these are eventually replaced by a single space. 10) What is pid? Pid is short for Process ID. It is used primarily to identify every process that runs on the UNIX system, whether it runs on the foreground or runs at the background. Every pid is considered unique. 11) How does the system know where one command ends and another begins? Normally, the newline character, which is generated by the ENTER or RETURN key, acts as the signpost. However, the semicolon and the ampersand characters can also serve as command terminators. 12) What is wild-card interpretation? When a command line contains wild-card characters such as * or ?, these are replaced by the shell with a sorted list of files whose pattern matches the input command. Wild-card characters are used to setup a list of files for processing, instead of having it specified one at a time. 13) What is the output of this command? $who | sort logfile > newfile In this command, the output from the command who becomes the input to the sort command. At the same time, sort opens logfile, arranges it together with the output from the command who, and places the final sorted output to the file newfile. 14) How do you switch from any user type to a super user type? In order to switch from any user type to a superuser, you use the su command. However, you will be asked to key in the correct superuser password before full access privileges are granted to you. 15) What would be the effect of changing the value of PATH to: .:/usr/della/bin: /bin: /usr/bin This would cause the shell to look in the /usr/della/bin directory after looking in the current directory and before looking in the /bin directory when searching for a command file. 16) Write a command that will display files in the current directory, in a colored, long format.
Answer: ls -l color 17) Write a command that will find all text files in a directory such that it does not contain the word amazing in any form (that is, it must include the words Amazing, AMAZING, or aMAZINg) Answer: grep vi amazing *.txt 18) Write a command that will output the sorted contents of a file named IN.TXT and place the output in another file named OUT.TXT, while at the same time excluding duplicate entries. Answer: sort IN.TXT | uniq > OUT.TXT 19) Write a command that will allow a UNIX system to shut down in 15 minutes, after which it will perform a reboot. Answer: /sbin/shutdown r +10 20) What command will change your prompt to MYPROMPT: ? To change a prompt, we use the PS1 command, such as this: PS1 = MYPROMPT: 21) What does this command do? cat food 1 > kitty Answer: it redirects the output of cat food into the file kitty; the command is the same as: cat food > kitty 22) What is wrong with this interactive shell script? echo What month is this? read $month echo $month is as good a month as any. Answer: Initially, the question mark should be escaped (\?) so that it is not interpreted as a shell metacharacter. Second, it should be read month, not read $month. 23) Write a shell script that requests the users age and then echoes it, along with some suitable comment. Answer: echo Hello! What\s your age\? read age echo $age! I\ll be obsolete by that age!
http://ctechz.blogspot.in/search/label/Shell%20Script
You might also like
- Linux System Administrator Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandLinux System Administrator Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- Unix IntDocument17 pagesUnix Intdebrajrouth2No ratings yet
- SHELL SCRIPTING TITLESDocument31 pagesSHELL SCRIPTING TITLESAditya BeheraNo ratings yet
- Shell Scripting Interview Questions PDFDocument13 pagesShell Scripting Interview Questions PDFKothasudarshan Kumar100% (2)
- Shell Scripting Examples #2Document8 pagesShell Scripting Examples #2DebendraNathSahuNo ratings yet
- UNIX Commands Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesUNIX Commands Interview QuestionsVelu PillaiNo ratings yet
- Shell Scripting Interview Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesShell Scripting Interview Questions and AnswerskdtftfjggjyhgNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Linux for Bioinformatics - An Intro to LinuxDocument27 pagesIntroduction to Linux for Bioinformatics - An Intro to LinuxMuthu KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIX Commands Interview Questions: Submitted by M Shuresh Be Project Associate Iit MadrasDocument6 pagesUNIX Commands Interview Questions: Submitted by M Shuresh Be Project Associate Iit MadrasSuresh MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Linux Admin Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesLinux Admin Interview QuestionsSree SankarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document14 pagesAssignment 2Muhammad Adil NaeemNo ratings yet
- Nixes and IntDocument43 pagesNixes and Intchaits258No ratings yet
- Linux Adminnn 5Document43 pagesLinux Adminnn 5chaits258No ratings yet
- Linux Admin 5Document44 pagesLinux Admin 5chaits258No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document14 pagesAssignment 1Birhaneselasie AbebeNo ratings yet
- Linux AdminDocument44 pagesLinux Adminchaits258No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: PracticalsDocument113 pagesGujarat Technological University: PracticalsSandip MouryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 - Getting StartedDocument14 pagesChapter 01 - Getting StartedapurbaNo ratings yet
- Linux Admin Interview Questions: Back To TopDocument40 pagesLinux Admin Interview Questions: Back To Topkoseyiw439No ratings yet
- Unix Commands Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesUnix Commands Interview QuestionsSavya MittalNo ratings yet
- Basic Linux Commands Cheat-SheetDocument2 pagesBasic Linux Commands Cheat-SheetJohn Paul TuohyNo ratings yet
- Linux Admin 4Document44 pagesLinux Admin 4chaits258No ratings yet
- Os Lab ManualDocument98 pagesOs Lab ManualSai KumarNo ratings yet
- Unix Sheel ProgrammingDocument63 pagesUnix Sheel ProgrammingAKASH PALNo ratings yet
- CyberAces Module1-Linux 3 CoreCommandsDocument19 pagesCyberAces Module1-Linux 3 CoreCommandsPedro FreitasNo ratings yet
- Linux Admin QuestionsDocument44 pagesLinux Admin Questionschaits258No ratings yet
- Tools & Applications Shell Kernel HardwareDocument11 pagesTools & Applications Shell Kernel HardwareMayur DuttaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document31 pagesAssignment 2SALIM TADVINo ratings yet
- Notes 1 Working On A Terminal 4aug2022Document10 pagesNotes 1 Working On A Terminal 4aug2022jeremyNo ratings yet
- Process Will Be Created To Execute Them. (Note That All These Commands Are NotDocument2 pagesProcess Will Be Created To Execute Them. (Note That All These Commands Are NotGupta AprajitaNo ratings yet
- 1 UnixDocument90 pages1 UnixRajinder SanwalNo ratings yet
- Unix Shell ScriptingDocument116 pagesUnix Shell ScriptingUddipta BgohainNo ratings yet
- Unix CommandsDocument5 pagesUnix Commandsmalleswari ChNo ratings yet
- UnixDocument45 pagesUnixSantosh SharmaNo ratings yet
- OS Lab ManualDocument37 pagesOS Lab ManualAmit SangaleNo ratings yet
- 1 UnixDocument90 pages1 Unixvivek_121079No ratings yet
- Unix Commands DocumentDocument21 pagesUnix Commands DocumentKaushik VelusamyNo ratings yet
- Linux Admin Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesLinux Admin Interview Questionsapi-3780913No ratings yet
- Explain The Following CommandsDocument7 pagesExplain The Following Commandsrsreddy434No ratings yet
- Os Package - The ShellDocument2 pagesOs Package - The ShellJaya shreeNo ratings yet
- Operating System LabDocument33 pagesOperating System LabCasey MoralesNo ratings yet
- Notes 1 Working With Terminal 4aug2022Document9 pagesNotes 1 Working With Terminal 4aug2022jeremyNo ratings yet
- Basic Unix Shell CommandsDocument7 pagesBasic Unix Shell CommandsJat SarkarNo ratings yet
- Basic Unix CommandsDocument10 pagesBasic Unix CommandsAazmi SayedNo ratings yet
- Unix Interview QuestionsDocument6 pagesUnix Interview QuestionsOmkar RayapeddiNo ratings yet
- LINUX Unit - 1Document7 pagesLINUX Unit - 1vjagarwalNo ratings yet
- Unix CommandsDocument10 pagesUnix CommandsMohammed ParvezNo ratings yet
- Operating System LAb 1Document7 pagesOperating System LAb 1ajnobi hueseNo ratings yet
- OS-Module 2Document36 pagesOS-Module 2Amrutha VNo ratings yet
- UnixDocument11 pagesUnixffrakeshNo ratings yet
- Linux Lab ManuelDocument23 pagesLinux Lab ManuelNikhil MaliNo ratings yet
- Shell Programming: NumberDocument12 pagesShell Programming: Numberpankajchandre30No ratings yet
- UNIX Concepts: 1. How Are Devices Represented in UNIX?Document16 pagesUNIX Concepts: 1. How Are Devices Represented in UNIX?Pradeep TiwariNo ratings yet
- OperatingSystem Lab - File FinalDocument21 pagesOperatingSystem Lab - File FinalVaishalee SinghNo ratings yet
- Unix BasicsDocument15 pagesUnix BasicsNancyNo ratings yet
- CLI Lab: Learning Command Line InterfaceDocument5 pagesCLI Lab: Learning Command Line InterfacecodelyokoNo ratings yet
- Unix Shell Programming Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandUnix Shell Programming Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- Contributor Guide Overview and Browser-Based TaskDocument105 pagesContributor Guide Overview and Browser-Based Task////No ratings yet
- Understanding UBE job queues in EnterpriseOne release 8.9Document63 pagesUnderstanding UBE job queues in EnterpriseOne release 8.9Zingadepp100% (3)
- Java NotesDocument88 pagesJava Notestushar pawarNo ratings yet
- GPAC DAMI Reference GuideDocument281 pagesGPAC DAMI Reference GuideMous100% (4)
- A Brief History of UnixDocument13 pagesA Brief History of UnixChaitra RaniNo ratings yet
- Manual Vbulletin Version 4.1.4Document347 pagesManual Vbulletin Version 4.1.4Gil GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Web Programming NotesDocument138 pagesWeb Programming NotesAshwani kumariNo ratings yet
- MS ShllinkDocument48 pagesMS ShllinkMirraz7No ratings yet
- PDFlib 8 Beta TutorialDocument314 pagesPDFlib 8 Beta TutorialzabbaikNo ratings yet
- N Fs Maestro ClientDocument320 pagesN Fs Maestro ClientapariciocoolNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis With STATA - Sample ChapterDocument22 pagesData Analysis With STATA - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- TsizeproDocument23 pagesTsizeproAli Salah100% (1)
- C# Essential Training Code SnippetsDocument18 pagesC# Essential Training Code SnippetsMichael Cole100% (1)
- InfacmdcmdDocument203 pagesInfacmdcmdseenaranjithNo ratings yet
- NewsDocument167 pagesNewsMahender ShahNo ratings yet
- 12 2 5 1 Engine Deployment Guide PDFDocument11 pages12 2 5 1 Engine Deployment Guide PDFRaghav PerivelaNo ratings yet
- Installation and User's Guide InformixDocument52 pagesInstallation and User's Guide Informixissa912721No ratings yet
- Whats NewDocument213 pagesWhats NewchinnaksNo ratings yet
- ROBODocument4 pagesROBOolmotrochNo ratings yet
- EDC-S User ManualDocument133 pagesEDC-S User ManualsharfizNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With SAP HANA 2.0, Express Edition (Virtual Machine Method)Document24 pagesGetting Started With SAP HANA 2.0, Express Edition (Virtual Machine Method)josecan77No ratings yet
- Blender Python Reference 2 61 ReleaseDocument1,518 pagesBlender Python Reference 2 61 ReleaseMatthew BledsoeNo ratings yet
- Ams Machinery Manager v5 71 Installation Guide en 4236422 PDFDocument68 pagesAms Machinery Manager v5 71 Installation Guide en 4236422 PDFgspozoNo ratings yet
- Installation Getting StartedDocument196 pagesInstallation Getting StartedanonNo ratings yet
- TIB Hawk 5.2 Concepts GuideDocument81 pagesTIB Hawk 5.2 Concepts GuidehidayatNo ratings yet
- XexTool - Extract and Modify Xbox 360 XEX FilesDocument7 pagesXexTool - Extract and Modify Xbox 360 XEX FilesGuilherme RetrogamesNo ratings yet
- Ocularis Recorder Configuration ManualDocument113 pagesOcularis Recorder Configuration ManualRodrigo HigueraNo ratings yet
- Windows XP Command LineDocument4 pagesWindows XP Command Linethesingh_0No ratings yet
- Install Shield 2012 Repackage R User GuideDocument220 pagesInstall Shield 2012 Repackage R User GuideAlephNullNo ratings yet